Chess is a
board game
A board game is a type of tabletop game that involves small objects () that are placed and moved in particular ways on a specially designed patterned game board, potentially including other components, e.g. dice. The earliest known uses of the ...
for two players. It is an
abstract strategy game
An abstract strategy game is a type of strategy game that has minimal or no narrative theme, an outcome determined only by player choice (with minimal or no randomness), and in which each player has perfect information about the game. For example ...
that involves
no hidden information and no elements of
chance. It is played on a square
board
Board or Boards may refer to:
Flat surface
* Lumber, or other rigid material, milled or sawn flat
** Plank (wood)
** Cutting board
** Sounding board, of a musical instrument
* Cardboard (paper product)
* Paperboard
* Fiberboard
** Hardboard, a ...
consisting of 64 squares arranged in an 8×8 grid. The players, referred to as
"White" and "Black", each control sixteen
pieces: one
king
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an Absolute monarchy, absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted Government, governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a Constitutional monarchy, ...
, one
queen
Queen most commonly refers to:
* Queen regnant, a female monarch of a kingdom
* Queen consort, the wife of a reigning king
* Queen (band), a British rock band
Queen or QUEEN may also refer to:
Monarchy
* Queen dowager, the widow of a king
* Q ...
, two
rooks, two
bishops
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of di ...
, two
knights
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of a knighthood by a head of state (including the pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church, or the country, especially in a military capacity.
The concept of a knighthood ...
, and eight
pawns, with each type of piece having a different pattern of movement. An enemy piece may be captured (removed from the board) by moving one's own piece onto the square it occupies. The object of the game is to "
checkmate
Checkmate (often shortened to mate) is any game position in chess and other chess-like games in which a player's king is in check (threatened with ) and there is no possible escape. Checkmating the opponent wins the game.
In chess, the king is ...
" (threaten with inescapable capture) the enemy king. There are also several ways a game can end in a
draw
Draw, drawing, draws, or drawn most commonly refer to:
* Draw (terrain), a terrain feature formed by two parallel ridges or spurs with low ground in between them
* Draw (tie), in a competition, where competitors achieve equal outcomes
* Draw ...
.
The recorded history of chess goes back to at least the emergence of
chaturanga
Chaturanga (, , ) is an Traditional games of India, ancient Indian Strategy game, strategy board game. It is first known from India around the seventh century AD.
While there is some uncertainty, the prevailing view among chess historians is t ...
—also thought to be an ancestor to
similar games like and —in seventh-century
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
. After its introduction in
Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, it spread to the Arab world and then to Europe. The modern rules of chess emerged in Europe at the end of the 15th century, with standardization and universal acceptance by the end of the 19th century. Today, chess is one of the world's most popular games, with millions of players worldwide.
Organized chess arose in the 19th century. Chess competition today is governed internationally by
FIDE
The International Chess Federation or World Chess Federation, commonly referred to by its French acronym FIDE ( , ), is an international organization based in Switzerland that connects the various national chess federations and acts as the Spor ...
(''Fédération Internationale des Échecs''), the International Chess Federation. The first universally recognized
World Chess Champion
The World Chess Championship is played to determine the world champion in chess. The current world champion is Gukesh Dommaraju, who defeated the previous champion Ding Liren in the World Chess Championship 2024, 2024 World Chess Championship. ...
,
Wilhelm Steinitz
William Steinitz (born Wilhelm Steinitz; May 14, 1836 – August 12, 1900) was a Bohemian-Austrian, and later American, chess player. From 1886 to 1894, he was the first World Chess Champion. He was also a highly influential writer and c ...
, claimed his title in
1886
Events January
* January 1 – Upper Burma is formally annexed to British rule in Burma, British Burma, following its conquest in the Third Anglo-Burmese War of November 1885.
* January 5–January 9, 9 – Robert Louis Stevenson ...
;
Gukesh Dommaraju
Gukesh Dommaraju (born 29 May 2006) is an Indian chess grandmaster and the reigning World Chess Champion. A chess prodigy, Gukesh is the youngest undisputed world champion, the youngest player to have surpassed a FIDE rating of 2750, doing s ...
is the current World Champion, having won the title in
2024
The year saw the list of ongoing armed conflicts, continuation of major armed conflicts, including the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the Myanmar civil war (2021–present), Myanmar civil war, the Sudanese civil war (2023–present), Sudane ...
.
A huge body of
chess theory
The game of chess is commonly divided into three phases: the chess opening, opening, Chess middlegame, middlegame, and Chess endgame, endgame. There is a large body of theory regarding how the game should be played in each of these phases, especi ...
has developed since the game's inception. Aspects of art are found in
chess composition
A chess problem, also called a chess composition, is a Chess puzzle, puzzle created by the composer using chess pieces on a chessboard, which presents the solver with a particular task. For instance, a position may be given with the instruction t ...
, and chess in its turn influenced
Western culture
Western culture, also known as Western civilization, European civilization, Occidental culture, Western society, or simply the West, refers to the Cultural heritage, internally diverse culture of the Western world. The term "Western" encompas ...
and
the arts
The arts or creative arts are a vast range of human practices involving creative expression, storytelling, and cultural participation. The arts encompass diverse and plural modes of thought, deeds, and existence in an extensive range of m ...
, and has connections with other fields such as
mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
,
computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ...
, and
psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feel ...
. One of the goals of early
computer scientists
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to applied disciplines (including the design an ...
was to create a
chess-playing machine
Computer chess includes both hardware (dedicated computers) and software capable of playing chess. Computer chess provides opportunities for players to practice even in the absence of human opponents, and also provides opportunities for analysi ...
. In 1997,
Deep Blue became the first computer to beat a reigning World Champion in
a match when it defeated
Garry Kasparov
Garry Kimovich Kasparov (born Garik Kimovich Weinstein on 13 April 1963) is a Russian Grandmaster (chess), chess grandmaster, former World Chess Champion (1985–2000), political activist and writer. His peak FIDE chess Elo rating system, ra ...
. Today's
chess engine
In computer chess, a chess engine is a computer program that analyzes chess or List of chess variants, chess variant positions, and generates a move or list of moves that it regards as strongest.
A chess software engine, engine is usually a Front ...
s are significantly stronger than the best human players and have deeply influenced the development of chess theory; however, chess is
not a solved game.
Rules
The rules of chess are published by
FIDE
The International Chess Federation or World Chess Federation, commonly referred to by its French acronym FIDE ( , ), is an international organization based in Switzerland that connects the various national chess federations and acts as the Spor ...
(Fédération Internationale des Échecs; "International Chess Federation"), chess's world governing body, in its ''Handbook''.
Rules published by
national governing bodies, or by unaffiliated chess organizations, commercial publishers, etc., may differ in some details. FIDE's rules were most recently revised in 2023.
Setup

Chess set
A chess set consists of a chessboard and White and Black in chess, white and black chess pieces for playing chess. There are sixteen pieces of each color: one King (chess), king, one Queen (chess), queen, two Rook (chess), rooks, two Bishop (chess ...
s come in a wide variety of styles. The
Staunton pattern is the most common, and is usually required for competition.
Chess sets come with
pieces in two colors, referred to as
''white'' and ''black'', regardless of their actual color; the players controlling the color sets are referred to as ''White'' and ''Black'', respectively. Each set comes with at least the following 16 pieces in both colors: one
king
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an Absolute monarchy, absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted Government, governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a Constitutional monarchy, ...
, one
queen
Queen most commonly refers to:
* Queen regnant, a female monarch of a kingdom
* Queen consort, the wife of a reigning king
* Queen (band), a British rock band
Queen or QUEEN may also refer to:
Monarchy
* Queen dowager, the widow of a king
* Q ...
, two
rooks, two
bishops
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of di ...
, two
knights
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of a knighthood by a head of state (including the pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church, or the country, especially in a military capacity.
The concept of a knighthood ...
, and eight
pawns.
[
The game is played on a square ]board
Board or Boards may refer to:
Flat surface
* Lumber, or other rigid material, milled or sawn flat
** Plank (wood)
** Cutting board
** Sounding board, of a musical instrument
* Cardboard (paper product)
* Paperboard
* Fiberboard
** Hardboard, a ...
of eight rows (called ') and eight columns (called '). Although it does not affect gameplay, by convention the 64 squares alternate in color and are referred to as and squares.
Movement
White moves first, after which players alternate turns. One piece is moved per turn (except when castling
Castling is a move in chess. It consists of moving the king (chess), king two squares toward a rook (chess), rook on the same and then moving the rook to the square that the king passed over. Castling is permitted only if neither the king ...
, during which two pieces are moved). In the diagrams, dots mark the squares to which each type of piece can move if unoccupied by friendly pieces and there are no intervening piece(s) of either color (except the knight, which leaps over any intervening pieces). With the sole exception of ''en passant
In chess, ''en passant'' (, "in passing") describes the capture by a Pawn (chess), pawn of an enemy pawn on the same and an adjacent that has just made an initial two-square advance. This is a special case in the rules of chess. The capturi ...
'', a piece captures an enemy piece by moving to the square it occupies, removing it from play and taking its place. The pawn is the only piece that does not capture the way it moves, and it is the only piece that moves and captures in only one direction (forwards from the player's perspective). A piece is said to ''control'' empty squares on which it could capture, ''attack'' squares with enemy pieces it could capture, and ''defend'' squares with pieces of the same color on which it could recapture. Moving is compulsory; a player may not skip a turn, even when having to move is detrimental.
* The king
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an Absolute monarchy, absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted Government, governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a Constitutional monarchy, ...
moves one square in any direction. There is also a special move called ''castling
Castling is a move in chess. It consists of moving the king (chess), king two squares toward a rook (chess), rook on the same and then moving the rook to the square that the king passed over. Castling is permitted only if neither the king ...
'' which moves the king and a rook. The king is the most valuable piece—it is illegal to play any move that puts one's king under attack by an opponent piece. A move that attacks the king must be parried immediately; if this cannot be done, the game is lost. (See .)
* A rook can move any number of squares along a rank or file. A rook is involved in the king's castling move.
* A bishop
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of di ...
can move any number of squares diagonally.
* A queen
Queen most commonly refers to:
* Queen regnant, a female monarch of a kingdom
* Queen consort, the wife of a reigning king
* Queen (band), a British rock band
Queen or QUEEN may also refer to:
Monarchy
* Queen dowager, the widow of a king
* Q ...
combines the power of a rook and bishop and can move any number of squares along a rank, file, or diagonal.
* A knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of a knighthood by a head of state (including the pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church, or the country, especially in a military capacity.
The concept of a knighthood ...
moves to any of the closest squares that are not on the same rank, file, or diagonal. (Thus the move forms an "L"-shape: two squares vertically and one square horizontally, or two squares horizontally and one square vertically.) The knight is the only piece that can leap over other pieces.
* A pawn
Pawn most often refers to:
* Pawn (chess), the weakest and most numerous chess piece in the game
* Pawnbroker or pawnshop, a business that provides loans by taking personal property as collateral
Pawn or The Pawn may also refer to:
Places
* Pa ...
can move forward to the unoccupied square immediately in front of it on the same file, or on its first move it can optionally advance two squares along the same file, provided both squares are unoccupied (diagram dots). A pawn can capture an opponent's piece on a square diagonally in front of it by moving to that square (diagram crosses). It capture a piece while advancing along the same file, nor can it move to either square diagonally in front without capturing. Pawns have two special moves: the ''en passant'' capture and promotion
Promotion may refer to:
Marketing
* Promotion (marketing), one of the four marketing mix elements, comprising any type of marketing communication used to inform or persuade target audiences of the relative merits of a product, service, brand or i ...
.
Check and checkmate
When a king is under immediate attack, it is ''in check
Check or cheque, may refer to:
Places
* Check, Virginia
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Check'' (film), a 2021 Indian Telugu-language film
* "The Check" (''The Amazing World of Gumball''), a 2015 episode of ''The Amazing World of Gumball''
...
''. A move in response to a check is legal only if it results in a position in which the king is no longer in check. There are three ways to counter a check:
* Capture the checking piece.
* Interpose a piece between the checking piece and the king (possible only if the attacking piece is a queen, rook, or bishop and there is a square between it and the king).
* Move the king to a square where it is not under attack.
The object of the game is to checkmate
Checkmate (often shortened to mate) is any game position in chess and other chess-like games in which a player's king is in check (threatened with ) and there is no possible escape. Checkmating the opponent wins the game.
In chess, the king is ...
the opponent; this occurs when the opponent's king is in check, and there is no legal way to get it out of check. In casual games, it is common to announce "check" when putting the opponent's king in check, but this is not required by the rules of chess and is usually not done in tournaments.
Castling
 Kings can ''castle'' once per game. Castling consists of moving the king two squares toward either rook of the same color, and then placing the rook on the square that the king crossed.
Castling is possible only if the following conditions are met:
Kings can ''castle'' once per game. Castling consists of moving the king two squares toward either rook of the same color, and then placing the rook on the square that the king crossed.
Castling is possible only if the following conditions are met:check
Check or cheque, may refer to:
Places
* Check, Virginia
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Check'' (film), a 2021 Indian Telugu-language film
* "The Check" (''The Amazing World of Gumball''), a 2015 episode of ''The Amazing World of Gumball''
...
and does not pass through or finish on a square controlled by an enemy piece.
Castling is still permitted if the rook is under attack, or if the rook crosses an attacked square.
Special pawn moves
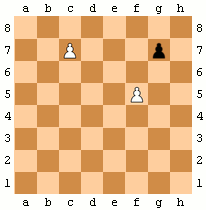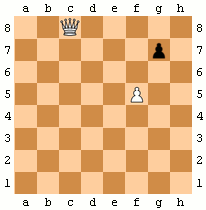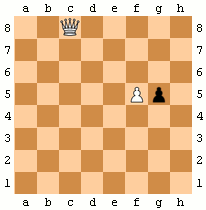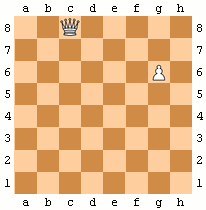 Pawns have two special moves:
* ''En passant'': when a pawn makes a two-square advance to the same rank as an opponent's pawn on an adjacent file, that pawn can capture it ''en passant'' ("in passing"), moving to one square behind the captured pawn. A pawn can only be captured ''en passant'' on the turn after it makes a two-square advance. In the animated diagram, the black pawn advances two squares from g7 to g5, and the white pawn on f5 takes it ''en passant'', landing on g6.
* ''Promotion'': when a pawn advances to its , it is ''promoted'' and replaced with the player's choice of a queen, rook, bishop, or knight. Usually, pawns are promoted to queens; choosing another piece is called
Pawns have two special moves:
* ''En passant'': when a pawn makes a two-square advance to the same rank as an opponent's pawn on an adjacent file, that pawn can capture it ''en passant'' ("in passing"), moving to one square behind the captured pawn. A pawn can only be captured ''en passant'' on the turn after it makes a two-square advance. In the animated diagram, the black pawn advances two squares from g7 to g5, and the white pawn on f5 takes it ''en passant'', landing on g6.
* ''Promotion'': when a pawn advances to its , it is ''promoted'' and replaced with the player's choice of a queen, rook, bishop, or knight. Usually, pawns are promoted to queens; choosing another piece is called underpromotion
In chess, promotion is the replacement of a pawn with a new piece when the pawn is moved to its . The player replaces the pawn immediately with a queen, rook, bishop, or knight of the same . The new piece does not have to be a previously captu ...
. In the animated diagram, the c7-pawn is advanced to c8 and promoted to a queen. If the required piece is not available (e.g. a second queen), an inverted rook is sometimes used as a substitute, but this is not recognized in FIDE-sanctioned games.
End of the game
Win
A game can be won in the following ways:
* ''Checkmate
Checkmate (often shortened to mate) is any game position in chess and other chess-like games in which a player's king is in check (threatened with ) and there is no possible escape. Checkmating the opponent wins the game.
In chess, the king is ...
:'' The opposing king is in check and the opponent has no legal move. (See .)
* ''Resignation
Resignation is the formal act of relinquishing or vacating one's office or position. A resignation can occur when a person holding a position gained by election or appointment steps down, but leaving a position upon the expiration of a term, or ...
:'' A player may resign, conceding the game to the opponent. If, however, the opponent has no way of checkmating the resigned player, this is a draw under FIDE Laws.time control
A time control is a mechanism in the tournament play of almost all two-player board games so that each round of the match can finish in a timely way and the tournament can proceed.
For turn-based games such as chess, shogi or go, time cont ...
, a player wins if the opponent runs out of time, even if the opponent has a superior position, as long as the player has a theoretical possibility to checkmate the opponent were the game to continue.
* ''Forfeit:'' A player who cheats, violates the rules, or violates the rules of conduct specified for the particular tournament can be forfeited. Occasionally, both players are forfeited.
Draw
There are several ways a game can end in a draw
Draw, drawing, draws, or drawn most commonly refer to:
* Draw (terrain), a terrain feature formed by two parallel ridges or spurs with low ground in between them
* Draw (tie), in a competition, where competitors achieve equal outcomes
* Draw ...
:
* ''Stalemate
Stalemate is a situation in chess where the player whose turn it is to move is not in check and has no legal move. Stalemate results in a draw. During the endgame, stalemate is a resource that can enable the player with the inferior position ...
:'' If the player to move has no legal move, but is not in check, the position is a stalemate, and the game is drawn.
* ''Dead position
The rules of chess (also known as the laws of chess) govern the play of the game of chess. Chess is a two-player Abstract strategy game, abstract strategy board game. Each player controls sixteen chess piece, pieces of six types on a chessboar ...
:'' If neither player is able to checkmate the other by any legal sequence of moves, the game is drawn. For example, if only the kings are on the board, all other pieces having been captured, checkmate is impossible, and the game is drawn by this rule. On the other hand, if both players still have a knight, there is a highly unlikely yet theoretical possibility of checkmate, so this rule does not apply. The dead position rule supersedes an older rule which referred to "insufficient material", extending it to include other positions where checkmate is impossible, such as blocked pawn endings where the pawns cannot be attacked.
* ''Draw by agreement
A game of chess can end in a draw by agreement. A player may offer a draw at any stage of a game; if the opponent accepts, the game is a draw. In some competitions, draws by agreement are restricted; for example draw offers may be subject to the d ...
:'' In tournament chess, draws are most commonly reached by mutual agreement between the players. The correct procedure is to verbally offer the draw, make a move, then start the opponent's clock. Traditionally, players have been allowed to agree to a draw at any point in the game, occasionally even without playing a move. More recently efforts have been made to discourage early draws, for example by forbidding draw offers before a certain number of moves have been completed, or even forbidding draw offers altogether.
* ''Threefold repetition
In chess, the threefold repetition rule states that a player may claim a draw if the same position occurs three times during the game. The rule is also known as repetition of position and, in the USCF rules, as triple occurrence of position.Artic ...
:'' This most commonly occurs when neither side is able to avoid repeating moves without incurring a disadvantage. The three occurrences of the position need not occur on consecutive moves for a claim to be valid. The addition of the fivefold repetition rule in 2014 requires the arbiter to intervene immediately and declare the game a draw after five occurrences of the same position, consecutive or otherwise, without requiring a claim by either player. FIDE rules make no mention of perpetual check
In the game of chess, perpetual check is a situation in which one player can play an unending series of checks from which the defending player cannot escape. This typically arises when the player who is checking feels their position in the game i ...
; this is merely a specific type of draw by threefold repetition.
* ''Fifty-move rule
The fifty-move rule in chess states that a player can claim a draw if no has been made and no pawn has been moved in the last fifty moves (where a "move" consists of a player completing a turn followed by the opponent completing a turn). The pur ...
:'' If during the previous 50 moves no pawn has been moved and no capture has been made, either player can claim a draw. The addition of the seventy-five-move rule
The fifty-move rule in chess states that a player can claim a draw if no has been made and no pawn has been moved in the last fifty moves (where a "move" consists of a player completing a turn followed by the opponent completing a turn). The pur ...
in 2014 requires the arbiter to intervene and immediately declare the game drawn after 75 moves without a pawn move or capture, without requiring a claim by either player. There are several known endgames where it is possible to force a mate but it requires more than 50 moves before a pawn move or capture is made; examples include some endgames with two knights against a pawn and some pawnless endgames such as queen against two bishops. Historically, FIDE has sometimes revised the fifty-move rule to make exceptions for these endgames, but these have since been repealed. Some correspondence chess
Correspondence chess is chess played by various forms of long-distance correspondence, traditionally through the postal system. Today it is usually played through a correspondence chess server, a public internet chess forum, or email. Less commo ...
organizations do not enforce the fifty-move rule.
* ''Draw on time:'' In games with a time control
A time control is a mechanism in the tournament play of almost all two-player board games so that each round of the match can finish in a timely way and the tournament can proceed.
For turn-based games such as chess, shogi or go, time cont ...
, the game is drawn if a player is out of time and no sequence of legal moves would allow the opponent to checkmate the player.
Time control
In competition, chess games are played with a time control
A time control is a mechanism in the tournament play of almost all two-player board games so that each round of the match can finish in a timely way and the tournament can proceed.
For turn-based games such as chess, shogi or go, time cont ...
. Time controls are generally divided into categories based on the amount of time given to each player, which range from classical time controls, which allot about 2 hours or more to each player and which can take upwards of seven hours (even longer if adjournments are permitted), to bullet chess
Fast chess, also known as speed chess, is a type of chess in which each player is given less time than classical chess time controls allow. Fast chess is subdivided, by decreasing time controls, into rapid chess, blitz chess, and bullet chess. A ...
, in which players receive less than three minutes each. Between these are rapid chess
Fast chess, also known as speed chess, is a type of chess in which each player is given less time than classical chess time controls allow. Fast chess is subdivided, by decreasing time controls, into rapid chess, blitz chess, and bullet chess. A ...
(ten to sixty minutes per player), popular in amateur tournaments, and blitz chess
Fast chess, also known as speed chess, is a type of chess in which each player is given less time than classical chess time controls allow. Fast chess is subdivided, by decreasing time controls, into rapid chess, blitz chess, and bullet chess. A ...
(three to ten minutes), popular online. Non-classical chess is sometimes referred to as fast chess
Fast chess, also known as speed chess, is a type of chess in which each player is given less time than classical chess time controls allow. Fast chess is subdivided, by decreasing time controls, into rapid chess, blitz chess, and bullet chess. A ...
.
Time is controlled using a chess clock
A chess clock is a device that comprises two adjacent clocks with buttons to stop one clock while starting the other, so that the two clocks never run simultaneously. The clocks are used in games where the time is allocated between two parties. T ...
with two displays, one for each player's remaining time. Analog chess clocks have been largely replaced by digital clocks, which allow for time controls with increments.
There are some aspects unique to online chess. A premove
In online chess, a premove is a move input made by a player during their opponent's turn, taking effect only after the opponent moves. A premove is performed in the same way as a normal move, most commonly by dragging the piece to its destination ...
allows a player to submit a move on the opponent's turn, which gets played automatically if possible using little to no time. Premoves, alongside the relative ease of digital inputs, make faster time controls feasible online.
Time controls are also enforced in correspondence chess
Correspondence chess is chess played by various forms of long-distance correspondence, traditionally through the postal system. Today it is usually played through a correspondence chess server, a public internet chess forum, or email. Less commo ...
competitions. A typical time control is 50 days for every 10 moves. Time is usually allotted per move in online correspondence chess.
Notation
Historically, many different notation
In linguistics and semiotics, a notation system is a system of graphics or symbols, Character_(symbol), characters and abbreviated Expression (language), expressions, used (for example) in Artistic disciplines, artistic and scientific disciplines ...
systems have been used to record chess moves; the standard system today is short-form algebraic notation. In this system, files are labeled ''a'' through ''h'' and ranks are labeled ''1'' through ''8''. Squares are identified by the file and rank they occur on; g3 is the square on the g file and the third rank. In English, the piece notations are: ''K'' (king), ''Q'' (queen), ''R'' (rook), ''B'' (bishop), and ''N'' (knight; N is used to avoid confusion with king). Different initials are used in other languages. Moves are recorded as follows:
: –
 For example, Qg5 means "queen moves to g5". No letter initial is used for pawns, so e4 means "pawn moves to e4". When multiple moves could be rendered the same way, the file or rank from which the piece moved is added to resolve ambiguity (e.g. Ngf3 means "knight from the g-file moves to the square f3"; R1e2 means "rook on the first rank moves to e2"). If a move may be disambiguated by rank or file, it is done by file, and in the rare case that both are needed, squares are listed normally (e.g. Qh4xe1).
If the move is a capture, "x" is usually inserted before the destination square, thus Bxf3 means "bishop captures on f3". When a pawn makes a capture, the file from which the pawn departed is often listed even when no disambiguation is necessary; for example, exd5.
If a pawn moves to its last rank, achieving promotion, the piece chosen is indicated after the move (for example, e1=Q or e1Q). Castling is indicated by the special notations 0-0 for castling and 0-0-0 for castling. A move that places the opponent's king in check usually has the notation "+" suffixed. Checkmate can be indicated by suffixing "#". At the end of the game, "1–0" means White won, "0–1" means Black won, and "½–½" indicates a draw.
For example, Qg5 means "queen moves to g5". No letter initial is used for pawns, so e4 means "pawn moves to e4". When multiple moves could be rendered the same way, the file or rank from which the piece moved is added to resolve ambiguity (e.g. Ngf3 means "knight from the g-file moves to the square f3"; R1e2 means "rook on the first rank moves to e2"). If a move may be disambiguated by rank or file, it is done by file, and in the rare case that both are needed, squares are listed normally (e.g. Qh4xe1).
If the move is a capture, "x" is usually inserted before the destination square, thus Bxf3 means "bishop captures on f3". When a pawn makes a capture, the file from which the pawn departed is often listed even when no disambiguation is necessary; for example, exd5.
If a pawn moves to its last rank, achieving promotion, the piece chosen is indicated after the move (for example, e1=Q or e1Q). Castling is indicated by the special notations 0-0 for castling and 0-0-0 for castling. A move that places the opponent's king in check usually has the notation "+" suffixed. Checkmate can be indicated by suffixing "#". At the end of the game, "1–0" means White won, "0–1" means Black won, and "½–½" indicates a draw.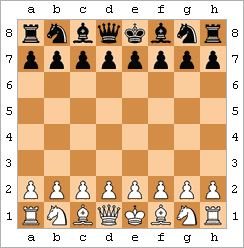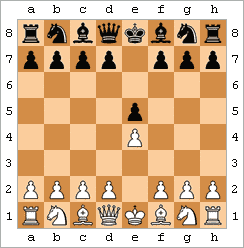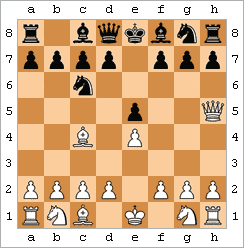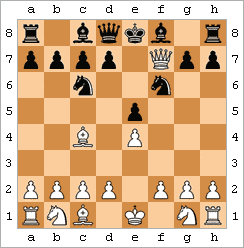 Moves are written as white/black pairs, preceded by the move number and a period. Individual white moves are also recorded this way, while black moves are rendered with an ellipsis after the move number. For example, one variation of a simple trap known as the
Moves are written as white/black pairs, preceded by the move number and a period. Individual white moves are also recorded this way, while black moves are rendered with an ellipsis after the move number. For example, one variation of a simple trap known as the Scholar's mate
In chess, scholar's mate is the checkmate achieved by the following moves, or similar:
:1. e4 e5
:2. Qh5 Nc6
:3. Bc4 Nf6
:4. Qxf7
The same mating pattern may be reached by various move orders. For example, White might play 2.Bc4. In a ...
(see animated diagram) can be recorded:
:1. e4 e5 2. Qh5 Nc6 3. Bc4 Nf6 4. Qxf7
The move 3... Nf6?? is recorded as a blunder, as it allows 4. Qxf7# checkmate.
Games or sequences may be recorded in Portable Game Notation
Portable Game Notation (PGN) is a standard plain text format for recording chess games (both the moves and related data), which can be read by humans and is also supported by most chess software.
History
PGN was devised around 1993, by Steven J ...
(PGN), a text-based file format with support for annotative symbols, commentary, and background information, such as player names. It is based on short form English algebraic notation incorporating markup language
A markup language is a Encoding, text-encoding system which specifies the structure and formatting of a document and potentially the relationships among its parts. Markup can control the display of a document or enrich its content to facilitate au ...
. PGN transcripts, stored digitally as PGN (.pgn) files can be processed by most chess software and are easily readable by humans.
Variants of algebraic notation include ''long algebraic'', in which both the departure and destination square are indicated; ''abbreviated algebraic'', in which capture signs, check signs, and ranks of pawn captures may be omitted; and ''figurine algebraic notation'', used in chess books and magazines, which uses graphic symbols instead of initials to indicate pieces for readability regardless of language.
Until about 1980, the majority of English language chess publications used descriptive notation
Descriptive notation is a chess notation system based on abbreviated natural language. Its distinctive features are that it refers to files by the piece that occupies the back rank square in the starting position and that it describes each square ...
, in which files are identified by the initial letter of the piece that occupies the first rank at the beginning of the game. In descriptive notation, the common opening move 1.e4 is rendered as "1.P-K4" ("pawn to king four"). Another system is ICCF numeric notation
ICCF numeric notation is the official chess notation system of the International Correspondence Chess Federation. The system was devised for use in international correspondence chess to avoid the potential confusion of using algebraic notation, ...
, recognized by the International Correspondence Chess Federation
International Correspondence Chess Federation (ICCF) was founded on 26 March 1951 as a new appearance of the International Correspondence Chess Association (ICCA), which was founded in 1945, as successor of the Internationaler Fernschachbund (IF ...
though its use is in decline.
In tournament games, players are normally required to keep a ' (written record of the game). This is a requirement in all FIDE-sanctioned games played at classical time controls.
Gameplay
Theory
Chess has an extensive literature. In 1913, the chess historian H.J.R. Murray
Harold James Ruthven Murray (24 June 1868 – 16 May 1955) was a British educationalist, inspector of schools, and prominent chess historian. His book, ''A History of Chess'', is widely regarded as the most authoritative and comprehensive his ...
estimated the total number of books, magazines, and chess columns in newspapers
The earliest known chess column appeared in the ''The Lancet, Lancet'' in 1823, but due to lack of popularity disappeared after less than a year.
Historical development
The first column to establish itself was that of George Walker (chess columni ...
to be about 5,000. B.H. Wood estimated the number, as of 1949, to be about 20,000.Kenneth Whyld
Kenneth Whyld (6 March 1926 – 11 July 2003) was a British chess author and researcher, best known as the co-author (with David Hooper) of ''The Oxford Companion to Chess'', a single-volume chess reference work in English.
Whyld was a st ...
write that, "Since then there has been a steady increase year by year of the number of new chess publications. No one knows how many have been printed."Cleveland Public Library
The Cleveland Public Library is a public library system in Cleveland, Ohio. Founded in 1869, it had a circulation of 3.5 million items in 2020. It operates the Main Library on Superior Avenue in downtown Cleveland, 27 branches throughout the cit ...
, with over 32,000 chess books and over 6,000 bound volumes of chess periodicals;National Library of the Netherlands
The KB National Library of the Netherlands (legal Dutch name: Koninklijke Bibliotheek or KB ; ''Royal Library'') is the national library of the Netherlands, based in The Hague, founded in 1798.
The KB collects everything that is published in ...
, with about 30,000 books.
Strategy
Chess strategy is concerned with the evaluation of chess positions and with setting up goals and long-term plans for future play. During the evaluation, players must take into account numerous factors such as the value of the pieces on the board, control of the center and centralization, the pawn structure
In a game of chess, the pawn structure (sometimes known as the pawn skeleton) is the configuration of pawn (chess), pawns on the chessboard. Because pawns are the least mobile of the chess pieces, the pawn structure is relatively static and thus ...
, king safety, and the control of key square
In chess, particularly in endgames, a key square (also known as a ''critical square'') is a square such that if a player's king can occupy it, he can force some gain such as the promotion of a pawn or the capture of an opponent's pawn. Key squ ...
s or groups of squares (for example, diagonals, open files, and dark or light squares).
The most basic step in evaluating a position is to count the total value of pieces of both sides. The point values used for this purpose are based on experience; usually, pawns are considered worth one point, knights and bishops about three points each, rooks about five points (the value difference between a rook and a bishop or knight being known as the exchange), and queens about nine points. The king is more valuable than all of the other pieces combined, since its checkmate loses the game, but is still capable as a fighting piece; in the endgame, the king is generally more powerful than a bishop or knight but less powerful than a rook. These basic values are then modified by other factors like position of the piece (e.g. advanced pawns are usually more valuable than those on their initial squares), coordination between pieces (e.g. a pair of bishops usually coordinate better than a bishop and a knight), or the type of position (e.g. knights are generally better in with many pawns while bishops are more powerful in ).
Another important factor in the evaluation of chess positions is ''pawn structure
In a game of chess, the pawn structure (sometimes known as the pawn skeleton) is the configuration of pawn (chess), pawns on the chessboard. Because pawns are the least mobile of the chess pieces, the pawn structure is relatively static and thus ...
'' (sometimes known as the ''pawn skeleton''): the configuration of pawns on the chessboard. Since pawns are the least mobile of the pieces, pawn structure is relatively static and largely determines the strategic nature of the position. Weaknesses in pawn structure include isolated, doubled, or backward pawn
In chess, a backward pawn is a pawn that is behind all pawns of the same color on the adjacent and cannot be safely advanced. In the diagram, the black pawn on the c6-square is backward.
Disadvantages
Backward pawns are usually a positional ...
s and ; once created, they are often permanent. Care must therefore be taken to avoid these weaknesses unless they are compensated by another valuable asset (for example, by the possibility of developing an attack).
Tactics
In chess, tactics generally refer to short-term maneuvers – so short-term that they can be calculated in advance by a human player. The possible depth of calculation depends on the player's ability. In positions with many possibilities on both sides, a deep calculation is more difficult and may not be practical, while in positions with a limited number of variations, strong players can calculate long sequences of moves.
Theoreticians describe many elementary tactical methods and typical maneuvers, for example: pins
A pin is a device, typically pointed, used for fastening objects or fabrics together. Pins can have the following sorts of body:
*a shaft of a rigid inflexible material meant to be inserted in a slot, groove, or hole (as with pivots, hinges, an ...
, forks
In cutlery or kitchenware, a fork (from 'pitchfork') is a Eating utensil, utensil, now usually made of metal, whose long handle terminates in a head that branches into several narrow and often slightly curved tine (structural), tines with whic ...
, skewers, batteries, discovered attack
In chess, a discovered attack is a direct attack revealed when one piece moves out of the way of another. Discovered attacks can be extremely powerful, as the piece moved can make a threat independently of the piece it reveals. Like many chess ...
s (especially discovered checks), zwischenzug
The zwischenzug ( German: , "intermediate move"; also called an in-between move or intermezzo) is a chess tactic in which a player, instead of playing the expected move (commonly a ), first interposes another move posing an immediate threat that ...
s, deflections, decoys
A decoy (derived from the Dutch ''de'' ''kooi'', literally "the cage" or possibly ''eenden kooi'', "Duck decoy (structure), duck cage") is usually a person, tool, device, or event which resembles what an individual or a group might be looking f ...
, sacrifices
Sacrifice is an act or offering made to a deity. A sacrifice can serve as propitiation, or a sacrifice can be an offering of praise and thanksgiving.
Evidence of ritual animal sacrifice has been seen at least since ancient Hebrews and Greeks ...
, underminings, overloadings, and interferences. Simple one-move or two-move tactical actions – threats, exchanges of , and double attacks – can be combined into longer sequences of tactical maneuvers that are often forced from the point of view of one or both players. A forced variation that involves a sacrifice and usually results in a tangible gain is called a ''combination
In mathematics, a combination is a selection of items from a set that has distinct members, such that the order of selection does not matter (unlike permutations). For example, given three fruits, say an apple, an orange and a pear, there are ...
''. Brilliant combinations – such as those in the Immortal Game
The Immortal Game was a chess game played in 1851 between Adolf Anderssen and Lionel Kieseritzky during the London 1851 chess tournament, an event in which both players participated. It was itself a game, however, not played as part of the to ...
– are considered beautiful and are admired by chess lovers.
A common type of chess exercise, aimed at developing players' tactical skills, is a position where a combination is available and the challenge is to find it. Such positions are usually taken from actual games or from analysis of actual games. Solutions usually result in checkmate, decisive advantage, or successful defense. Tactical exercises are commonly found in instructional books, chess magazines, newspaper chess columns, and internet chess sites.
Phases
Chess theory divides chess games into three phases with different sets of strategies: the opening
Opening may refer to:
Types of openings
* Hole
* A title sequence or opening credits
* Grand opening of a business or other institution
* Inauguration
* Keynote
* Opening sentence
* Opening sequence
* Opening statement, a beginning statemen ...
, the middlegame, and lastly the endgame. There is no universally accepted way to delineate the three phases of the game; the middlegame is typically considered to have begun after 10–20 moves, and the endgame when only a few pieces remain.
Opening
Competitive players typically learn, memorize, and play well-documented sequences of opening moves. The most common starting moves for White are 1.e4 and 1.d4, which usually lead to substantially different types of positions, and Black has multiple viable responses to both.
Sequences of opening moves are referred to as ''openings'' and are catalogued in reference works, such as the ''Encyclopaedia of Chess Openings
The ''Encyclopaedia of Chess Openings'' (''ECO'') is a reference work describing the state of Chess theory#Opening theory, opening theory in chess, originally published in five volumes from 1974 to 1979 by the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugos ...
''. There are thousands of openings, though only a small fraction of them are commonly played; variations of openings may also be given names. Openings vary widely in character from quiet (for example, the Réti Opening
The Réti Opening is a hypermodern chess opening whose "traditional" or "classic method" begins with the moves:
: 1. Nf3 d5
: 2. c4
White attacks Black's pawn from the , which may occasion 2...dxc4. White may couple this plan with a fian ...
) to aggressive play (like the Latvian Gambit
The Latvian Gambit (or Greco Countergambit) is a chess opening characterised by the moves:
:1. e4 e5
:2. Nf3 f5
It is one of the oldest chess openings, having been analysed in the 16th century by Giulio Cesare Polerio and then the 17th cent ...
). In some opening lines, the exact sequence considered best for both sides has been worked out to more than 30 moves.
The fundamental strategic aims of most openings are similar:
* ''Development:'' moving pieces (particularly bishops and knights) forward to squares on which they are useful (defending, attacking, and controlling important squares) or have the potential to take part in future plans and ideas.
* ''Control of the :'' control of the central squares allows pieces to be moved to any part of the board relatively easily, and can inhibit the mobility of the opponent's pieces.
* ''King safety:'' typically secured by castling; incorrectly timed castling can be wasteful or even harmful, however.
* ''Pawn structure
In a game of chess, the pawn structure (sometimes known as the pawn skeleton) is the configuration of pawn (chess), pawns on the chessboard. Because pawns are the least mobile of the chess pieces, the pawn structure is relatively static and thus ...
:'' players strive to avoid the creation of pawn weaknesses such as isolated, doubled, or backward pawns – and to force such weaknesses in the opponent's position.
Most players and theoreticians consider that White, by virtue of the initiative
Popular initiative
A popular initiative (also citizens' initiative) is a form of direct democracy by which a petition meeting certain hurdles can force a legal procedure on a proposition.
In direct initiative, the proposition is put direct ...
granted from moving first, begins the game with a small advantage. Black usually strives to neutralize White's advantage and achieve , or to develop in an unbalanced position.
Middlegame
The middlegame is the part of the game that starts after the opening. Because the opening theory has ended, players have to form plans based on the features of the position, and at the same time take into account the tactical possibilities of the position. The middlegame is the phase in which most combinations
In mathematics, a combination is a selection of items from a set that has distinct members, such that the order of selection does not matter (unlike permutations). For example, given three fruits, say an apple, an orange and a pear, there are t ...
occur. Combinations are a series of tactical moves executed to achieve some gain. Middlegame combinations are often connected with an attack against the opponent's king. Some typical patterns have their own names; for example, the Boden's Mate
Boden's Mate is a checkmating pattern in chess characterized by bishops on two criss-crossing diagonals (for example, bishops on a6 and f4 delivering mate to a king on c8), with possible flight squares for the king being occupied by friendly piece ...
or the Lasker–Bauer combination.
Specific plans or strategic themes will often arise from particular groups of openings that result in a specific type of pawn structure. An example is the , which is the attack of queenside pawns against an opponent who has more pawns on the queenside. The study of openings is therefore connected to the preparation of plans that are typical of the resulting middlegames.
Another important strategic question in the middlegame is whether and how to reduce material and transition into an endgame (i.e. ). Minor material advantages can generally be transformed into victory only in an endgame, and therefore the stronger side must choose an appropriate way to achieve an ending. Not every reduction of material is good for this purpose; for example, if one side keeps a light-squared bishop and the opponent has a dark-squared one, the transformation into a bishops and pawns ending is usually advantageous for the weaker side only, because an endgame with bishops on opposite colors is likely to be a draw, even with an advantage of a pawn, or sometimes even with a two-pawn advantage.
Endgame
The endgame (also ''end game'' or ''ending'') is the stage of the game when there are few pieces left on the board. There are three main strategic differences between earlier stages of the game and the endgame:
* Pawns become more important. Endgames often revolve around endeavors to promote a pawn by advancing it to the furthest .
* The king, which requires safeguarding from attack during the middlegame, emerges as a strong piece in the endgame. It is often used to protect its own pawns, attack enemy pawns, and hinder moves of the opponent's king.
* Zugzwang
Zugzwang (; ) is a situation found in chess and other turn-based games wherein one player is put at a disadvantage because of their obligation to make a move; a player is said to be "in zugzwang" when any legal move will worsen their position.
A ...
, a situation in which the player who is to move is forced to incur a disadvantage, is often a factor in endgames but rarely in other stages of the game. In the example diagram, either side having the move is in zugzwang: Black to move must play 1...Kb7 allowing White to promote the pawn after 2.Kd7; White to move must permit a draw, either by 1.Kc6 stalemate
Stalemate is a situation in chess where the player whose turn it is to move is not in check and has no legal move. Stalemate results in a draw. During the endgame, stalemate is a resource that can enable the player with the inferior position ...
or by losing the pawn after any other legal move.
Endgames can be classified according to the type of pieces remaining on the board. Basic checkmates are positions in which one side has only a king and the other side has one or two pieces and can checkmate the opposing king, with the pieces working together with their king. For example, king and pawn endgame
The endgame (or ending) is the final stage of a chess game which occurs after the middlegame. It begins when few pieces are left on the board.
The line between the middlegame and the endgame is often not clear, and may occur gradually or with ...
s involve only kings and pawns on one or both sides, and the task of the stronger side is to promote one of the pawns. Other more complicated endings are classified according to pieces on the board other than kings, such as "rook and pawn versus rook
The rook and pawn versus rook endgame is a fundamentally important, widely studied chess endgame. Precise play is usually required in these positions. With Best response, optimal play, some complicated wins require sixty moves to either checkmate ...
" endgames.
Problems and studies
Chess problems
A chess problem, also called a chess composition, is a puzzle created by the composer using chess pieces on a chessboard, which presents the solver with a particular task. For instance, a position may be given with the instruction that White i ...
(also called chess compositions) are composed positions, usually created for artistic effect rather than practical application. The creator is known as a chess composer
A chess composer is a person who creates endgame studies or chess problems. Chess composers usually specialize in a particular genre, e.g. endgame studies, twomovers, threemovers, moremovers, helpmates, selfmates, fairy problems, or retro ...
.
There are many types of chess problems, the most common being , in which White is required to move and checkmate Black within a specified number of moves, usually two or three, against any defense.
These are commonly referred to as "two-movers", "three-movers", or "more-movers". "Many-movers" (also known as "long-range problems") of over 100 moves have been composed, the current record standing at over 200; these usually require repetitions of the same manoeuvre in order to produce a repeated zugzwang
Zugzwang (; ) is a situation found in chess and other turn-based games wherein one player is put at a disadvantage because of their obligation to make a move; a player is said to be "in zugzwang" when any legal move will worsen their position.
A ...
and force detrimental pawn advances.
Directmates usually consist of positions unlikely to occur in an actual game, and are intended to illustrate a particular ', usually requiring a surprising or counterintuitive ' move. Themes associated with chess problems occasionally appear in actual games, when they are referred to as "problem-like" moves.
Other common types of problems include:
*Helpmate
A helpmate is a type of chess problem in which both sides cooperate in order to achieve the goal of checkmating Black. In a helpmate in ''n'' moves, Black moves first, then White, each side moving ''n'' times, to culminate in White's ''nth'' m ...
s, in which Black moves first and cooperates with White to get Black's king checkmated
*Selfmate
A selfmate is a chess problem in which White, moving first, must force Black to deliver checkmate within a specified number of moves. Selfmates were once known as sui-mates.
Example
The problem shown is a relatively simple example. It is a sel ...
s, in which White moves first and forces Black to checkmate White
* Retrograde analysis problems, in which the solver is required to work out what has previously occurred in the game, for example to prove that castling is illegal in the current position
The above type of problems are usually considered orthodox, in the sense that the standard rules of chess are observed.
Fairy chess
Fairy chess is the area of chess composition in which there are some changes to the rules of chess. It may involve changes to the board, pieces, or rules to express an idea or theme impossible in orthodox chess. An altered piece used in fairy ...
problems, also called heterodox problems, involve altered rules, such as the use of unconventional pieces or boards, or stipulations that contradict the standard rules of chess such as reflexmate
A reflexmate is a chess problem in which White, moving first, must force Black to deliver checkmate within a specified number of moves against their will – with the added condition that if either player can give checkmate, they must. If this c ...
s or seriesmover
A ''seriesmover'' is a chess problem in which one side makes a series of legal moves without reply at the end of which the other side makes a single move, giving checkmate or yielding stalemate, depending on the precise stipulation. Checks canno ...
s.
Studies are usually considered distinct from problems, although there is some overlap. In a study, the stipulation is that White to play must win or draw, without specifying any particular number of moves. The majority of studies are endgame positions, with varying degrees of realism or practical application.
Tournaments for composition and solving of chess problems and studies are organized by the World Federation for Chess Composition The World Federation for Chess Composition (WFCC) is the highest body governing the official activities in the chess composition. It was known as the Permanent Commission of the FIDE for Chess Compositions (PCCC) from its inception in 1956 until Oct ...
(WFCC), which works cooperatively with but independent of FIDE. The WFCC awards titles for composing and solving chess problems.
Chess in public spaces
Chess is often played in public spaces such as parks and town squares. Although the nature of these games is often , the chess hustling
Hustling is the deceptive act of disguising one's skill in a sport or game with the intent of luring someone of probably lesser skill into gambling (or gambling for higher than current stakes) with the hustler, as a form of both a confidence tri ...
scene has seen growth in urban areas such as New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
.
Organized competition
Tournaments and matches
 Contemporary chess is an organized sport with structured international and national leagues, tournaments, and
Contemporary chess is an organized sport with structured international and national leagues, tournaments, and congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
es. Thousands of chess tournaments, matches, and festivals are held around the world every year catering to players of all levels.
Tournaments with a small number of players may use the round-robin format, in which every player plays one game against every other player. For a large number of players, the Swiss system may be used, in which each player is paired against an opponent who has the same (or as similar as possible) score in each round. In either case, a player's score is usually calculated as 1 point for each game won and one-half point for each game drawn. Variations such as "football scoring" (3 points for a win, 1 point for a draw) may be used by tournament organizers, but ratings are always calculated on the basis of standard scoring. A player's score may be reported as total score out of games played (e.g. 5½/8), points for versus points against (e.g. 5½–2½), or by number of wins, losses and draws (e.g. +4−1=3).
The term "match" refers not to an individual game, but to either a series of games between two players, or a team competition in which each player of one team plays one game against a player of the other team.
Governance
Chess's international governing body is usually known by its French acronym FIDE
The International Chess Federation or World Chess Federation, commonly referred to by its French acronym FIDE ( , ), is an international organization based in Switzerland that connects the various national chess federations and acts as the Spor ...
(pronounced FEE-day) ( French: Fédération Internationale des Échecs), or International Chess Federation. FIDE's membership consists of the national chess organizations of over 180 countries; there are also several associate members, including various supra-national organizations, the International Braille Chess Association
The International Braille Chess Association (IBCA) is an organization for blind and visually impaired chess players. The IBCA is a FIDE-affiliated chess organization as well as a part of the International Blind Sports Federation. The Internation ...
(IBCA), International Chess Committee of the Deaf (ICCD), and the International Physically Disabled Chess Association
International is an adjective (also used as a noun) meaning "between nations".
International may also refer to:
Music Albums
* ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011
* ''International'' (New Order album), 2002
* ''International'' (The T ...
(IPCA). FIDE is recognized as a sports governing body
A sports governing body is a sports organisation that has a regulatory or sanctioning function.
Sports governing bodies come in various forms and have a variety of regulatory functions, including disciplinary action for rule infractions and dec ...
by the International Olympic Committee
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; , CIO) is the international, non-governmental, sports governing body of the modern Olympic Games. Founded in 1894 by Pierre de Coubertin and Demetrios Vikelas, it is based i ...
, but chess has never been part of the Olympic Games
The modern Olympic Games (Olympics; ) are the world's preeminent international Olympic sports, sporting events. They feature summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a Multi-s ...
.
 FIDE's most visible activity is organizing the
FIDE's most visible activity is organizing the World Chess Championship
The World Chess Championship is played to determine the world champion in chess. The current world champion is Gukesh Dommaraju, who defeated the previous champion Ding Liren in the World Chess Championship 2024, 2024 World Chess Championship. ...
, a role it assumed in 1948. The current World Champion is Gukesh Dommaraju
Gukesh Dommaraju (born 29 May 2006) is an Indian chess grandmaster and the reigning World Chess Champion. A chess prodigy, Gukesh is the youngest undisputed world champion, the youngest player to have surpassed a FIDE rating of 2750, doing s ...
of India.Ju Wenjun
Ju Wenjun (; born 31 January 1991) is a Chinese chess grandmaster. She is the reigning five-time Women's World Champion, the reigning Women's World Blitz Chess Champion, and a two-time Women's World Rapid Chess Champion. In March 2017, she be ...
from China.
Other competitions for individuals include the World Junior Chess Championship
The World Junior Chess Championship is an under-20 chess tournament (players must have been under 20 years old on 1 January in the year of competition) organized by the World Chess Federation (FIDE).
The idea was the brainchild of William Rits ...
, the European Individual Chess Championship
The European Individual Chess Championship is a chess tournament organised by the European Chess Union. It was established in 2000 and has since then taken place on a yearly basis.
Apart from determining the European champions (open and women's) ...
, the tournaments for the World Championship qualification cycle, and the various national championships
A national championship(s) is the top achievement for any sport or competition, contest within a league of a particular nation or nation state. The title is usually awarded by contests, ranking systems, stature, ability, etc. This determines the be ...
. Invitation-only tournaments regularly attract the world's strongest players. Examples include Spain's Linares event, Monte Carlo's Melody Amber
The Amber chess tournament (officially the ''Amber Rapid and Blindfold Chess Tournament'', previously ''Melody Amber'') was an annual invitation-only event for some of the world's best players, from 1992 to 2011. Since the second edition, the event ...
tournament, the Dortmund Sparkassen meeting, Sofia's M-tel Masters, and Wijk aan Zee
Wijk aan Zee (; ) is a village on the coast of the North Sea in the municipality of Beverwijk, the province of North Holland of the Netherlands. The prestigious Tata Steel Chess Tournament (formerly called the Corus chess tournament or the Hoogove ...
's Tata Steel
Tata Steel Limited is an Indian multinational steel-making company headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra, with its primary operations based in Jamshedpur, Jharkhand. It is a subsidiary of the Tata Group.
Formerly known as Tata Iron and Steel ...
tournament.
Regular team chess events include the Chess Olympiad
The Chess Olympiad is a biennial chess tournament in which teams representing nations of the world compete. FIDE organises the tournament and selects the host nation. Amidst the COVID-19 pandemic, FIDE held an Online Chess Olympiad in FIDE Onli ...
and the European Team Chess Championship
The European Team Championship (often abbreviated in texts and games databases as ''ETC'') is an international team chess event, eligible for the participation of European nations whose chess federations are located in zones 1.1 to 1.9. This more ...
.
The World Chess Solving Championship
The World Chess Solving Championship (WCSC) is an annual competition in the solving of chess problems (also known as chess puzzles) organized by the World Federation for Chess Composition (WFCC), previously by FIDE via the Permanent Commission of ...
and World Correspondence Chess Championship include both team and individual events. These are held independently of FIDE by, respectively, the World Federation for Chess Composition The World Federation for Chess Composition (WFCC) is the highest body governing the official activities in the chess composition. It was known as the Permanent Commission of the FIDE for Chess Compositions (PCCC) from its inception in 1956 until Oct ...
(WFCC), and the International Correspondence Chess Federation
International Correspondence Chess Federation (ICCF) was founded on 26 March 1951 as a new appearance of the International Correspondence Chess Association (ICCA), which was founded in 1945, as successor of the Internationaler Fernschachbund (IF ...
(ICCF).
Titles and rankings
In order to rank players, FIDE, ICCF, and most national chess organizations use the Elo rating system
The Elo rating system is a method for calculating the relative skill levels of players in zero-sum games such as chess or esports. It is named after its creator Arpad Elo, a Hungarian-American chess master and physics professor.
The Elo system wa ...
developed by Arpad Elo
Arpad Emmerich Elo ( August 25, 1903 – November 5, 1992) was a Hungarian-American physics professor who created the Elo rating system for two-player games such as chess.
Born in Egyházaskesző, Kingdom of Hungary, he moved to the Uni ...
. An average club player has a rating of about 1500; the highest FIDE rating of all time, 2882, was achieved by Magnus Carlsen
Sven Magnus Øen Carlsen (born 30 November 1990) is a Norwegian Grandmaster (chess), chess grandmaster. Carlsen is a five-time World Chess Championship, World Chess Champion, five-time World Rapid Chess Championship, World Rapid Chess Champio ...
on the March 2014 FIDE rating list.
Players may be awarded lifetime titles by FIDE:
* Grandmaster (GM) is the highest title a chess player can attain. For the GM title, a player must have had an Elo rating of 2500 or more at least once and must achieve three results of a prescribed standard (called norms) in tournaments involving other grandmasters, including some from countries other than the applicant's. There are other milestones that can substitute for norms, such as winning the World Junior Championship.
* International Master
FIDE titles are awarded by the international chess governing body FIDE (''Fédération Internationale des Échecs'') for outstanding performance. The highest such title is Grandmaster (GM). Titles generally require a combination of Elo rating and ...
(IM). The conditions are similar to GM, but less demanding. The minimum rating for the IM title is 2400.
* FIDE Master
FIDE titles are awarded by the international chess governing body FIDE (''Fédération Internationale des Échecs'') for outstanding performance. The highest such title is Grandmaster (GM). Titles generally require a combination of Elo rating and ...
(FM). The usual way for a player to qualify for the FIDE Master title is by achieving a FIDE rating of 2300 or more.
* Candidate Master
FIDE titles are awarded by the international chess governing body FIDE (''Fédération Internationale des Échecs'') for outstanding performance. The highest such title is Grandmaster (chess), Grandmaster (GM). Titles generally require a combinatio ...
(CM). Similar to FM, but with a FIDE rating of at least 2200.
The above titles are known as "open" titles, obtainable by both men and women. There are also separate women-only titles; Woman Grandmaster (WGM), Woman International Master (WIM), Woman FIDE Master (WFM) and Woman Candidate Master (WCM). These require a performance level approximately 200 rating points below their respective open titles, and their continued existence has sometimes been controversial. Beginning with Nona Gaprindashvili
Nona Gaprindashvili ( ka, ნონა გაფრინდაშვილი; born 3 May 1941) is a Georgian chess Grandmaster. Noted for her aggressive style of play, she was the women's world chess champion from 1962 to 1978, and in 1978 ...
in 1978, a number of women have earned the open GM title: 40 .[Current FIDE lists of top players with their titles are online at ]
FIDE also awards titles for arbiters and trainers. International titles are also awarded to composers and solvers of chess problems and to correspondence chess players (by the International Correspondence Chess Federation
International Correspondence Chess Federation (ICCF) was founded on 26 March 1951 as a new appearance of the International Correspondence Chess Association (ICCA), which was founded in 1945, as successor of the Internationaler Fernschachbund (IF ...
). National chess organizations may also award titles.
History
Origins
Texts referring to the origins of chess date from the beginning of the seventh century. Three are written in ''Pahlavi'' (Middle Persian
Middle Persian, also known by its endonym Pārsīk or Pārsīg ( Inscriptional Pahlavi script: , Manichaean script: , Avestan script: ) in its later form, is a Western Middle Iranian language which became the literary language of the Sasania ...
) and one, the ''Harshacharita
The ''Harshacharita'' (, ; English: ''The deeds of Harsha'') is the biography of Indian emperor Harsha by Banabhatta, also known as Bana, who was a Sanskrit writer of seventh-century CE India. He was the ''Asthana Kavi'', meaning ''Court Poet ...
'', is in Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
. One of these texts, the ''Chatrang-namak'', represents one of the earliest written accounts of chess. The narrator Bozorgmehr
Bozorgmehr-e Bokhtagan (Middle Persian: ''Wuzurgmihr ī Bōkhtagān''), also known as Burzmihr, Dadmihr and Dadburzmihr, was an Iranian peoples, Iranian sage and dignitary from the House of Karen, Karen family, who served as minister (''Wuzurg fr ...
explains that ''Chatrang'', "Chess" in Pahlavi, was introduced to Persia by ' Dewasarm, a great ruler of India' during the reign of Khosrow I
Khosrow I (also spelled Khosrau, Khusro or Chosroes; ), traditionally known by his epithet of Anushirvan ("the Immortal Soul"), was the Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 531 to 579. He was the son and successor of Kavad I ().
Inheriting a rei ...
:
 The oldest known chess manual was in Arabic and dates to about 840, written by
The oldest known chess manual was in Arabic and dates to about 840, written by al-Adli ar-Rumi
Al-Adli al-Rumi (), was an Arab player and theoretician of Shatranj, an ancient form of chess from Persia. Originally from Anatolia, he authored one of the first treatises on Shatranj in 842, called ''Kitab ash-shatranj'' ('Book of Chess').
He wa ...
(800–870), a renowned Arab chess player, titled ''Kitab ash-shatranj'' (The Book of Chess). This is a lost manuscript, but is referenced in later works. Here also, al-Adli attributes the origins of Persian chess to India, along with the eighth-century collection of fables Kalīla wa-Dimna
''Kalīla wa-Dimna'' or ''Kelileh o Demneh'' () is a collection of fables. The book consists of fifteen chapters containing many fables whose heroes are animals. A remarkable animal character is the lion, who plays the role of the king; he has ...
.India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
in the early seventh century. More recently, this consensus has been the subject of further scrutiny.
The early forms of chess in India were known as '' chaturaṅga'' (), literally "four divisions" f the military
F, or f, is the sixth Letter (alphabet), letter of the Latin alphabet and many modern alphabets influenced by it, including the English alphabet, modern English alphabet and the alphabets of all other modern western European languages. Its n ...
nbsp;– infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadl ...
, cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from ''cheval'' meaning "horse") are groups of soldiers or warriors who Horses in warfare, fight mounted on horseback. Until the 20th century, cavalry were the most mob ...
, elephants
Elephants are the Largest and heaviest animals, largest living land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant (''Loxodonta africana''), the African forest elephant (''L. cyclotis''), and the Asian ele ...
, and chariot
A chariot is a type of vehicle similar to a cart, driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid Propulsion, motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk O ...
ry – represented by pieces that would later evolve into the modern pawn, knight, bishop, and rook, respectively. Chaturanga was played on an 8×8 uncheckered board, called ''ashtāpada
Ashtāpada () or Ashtapadi is an Indian board game. Although it is played on a checkered board similar to chess, Ashtāpada predates it and differs in its mechanics and victory conditions. The game was mentioned on the list of games that Gautama ...
''. Thence it spread eastward and westward along the Silk Road
The Silk Road was a network of Asian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over , it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the ...
. The earliest evidence of chess is found in nearby Sasanian Persia
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranian peoples, Iranians"), was an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, th ...
around 600 A.D., where the game came to be known by the name '' chatrang'' (). Chatrang was taken up by the Muslim world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
after the Islamic conquest of Persia
As part of the early Muslim conquests, which were initiated by Muhammad in 622, the Rashidun Caliphate conquered the Sasanian Empire between 632 and 654. This event led to the decline of Zoroastrianism, which had been the official religion of ...
(633–51), where it was then named ''shatranj
Shatranj (, ; from Middle Persian ) is an old form of chess, as played in the Sasanian Empire. Its origins lie in the South Asian game of chaturanga. Modern chess gradually developed from this game, as it was introduced to Europe by contacts in ...
'' (; ), with the pieces largely retaining their Persian names. In Spanish, "shatranj" was rendered as ''ajedrez'' ("al-shatranj"), in Portuguese as ''xadrez'', and in Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
as ζατρίκιον (''zatrikion'', which comes directly from the Persian ''chatrang''), but in the rest of Europe it was replaced by versions of the Persian ''shāh'' ("king"), from which the English words "check" and "chess" descend. The word "checkmate
Checkmate (often shortened to mate) is any game position in chess and other chess-like games in which a player's king is in check (threatened with ) and there is no possible escape. Checkmating the opponent wins the game.
In chess, the king is ...
" is derived from the Persian ''shāh māt'' ("the king is dead").

Xiangqi
Xiangqi (; ), commonly known as Chinese chess or elephant chess, is a Strategy game, strategy board game for two players. It is the most popular board game in China. Xiangqi is in the same family of games as shogi, janggi, chess, Western ches ...
is the form of chess best known in China. The eastern migration of chess, into China and Southeast Asia, has even less documentation than its migration west, making it largely conjectured. The word ''xiàngqí'' () was used in China to refer to a game from 569 A.D. at the latest, but it has not been proven that this game was directly related to chess.
The first reference to Chinese chess appears in a book entitled ''Xuánguaì Lù'' (; "Record of the Mysterious and Strange"), dating to about 800. A minority view holds that Western chess arose from xiàngqí or one of its predecessors. Chess historians Jean-Louis Cazaux and Rick Knowlton contend that xiangqi's intrinsic characteristics make it easier to construct an evolutionary path from China to India/Persia than the opposite direction.
The oldest archaeological chess artifacts – ivory pieces – were excavated in ancient Afrasiab
Afrasiyab ( ''afrāsiyāb''; ; Middle-Persian: ''Frāsiyāv, Frāsiyāk'') is the name of the mythical king and hero of Turan. He is the main antagonist of the Persian epic ''Shahnameh'', written by Ferdowsi.
Name and origin
''Afrā'' is the po ...
, today's Samarkand
Samarkand ( ; Uzbek language, Uzbek and Tajik language, Tajik: Самарқанд / Samarqand, ) is a city in southeastern Uzbekistan and among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in Central As ...
, in Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
, Central Asia, and date to about 760, with some of them possibly being older. Remarkably, almost all findings of the oldest pieces come from along the Silk Road, from the former regions of the Tarim Basin (today's Xinjiang in China), Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (, now called the Amu Darya) is the Latin name for the region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
, Sogdiana
Sogdia () or Sogdiana was an ancient Iranian civilization between the Amu Darya and the Syr Darya, and in present-day Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan. Sogdiana was also a province of the Achaemenid Empire, and l ...
, Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian language, Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization in Central Asia based in the area south of the Oxus River (modern Amu Darya) and north of the mountains of the Hindu Kush, an area ...
, Gandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending ...
, to Iran on one end and to India through Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir P ...
on the other.
 The game reached Western Europe and Russia via at least three routes, the earliest being in the ninth century. By the year 1000, it had spread throughout both the Muslim Iberia and
The game reached Western Europe and Russia via at least three routes, the earliest being in the ninth century. By the year 1000, it had spread throughout both the Muslim Iberia and Latin Europe
The term Latins has been used throughout history to refer to various peoples, ethnicities and religious groups using Latin or the Latin-derived Romance languages, as part of the legacy of the Roman Empire. In the Ancient World, it referred to th ...
. A Latin poem called ''Versus de scachis
(Latin: "Verses on Chess"), also known as the ''Einsiedeln Poem'' in some literature, is the title given to a 10th-century Medieval Latin poem about chess. It is the first known European text to provide a technical description of chess for did ...
'' ("Verses on Chess") dated to the late 10th century, has been preserved at Einsiedeln Abbey
Einsiedeln Abbey () is a Catholic monastery administered by the Benedictine Order in the village of Einsiedeln, Switzerland.
The Abbey of Einsiedeln is one of the most important baroque monastic sites and the largest place of pilgrimage in Swit ...
in Switzerland.
1200–1700: Origins of the modern game
The game of chess was then played and known in all European countries. A famous 13th-century Spanish manuscript covering chess, backgammon
Backgammon is a two-player board game played with counters and dice on tables boards. It is the most widespread Western member of the large family of tables games, whose ancestors date back at least 1,600 years. The earliest record of backgammo ...
, and dice
A die (: dice, sometimes also used as ) is a small, throwable object with marked sides that can rest in multiple positions. Dice are used for generating random values, commonly as part of tabletop games, including dice games, board games, ro ...
is known as the , which is the earliest Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
an treatise on chess as well as being the oldest document on European tables games
Tables games are a class of board game that includes backgammon and which are played on a tables board, typically with two rows of 12 vertical markings called point (tables game), points. Players roll dice to determine the movement of pieces. Tab ...
. The rules were fundamentally similar to those of the Arabic shatranj
Shatranj (, ; from Middle Persian ) is an old form of chess, as played in the Sasanian Empire. Its origins lie in the South Asian game of chaturanga. Modern chess gradually developed from this game, as it was introduced to Europe by contacts in ...
. The differences were mostly in the use of a checkered board instead of a plain monochrome board used by Arabs and the habit of allowing some or all pawns to make an initial double step. In some regions, the queen, which had replaced the wazir, or the king could also make an initial two-square leap under some conditions.
 Around 1200, the rules of shatranj started to be modified in Europe, culminating, several major changes later, in the emergence of modern chess practically as it is known today. A major change was the modern piece movement rules, which began to appear in intellectual circles in
Around 1200, the rules of shatranj started to be modified in Europe, culminating, several major changes later, in the emergence of modern chess practically as it is known today. A major change was the modern piece movement rules, which began to appear in intellectual circles in Valencia
Valencia ( , ), formally València (), is the capital of the Province of Valencia, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Valencian Community, the same name in Spain. It is located on the banks of the Turia (r ...
, Spain, around 1475, which established the foundations and brought it very close to current chess. These new rules then were quickly adopted in Italy and Southern France before diffusing into the rest of Europe.queen
Queen most commonly refers to:
* Queen regnant, a female monarch of a kingdom
* Queen consort, the wife of a reigning king
* Queen (band), a British rock band
Queen or QUEEN may also refer to:
Monarchy
* Queen dowager, the widow of a king
* Q ...
replaced the earlier vizier
A vizier (; ; ) is a high-ranking political advisor or Minister (government), minister in the Near East. The Abbasids, Abbasid caliphs gave the title ''wazir'' to a minister formerly called ''katib'' (secretary), who was at first merely a help ...
chess piece toward the end of the 10th century and by the 15th century had become the most powerful piece; in light of that, modern chess was often referred to at the time as "Queen's Chess" or "Mad Queen Chess". Castling, derived from the "king's leap", usually in combination with a pawn or rook move to bring the king to safety, was introduced. These new rules quickly spread throughout Western Europe.
Writings about chess theory
The game of chess is commonly divided into three phases: the chess opening, opening, Chess middlegame, middlegame, and Chess endgame, endgame. There is a large body of theory regarding how the game should be played in each of these phases, especi ...
began to appear in the late 15th century. An anonymous treatise on chess of 1490 with the first part containing some openings and the second 30 endgames is deposited in the library of the University of Göttingen
The University of Göttingen, officially the Georg August University of Göttingen (, commonly referred to as Georgia Augusta), is a Public university, public research university in the city of Göttingen, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1734 ...
.Francesc Vicent
Francesc Vicent (1450 in Segorbe – c. 1512) was a Valencian author who wrote the first treatise about chess using the present-day moves for the queen (chess), queen and the bishop (chess), bishop. ''Libre dels jochs partits dels schacs en nombr ...
in Segorbe
Segorbe is a municipality in the mountainous coastal province of Castelló, Valencia (autonomous community), autonomous community of Valencia, Spain. The former Palace of the Dukes of Medinaceli now houses the city's mayor. Segorbe's bull-running ...
in 1495, but no copy of this work has survived.Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
churchman Luis Ramírez de Lucena
Luis Ramírez de Lucena (c. 1465 – c. 1530) was a Spanish chess player who published the first extant chess book. He is believed to be the son of humanist writer and diplomat Juan de Lucena.
Book
Lucena wrote the oldest surviving printed boo ...
was published in Salamanca
Salamanca () is a Municipality of Spain, municipality and city in Spain, capital of the Province of Salamanca, province of the same name, located in the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is located in the Campo Charro comarca, in the ...
in 1497.Pedro Damiano
Pedro Damiano (; ''Damiano'' is the Italian form, much like the Latin ''Damianus''; 1480–1544) was a Portuguese chess player. A native of Odemira, he was a pharmacist by profession. He wrote ''Questo libro e da imparare giocare a scachi et d ...
, Italians Giovanni Leonardo Di Bona
Giovanni Leonardo di Bona or Giovanni Leonardo da Cutro (both given names can also be seen in the reversed order Leonardo Giovanni), known as Il Puttino () (1533–1578), was an early Italian chess master.
Giovanni Leonardo was born in Cutro, ...
, Giulio Cesare Polerio
Giulio Cesare Polerio (c. 1555, – c. 1610; reconstruction of places and dates by Adriano Chicco) was an Italian chess theoretician and player.
Name affixes used for him are ''l'Apruzzese'', Giu io Cesare ''da Lanciano'' (Salvio/Walker), and ...
and Gioachino Greco
Gioachino Greco ( – ), surnamed Cusentino and more frequently ''il Calabrese'', was an Italian chess player and writer. He recorded some of the earliest chess games known in their entirety. His games, which never indicated players, were q ...
, and Spanish bishop Ruy López de Segura
Rodrigo "Ruy" López de Segura ( – c. 1580) was a Spanish chess player, author, and Catholic priest
The priesthood is the office of the ministers of religion, who have been commissioned ("ordained") with the holy orders of the Catho ...
developed elements of opening theory and started to analyze simple endgames.
1700–1873: Romantic era
In the 18th century, the center of European chess life moved from Southern Europe to mainland France. The two most important French masters were François-André Danican Philidor
François-André Danican Philidor (7 September 1726 – 31 August 1795), often referred to as André Danican Philidor during his lifetime, was a French composer and chess player. He contributed to the early development of the ''opéra comique''. ...
, a musician by profession, who discovered the importance of pawns for chess strategy, and later Louis-Charles Mahé de La Bourdonnais
Louis-Charles Mahé de La Bourdonnais (1795 – December 1840) was a French chess master, possibly the strongest player in the early 19th century.
Early life
La Bourdonnais was born on the island of Réunion in the Indian Ocean in 1795. He w ...
, who won a famous series of matches against Irish master Alexander McDonnell Alexander McDonnell may refer to:
* Alexander McDonnell (chess player) (1798–1835), Irish chess master
*Alexander McDonnell (engineer)
Alexander McDonnell was an Irish locomotive engineer and civil engineer. He was born in Dublin on 18 Dece ...
in 1834. Centers of chess activity in this period were coffee house
A coffeehouse, coffee shop, or café (), is an establishment that serves various types of coffee, espresso, latte, Caffè americano, americano and cappuccino, among other hot beverages. Many coffeehouses in West Asia offer ''shisha'' (actually ...
s in major European cities like ''Café de la Régence
The Café de la Régence in Paris was an important European centre of chess in the 18th and 19th centuries. All important chess masters of the time played there.
The Café's masters included, but are not limited to:
* Paul Morphy
* Françoi ...
'' in Paris and '' Simpson's Divan'' in London.
At the same time, the Romantic intellectual movement had had a far-reaching impact on chess, with aesthetics and tactical beauty being held in higher regard than objective soundness and strategic planning. As a result, virtually all games began with the Open Game
An Open Game (or Double King's Pawn Opening) is a generic term for a family of chess openings beginning with the moves:
:1. b:Chess Opening Theory/1. e4, e4 b:Chess Opening Theory/1. e4/1...e5, e5
White has moved the king's pawn two squares and Bl ...
, and it was considered unsportsmanlike to decline gambits that invited tactical play such as the King's Gambit
The King's Gambit is a chess opening that begins with the moves:
:1. e4 e5
:2. f4
White offers a pawn to divert the black e-pawn. If Black accepts the gambit, White may play d4 and Bxf4, regaining the gambit pawn with domination, or direc ...
and the Evans Gambit
The Evans Gambit is a chess opening characterised by the moves:
:1. e4 e5
:2. Nf3 Nc6
:3. Bc4 Bc5
:4. b4
The Evans Gambit is an attacking line of the Giuoco Piano. White offers a pawn to divert the black bishop on c5. If Black accepts, W ...
.Romantic chess
Romantic chess is a style of chess popular in the 18th century until its decline in the 1880s. This style of chess emphasizes quick, tactical maneuvers rather than long-term strategic planning. Romantic players consider winning to be secondary to w ...
, and its sharp, tactical style of play was predominant until the late 19th century.
The rules concerning stalemate were finalized in the early 19th century. Also in the 19th century, the convention that White moves first was established (formerly either White or Black could move first). Finally, the rules around castling and en passant captures were standardized – variations in these rules persisted in Italy until the late 19th century. The resulting standard game is sometimes referred to as ''Western chess'' or ''international chess'', particularly in Asia where other games of the chess family such as xiangqi
Xiangqi (; ), commonly known as Chinese chess or elephant chess, is a Strategy game, strategy board game for two players. It is the most popular board game in China. Xiangqi is in the same family of games as shogi, janggi, chess, Western ches ...
are prevalent. Since the 19th century, the only rule changes, such as the establishment of the correct procedure for claiming a draw by repetition, have been technical in nature.
As the 19th century progressed, chess organization developed quickly. Many chess club
A chess club is a club formed for the purpose of playing the board game of chess. Chess clubs often provide for both informal and tournament games and sometimes offer league play. Traditionally clubs play over the board and face to face chess a ...
s, chess books, and chess journals appeared. There were correspondence matches between cities; for example, the London Chess Club played against the Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. The city is located in southeast Scotland and is bounded to the north by the Firth of Forth and to the south by the Pentland Hills. Edinburgh ...
Chess Club in 1824. Chess problems
A chess problem, also called a chess composition, is a puzzle created by the composer using chess pieces on a chessboard, which presents the solver with a particular task. For instance, a position may be given with the instruction that White i ...
became a regular part of 19th-century newspapers; Bernhard Horwitz
Bernhard Horwitz (1807 in Neustrelitz – 1885 in London) was a German and British chess master, chess writer and chess composer.
Horwitz was born in Neustrelitz and went to school in Berlin, where he studied art. From 1837 to 1843, he was part ...
, Josef Kling
Josef Kling (19 March 1811 – 1 December 1876), also found in English-language sources as Joseph Kling, was a German chess master and chess composer. He has been called "a pioneer of the modern style of chess." Although Kling was an expert on ...
, and Samuel Loyd
Samuel Loyd (January 30, 1841 – April 10, 1911) was an American chess player, chess composer, puzzle author, and recreational mathematics, recreational mathematician. Loyd was born in Philadelphia but raised in New York City.
As a chess comp ...
composed some of the most influential problems. In 1843, von der Lasa published his and Bilguer's ''Handbuch des Schachspiels
''Handbuch des Schachspiels'' (''Handbook of Chess'', often simply called the ''Handbuch'') is a chess book, first published in 1843 by Tassilo von Heydebrand und der Lasa. It was a comprehensive reference book on the game, and one of the most i ...
'' (''Handbook of Chess''), the first comprehensive manual of chess theory.
The first modern chess tournament was organized by Howard Staunton
Howard Staunton (April 1810 – 22 June 1874) was an English chess master who is generally regarded as the world's strongest player from 1843 to 1851, largely as a result of his 1843 victory over Pierre Charles Fournier de Saint-A ...
, a leading English chess player, and was held in London in 1851. It was won by the German Adolf Anderssen
Karl Ernst Adolf Anderssen (6 July 1818 – 13 March 1879)"Anderssen, Adolf" in ''Encyclopædia Britannica, The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 385. was a German chess master. ...
, who was hailed as the leading chess master. His brilliant, energetic attacking style was typical for the time. Sparkling games like Anderssen's Immortal Game
The Immortal Game was a chess game played in 1851 between Adolf Anderssen and Lionel Kieseritzky during the London 1851 chess tournament, an event in which both players participated. It was itself a game, however, not played as part of the to ...
and Evergreen Game
The Evergreen Game is a famous chess game won by Adolf Anderssen against Jean Dufresne in 1852.
This was probably an . At the time, there was no formal title of "World Champion", but the German mathematics professor Anderssen was widely consider ...
or Morphy's " Opera Game" were regarded as the highest possible summit of the art of chess.
Deeper insight into the nature of chess came with the American Paul Morphy
Paul Charles Morphy (June 22, 1837July 10, 1884) was an American chess player. During his brief career in the late 1850s, Morphy was acknowledged as the world's greatest chess master.
A prodigy, Morphy emerged onto the chess scene in 1857 ...
, an extraordinary chess prodigy
Chess is a board game for two players. It is an abstract strategy game that involves no hidden information and no elements of chance. It is played on a square board consisting of 64 squares arranged in an 8×8 grid. The players, referred to ...
. Morphy won against all important competitors (except Staunton, who refused to play), including Anderssen, during his short chess career between 1857 and 1863. Morphy's success stemmed from a combination of brilliant attacks and sound strategy; he intuitively knew how to prepare attacks.
1873–1945: Birth of a sport

Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
-born Wilhelm Steinitz
William Steinitz (born Wilhelm Steinitz; May 14, 1836 – August 12, 1900) was a Bohemian-Austrian, and later American, chess player. From 1886 to 1894, he was the first World Chess Champion. He was also a highly influential writer and c ...
laid the foundations for a scientific approach to the game, the art of breaking a position down into components and preparing correct plans. In addition to his theoretical achievements, Steinitz founded an important tradition: his triumph over the leading German master Johannes Zukertort
Johannes Hermann Zukertort (; 7 September 1842 – 20 June 1888) was a Polish-born British-German chess master. He was one of the leading world players for most of the 1870s and 1880s, but lost to Wilhelm Steinitz in the World Chess Championship ...
in 1886 is regarded as the first official World Chess Championship
The World Chess Championship is played to determine the world champion in chess. The current world champion is Gukesh Dommaraju, who defeated the previous champion Ding Liren in the World Chess Championship 2024, 2024 World Chess Championship. ...
. This win marked a stylistic transition at the highest levels of chess from an attacking, tactical style predominant in the Romantic era to a more positional, strategic style introduced to the chess world by Steinitz. Steinitz lost his crown in 1894 to a much younger player, the German mathematician Emanuel Lasker
Emanuel Lasker (; December 24, 1868 – January 11, 1941) was a German chess player, mathematician, and philosopher. He was the second World Chess Champion, holding the title for 27 years, from 1894 to 1921, the longest reign of any officially ...
, who maintained this title for 27 years, the longest tenure of any world champion.
After the end of the 19th century, the number of master tournaments and matches held annually quickly grew. The first Olympiad
An olympiad (, ''Olympiás'') is a period of four years, particularly those associated with the Ancient Olympic Games, ancient and Olympic Games, modern Olympic Games.
Although the ancient Olympics were established during Archaic Greece, Greece ...
was held in Paris in 1924, and FIDE
The International Chess Federation or World Chess Federation, commonly referred to by its French acronym FIDE ( , ), is an international organization based in Switzerland that connects the various national chess federations and acts as the Spor ...
was founded initially for the purpose of organizing that event. In 1927, the Women's World Chess Championship
The Women's World Chess Championship is a chess match played to determine the Women's World Chess Champion. It has been administered by FIDE since its inception in 1927, unlike the absolute World Chess Championship, which only came under FIDE's ...
was established; the first to hold the title was Czech-English master Vera Menchik
Vera Francevna Mencikova (, ''Vera Frantsevna Menchik''; ; 16 February 1906 – 26 June 1944), was a Russian-born Czechoslovak chess player who primarily resided in England. She was the first and longest-reigning Women's World Chess Champ ...
.
A prodigy from Cuba, José Raúl Capablanca
José Raúl Capablanca y Graupera (19 November 1888 – 8 March 1942) was a Cuban chess player who was the third World Chess Championship, world chess champion from 1921 to 1927. A chess prodigy, he was widely renowned for his exceptional Chess ...
, known for his skill in endgames, won the World Championship from Lasker in 1921. Capablanca was undefeated in tournament play for eight years, from 1916 to 1924. His successor (1927) was the Russian-French Alexander Alekhine
Alexander Aleksandrovich Alekhine. He disliked when Russians sometimes pronounced the of as , , which he regarded as a Yiddish distortion of his name, and insisted that the correct Russian pronunciation was . (March 24, 1946) was a Russian ...
, a strong attacking player who died as the world champion in 1946. Alekhine briefly lost the title to Dutch player Max Euwe
Machgielis "Max" Euwe (; May 20, 1901 – November 26, 1981) was a Dutch chess player, mathematician, author, and chess administrator. He was the fifth player to become World Chess Championship, World Chess Champion, a title he held from 1935 ...
in 1935 and regained it two years later.
In the interwar period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period, also known as the interbellum (), lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days) – from the end of World War I (WWI) to the beginning of World War II ( ...
, chess was revolutionized by the new theoretical school of so-called hypermodernists like Aron Nimzowitsch
Aron Nimzowitsch (; , ''Aron Isayevich Nimtsovich''; 7 November 1886 – 16 March 1935) was a Latvian-born Danish chess player and writer. In the late 1920s, Nimzowitsch was one of the best chess players in the world. He was the foremost f ...
and Richard Réti
Richard Réti (28 May 1889 – 6 June 1929) was an Austro-Hungarian and later Czechoslovak chess player, chess author and composer of endgame studies.
He was one of the principal proponents of hypermodernism in chess. With the exception of N ...
. They advocated controlling the of the board with distant pieces rather than with pawns, thus inviting opponents to occupy the center with pawns, which become objects of attack. Among the innovations popularized by hypermodernists was the fianchetto
In chess, the fianchetto ( or spelling pronunciation ; "little flank") is a pattern of wherein a bishop is developed to the second of the adjacent b- or g-, the having been moved one or two squares forward.
The fianchetto is a staple of man ...
: the development of bishops away from, rather than towards, the center, onto the b- and g-files.
1945–1990: Post-World War II era
 After the death of Alekhine, a new World Champion was sought. FIDE, which has controlled the title since then, ran a tournament of elite players. The winner of the 1948 tournament was Russian
After the death of Alekhine, a new World Champion was sought. FIDE, which has controlled the title since then, ran a tournament of elite players. The winner of the 1948 tournament was Russian Mikhail Botvinnik
Mikhail Moiseyevich Botvinnik (; ; – May 5, 1995) was a Soviet and Russian chess grandmaster who held five world titles in three different reigns. The sixth World Chess Champion, he also worked as an electrical engineer and computer sci ...
. In 1950, FIDE established a system of titles, conferring the title of Grandmaster on 27 players. (Some sources state that, in 1914, the title of chess Grandmaster was first formally conferred by Tsar Nicholas II of Russia
Nicholas II (Nikolai Alexandrovich Romanov; 186817 July 1918) or Nikolai II was the last reigning Emperor of Russia, Congress Poland, King of Congress Poland, and Grand Duke of Finland from 1 November 1894 until Abdication of Nicholas II, hi ...
to Lasker, Capablanca, Alekhine, Tarrasch, and Marshall
Marshall may refer to:
Places
Australia
*Marshall, Victoria, a suburb of Geelong, Victoria
** Marshall railway station
Canada
* Marshall, Saskatchewan
* The Marshall, a mountain in British Columbia
Liberia
* Marshall, Liberia
Marshall Is ...
, but this is a disputed claim.)
Botvinnik started an era of Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
dominance in the chess world, which mainly through the Soviet government's politically inspired efforts to demonstrate intellectual superiority over the West stood almost uninterrupted for more than a half-century. Until the dissolution of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was formally dissolved as a sovereign state and subject of international law on 26 December 1991 by Declaration No. 142-N of the Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union. Declaration No. 142-Н of ...
, there was only one non-Soviet champion, American Bobby Fischer
Robert James Fischer (March 9, 1943January 17, 2008) was an American Grandmaster (chess), chess grandmaster and the eleventh World Chess Championship, World Chess Champion. A chess prodigy, he won his first of a record eight US Chess Champi ...
(champion 1972–1975). Botvinnik also revolutionized opening theory. Previously, Black strove for equality, attempting to neutralize White's first-move advantage. As Black, Botvinnik strove for the initiative from the beginning. In the previous informal system of World Championships, the current champion decided which challenger he would play for the title and the challenger was forced to seek sponsors for the match. FIDE set up a new system of qualifying tournaments and matches. The world's strongest players were seeded into Interzonal
Interzonal chess tournaments were tournaments organized by the World Chess Federation FIDE from the 1950s to the 1990s. They were a stage in the triennial World Chess Championship cycle and were held after the Zonal tournaments, and before the Ca ...
tournaments, where they were joined by players who had qualified from Zonal tournaments. The leading finishers in these Interzonals would go through the "Candidates
A candidate, or nominee, is a prospective recipient of an award or honor, or a person seeking or being considered for some kind of position. For example, one can be a candidate for membership in a group or election to an office, in which case a ...
" stage, which was initially a tournament, and later a series of knockout matches. The winner of the Candidates would then play the reigning champion for the title. A champion defeated in a match had a right to play a rematch a year later. This system operated on a three-year cycle. Botvinnik participated in championship matches over a period of fifteen years. He won the world championship tournament in 1948 and retained the title in tied matches in 1951 and 1954. In 1957, he lost to Vasily Smyslov
Vasily Vasilyevich Smyslov (; 24 March 1921 – 27 March 2010) was a Soviet and Russian chess grandmaster who was the seventh World Chess Champion from 1957 to 1958. He was a Candidates Tournament, Candidate for the World Chess Championship on ...
, but regained the title in a rematch in 1958. In 1960, he lost the title to the 23-year-old Latvian prodigy Mikhail Tal
Mikhail Tal (9 November 1936 – 28 June 1992) was a Soviet and Latvian chess player and the eighth World Chess Champion. He is considered a creative genius and is widely regarded as Comparison of top chess players throughout history, one ...
, an accomplished tactician and attacking player who is widely regarded as one of the most creative players ever, hence his nickname "the magician from Riga". Botvinnik again regained the title in a rematch in 1961.
 Following the 1961 event, FIDE abolished the automatic right of a deposed champion to a rematch, and the next champion, Armenian
Following the 1961 event, FIDE abolished the automatic right of a deposed champion to a rematch, and the next champion, Armenian Tigran Petrosian
Tigran Vardani Petrosian (; ; 17 June 1929 – 13 August 1984) was a Soviet-Armenian chess grandmaster and the ninth World Chess Champion from 1963 to 1969. He was nicknamed "Iron Tigran" due to his almost-impenetrable defensive playing s ...
, a player renowned for his defensive and positional skills, held the title for two cycles, 1963–1969. His successor, Boris Spassky
Boris Vasilyevich Spassky (; January 30, 1937 – February 27, 2025) was a Russian chess grandmaster who was the tenth World Chess Champion, holding the title from 1969 to 1972. Spassky played three world championship matches: he lost to Tigra ...
from Russia (champion 1969–1972), won games in both positional and sharp tactical style. The next championship, the so-called Match of the Century, saw the first non-Soviet challenger since World War II, American Bobby Fischer
Robert James Fischer (March 9, 1943January 17, 2008) was an American Grandmaster (chess), chess grandmaster and the eleventh World Chess Championship, World Chess Champion. A chess prodigy, he won his first of a record eight US Chess Champi ...
. Fischer defeated his opponents in the Candidates
A candidate, or nominee, is a prospective recipient of an award or honor, or a person seeking or being considered for some kind of position. For example, one can be a candidate for membership in a group or election to an office, in which case a ...
matches by unheard-of margins, and convincingly defeated Spassky for the world championship. The match was followed closely by news media of the day, leading to a surge in popularity for chess; it also held significant political importance at the height of the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
, with the match being seen by both sides as a microcosm of the conflict between East and West. In 1975, however, Fischer refused to defend his title against Soviet Anatoly Karpov
Anatoly Yevgenyevich Karpov (, ; born May 23, 1951) is a Russian and former Soviet Grandmaster (chess), chess grandmaster, former World Chess Championship, World Chess Champion, and politician. He was the 12th World Chess Champion from 1975 ...
when he was unable to reach agreement on conditions with FIDE, and Karpov obtained the title by default. Fischer modernized many aspects of chess, especially by extensively preparing openings.
Karpov defended his title twice against Viktor Korchnoi
Viktor Lvovich Korchnoi (, ; 23 March 1931 – 6 June 2016) was a Soviet (before 1976) and Swiss (after 1980) chess grandmaster (GM) and chess writer. He is considered one of the strongest players never to have become World Chess Champion.
Bor ...
and dominated the 1970s and early 1980s with a string of tournament successes. In the 1984 World Chess Championship
Events
January
* January 1 – The Bornean Sultanate of Brunei gains full independence from the United Kingdom, having become a British protectorate in 1888.
* January 7 – Brunei becomes the sixth member of the Association of Southeas ...
, Karpov faced his toughest challenge to date, the young Garry Kasparov
Garry Kimovich Kasparov (born Garik Kimovich Weinstein on 13 April 1963) is a Russian Grandmaster (chess), chess grandmaster, former World Chess Champion (1985–2000), political activist and writer. His peak FIDE chess Elo rating system, ra ...
from Baku
Baku (, ; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Azerbaijan, largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and in the Caucasus region. Baku is below sea level, which makes it the List of capital ci ...
, Soviet Azerbaijan
The Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic, also referred to as the Azerbaijani Soviet Socialist Republic, Azerbaijan SSR, Azerbaijani SSR, AzSSR, Soviet Azerbaijan or simply Azerbaijan, was one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent re ...
. The match was aborted in controversial circumstances after 5 months and 48 games with Karpov leading by 5 wins to 3, but evidently exhausted; many commentators believed Kasparov, who had won the last two games, would have won the match had it continued. Kasparov won the 1985 rematch. Kasparov and Karpov contested three further closely fought matches in 1986, 1987 and 1990, Kasparov winning them all. Kasparov became the dominant figure of world chess from the mid-1980s until his retirement from competition in 2005.
Beginnings of chess technology
Chess-playing computer programs (later known as chess engines
Chess is a board game for two players. It is an abstract strategy game that involves no hidden information and no elements of chance. It is played on a square board consisting of 64 squares arranged in an 8×8 grid. The players, referred to ...
) began to appear in the 1960s. In 1970, the first major computer chess tournament, the North American Computer Chess Championship
The North American Computer Chess Championship was a computer chess championship held from 1970 to 1994. It was organised by the Association for Computing Machinery and by Monty Newborn, professor of computer science at McGill University. It was o ...
, was held, followed in 1974 by the first World Computer Chess Championship
World Computer Chess Championship (WCCC) was an event held periodically from 1974 to 2024 where computer chess engines compete against each other. The event is organized by the ''International Computer Games Association'' (ICGA, until 2002 ICCA). I ...
. In the late 1970s, dedicated home chess computers such as Fidelity Electronics' ''Chess Challenger
Chess is a board game for two players. It is an abstract strategy game that involves Perfect information, no hidden information and no elements of game of chance, chance. It is played on a square chessboard, board consisting of 64 squares arran ...
'' became commercially available, as well as software to run on home computers. The overall standard of computer chess was low, however, until the 1990s.
The first endgame tablebases
In chess, the endgame tablebase, or simply the tablebase, is a computerised database containing precalculated evaluations of endgame positions. Tablebases are used to analyse finished games, as well as by chess engines to evaluate positions duri ...
, which provided perfect play
Perfect commonly refers to:
* Perfection; completeness, and excellence
* Perfect (grammar), a grammatical category in some languages
Perfect may also refer to:
Film and television
* ''Perfect'' (1985 film), a romantic drama
* ''Perfect'' ( ...
for relatively simple endgames such as king and rook versus king and bishop, appeared in the late 1970s. This set a precedent to the complete six- and seven-piece tablebases that became available in the 2000s and 2010s respectively.
The first commercial chess database A chess database is a database of chess games.
List of notable chess databases
* Chess Assistant
* Chess Informant Expert
* Chess opening book (computers)
* Chess.com
* chess24
* ChessBase
* Lichess
* Shane's Chess Information Database
...
, a collection of chess games searchable by move and position, was introduced by the German company ChessBase
ChessBase is a German company that develops and sells chess software, maintains a chess news site, and operates an internet chess server for online chess. Founded in 1986, it maintains and sells large-scale databases containing the moves of recor ...
in 1987. Databases containing millions of chess games have since had a profound effect on opening theory and other areas of chess research.
Digital chess clocks
A chess clock is a device that comprises two adjacent clocks with buttons to stop one clock while starting the other, so that the two clocks never run simultaneously. The clocks are used in games where the time is allocated between two parties. T ...
were invented in 1973, though they did not become commonplace until the 1990s. Digital clocks allow for time controls involving increments and delays.
1990–present: Rise of computers and online chess
Technology
The Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the Global network, global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a internetworking, network of networks ...
enabled online chess
Online chess is chess that is played over the Internet, allowing players to play against each other. This was first done asynchronously through PLATO and email in the 1970s. In 1992, the Internet Chess Server facilitated live online play via t ...
as a new medium of playing, with chess servers
Online chess is chess that is played over the Internet, allowing players to play against each other. This was first done asynchronously through PLATO and email in the 1970s. In 1992, the Internet Chess Server facilitated live online play via te ...
allowing users to play other people from different parts of the world in real time. The first such server, known as Internet Chess Server
The American Internet Chess Server, commonly known as Internet Chess Server (ICS) was a telnet-based chess server which allowed users to play live chess over the internet.
History
In the 1970s, one could play correspondence chess in a PLAT ...
(ICS), was developed at the University of Utah in 1992. ICS formed the basis for the first commercial chess server, the Internet Chess Club
The Internet Chess Club (ICC) is a commercial Internet chess server devoted to the play and discussion of chess and chess variants. ICC had over 30,000 subscribing members in 2005. It was the first Internet chess server and was the largest p ...
, which was launched in 1995, and for other early chess servers such as Free Internet Chess Server
The Free Internet Chess Server (FICS) is a volunteer-run online chess platform. When the original Internet Chess Server (ICS) was commercialized and rebranded as the Internet Chess Club (ICC) in 1995, a group of users and developers came togethe ...
(FICS). Since then, many other platforms have appeared, and online chess began to rival over-the-board chess in popularity. During the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
, the isolation ensuing from quarantine
A quarantine is a restriction on the movement of people, animals, and goods which is intended to prevent the spread of disease or pests. It is often used in connection to disease and illness, preventing the movement of those who may have bee ...
s imposed in many places around the world, combined with the success of the popular Netflix
Netflix is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming service. The service primarily distributes original and acquired films and television shows from various genres, and it is available internationally in multiple lang ...
show '' The Queen's Gambit'' and other factors such as the popularity of online tournaments (notably PogChamps) and chess Twitch
Twitch may refer to:
Biology
* Muscle contraction
** Convulsion, rapid and repeated muscle contraction and relaxation
** Fasciculation, a small, local, involuntary muscle contraction
** Myoclonic twitch, a jerk usually caused by sudden muscle c ...
streamers, resulted in a surge of popularity not only for online chess, but for the game of chess in general; this phenomenon has been referred to in the media as the 2020 online chess boom.
Computer chess
Computer chess includes both hardware (dedicated computers) and software capable of playing chess. Computer chess provides opportunities for players to practice even in the absence of human opponents, and also provides opportunities for analysi ...
has also seen major advances. By the 1990s, chess engines could consistently defeat most amateurs, and in 1997 Deep Blue defeated World Champion Garry Kasparov in a six-game match, starting an era of computer dominance at the highest level of chess. In the 2010s, engines significantly stronger than even the best human players became accessible for free on a number of PC and mobile platforms, and free engine analysis became a commonplace feature on internet chess servers. An adverse effect of the easy availability of engine analysis on hand-held devices and personal computers has been the rise of computer cheating, which has grown to be a major concern in both over-the-board and online chess. In 2017, AlphaZero
AlphaZero is a computer program developed by artificial intelligence research company DeepMind to master the games of chess, shogi and Go (game), go. This algorithm uses an approach similar to AlphaGo Zero.
On December 5, 2017, the DeepMind ...
– a neural network
A neural network is a group of interconnected units called neurons that send signals to one another. Neurons can be either biological cells or signal pathways. While individual neurons are simple, many of them together in a network can perfor ...
also capable of playing shogi
, also known as Japanese chess, is a Strategy game, strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as chess, Western chess, chaturanga, xiangqi, Indian chess, and janggi. ...
and Go – was introduced. Since then, many chess engines based on neural network evaluation have been written, the best of which have surpassed the traditional " brute-force" engines. AlphaZero also introduced many novel ideas and ways of playing the game, which affected the style of play at the top level.
As endgame tablebases
In chess, the endgame tablebase, or simply the tablebase, is a computerised database containing precalculated evaluations of endgame positions. Tablebases are used to analyse finished games, as well as by chess engines to evaluate positions duri ...
developed, they began to provide perfect play
Perfect commonly refers to:
* Perfection; completeness, and excellence
* Perfect (grammar), a grammatical category in some languages
Perfect may also refer to:
Film and television
* ''Perfect'' (1985 film), a romantic drama
* ''Perfect'' ( ...
in endgame positions in which the game-theoretical outcome was previously unknown, such as positions with king, queen and pawn against king and queen. In 1991, Lewis Stiller published a tablebase for select six-piece endgames, and by 2005, following the publication of Nalimov tablebases, all six-piece endgame positions were solved. In 2012, Lomonosov tablebases were published which solved all seven-piece endgame positions. Use of tablebases enhances the performance of chess engines by providing definitive results in some branches of analysis.
Technological progress made in the 1990s and the 21st century has influenced the way that chess is studied at all levels, as well as the state of chess as a spectator sport
A spectator sport is a sport that is characterized by the presence of spectators, or watchers, at its competitions. Spectator sports may be professional sports or amateur sports. They often are distinguished from participant sports, which are mor ...
.
Previously, preparation at the professional level required an extensive chess library and several subscriptions to publications such as ''Chess Informant
Chess Informant () is a publishing company from Belgrade, Serbia, that periodically (since 2012, four volumes per year) produces volumes of a book entitled ''Chess Informant'', as well as the ''Encyclopaedia of Chess Openings'', ''Encyclopaedia ...
'' to keep up with opening developments and study opponents' games. Today, preparation at the professional level involves the use of databases containing millions of games, and engines to analyze different opening variations and prepare novelties. A number of online learning resources are also available for players of all levels, such as online courses, tactics trainers, and video lessons.
Since the late 1990s, it has been possible to follow major international chess events online, the players' moves being relayed in real time. Sensory boards have been developed to enable automatic transmission of moves. Chess players will frequently run engines while watching these games, allowing them to quickly identify mistakes by the players and spot tactical opportunities. While in the past the moves have been relayed live, today chess organizers will often impose a half-hour delay as an anti-cheating measure. In the mid-to-late 2010s – and especially following the 2020 online boom – it became commonplace for supergrandmasters, such as Hikaru Nakamura
Christopher Hikaru Nakamura[Magnus Carlsen
Sven Magnus Øen Carlsen (born 30 November 1990) is a Norwegian Grandmaster (chess), chess grandmaster. Carlsen is a five-time World Chess Championship, World Chess Champion, five-time World Rapid Chess Championship, World Rapid Chess Champio ...](_blank)
, to livestream
Livestreaming, live-streaming, or live streaming is the streaming media, streaming of video or Digital audio, audio in real-time communication, real time or near real time. While often referred to simply as ''streaming'', the real-time nature ...
chess content on platforms such as Twitch
Twitch may refer to:
Biology
* Muscle contraction
** Convulsion, rapid and repeated muscle contraction and relaxation
** Fasciculation, a small, local, involuntary muscle contraction
** Myoclonic twitch, a jerk usually caused by sudden muscle c ...
. Also following the boom, online chess started being viewed as an esport
Esports (), short for electronic sports, is a form of competition using video games. Esports often takes the form of organized, multiplayer video game competitions, particularly between professional players, played individually or as teams. ...
, with esport teams signing chess players for the first time in 2020. The number of esport teams signing chess players rose considerably in 2025, after chess was added to Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
's Esports World Cup
The Esports World Cup (EWC) is an annual international esports tournament series run by the Esports World Cup Foundation, a nonprofit organization. It is considered the largest professional esports event in the world both financially and in terms ...
.
Growth
Organized chess even for young children has become common. FIDE holds world championships for age levels down to 8 years old. The largest tournaments, in number of players, are those held for children.
The number of grandmasters and other chess professionals has also grown in the modern era. Kenneth Regan and Guy Haworth conducted research involving comparison of move choices by players of different levels and from different periods with the analysis of strong chess engines. They concluded that the increase in the number of grandmasters and higher Elo ratings of the top players reflect an actual increase in the average standard of play, rather than "rating inflation" or "title inflation".
Professional chess
In 1993, Garry Kasparov and Nigel Short
Nigel David Short (born 1 June 1965) is an English Grandmaster (chess), chess grandmaster, columnist, coach and commentator who has been the FIDE Director for Chess Development since September 2022. Short earned the title of grandmaster at the ...
broke ties with FIDE to organize their own match for the World Championship and formed a competing Professional Chess Association
The Professional Chess Association (PCA), which existed between 1993 and 1996, was a rival organisation to FIDE, the International Chess Federation. The PCA was created in 1993 by Garry Kasparov and Nigel Short for the marketing and organization of ...
(PCA). From then until 2006, there were two simultaneous World Championships and respective World Champions: the PCA or "classical" champions extending the Steinitzian tradition in which the current champion plays a challenger in a series of games, and the other following FIDE's new format of many players competing in a large knockout tournament to determine the champion. Kasparov lost his PCA title in 2000
2000 was designated as the International Year for the Culture of Peace and the World Mathematics, Mathematical Year.
Popular culture holds the year 2000 as the first year of the 21st century and the 3rd millennium, because of a tende ...
to Vladimir Kramnik
Vladimir Borisovich Kramnik (; born 25 June 1975) is a Russian Grandmaster (chess), chess grandmaster. He was the World Chess Champion#Split title (1993–2006), Classical World Chess Champion from 2000 to 2006, and the 14th undisputed World Ch ...
of Russia. Due to the complicated state of world chess politics and difficulties obtaining commercial sponsorships, Kasparov was never able to challenge for the title again. Despite this, he continued to dominate in top level tournaments and remained the world's highest rated player until his retirement from competitive chess in 2005.
The World Chess Championship 2006
The World Chess Championship 2006 was a match between Classical World Chess Champion Vladimir Kramnik and FIDE World Chess Champion Veselin Topalov. The title of World Chess Champion had been split for 13 years. This match, played between Septemb ...
, in which Kramnik beat the FIDE World Champion Veselin Topalov
Veselin Aleksandrov Topalov (pronounced ; ; born 15 March 1975) is a Bulgarian Grandmaster (chess), chess grandmaster and former FIDE World Chess Championship, World Chess Champion.
Topalov became FIDE World Chess Champion by winning the FIDE ...
, reunified the titles and made Kramnik the undisputed World Chess Champion. In September 2007, he lost the title to Viswanathan Anand
Viswanathan "Vishy" Anand (born 11 December 1969) is an Indian chess grandmaster. Anand is a five-time World Chess Champion, a two-time World Rapid Chess Champion, a two-time Chess World Cup Champion and a World Blitz Chess Cup Champion. ...
of India. Anand defended his title in the revenge match of 2008, 2010 and 2012. Magnus Carlsen
Sven Magnus Øen Carlsen (born 30 November 1990) is a Norwegian Grandmaster (chess), chess grandmaster. Carlsen is a five-time World Chess Championship, World Chess Champion, five-time World Rapid Chess Championship, World Rapid Chess Champio ...
defeated Anand in 2013
2013 was the first year since 1987 to contain four unique digits (a span of 26 years).
2013 was designated as:
*International Year of Water Cooperation
*International Year of Quinoa
Events
January
* January 5 – 2013 Craig, Alask ...
, defending his title in 2014
The year 2014 was marked by the surge of the Western African Ebola epidemic, West African Ebola epidemic, which began in 2013, becoming the List of Ebola outbreaks, most widespread outbreak of the Ebola, Ebola virus in human history, resul ...
, 2016
2016 was designated as:
* International Year of Pulses by the sixty-eighth session of the United Nations General Assembly.
* International Year of Global Understanding (IYGU) by the International Council for Science (ICSU), the Internationa ...
, 2018
Events January
* January 1 – Bulgaria takes over the Presidency of the Council of the European Union, after the Estonian presidency.
* January 4 – SPLM-IO rebels loyal to Chan Garang Lual start a raid against Juba, capital of ...
, and 2021
Like the year 2020, 2021 was also heavily defined by the COVID-19 pandemic, due to the emergence of multiple Variants of SARS-CoV-2, COVID-19 variants. The major global rollout of COVID-19 vaccines, which began at the end of 2020, continued ...
, whereafter he announced that he would not defend his title a fifth time. The 2023 championship was played between the winner and runner-up of the Candidates Tournament 2022
The 2022 Candidates Tournament was an eight-player chess tournament to decide the challenger for the World Chess Championship 2023. The tournament took place at the Palacio de Santoña in Madrid, Spain, from June 16 to July 5, 2022,[Ian Nepomniachtchi
Ian Alexandrovich Nepomniachtchi ( rus, Ян Алекса́ндрович Непо́мнящий, r=Yan Aleksandrovich Nepomnyashchiy, p=ˈjan ɐlʲɪkˈsandrəvʲɪtɕ nʲɪˈpomnʲɪɕːɪj, a=Ru-Ian Alexandrovich Nepomnyashchij.ogg; born 14 J ...]
of Russia and Ding Liren
Ding Liren ( zh, c=丁立人; born 24October 1992) is a Chinese chess grandmaster who was the 17th World Chess Champion from 2023–24. He is also a three-time Chinese Chess Champion, was a member of the Chinese chess teams that won the Chess ...
of China. Ding beat Nepomniachtchi, making him the world champion.2024
The year saw the list of ongoing armed conflicts, continuation of major armed conflicts, including the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the Myanmar civil war (2021–present), Myanmar civil war, the Sudanese civil war (2023–present), Sudane ...
, Indian Gukesh Dommaraju
Gukesh Dommaraju (born 29 May 2006) is an Indian chess grandmaster and the reigning World Chess Champion. A chess prodigy, Gukesh is the youngest undisputed world champion, the youngest player to have surpassed a FIDE rating of 2750, doing s ...
beat Ding.
Connections to other fields
Arts and humanities
In the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
and during the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
, chess was a part of noble
A noble is a member of the nobility.
Noble may also refer to:
Places Antarctica
* Noble Glacier, King George Island
* Noble Nunatak, Marie Byrd Land
* Noble Peak, Wiencke Island
* Noble Rocks, Graham Land
Australia
* Noble Island, Gr ...
culture; it was used to teach war strategy and was dubbed the "King's Game
''King's Game'' (''Kongekabale'') is a 2004 Danish political thriller film directed by Nikolaj Arcel. It stars Anders W. Berthelsen and Nicolas Bro as reporters uncovering a Government conspiracy. The film received critical praise and won many ...
". Gentlemen are "to be meanly seene in the play at Chestes", says the overview at the beginning of Baldassare Castiglione
Baldassare Castiglione, Count of Casatico (; 6 December 1478 – 2 February 1529),Dates of birth and death, and cause of the latter, fro, ''Italica'', Rai International online. was an Italian courtier, diplomat, soldier and a prominent Renaissan ...
's ''The Book of the Courtier
''The Book of the Courtier'' ( ) by Baldassare Castiglione is a lengthy philosophical dialogue on the topic of what constitutes an ideal courtier or (in the third chapter) court lady, worthy to befriend and advise a prince or political leader. ...
'' (1528, English 1561 by Sir Thomas Hoby), but chess should not be a gentleman's main passion. Castiglione explains it further:
 Some of the elaborate chess sets used by the aristocracy at least partially survive, such as the Lewis chessmen.
Chess was often used as a basis of sermons on
Some of the elaborate chess sets used by the aristocracy at least partially survive, such as the Lewis chessmen.
Chess was often used as a basis of sermons on morality
Morality () is the categorization of intentions, Decision-making, decisions and Social actions, actions into those that are ''proper'', or ''right'', and those that are ''improper'', or ''wrong''. Morality can be a body of standards or principle ...
. An example is ''Liber de moribus hominum et officiis nobilium sive super ludo scacchorum'' ('Book of the customs of men and the duties of nobles or the Book of Chess'), written by an Italian Dominican friar Jacobus de Cessolis
Jacobus de Cessolis (; c. 1250 – c. 1322) was an Italian author of the most famous morality book on chess in the Middle Ages.
In the second half of the 13th century, Jacobus de Cessolis, a Dominican friar in Cessole (Asti district, Piemonte, N ...
. This book was one of the most popular of the Middle Ages. The work was translated into many other languages (the first printed edition was published at Utrecht in 1473) and was the basis for William Caxton
William Caxton () was an English merchant, diplomat and writer. He is thought to be the first person to introduce a printing press into Kingdom of England, England in 1476, and as a Printer (publishing), printer to be the first English retailer ...
's ''The Game and Playe of the Chesse'' (1474), one of the first books printed in English. Different chess pieces were used as metaphors for different classes of people, and human duties were derived from the rules of the game or from visual properties of the chess pieces:
Known in the circles of clerics, students, and merchants, chess entered into the popular culture of the Middle Ages. An example is the 209th song of Carmina Burana
''Carmina Burana'' (, Latin for "Songs from Benediktbeuern" 'Buria'' in Latin is a manuscript of 254 poems and dramatic texts mostly from the 11th or 12th century, although some are from the 13th century. The pieces are mostly bawdy, irreveren ...
from the 13th century, which starts with the names of chess pieces, ''Roch, pedites, regina...'' The game of chess, at times, has been discouraged by various religious authorities in Middle Ages: Jewish, Catholic and Orthodox. Some Muslim authorities prohibited it even recently, for example Ruhollah Khomeini
Ruhollah Musavi Khomeini (17 May 1900 or 24 September 19023 June 1989) was an Iranian revolutionary, politician, political theorist, and religious leader. He was the founder of the Islamic Republic of Iran and the main leader of the Iranian ...
in 1979 and Abdul-Aziz ash-Sheikh even later.Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment (also the Age of Reason and the Enlightenment) was a Europe, European Intellect, intellectual and Philosophy, philosophical movement active from the late 17th to early 19th century. Chiefly valuing knowledge gained th ...
, chess was viewed as a means of self-improvement. Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin (April 17, 1790) was an American polymath: a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher and Political philosophy, political philosopher.#britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the m ...
, in his article " The Morals of Chess" (1786), wrote:
 Chess was occasionally criticized in the 19th century as a waste of time.
Chess is taught to children in schools around the world today. Many schools host chess clubs, and there are many scholastic tournaments specifically for children. Tournaments are held regularly in many countries, hosted by organizations such as the
Chess was occasionally criticized in the 19th century as a waste of time.
Chess is taught to children in schools around the world today. Many schools host chess clubs, and there are many scholastic tournaments specifically for children. Tournaments are held regularly in many countries, hosted by organizations such as the United States Chess Federation
The United States Chess Federation (also known as US Chess or USCF) is the governing body for chess competition in the United States and represents the U.S. in FIDE, The World Chess Federation (FIDE). USCF administers the official national Chess ...
and the National Scholastic Chess Foundation.
Chess is many times depicted in the arts
The arts or creative arts are a vast range of human practices involving creative expression, storytelling, and cultural participation. The arts encompass diverse and plural modes of thought, deeds, and existence in an extensive range of m ...
; significant works where chess plays a key role range from Thomas Middleton's ''A Game at Chess
''A Game at Chess'' is a comic satirical play by Thomas Middleton, first staged in August 1624 by the King's Men at the Globe Theatre. The play is notable for its political content, dramatizing a conflict between Spain and England.
The plot t ...
'' to ''Through the Looking-Glass
''Through the Looking-Glass, and What Alice Found There'' is a novel published in December 1871 by Lewis Carroll, the pen name of Charles Lutwidge Dodgson, a mathematics lecturer at Christ Church, Oxford, Christ Church, University of Oxford. I ...
'' by Lewis Carroll, to Vladimir Nabokov's ''The Defense
''The Defense'' (also known as ''The Luzhin Defense''; ) is the third novel written by Vladimir Nabokov after he had immigrated to Berlin. It was first published in Russian 1930 and later in English in 1964.
Publication
The novel appeared first ...
'', to ''The Royal Game
''The Royal Game'' (also known as Chess Story; in the original German ''Schachnovelle'', "Chess Novella") is a novella by the Austrian author Stefan Zweig written in 1941, the year before the author's death by suicide. In some editions, the title ...
'' by Stefan Zweig. Chess has also featured in film classics such as Ingmar Bergman
Ernst Ingmar Bergman (14 July 1918 – 30 July 2007) was a Swedish film and theatre director and screenwriter. Widely considered one of the greatest and most influential film directors of all time, his films have been described as "profoun ...
's ''The Seventh Seal
''The Seventh Seal'' () is a 1957 Swedish historical fantasy film written and directed by Ingmar Bergman. Set in Sweden during the Black Death, it tells of the journey of a medieval knight (Max von Sydow) and a game of chess he plays with the p ...
'', Satyajit Ray
Satyajit Ray (; 2 May 1921 – 23 April 1992) was an Indian film director, screenwriter, author, lyricist, magazine editor, illustrator, calligraphy, calligrapher, and composer. He is widely considered to be one of the greatest and most influ ...
's '' The Chess Players'', and Powell and Pressburger
The British film-making partnership of Michael Powell (1905–1990) and Emeric Pressburger (1902–1988)—together often known as The Archers, the name of their production company—made a series of influential films in the 1940s and 1950s. T ...
's '' A Matter of Life and Death''.
Chess is also present in contemporary popular culture. For example, the characters in ''Star Trek
''Star Trek'' is an American science fiction media franchise created by Gene Roddenberry, which began with the Star Trek: The Original Series, series of the same name and became a worldwide Popular culture, pop-culture Cultural influence of ...
'' play a futuristic version of the game called "Federation
A federation (also called a federal state) is an entity characterized by a political union, union of partially federated state, self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a #Federal governments, federal government (federalism) ...
Tri-Dimensional Chess", and "Wizard's Chess
The following is a list of magical objects that appear in the ''Harry Potter'' novels and film adaptations.
Deathly Hallows
The Deathly Hallows are three magical objects that appear in ''Harry Potter and the'' ''Deathly Hallows''. They ...
" is played in J.K. Rowling's ''Harry Potter
''Harry Potter'' is a series of seven Fantasy literature, fantasy novels written by British author J. K. Rowling. The novels chronicle the lives of a young Magician (fantasy), wizard, Harry Potter (character), Harry Potter, and his friends ...
''.
Mathematics
The game structure and nature of chess are related to several branches of mathematics. Many combinatorical and topological
Topology (from the Greek words , and ) is the branch of mathematics concerned with the properties of a geometric object that are preserved under continuous deformations, such as stretching, twisting, crumpling, and bending; that is, wit ...
problems connected to chess, such as the knight's tour
A knight's tour is a sequence of moves of a knight on a chessboard such that the knight visits every square exactly once. If the knight ends on a square that is one knight's move from the beginning square (so that it could tour the board again im ...
and the eight queens puzzle
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other; thus, a solution requires that no two queens share the same row, column, or diagonal. There are 92 solutions. ...
, have been known for hundreds of years.
The number of legal positions in chess is estimated to be with a 95% confidence level, with a game-tree complexity
Combinatorial game theory measures game complexity in several ways:
#State-space complexity (the number of legal game positions from the initial position)
#Game tree size (total number of possible games)
#Decision complexity (number of leaf nod ...
of approximately 10123. The game-tree complexity of chess was first calculated by Claude Shannon
Claude Elwood Shannon (April 30, 1916 – February 24, 2001) was an American mathematician, electrical engineer, computer scientist, cryptographer and inventor known as the "father of information theory" and the man who laid the foundations of th ...
as 10120, a number known as the Shannon number. An average position typically has thirty to forty possible moves, but there may be as few as zero (in the case of checkmate or stalemate) or (in a constructed position) as many as 218.
In 1913, Ernst Zermelo
Ernst Friedrich Ferdinand Zermelo (; ; 27 July 187121 May 1953) was a German logician and mathematician, whose work has major implications for the foundations of mathematics. He is known for his role in developing Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory, Z ...
used chess as a basis for his theory of game strategies, which is considered one of the predecessors of game theory
Game theory is the study of mathematical models of strategic interactions. It has applications in many fields of social science, and is used extensively in economics, logic, systems science and computer science. Initially, game theory addressed ...
. Zermelo's theorem states that it is possible to solve chess, i.e. to determine with certainty the outcome of a perfectly played game (either White can force a win, or Black can force a win, or both sides can force at least a draw). With 1043 legal positions in chess, however, it will take an impossibly long time to compute a perfect strategy with any feasible technology.
Applied mathematics
A novel methodology in steganography
Steganography ( ) is the practice of representing information within another message or physical object, in such a manner that the presence of the concealed information would not be evident to an unsuspecting person's examination. In computing/ ...
explores the use of chess-based covers (such as puzzles, chess problems, game reports, training documents, news articles, etc.) for concealing data within a selection of , each hiding some bit
The bit is the most basic unit of information in computing and digital communication. The name is a portmanteau of binary digit. The bit represents a logical state with one of two possible values. These values are most commonly represented as ...
s. Several proof-of-concept projects have been developed that convert text or files into binary code
A binary code represents plain text, text, instruction set, computer processor instructions, or any other data using a two-symbol system. The two-symbol system used is often "0" and "1" from the binary number, binary number system. The binary cod ...
, which is then converted into a series of legal chess moves, that can then be decrypted and downloaded.
Correspondence chess
Correspondence chess is chess played by various forms of long-distance correspondence, traditionally through the postal system. Today it is usually played through a correspondence chess server, a public internet chess forum, or email. Less commo ...
has been historically suspected of being a potential steganographic medium. Melville Davisson Post documented a chess problem
A chess problem, also called a chess composition, is a puzzle created by the composer using chess pieces on a chessboard, which presents the solver with a particular task. For instance, a position may be given with the instruction that White is t ...
that was used to create a pictorial cipher
In cryptography, a cipher (or cypher) is an algorithm for performing encryption or decryption—a series of well-defined steps that can be followed as a procedure. An alternative, less common term is ''encipherment''. To encipher or encode i ...
during World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, extensive postal censorship
Postal censorship is the inspection or examination of mail, most often by governments. It can include opening, reading and total or selective obliteration of letters and their contents, as well as Cover (philately), covers, postcards, Parcel pos ...
was imposed on military personnel
Military personnel or military service members are members of the state's armed forces. Their roles, pay, and obligations differ according to their military branch (army, navy, marines, coast guard, air force, and space force), rank ( office ...
from the United States and Canada that made playing correspondence chess impossible, arising from suspicion that chess could be used to send secret messages to the enemies.
Psychology
There is an extensive scientific literature on chess psychology. Alfred Binet
Alfred Binet (; ; 8 July 1857 – 18 October 1911), born Alfredo Binetti, was a French psychologist who together with Théodore Simon invented the first practical intelligence test, the Binet–Simon test. In 1904, Binet took part in a comm ...
and others showed that knowledge
Knowledge is an Declarative knowledge, awareness of facts, a Knowledge by acquaintance, familiarity with individuals and situations, or a Procedural knowledge, practical skill. Knowledge of facts, also called propositional knowledge, is oft ...
and verbal, rather than visuospatial, ability lies at the core of expertise. In his doctoral thesis, Adriaan de Groot
Adrianus Dingeman (Adriaan) de Groot ( Santpoort, 26 October 1914 – Schiermonnikoog, 14 August 2006) was a Dutch chess master and psychologist, who conducted some of the most famous chess experiments of all time in the 1940s-60. In 1946 he ...
showed that chess masters can rapidly perceive the key features of a position. According to de Groot, this perception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous syste ...
, made possible by years of practice and study, is more important than the sheer ability to anticipate moves. De Groot showed that chess masters can memorize positions shown for a few seconds almost perfectly. The ability to memorize does not alone account for chess-playing skill, since masters and novices, when faced with random arrangements of chess pieces, had equivalent recall (about six positions in each case). Rather, it is the ability to recognize patterns, which are then memorized, which distinguished the skilled players from the novices. When the positions of the pieces were taken from an actual game, the masters had almost total positional recall.
More recent research has focused on chess as mental training
There are efforts to use the game of chess as a tool to aid the intellectual development of young people. Chess is significant in cognitive psychology and artificial intelligence (AI) studies, because it represents the domain in which expert perfor ...
; the respective roles of knowledge and look-ahead search; brain imaging
Neuroimaging is the use of quantitative (computational) techniques to study the structure and function of the central nervous system, developed as an objective way of scientifically studying the healthy human brain in a non-invasive manner. Incre ...
studies of chess masters and novices; blindfold chess
Blindfold chess, also known as ''sans voir'', is a form of chess play wherein the players do not see the positions of the pieces and do not touch them. This forces players to maintain a mental model of the positions of the pieces. Moves are commun ...
; the role of personality
Personality is any person's collection of interrelated behavioral, cognitive, and emotional patterns that comprise a person’s unique adjustment to life. These interrelated patterns are relatively stable, but can change over long time per ...
and intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. It can be described as t ...
in chess skill; gender differences; and computational models of chess expertise. The role of practice and talent in the development of chess and other domains of expertise has led to much empirical investigation. Ericsson and colleagues have argued that deliberate practice is sufficient for reaching high levels of expertise in chess. Recent research, however, fails to replicate their results and indicates that factors other than practice are also important.[Gobet, F. & Chassy, P. (in press). ''Journal of Biosocial Science''. ]
Gobet, F. & Campitelli, G. (2007). ''Developmental Psychology'', 43, 159–72. Both retrieved 2007-07-15.
For example, Fernand Gobet
Fernand Gobet (born February 12, 1962, in Switzerland) is a cognitive scientist and a cognitive psychologist, currently Professorial Research Fellow at the London School of Economics and Professor of Cognitive Psychology at the University of Roe ...
and colleagues have shown that stronger players started playing chess at a young age and that experts born in the Northern Hemisphere are more likely to have been born in late winter and early spring. Compared to the general population, chess players are more likely to be non-right-handed, though they found no correlation between handedness and skill.
Online chess
Online chess is chess played over the internet. This is done through the use of internet chess platforms, which use Elo ratings
The Elo rating system is a method for calculating the relative skill levels of players in zero-sum games such as chess or esports. It is named after its creator Arpad Elo, a Hungarian-American chess master and physics professor.
The Elo system w ...
or similar systems to pair up individual players. Online chess saw a spike in growth during the quarantine
A quarantine is a restriction on the movement of people, animals, and goods which is intended to prevent the spread of disease or pests. It is often used in connection to disease and illness, preventing the movement of those who may have bee ...
s of the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
.Netflix
Netflix is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming service. The service primarily distributes original and acquired films and television shows from various genres, and it is available internationally in multiple lang ...
miniseries '' The Queen's Gambit'', which was released in October 2020.App Store
An app store, also called an app marketplace or app catalog, is a type of digital distribution platform for computer software called applications, often in a mobile context. Apps provide a specific set of functions which, by definition, do not i ...
and Google Play Store
Google Play, also known as the Google Play Store, Play Store, or sometimes the Android Store (and was formerly Android Market), is a digital distribution service operated and developed by Google. It serves as the official app store for certifie ...
rose by 63% after the show debuted.Chess.com
Chess.com is an internet chess server and social networking website. One of the largest chess platforms in the world, the site operates on a freemium model in which some features are available for free, and others are available via subscription ...
saw more than twice as many account registrations in November as it had in previous months, and the number of games played monthly on Lichess
Lichess (; ) is a free and open-source software, free and open-source Internet chess server run by a Nonprofit organization, non-profit organization of the same name. Users of the site can play online chess anonymously and optionally register an ...
doubled as well. There was also a demographic shift in players, with female registration on Chess.com shifting from 22% to 27% of new players. GM Maurice Ashley
Maurice Ashley (born March 6, 1966) is a Jamaican and American chess player, author, and commentator. In 1999, he earned the FIDE title of Grandmaster (chess), Grandmaster (GM).
Ashley is well known as a commentator for high-profile chess even ...
said "A boom is taking place in chess like we have never seen maybe since the Bobby Fischer days", attributing the growth to an increased desire to do something constructive during the pandemic. USCF Women's Program Director Jennifer Shahade
Jennifer Shahade (born December 31, 1980) is an American chess player, poker player, commentator and writer. She is a two-time United States Women's Champion and has the FIDE title of Woman Grandmaster. Shahade is the author of the books ''Ches ...
stated that chess works well on the internet, since pieces do not need to be reset and matchmaking
Matchmaking is the process of pairing two or more people together, usually for the purpose of marriage, in which case the intermediary or matchmaker is also known as a marriage broker. Matchmaking may be done as a profession for a fee or it may ...
is virtually instant.
Computer chess
The idea of creating a chess-playing machine dates to the 18th century; around 1769, the chess-playing automaton
An automaton (; : automata or automatons) is a relatively self-operating machine, or control mechanism designed to automatically follow a sequence of operations, or respond to predetermined instructions. Some automata, such as bellstrikers i ...
called The Turk became famous before being exposed as a hoax
A hoax (plural: hoaxes) is a widely publicised falsehood created to deceive its audience with false and often astonishing information, with the either malicious or humorous intent of causing shock and interest in as many people as possible.
S ...
. Serious trials based on automata, such as El Ajedrecista
''El Ajedrecista'' (, ) is an automaton built in 1912 by Leonardo Torres Quevedo in Madrid, a pioneering autonomous machine capable of playing chess. As opposed to the human-operated Mechanical Turk and Ajeeb, ''El Ajedrecista'' had a true integr ...
, were too complex and limited to be useful. Since the advent of the digital computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to automatically carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as ''programs'', wh ...
in the 1950s, chess enthusiasts, computer engineer
Computer engineering (CE, CoE, or CpE) is a branch of engineering specialized in developing computer hardware and software.
It integrates several fields of electrical engineering, electronics engineering and computer science.
Computer engine ...
s, and computer scientists have built, with increasing degrees of seriousness and success, chess-playing machines and computer programs. The groundbreaking paper on computer chess, "Programming a Computer for Playing Chess", was published in 1950 by Claude Shannon
Claude Elwood Shannon (April 30, 1916 – February 24, 2001) was an American mathematician, electrical engineer, computer scientist, cryptographer and inventor known as the "father of information theory" and the man who laid the foundations of th ...
. He wrote:
 The
The Association for Computing Machinery
The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) is a US-based international learned society for computing. It was founded in 1947 and is the world's largest scientific and educational computing society. The ACM is a non-profit professional membe ...
(ACM) held the first major chess tournament for computers, the North American Computer Chess Championship
The North American Computer Chess Championship was a computer chess championship held from 1970 to 1994. It was organised by the Association for Computing Machinery and by Monty Newborn, professor of computer science at McGill University. It was o ...
, in September 1970. CHESS 3.0, a chess program from Northwestern University
Northwestern University (NU) is a Private university, private research university in Evanston, Illinois, United States. Established in 1851 to serve the historic Northwest Territory, it is the oldest University charter, chartered university in ...
, won the championship. The first World Computer Chess Championship
World Computer Chess Championship (WCCC) was an event held periodically from 1974 to 2024 where computer chess engines compete against each other. The event is organized by the ''International Computer Games Association'' (ICGA, until 2002 ICCA). I ...
, held in 1974, was won by the Soviet program Kaissa
Kaissa () was a chess program developed in the Soviet Union in the 1960s. It was named so after Caissa, the goddess of chess. Kaissa became the first world computer chess champion in 1974 in Stockholm.
History
By 1967, a computer program by ...
. At first considered only a curiosity, the best chess playing programs have become extremely strong. In 1997, a computer won a chess match using classical time controls against a reigning World Champion for the first time: IBM's Deep Blue beat Garry Kasparov
Garry Kimovich Kasparov (born Garik Kimovich Weinstein on 13 April 1963) is a Russian Grandmaster (chess), chess grandmaster, former World Chess Champion (1985–2000), political activist and writer. His peak FIDE chess Elo rating system, ra ...
3½–2½ (it scored two wins, one loss, and three draws). There was some controversy over the match, and human–computer matches were relatively close over the next few years, until convincing computer victories in 2005
2005 was designated as the International Year for Sport and Physical Education and the International Year of Microcredit. The beginning of 2005 also marked the end of the International Decade of the World's Indigenous Peoples, Internationa ...
and in 2006
2006 was designated as the International Year of Deserts and Desertification.
Events
January
* January 1– 4 – Russia temporarily cuts shipment of natural gas to Ukraine during a price dispute.
* January 12 – A stampede during t ...
.
In 2009, a mobile phone
A mobile phone or cell phone is a portable telephone that allows users to make and receive calls over a radio frequency link while moving within a designated telephone service area, unlike fixed-location phones ( landline phones). This rad ...
won a category
Category, plural categories, may refer to:
General uses
*Classification, the general act of allocating things to classes/categories Philosophy
* Category of being
* ''Categories'' (Aristotle)
* Category (Kant)
* Categories (Peirce)
* Category ( ...
6 tournament with a performance rating of 2898: chess engine Hiarcs 13 running on the mobile phone HTC Touch HD
The HTC Touch HD, also known as the HTC T828X or its codename the HTC Blackstone, is a Windows Mobile 6.1 Pocket PC designed and manufactured by HTC launched in 2008.
Part of the HTC Touch Family, it features a larger, higher-resolution displa ...
won the Copa Mercosur tournament with nine wins and one draw. The best chess programs are now able to consistently beat the strongest human players, to the extent that human–computer matches no longer attract interest from chess players or the media. While the World Computer Chess Championship
World Computer Chess Championship (WCCC) was an event held periodically from 1974 to 2024 where computer chess engines compete against each other. The event is organized by the ''International Computer Games Association'' (ICGA, until 2002 ICCA). I ...
still exists, the Top Chess Engine Championship
Top Chess Engine Championship, formerly known as Thoresen Chess Engines Competition (TCEC or nTCEC), is a computer chess tournament that has been run since 2010. It was organized, directed, and hosted by Martin Thoresen until the end of Season 6; f ...
(TCEC) is widely regarded as the unofficial world championship for chess engines
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.
Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power gen ...
. The current champion is Stockfish
Stockfish is unsalted fish, especially cod, dried by cold air and wind on wooden racks (which are called "hjell" in Norway) on the foreshore. The drying of food is the world's oldest known preservation method, and dried fish has a storage li ...
.
With huge databases of past games and high analytical ability, computers can help players to learn chess and prepare for matches. Internet Chess Server
The American Internet Chess Server, commonly known as Internet Chess Server (ICS) was a telnet-based chess server which allowed users to play live chess over the internet.
History
In the 1970s, one could play correspondence chess in a PLAT ...
s allow people to find and play opponents worldwide. The presence of computers and modern communication tools have raised concerns regarding cheating during games.
Related games
 Related games include:
* direct predecessors of chess, such as
Related games include:
* direct predecessors of chess, such as chaturanga
Chaturanga (, , ) is an Traditional games of India, ancient Indian Strategy game, strategy board game. It is first known from India around the seventh century AD.
While there is some uncertainty, the prevailing view among chess historians is t ...
and shatranj
Shatranj (, ; from Middle Persian ) is an old form of chess, as played in the Sasanian Empire. Its origins lie in the South Asian game of chaturanga. Modern chess gradually developed from this game, as it was introduced to Europe by contacts in ...
;
* traditional national or regional games that share common ancestors with Western chess such as xiangqi
Xiangqi (; ), commonly known as Chinese chess or elephant chess, is a Strategy game, strategy board game for two players. It is the most popular board game in China. Xiangqi is in the same family of games as shogi, janggi, chess, Western ches ...
(Chinese chess), shogi
, also known as Japanese chess, is a Strategy game, strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as chess, Western chess, chaturanga, xiangqi, Indian chess, and janggi. ...
(Japanese chess), janggi
Janggi (, also Romanization of Korean, romanized as ''changgi'' or ''jangki''), sometimes called Korean chess, is a Strategy game, strategy board game popular on the Korean Peninsula. The game was derived from xiangqi (Chinese chess), and is v ...
(Korean chess), ouk chatrang (Cambodian chess), makruk
Makruk (; ; ), or Thai chess (; ; ), is a Strategy game, strategy board game that is descended from the 6th-century Indian game of chaturanga or a close relative thereof, and is therefore related to chess. It is part of the family of chess varian ...
(Thai chess), sittuyin
Sittuyin (), also known as Burmese chess, is a strategy board game created in Myanmar. It is a direct offspring of the Indian game of chaturanga, which arrived in Myanmar in the 8th century thus it is part of the same family of games such as ches ...
(Burmese chess), and shatar
Shatar ( Mongolian: ''Monggol sitar-a'', "Mongolian shatranj"; a.k.a. shatar) and hiashatar are two chess variants played in Mongolia.
Game rules
The rules are similar to standard chess; the differences being that:
* The ''noyan'' (, ''lor ...
(Mongolian chess);
In the comparison of chess with games often referred to as national forms of chess, chess may be referred to as ''Western chess'' or ''international chess''.["Western culture regards Chess as a particular game with a particular set of rules governed by an international authority (FIDE – the Fédération Internationale des Echecs). Variously known as International Chess, World Chess, Orthochess, and so on .. ]
Chess variants
There are more than two thousand published chess variants, games with similar but different rules, most of which are of relatively recent origin.[Pritchard details 1,450 of them in "Of these, about half date from between 700 and 1970 (1,200 years!), half from the last quarter of the twentieth century." ] They include modern variations employing different rules (e.g. losing chess
Losing chess is one of the most popular chess variants. The objective of each player is to lose all of their pieces or be stalemated, that is, a misère version. In some variations, a player may also win by checkmating or by being checkmate ...
and Chess960
Chess960, also known as Fischer Random Chess, is a chess variant that randomizes the starting position of the pieces on the back rank. It was introduced by former world chess champion Bobby Fischer in 1996 to reduce the emphasis on opening prepa ...
), different forces (e.g. Dunsany's chess), Fairy piece, non-standard pieces (e.g. Grand Chess), and different board geometries (e.g. hexagonal chess and infinite chess);
In the context of chess variants, chess is commonly referred to as ''orthodox chess'', ''orthochess'', and ''classic chess''.
See also
* Glossary of chess
* Glossary of chess problems
* List of abstract strategy games
* List of chess players
* List of World Chess Championships
* Outline of chess
* Women in chess
Notes
References
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* (see the included supplement, "How Do You Play Chess")
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
; International organizations
FIDE
nbsp;– FIDE, World Chess Federation
ICCF
nbsp;– International Correspondence Chess Federation
International Correspondence Chess Federation (ICCF) was founded on 26 March 1951 as a new appearance of the International Correspondence Chess Association (ICCA), which was founded in 1945, as successor of the Internationaler Fernschachbund (IF ...
; News
Chessbase news
The Week in Chess
; History
{{Subject bar
, b = y
, commons = y
, d = y
, n = y
, q = y
, s = y
, species = no
, v = y
, voy = y
, wikt = y
, portal = Chess, Games
Chess,
Abstract strategy games
Individual sports
Traditional board games
Partially solved games
Games related to chaturanga

 Pawns have two special moves:
* ''En passant'': when a pawn makes a two-square advance to the same rank as an opponent's pawn on an adjacent file, that pawn can capture it ''en passant'' ("in passing"), moving to one square behind the captured pawn. A pawn can only be captured ''en passant'' on the turn after it makes a two-square advance. In the animated diagram, the black pawn advances two squares from g7 to g5, and the white pawn on f5 takes it ''en passant'', landing on g6.
* ''Promotion'': when a pawn advances to its , it is ''promoted'' and replaced with the player's choice of a queen, rook, bishop, or knight. Usually, pawns are promoted to queens; choosing another piece is called
Pawns have two special moves:
* ''En passant'': when a pawn makes a two-square advance to the same rank as an opponent's pawn on an adjacent file, that pawn can capture it ''en passant'' ("in passing"), moving to one square behind the captured pawn. A pawn can only be captured ''en passant'' on the turn after it makes a two-square advance. In the animated diagram, the black pawn advances two squares from g7 to g5, and the white pawn on f5 takes it ''en passant'', landing on g6.
* ''Promotion'': when a pawn advances to its , it is ''promoted'' and replaced with the player's choice of a queen, rook, bishop, or knight. Usually, pawns are promoted to queens; choosing another piece is called  Moves are written as white/black pairs, preceded by the move number and a period. Individual white moves are also recorded this way, while black moves are rendered with an ellipsis after the move number. For example, one variation of a simple trap known as the
Moves are written as white/black pairs, preceded by the move number and a period. Individual white moves are also recorded this way, while black moves are rendered with an ellipsis after the move number. For example, one variation of a simple trap known as the  Contemporary chess is an organized sport with structured international and national leagues, tournaments, and
Contemporary chess is an organized sport with structured international and national leagues, tournaments, and  FIDE's most visible activity is organizing the
FIDE's most visible activity is organizing the  The oldest known chess manual was in Arabic and dates to about 840, written by
The oldest known chess manual was in Arabic and dates to about 840, written by 
 The game reached Western Europe and Russia via at least three routes, the earliest being in the ninth century. By the year 1000, it had spread throughout both the Muslim Iberia and
The game reached Western Europe and Russia via at least three routes, the earliest being in the ninth century. By the year 1000, it had spread throughout both the Muslim Iberia and  Around 1200, the rules of shatranj started to be modified in Europe, culminating, several major changes later, in the emergence of modern chess practically as it is known today. A major change was the modern piece movement rules, which began to appear in intellectual circles in
Around 1200, the rules of shatranj started to be modified in Europe, culminating, several major changes later, in the emergence of modern chess practically as it is known today. A major change was the modern piece movement rules, which began to appear in intellectual circles in 
 After the death of Alekhine, a new World Champion was sought. FIDE, which has controlled the title since then, ran a tournament of elite players. The winner of the 1948 tournament was Russian
After the death of Alekhine, a new World Champion was sought. FIDE, which has controlled the title since then, ran a tournament of elite players. The winner of the 1948 tournament was Russian  Following the 1961 event, FIDE abolished the automatic right of a deposed champion to a rematch, and the next champion, Armenian
Following the 1961 event, FIDE abolished the automatic right of a deposed champion to a rematch, and the next champion, Armenian  Some of the elaborate chess sets used by the aristocracy at least partially survive, such as the Lewis chessmen.
Chess was often used as a basis of sermons on
Some of the elaborate chess sets used by the aristocracy at least partially survive, such as the Lewis chessmen.
Chess was often used as a basis of sermons on  Chess was occasionally criticized in the 19th century as a waste of time.
Chess is taught to children in schools around the world today. Many schools host chess clubs, and there are many scholastic tournaments specifically for children. Tournaments are held regularly in many countries, hosted by organizations such as the
Chess was occasionally criticized in the 19th century as a waste of time.
Chess is taught to children in schools around the world today. Many schools host chess clubs, and there are many scholastic tournaments specifically for children. Tournaments are held regularly in many countries, hosted by organizations such as the