Category III approach on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 An ''instrument landing system'' operates as a ground-based
An ''instrument landing system'' operates as a ground-based
 Many illustrations of the ILS concept often show the system operating more similarly to beam systems with the 90 Hz signal on one side and the 150 on the other. These illustrations are inaccurate; both signals are radiated across the entire beam pattern, it is their relative difference in the depth of modulation (DDM) that changes dependent upon the position of the approaching aircraft.
Many illustrations of the ILS concept often show the system operating more similarly to beam systems with the 90 Hz signal on one side and the 150 on the other. These illustrations are inaccurate; both signals are radiated across the entire beam pattern, it is their relative difference in the depth of modulation (DDM) that changes dependent upon the position of the approaching aircraft.
 A localizer (LOC, or LLZ until ICAO standardisation) is an
A localizer (LOC, or LLZ until ICAO standardisation) is an

 The pilot controls the aircraft so that the glide slope indicator remains centered on the display to ensure the aircraft is following the glide path of approximately 3° above horizontal (ground level) to remain above obstructions and reach the runway at the proper touchdown point (i.e. it provides vertical guidance).
The pilot controls the aircraft so that the glide slope indicator remains centered on the display to ensure the aircraft is following the glide path of approximately 3° above horizontal (ground level) to remain above obstructions and reach the runway at the proper touchdown point (i.e. it provides vertical guidance).
 In contrast to other operations, CAT III weather minima do not provide sufficient visual references to allow a manual landing to be made. CAT IIIb minima depend on roll-out control and redundancy of the autopilot, because they give only enough time for the pilot to decide whether the aircraft will land in the touchdown zone (basically CAT IIIa) and to ensure safety during rollout (basically CAT IIIb). Therefore, an automatic landing system is mandatory to perform Category III operations. Its reliability must be sufficient to control the aircraft to touchdown in CAT IIIa operations and through rollout to a safe taxi speed in CAT IIIb (and CAT IIIc when authorized). However, special approval has been granted to some operators for hand-flown CAT III approaches using a
In contrast to other operations, CAT III weather minima do not provide sufficient visual references to allow a manual landing to be made. CAT IIIb minima depend on roll-out control and redundancy of the autopilot, because they give only enough time for the pilot to decide whether the aircraft will land in the touchdown zone (basically CAT IIIa) and to ensure safety during rollout (basically CAT IIIb). Therefore, an automatic landing system is mandatory to perform Category III operations. Its reliability must be sufficient to control the aircraft to touchdown in CAT IIIa operations and through rollout to a safe taxi speed in CAT IIIb (and CAT IIIc when authorized). However, special approval has been granted to some operators for hand-flown CAT III approaches using a  Some commercial aircraft are equipped with automatic landing systems that allow the aircraft to land without transitioning from instruments to visual conditions for a normal landing. Such
Some commercial aircraft are equipped with automatic landing systems that allow the aircraft to land without transitioning from instruments to visual conditions for a normal landing. Such
 Tests of the ILS began in 1929 in the United States, with
Tests of the ILS began in 1929 in the United States, with
Aeronautical Information Manual
FAA – February 11, 2010
Digital Terminal Procedures
FAA – May 2010
– U.S. Centennial of Flight Commission
"Happy Landings In Fog", June 1933, Popular Mechanics
article on the early system setup in the USA.
ILS Tutorial Animations
Website dedicated to the description of ILS
ILS Tutorial Animation
- Illustrates and describes how ILS navigation signals are displayed on board of an aircraft in various positions, which may occur during a safe approach for landing.
* {{Authority control 1929 in aviation Navigational aids Aircraft landing systems Avionics Radio navigation Radio stations and systems ITU Runway safety Types of final approach (aviation)

 In
In aviation
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' includes fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air craft such as hot air ...
, the instrument landing system (ILS) is a precision radio navigation
Radio navigation or radionavigation is the application of radio frequencies to determine a position of an object on the Earth, either the vessel or an obstruction. Like radiolocation, it is a type of radiodetermination.
The basic principles a ...
system that provides short-range guidance to aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines ...
to allow them to approach a runway
According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a runway is a "defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and takeoff of aircraft". Runways may be a man-made surface (often asphalt concrete, as ...
at night or in bad weather. In its original form, it allows an aircraft to approach until it is over the ground, within a of the runway. At that point the runway should be visible to the pilot; if it is not, they perform a missed approach
Missed approach is a procedure followed by a pilot when an instrument approach cannot be completed to a full-stop landing. The instructions for the missed approach may be assigned by air traffic control (ATC) prior to the clearance for the approac ...
. Bringing the aircraft this close to the runway dramatically increases the range of weather conditions in which a safe landing
Landing is the last part of a flight, where a flying animal, aircraft, or spacecraft returns to the ground. When the flying object returns to water, the process is called alighting, although it is commonly called "landing", "touchdown" or ...
can be made. Other versions of the system, or "categories", have further reduced the minimum altitudes, runway visual ranges (RVRs), and transmitter and monitoring configurations designed depending on the normal expected weather patterns and airport safety requirements.
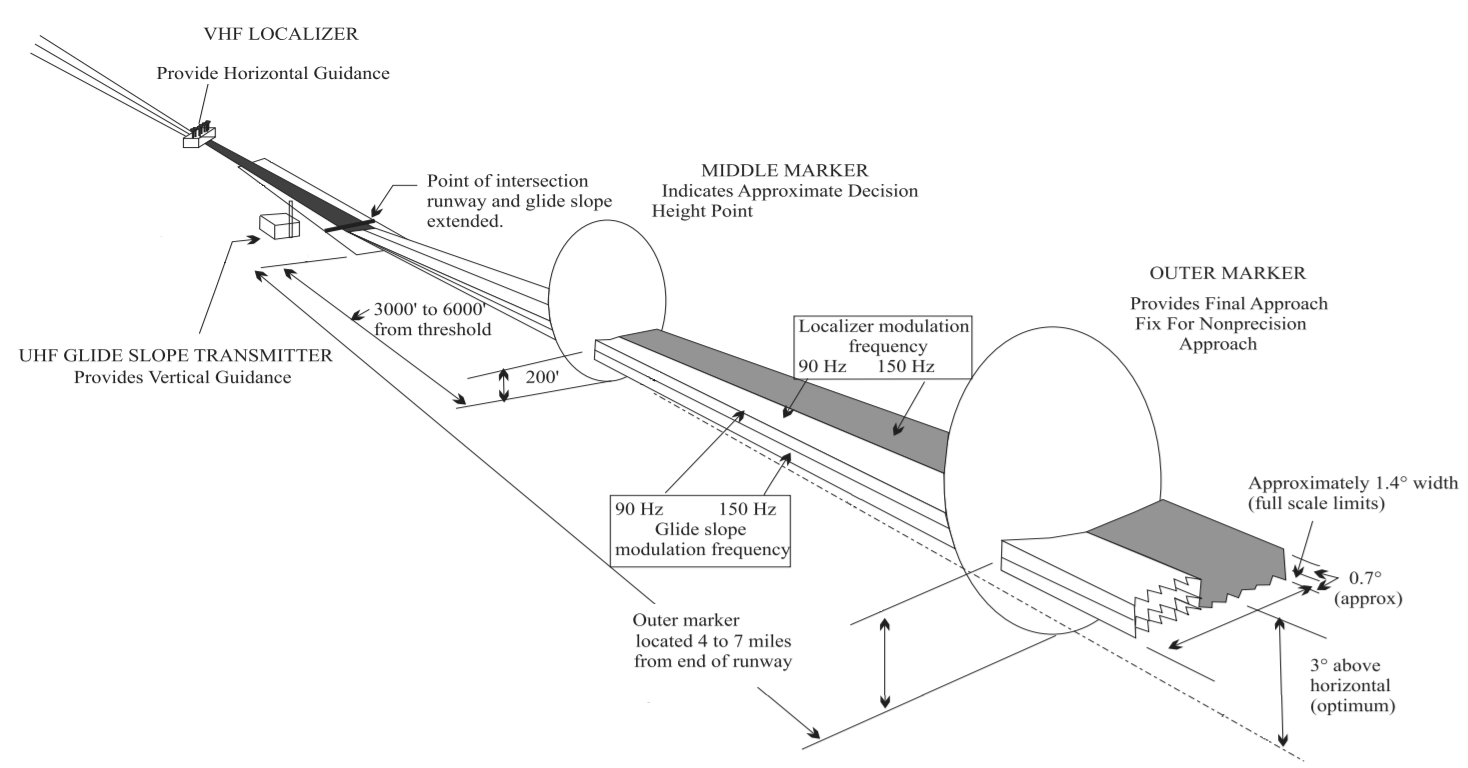
ILS uses two directional radio signal
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies of 300 gigahertz (GHz) and below. At 300 GHz, the corresponding wavelength is 1 mm (shor ...
s, the ''localizer'' (108 to 112 MHz frequency), which provides horizontal guidance, and the ''glideslope'' (329.15 to 335 MHz frequency) for vertical guidance. The relationship between the aircraft's position and these signals is displayed on an aircraft instrument, often additional pointers in the attitude indicator
The attitude indicator (AI), formerly known as the gyro horizon or artificial horizon, is a flight instrument that informs the pilot of the aircraft orientation relative to Earth's horizon, and gives an immediate indication of the smallest o ...
. The pilot attempts to manoeuvre the aircraft to keep the indicators centered while they approach the runway to the decision height
In aviation, an instrument approach or instrument approach procedure (IAP) is a series of predetermined maneuvers for the orderly transfer of an aircraft operating under instrument flight rules from the beginning of the initial approach to a landi ...
. Optional '' Marker Beacon(s)'' provide distance information as the approach proceeds, including the ''middle marker'' (MM), placed close to the position of the (CAT 1) decision height. Markers are largely being phased out and replaced by distance measuring equipment
In aviation, distance measuring equipment (DME) is a radio navigation technology that measures the slant range (distance) between an aircraft and a ground station by timing the propagation delay of radio signals in the frequency band between 9 ...
(DME). The ILS usually includes high-intensity lighting at the end of the runways to help the pilot locate the runway and transition from the approach to a visual landing.
A number of radio-based landing systems were developed between the 1920s and 1940s, notably the Lorenz beam The Lorenz beam was a blind-landing radio navigation system developed by C. Lorenz AG in Berlin. The first system had been installed in 1932 at Berlin-Tempelhof Central Airport, followed by Dübendorf in Switzerland (1934) and others all over the ...
which saw relatively wide use in Europe prior to the war. The US-developed SCS-51 system was more accurate while also adding vertical guidance. Many sets were installed at airbases in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, which led to it being selected as the international standard after the formation of the International Civil Aviation Organization
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO, ) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that coordinates the principles and techniques of international air navigation, and fosters the planning and development of international sc ...
(ICAO) in 1947. Several competing landing systems have been developed, including the radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, w ...
-based ground-controlled approach (GCA) and the more recent microwave landing system
The microwave landing system (MLS) is an all-weather, precision radio guidance system intended to be installed at large airports to assist aircraft in landing, including 'blind landings'. MLS enables an approaching aircraft to determine when it ...
(MLS), but few of these systems have been deployed. ILS remains a widespread standard to this day.
The introduction of precision approach
In aviation, an instrument approach or instrument approach procedure (IAP) is a series of predetermined maneuvers for the orderly transfer of an aircraft operating under instrument flight rules from the beginning of the initial approach to a landi ...
es using global navigation satellite systems
A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning. It allows satellite navigation devices to determine their location (longitude, latitude, and altitude/elevation) to high pr ...
(GNSSs) instead of requiring expensive airport infrastructure is leading to the replacement of ILS. Providing the required accuracy with GNSS normally requires only a low-power omnidirectional augmentation signal to be broadcast from the airport, which is dramatically less expensive than the multiple, large and powerful transmitters required for a full ILS implementation. By 2015, the number of US airports supporting ILS-like LPV approaches exceeded the number of ILS installations, and this is expected to lead to the eventual removal of ILS at most airports.
Principle of operation
instrument approach
In aviation, an instrument approach or instrument approach procedure (IAP) is a series of predetermined maneuvers for the orderly transfer of an aircraft operating under instrument flight rules from the beginning of the initial approach to a landi ...
system that provides precision lateral and vertical guidance to an aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines ...
approaching and landing on a runway
According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a runway is a "defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and takeoff of aircraft". Runways may be a man-made surface (often asphalt concrete, as ...
, using a combination of radio signals and, in many cases, high-intensity lighting arrays to enable a safe landing during instrument meteorological conditions (IMC), such as low ceilings
A ceiling is an overhead interior surface that covers the upper limits of a room. It is not generally considered a structural element, but a finished surface concealing the underside of the roof structure or the floor of a story above. Ceilings ...
or reduced visibility due to fog, rain, or blowing snow.
Beam systems
Previous blind landing radio aids typically took the form of ''beam'' systems of various types. These normally consisted of a radio transmitter that was connected to a motorized switch to produce a pattern ofMorse code
Morse code is a method used in telecommunication to encode text characters as standardized sequences of two different signal durations, called ''dots'' and ''dashes'', or ''dits'' and ''dahs''. Morse code is named after Samuel Morse, one of ...
dots and dashes. The switch also controlled which of two directional antennae the signal was sent to. The resulting signal sent into the air consists of dots sent to one side of the runway and dashes to the other. The beams were wide enough so they overlapped in the center.
To use the system an aircraft only needed a conventional radio receiver. As they approached the airport they would tune in the signal and listen to it in their headphones. They would hear dots and dashes (Morse code "A" or "N"), if they were to the side of the runway, or if they were properly aligned, the two mixed together to produce a steady tone, the ''equisignal''. The accuracy of this measurement was highly dependent on the skill of the operator, listening to the signal on earphones in a noisy aircraft often whilst communicating with the tower at the same time.
Accuracy of the system was normally on the order of 3 degrees in azimuth. While this was useful for bringing the aircraft onto the direction of the runway, it was not accurate enough to safely bring the aircraft to visual range in bad weather; the radio course beams were used only for lateral guidance, and the system was not enough on its own to perform landings in heavy rain or fog. Nevertheless, the final decision to land was made at only from the airport.
ILS concept
The ILS, developed just prior to the start ofWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, used a more complex system of signals and an antenna array to achieve higher accuracy. This requires significantly more complexity in the ground station and transmitters, with the advantage that the signals can be accurately decoded in the aircraft using simple electronics and displayed directly on analog instruments. The instruments can be placed in front of the pilot, eliminating the need for a radio operator to continually monitor the signals and relay the results to the pilot over the intercom
An intercom, also called an intercommunication device, intercommunicator, or interphone, is a stand-alone voice communications system for use within a building or small collection of buildings which functions independently of the public telephon ...
.
Key to its operation is a concept known as the amplitude modulation index, a measure of how strongly the amplitude modulation
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the amplitude (signal strength) of the wave is varied in proportion to ...
is applied to the carrier frequency
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a waveform (usually sinusoidal) that is modulated (modified) with an information-bearing signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave usually has a m ...
. In the earlier beam systems, the signal was turned on and off entirely, corresponding to a modulation index of 100%. The determination of angle within the beam is based on the comparison of the audible strength of the two signals.
In ILS, a more complex system of signals and antennas varies the modulation of two signals across the entire width of the beam pattern. The system relies on the use of sideband
In radio communications, a sideband is a band of frequencies higher than or lower than the carrier frequency, that are the result of the modulation process. The sidebands carry the information transmitted by the radio signal. The sidebands co ...
s, secondary frequencies that are created when two different signals are mixed. For instance, if one takes a radio frequency signal at 10 MHz and mixes that with an audible tone at 2500 Hz, four signals will be produced, at the original signals’ frequencies of 2500 and 10000000 hertz, and sidebands 9997500 and 10002500 hertz. The original 2500 Hz signal's frequency is too low to travel far from an antenna, but the other three signals are all radio frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the upp ...
and can be effectively transmitted.
ILS starts by mixing two modulating signals to the carrier, one at 90 Hz and another at 150. This creates a signal with five radio frequencies in total, the carrier and four sidebands. This combined signal, known as the CSB for "carrier and sidebands", is sent out evenly from an antenna array. The CSB is also sent into a circuit that suppresses the original carrier, leaving only the four sideband signals. This signal, known as SBO for "sidebands only", is also sent to the antenna array.
For lateral guidance, known as the ''localizer'', the antenna is normally placed centrally at the far end of the runway and consists of multiple antennas in an array normally about the same width of the runway. Each individual antenna has a particular phase shift and power level applied only to the SBO signal such that the resulting signal is retarded 90 degrees on the left side of the runway and advanced 90 degrees on the right. Additionally, the 150 Hz signal is inverted on one side of the pattern, another 180 degree shift. Due to the way the signals mix in space
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consider ...
the SBO signals destructively interfere with and almost eliminate each other along the centerline, leaving just the CSB signal predominating. At any other location, on either side of the centerline, the SBO and CSB signals combine in different ways so that one modulating signal predominates.
A receiver in front of the array will receive both of these signals mixed together. Using simple electronic filters, the original carrier and two sidebands can be separated and demodulated to extract the original amplitude-modulated 90 and 150 Hz signals. These are then averaged to produce two direct current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even ...
(DC) signals. Each of these signals represents not the strength of the original signal, but the strength of the modulation relative to the carrier, which varies across the beam pattern. This has the great advantage that the measurement of angle is independent of range.
The two DC signals are then sent to a conventional voltmeter
A voltmeter is an instrument used for measuring electric potential difference between two points in an electric circuit. It is connected in parallel. It usually has a high resistance so that it takes negligible current from the circuit.
Ana ...
, with the 90 Hz output pulling the needle right and the other left. Along the centreline the two modulating tones of the sidebands will be cancelled out and both voltages will be zero, leaving the needle centered in the display. If the aircraft is far to the left, the 90 Hz signal will produce a strong DC voltage (predominates), and the 150 Hz signal is minimised, pulling the needle all the way to the right. This means the voltmeter directly displays both the direction and magnitude of the turn needed to bring the aircraft back to the runway centreline. As the measurement compares different parts of a single signal entirely in electronics, it provides angular resolution of less than a degree, and allows the construction of a precision approach
In aviation, an instrument approach or instrument approach procedure (IAP) is a series of predetermined maneuvers for the orderly transfer of an aircraft operating under instrument flight rules from the beginning of the initial approach to a landi ...
.
Although the encoding scheme is complex, and requires a considerable amount of ground equipment, the resulting signal is both far more accurate than the older beam-based systems and is far more resistant to common forms of interference. For instance, static
Static may refer to:
Places
*Static Nunatak, a nunatak in Antarctica
United States
* Static, Kentucky and Tennessee
*Static Peak, a mountain in Wyoming
**Static Peak Divide, a mountain pass near the peak
Science and technology Physics
*Static el ...
in the signal will affect both sub-signals equally, so it will have no effect on the result. Similarly, changes in overall signal strength as the aircraft approaches the runway, or changes due to fading
In wireless communications, fading is variation of the attenuation of a signal with various variables. These variables include time, geographical position, and radio frequency. Fading is often modeled as a random process. A fading channel is a ...
, will have little effect on the resulting measurement because they would normally affect both channels equally. The system is subject to multipath distortion
In radio communication, multipath is the propagation phenomenon that results in radio signals reaching the receiving antenna by two or more paths. Causes of multipath include atmospheric ducting, ionospheric reflection and refraction, and reflecti ...
effects due to the use of multiple frequencies, but because those effects are dependent on the terrain, they are generally fixed in location and can be accounted for through adjustments in the antenna or phase shifters.
Additionally, because it is the encoding of the signal within the beam that contains the angle information, not the strength of the beam, the signal does not have to be tightly focussed in space. In the older beam systems, the accuracy of the equisignal area was a function of the pattern of the two directional signals, which demanded that they be relatively narrow. The ILS pattern can be much wider. ILS installations are normally required to be usable within 10 degrees on either side of the runway centerline at , and 35 degrees on either side at . This allows for a wide variety of approach paths.
The ''glideslope'' works in the same general fashion as the localizer and uses the same encoding, but is normally transmitted to produce a centerline at an angle of 3 degrees above horizontal from an antenna beside the runway instead of the end. The only difference between the signals is that the localizer is transmitted using lower carrier frequencies, using 40 selected channels between 108.10 MHz and 111.95 MHz, whereas the glideslope has a corresponding set of 40 channels between 328.6 and 335.4 MHz. The higher frequencies generally result in the glideslope radiating antennas being smaller. The channel pairs are not linear; localizer channel 1 is at 108.10 and paired with glideslope at 334.70, whereas channel two is 108.15 and 334.55. There are gaps and jumps through both bands.
Using ILS
An instrument approach procedure chart (or 'approach plate
Approach plates (or, more formally, instrument approach procedure charts) are the printed charts of instrument approach procedures that pilots use to fly instrument approaches during instrument flight rules (IFR) operations. Each country maintains ...
') is published for each ILS approach to provide the information needed to fly an ILS approach during instrument flight rules (IFR) operations. A chart includes the radio frequencies used by the ILS components or navaids and the prescribed minimum visibility requirements.
An aircraft approaching a runway is guided by the ILS receivers in the aircraft by performing modulation depth comparisons. Many aircraft can route signals into the autopilot
An autopilot is a system used to control the path of an aircraft, marine craft or spacecraft without requiring constant manual control by a human operator. Autopilots do not replace human operators. Instead, the autopilot assists the operator' ...
to fly the approach automatically. An ILS consists of two independent sub-systems. The localizer provides lateral guidance; the glide slope provides vertical guidance.
Localizer
 A localizer (LOC, or LLZ until ICAO standardisation) is an
A localizer (LOC, or LLZ until ICAO standardisation) is an antenna
Antenna ( antennas or antennae) may refer to:
Science and engineering
* Antenna (radio), also known as an aerial, a transducer designed to transmit or receive electromagnetic (e.g., TV or radio) waves
* Antennae Galaxies, the name of two collid ...
array
An array is a systematic arrangement of similar objects, usually in rows and columns.
Things called an array include:
{{TOC right
Music
* In twelve-tone and serial composition, the presentation of simultaneous twelve-tone sets such that the ...
normally located beyond the departure end of the runway and generally consists of several pairs of directional antennas.
The localizer will allow the aircraft to turn and match the aircraft with the runway. After that, the pilots will activate approach phase (APP).
Glide slope (G/S)

Limitations
Due to the complexity of ILS localizer and glide slope systems, there are some limitations. Localizer systems are sensitive to obstructions in the signal broadcast area, such as large buildings or hangars. Glide slope systems are also limited by the terrain in front of the glide slope antennas. If terrain is sloping or uneven, reflections can create an uneven glidepath, causing unwanted needle deflections. Additionally, since the ILS signals are pointed in one direction by the positioning of the arrays, glide slope supports only straight-line approaches with a constant angle of descent. Installation of an ILS can be costly because of siting criteria and the complexity of the antenna system. ILS critical areas and ILS sensitive areas are established to avoid hazardous reflections that would affect the radiated signal. The location of these critical areas can prevent aircraft from using certain taxiways leading to delays in takeoffs, increased hold times, and increased separation between aircraft.Variant
* Instrument guidance system (IGS) (localizer type directional aid
A localizer type directional aid (LDA) or Instrument Guidance System (IGS) is a type of localizer-based instrument approach to an airport. It is used in places where, due to terrain and other factors, the localizer antenna array is not aligned wit ...
(LDA) in the United States) – a modified ILS to accommodate a non-straight approach; the most famous example was for the approach to runway 13 at Kai Tak Airport
Kai Tak Airport was the international airport of Hong Kong from 1925 until 1998. Officially known as Hong Kong International Airport from 1954 to 6 July 1998, it is often referred to as Hong Kong International Airport, Kai Tak, or simply Ka ...
, Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China ( abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delt ...
.
* Instrument carrier landing system (ICLS) – a modified ILS for carrier landing.
Identification
In addition to the previously mentioned navigational signals, the localizer provides for ILS facility identification by periodically transmitting a 1,020 HzMorse code
Morse code is a method used in telecommunication to encode text characters as standardized sequences of two different signal durations, called ''dots'' and ''dashes'', or ''dits'' and ''dahs''. Morse code is named after Samuel Morse, one of ...
identification signal. For example, the ILS for runway 4R at John F. Kennedy International Airport
John F. Kennedy International Airport (colloquially referred to as JFK Airport, Kennedy Airport, New York-JFK, or simply JFK) is the main international airport serving New York City. The airport is the busiest of the seven airports in the Avia ...
transmits IJFK to identify itself, while runway 4L is known as IHIQ. This lets users know the facility is operating normally and that they are tuned to the correct ILS. The glide slope station transmits no identification signal, so ILS equipment relies on the localizer for identification.
Monitoring
It is essential that any failure of the ILS to provide safe guidance be detected immediately by the pilot. To achieve this, monitors continually assess the vital characteristics of the transmissions. If any significant deviation beyond strict limits is detected, either the ILS is automatically switched off or the navigation and identification components are removed from the carrier. Either of these actions will activate an indication ('failure flag') on the instruments of an aircraft using the ILS.Localizer back course
Modern localizer antennas are highly directional. However, usage of older, less directional antennas allows a runway to have a non-precision approach called a ''localizer back course''. This lets aircraft land using the signal transmitted from the back of the localizer array. Highly directional antennas do not provide a sufficient signal to support a back course. In the United States, back course approaches are typically associated with Category I systems at smaller airports that do not have an ILS on both ends of the primary runway. Pilots flying a back course should disregard any glide slope indication.Marker beacons
On some installations,marker beacon
A marker beacon is a particular type of VHF radio beacon used in aviation, usually in conjunction with an instrument landing system (ILS), to give pilots a means to determine position along an established route to a destination such as a runway. ...
s operating at a carrier frequency
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a waveform (usually sinusoidal) that is modulated (modified) with an information-bearing signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave usually has a m ...
of 75 MHz are provided. When the transmission from a marker beacon is received it activates an indicator on the pilot's instrument panel and the tone of the beacon is audible to the pilot. The distance from the runway at which this indication should be received is published in the documentation for that approach, together with the height at which the aircraft should be if correctly established on the ILS. This provides a check on the correct function of the glide slope. In modern ILS installations, a DME is installed, co-located with the ILS, to augment or replace marker beacons. A DME continuously displays the aircraft's distance to the runway.
DME substitution
Distance measuring equipment
In aviation, distance measuring equipment (DME) is a radio navigation technology that measures the slant range (distance) between an aircraft and a ground station by timing the propagation delay of radio signals in the frequency band between 9 ...
(DME) provides pilots with a slant range
In radio electronics, especially radar terminology, slant range or slant distance is the distance along the relative direction between two points. If the two points are at the same level (relative to a specific datum), the slant distance equals t ...
measurement of distance to the runway. DMEs are augmenting or replacing markers in many installations. The DME provides more accurate and continuous monitoring of correct progress on the ILS glide slope to the pilot, and does not require an installation outside the airport boundary. When used in conjunction with an ILS, the DME is often sited midway between the reciprocal runway thresholds with the internal delay
Delay (from Latin: dilatio) may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Delay 1968'', a 1981 album by German experimental rock band Can
* ''The Delay'', a 2012 Uruguayan film
People
* B. H. DeLay (1891–1923), American aviator and acto ...
modified so that one unit can provide distance information to either runway threshold. For approaches where a DME is specified in lieu of marker beacons, ''DME required'' is noted on the instrument approach procedure and the aircraft must have at least one operating DME unit, or an IFR-approved system using a GNSS (an RNAV
Area navigation (RNAV, usually pronounced as "''ar-nav"'') is a method of instrument flight rules (IFR) navigation that allows an aircraft to choose any course within a network of navigation beacons, rather than navigate directly to and from t ...
system meeting TSO-C129/ -C145/-C146), to begin the approach.
Approach lighting
Some installations include medium- or high-intensity approach light systems (abbreviated ''ALS''). Most often, these are at larger airports but many small general aviation airports in the U.S. have approach lights to support their ILS installations and obtain low-visibility minimums. The ALS assists the pilot in transitioning from instrument to visual flight, and to align the aircraft visually with the runway centerline. Pilot observation of the approach lighting system at the Decision Altitude allows the pilot to continue descending towards the runway, even if the runway or runway lights cannot be seen, since the ALS counts as runway end environment. In the U.S., an ILS without approach lights may have CAT I ILS visibility minimums as low as (runway visual range of ) if the required obstacle clearance surfaces are clear of obstructions. Visibility minimums of (runway visual range of ) are possible with a CAT I ILS approach supported by a ALS, and visibility visual range is possible if the runway has high-intensity edge lights, touchdown zone and centerline lights, and an ALS that is at least long (see Table 3-3-1 "Minimum visibility values" in FAA Order 8260.3C). In effect, ALS extends the runway environment out towards the landing aircraft and allows low-visibility operations. CAT II and III ILS approaches generally require complex high-intensity approach light systems, while medium-intensity systems are usually paired with CAT I ILS approaches. At somenon-towered airport
In aviation, a non-towered airport is an airport without a control tower, or air traffic control (ATC) unit. The vast majority of the world's airports are non-towered. In the United States, there are close to 20,000 non-towered airports compared ...
s, the pilot controls the lighting system; for example, the pilot can key the microphone seven times to turn on the lights on the high intensity, five times to medium intensity or three times for low intensity.
Decision altitude and height
Once established on an approach, the pilot follows the ILS approach path indicated by the localizer and descends along the glide path to the decision height. This is the height at which the pilot must have adequate visual reference to the landing environment (e.g. approach or runway lighting) to decide whether to continue the descent to a landing; otherwise, the pilot must execute amissed approach
Missed approach is a procedure followed by a pilot when an instrument approach cannot be completed to a full-stop landing. The instructions for the missed approach may be assigned by air traffic control (ATC) prior to the clearance for the approac ...
procedure, then try the same approach again, try a different approach, or divert to another airport.
ILS categories
Smaller aircraft generally are equipped to fly only a CAT I ILS. On larger aircraft, these approaches typically are controlled by the flight control system with the flight crew providing supervision. CAT I relies only on altimeter indications for decision height, whereas CAT II and CAT III approaches useradio altimeter
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmit ...
(RA) to determine decision height.
An ILS must shut down upon internal detection of a fault condition. Higher categories require shorter response times; therefore, ILS equipment is required to shut down more quickly. For example, a CAT I localizer must shut down within 10 seconds of detecting a fault, but a CAT III localizer must shut down in less than 2 seconds.
Special CAT II and CAT III operations
head-up display
A head-up display, or heads-up display, also known as a HUD (), is any transparent display that presents data without requiring users to look away from their usual viewpoints. The origin of the name stems from a pilot being able to view informa ...
(HUD) guidance that provides the pilot with an image viewed through the windshield with eyes focused at infinity, of necessary electronic guidance to land the airplane with no true outside visual references.
In the United States, airports with CAT III approaches have listings for CAT IIIa and IIIb or just CAT III on the instrument approach plate (U.S. Terminal Procedures). CAT IIIb RVR minimums are limited by the runway/taxiway lighting and support facilities, and are consistent with the airport surface movement guidance control system (SMGCS) plan. Operations below 600 ft RVR require taxiway centerline lights and taxiway red stop bar lights. If the CAT IIIb RVR minimums on a runway end are , which is a common figure in the U.S., ILS approaches to that runway end with RVR below qualify as CAT IIIc and require special taxi procedures, lighting, and approval conditions to permit the landings. FAA Order 8400.13D limits CAT III to 300 ft RVR or better. Order 8400.13D (2009) allows ''special authorization CAT II'' approaches to runways without ALSF-2 approach lights and/or touchdown zone/centerline lights, which has expanded the number of potential CAT II runways.
In each case, a suitably equipped aircraft and appropriately qualified crew are required. For example, CAT IIIb requires a fail-operational system, along with a crew who are qualified and current, while CAT I does not. A HUD that allows the pilot to perform aircraft maneuvers rather than an automatic system is considered as fail-operational. A HUD allows the flight crew to fly the aircraft using the guidance cues from the ILS sensors such that if a safe landing is in doubt, the crew can respond in an appropriate and timely manner. HUD is becoming increasingly popular with "feeder" airlines and most manufacturers of regional jets are now offering HUDs as either standard or optional equipment. A HUD can provide capability to take off in low visibility.
 Some commercial aircraft are equipped with automatic landing systems that allow the aircraft to land without transitioning from instruments to visual conditions for a normal landing. Such
Some commercial aircraft are equipped with automatic landing systems that allow the aircraft to land without transitioning from instruments to visual conditions for a normal landing. Such autoland
In aviation, autoland describes a system that fully automates the landing procedure of an aircraft's flight, with the flight crew supervising the process. Such systems enable airliners to land in weather conditions that would otherwise be dangero ...
operations require specialized equipment, procedures and training, and involve the aircraft, airport, and the crew. Autoland is the only way some major airports such as Charles de Gaulle Airport
Paris Charles de Gaulle Airport (french: Aéroport de Paris-Charles-de-Gaulle, ), also known as Roissy Airport or simply Paris CDG, is the principal airport serving the French capital, Paris ( and its metropolitan area), and the largest intern ...
remain operational every day of the year. Some modern aircraft are equipped with enhanced flight vision systems based on infrared sensors, that provide a day-like visual environment and allow operations in conditions and at airports that would otherwise not be suitable for a landing. Commercial aircraft also frequently use such equipment for takeoffs when ''takeoff minima'' are not met.
For both automatic and HUD landing systems, the equipment requires special approval for its design and also for each individual installation. The design takes into consideration additional safety requirements for operating an aircraft close to the ground and the ability of the flight crew to react to a system anomaly. The equipment also has additional maintenance requirements to ensure that it is capable of supporting reduced visibility operations.
Of course nearly all of this pilot training and qualification work is done in simulators with various degrees of fidelity.
Use
At a controlled airport,air traffic control
Air traffic control (ATC) is a service provided by ground-based air traffic controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and through a given section of controlled airspace, and can provide advisory services to aircraft in non-controlled airs ...
will direct aircraft to the localizer course via assigned headings, making sure aircraft do not get too close to each other (maintain separation), but also avoiding delay as much as possible. Several aircraft can be on the ILS at the same time, several miles apart. An aircraft that has turned onto the inbound heading and is within two and a half degrees of the localizer course (half scale deflection or less shown by the course deviation indicator) is said to be ''established'' on the approach. Typically, an aircraft is established by at least prior to the final approach fix
In aeronautics, the final approach (also called the final leg and final approach leg) is the last leg in an aircraft's approach to landing, when the aircraft is lined up with the runway and descending for landing.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of ...
(glideslope intercept at the specified altitude).
Aircraft deviation from the optimal path is indicated to the flight crew by means of a display dial (a carryover from when an analog meter movement indicated deviation from the course line via voltages sent from the ILS receiver).
The output from the ILS receiver goes to the display system (head-down display and head-up display
A head-up display, or heads-up display, also known as a HUD (), is any transparent display that presents data without requiring users to look away from their usual viewpoints. The origin of the name stems from a pilot being able to view informa ...
if installed) and may go to a Flight Control Computer. An aircraft landing procedure can be either ''coupled'' where the autopilot or Flight Control Computer directly flies the aircraft and the flight crew monitor the operation, or ''uncoupled'' where the flight crew flies the aircraft manually to keep the localizer and glideslope indicators centered.
History
 Tests of the ILS began in 1929 in the United States, with
Tests of the ILS began in 1929 in the United States, with Jimmy Doolittle
James Harold Doolittle (December 14, 1896 – September 27, 1993) was an American military general and aviation pioneer who received the Medal of Honor for his daring raid on Japan during World War II. He also made early coast-to-coast flights ...
becoming the first pilot to take off, fly and land an airplane using instruments
Instrument may refer to:
Science and technology
* Flight instruments, the devices used to measure the speed, altitude, and pertinent flight angles of various kinds of aircraft
* Laboratory equipment, the measuring tools used in a scientific lab ...
alone, without a view outside the cockpit. A basic system, fully operative, was introduced in 1932 at Berlin-Tempelhof Central Airport
Berlin Tempelhof Airport (german: Flughafen Berlin-Tempelhof) was one of the first airports in Berlin, Germany. Situated in the south-central Berlin borough of Tempelhof-Schöneberg, the airport ceased operating in 2008 amid controversy, leav ...
(Germany) named LFF or "Lorenz beam The Lorenz beam was a blind-landing radio navigation system developed by C. Lorenz AG in Berlin. The first system had been installed in 1932 at Berlin-Tempelhof Central Airport, followed by Dübendorf in Switzerland (1934) and others all over the ...
" due its inventor, the C. Lorenz AG company. The Civil Aeronautics Board (CAB) of the United States authorized installation of the system in 1941 at six locations. The first landing of a scheduled U.S. passenger airliner using ILS was on January 26, 1938, when a Pennsylvania Central Airlines
Capital Airlines was an airline serving the eastern, southern, southeastern, and midwestern United States. Capital's headquarters were located at Washington Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport, National Airport (now Reagan Washington Natio ...
Boeing 247
The Boeing Model 247 is an early United States airliner, and one of the first such aircraft to incorporate advances such as all-metal (Anodizing#Anodized aluminium, anodized aluminum) semimonocoque construction, a fully Cantilever#Aircraft, cant ...
D flew from Washington, D.C., to Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, and landed in a snowstorm using only the Instrument Landing System. The first fully automatic landing
In aviation, autoland describes a system that fully automates the landing procedure of an aircraft's flight, with the flight crew supervising the process. Such systems enable airliners to land in weather conditions that would otherwise be dangero ...
using ILS occurred in March 1964 at Bedford Airport in the UK.
Market
The instrument landing systems market revenue was US$1,215 Million in 2019, and is expected to reach US$1,667 Million in 2025, with a CAGR of 5.41% during 2020-2025 even with the negative effects of theCOVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
.
Suppliers
The top 10 manufacturers in the instrument landing systems market are: * Airport Lighting Specialists * Saab Sensis * Advanced Navigation and Positioning * ADB Airfield Solutions *Universal Avionics
Universal Avionics Systems Corporation, also known as Universal Avionics, is an international company headquartered in Tucson, Arizona in the United States. It primarily focuses on flight management systems (FMS) and cockpit instrument displays fo ...
*Honeywell
Honeywell International Inc. is an American publicly traded, multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina. It primarily operates in four areas of business: aerospace, building technologies, performance ma ...
*Astronics
Astronics Corporation is an American aerospace electronics corporation founded in 1968, headquartered in East Aurora, New York. It is traded on NASDAQ as . It is known for lighting and electronics integrations on military, commercial, and busines ...
*Liberty Airport Systems
Liberty is the ability to do as one pleases, or a right or immunity enjoyed by prescription or by grant (i.e. privilege). It is a synonym for the word freedom.
In modern politics, liberty is understood as the state of being free within society fr ...
*Thales
Thales of Miletus ( ; grc-gre, Θαλῆς; ) was a Greek mathematician, astronomer, statesman, and pre-Socratic philosopher from Miletus in Ionia, Asia Minor. He was one of the Seven Sages of Greece. Many, most notably Aristotle, regarded him ...
*Rockwell Collins
Rockwell Collins was a multinational corporation headquartered in Cedar Rapids, Iowa, providing avionics and information technology systems and services to government agencies and aircraft manufacturers. It was formed when the Collins Radio Comp ...
Other manufacturers include:
* Indra (Normarc ILS)
Alternatives
* TheMicrowave Landing System
The microwave landing system (MLS) is an all-weather, precision radio guidance system intended to be installed at large airports to assist aircraft in landing, including 'blind landings'. MLS enables an approaching aircraft to determine when it ...
(MLS) allowed for curved approaches. It was introduced in the 1970s to replace ILS but fell out of favor because of the introduction of satellite based systems. In the 1980s, there was a major US and European effort to establish MLS. But a combination of airline
An airline is a company that provides civil aviation, air transport services for traveling passengers and freight. Airlines use aircraft to supply these services and may form partnerships or Airline alliance, alliances with other airlines for ...
reluctance to invest and the rise of Global Navigation Satellite System
A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning. It allows satellite navigation devices to determine their location (longitude, latitude, and altitude/elevation) to high pr ...
(GNSS) resulted in its not being adopted in civil aviation. At the time ILS and MLS were the only standardized systems in Civil Aviation that meet requirements for Category III automated landings. The first Category III MLS for civil aviation was commissioned at Heathrow airport in March 2009 and removed from service in 2017.
* Transponder Landing System (TLS) can be used where a conventional ILS cannot work or is not cost-effective.
* Localizer Performance with Vertical guidance (LPV) is based on the Wide Area Augmentation System
The Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS) is an air navigation aid developed by the Federal Aviation Administration to augment the Global Positioning System (GPS), with the goal of improving its accuracy, integrity, and availability. Essential ...
(WAAS), LPV has similar minima to ILS for appropriately equipped aircraft. , the FAA has published more LPV approaches than Category I ILS procedures.
* Ground-Based Augmentation System (GBAS) (Local Area Augmentation System
The local-area augmentation system (LAAS) is an all-weather aircraft landing system based on real-time differential correction of the GPS signal. Local reference receivers located around the airport send data to a central location at the airpor ...
in the United States) is a safety-critical system that augments the GNSS Standard Positioning Service (SPS) and provides enhanced levels of service. It supports all phases of approach, landing, departure, and surface operations within the VHF coverage volume. GBAS is expected to play a key role in modernization and in all-weather operations capability at CATI/II and III airports, terminal area navigation, missed approach guidance and surface operations. GBAS provides the capability to service the entire airport with a single frequency (VHF transmission) whereas ILS requires a separate frequency for each runway end. GBAS CAT-I is seen as a necessary step towards the more stringent operations of CAT-II/III precision approach and landing. The technical risk of implementing GBAS delayed widespread acceptance of the technology. The FAA, along with industry, have fielded Provably Safe Prototype GBAS stations that mitigate the impact of satellite signal deformation, ionosphere differential error, ephemeris error, and multipath.
Future
The advent of theGlobal Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
(GPS) provides an alternative source of approach guidance for aircraft. In the US, the Wide Area Augmentation System
The Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS) is an air navigation aid developed by the Federal Aviation Administration to augment the Global Positioning System (GPS), with the goal of improving its accuracy, integrity, and availability. Essential ...
(WAAS) has been available in many regions to provide precision guidance to Category I standards since 2007. The equivalent European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service
The European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS) is a satellite-based augmentation system (SBAS) developed by the European Space Agency and EUROCONTROL on behalf of the European Commission. Currently, it supplements the GPS by repor ...
(EGNOS) was certified for use in safety of life applications in March 2011. As such, the number of Cat I ILS installations may be reduced, however there are no plans in the United States to phase out any Cat II or Cat III systems.
Local Area Augmentation System
The local-area augmentation system (LAAS) is an all-weather aircraft landing system based on real-time differential correction of the GPS signal. Local reference receivers located around the airport send data to a central location at the airpor ...
(LAAS) is under development to provide for Category III minimums or lower. The FAA Ground-Based Augmentation System (GBAS) office is currently working with the industry in anticipation of the certification of the first GBAS ground stations in Memphis, TN; Sydney, Australia; Bremen, Germany; Spain; and Newark, NJ. All four countries have installed GBAS ground stations and are involved in technical and operational evaluation activities.
The Honeywell and FAA team obtained System Design Approval of the world's first non-federal U.S. approval for LAAS Category I at Newark Liberty International Airport, operations in September 2009 and Operational Approval on September 28, 2012.
In Norway, a D-GPS based landing system, called SCAT-I, is in operation on some short runway airports.
See also
*Acronyms and abbreviations in avionics
Below are abbreviations used in aviation, avionics, aerospace and aeronautics.
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
N numbers (turbines)
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
V speeds
W
X
Y
Z
See also
* List of avia ...
* Airspeed
In aviation, airspeed is the speed of an aircraft relative to the air. Among the common conventions for qualifying airspeed are:
* Indicated airspeed ("IAS"), what is read on an airspeed gauge connected to a Pitot-static system;
* Calibrated a ...
* AN/CRN-2
* Autoland
In aviation, autoland describes a system that fully automates the landing procedure of an aircraft's flight, with the flight crew supervising the process. Such systems enable airliners to land in weather conditions that would otherwise be dangero ...
* Blind approach beacon system (BABS)
* CFIT
* Distance measuring equipment
In aviation, distance measuring equipment (DME) is a radio navigation technology that measures the slant range (distance) between an aircraft and a ground station by timing the propagation delay of radio signals in the frequency band between 9 ...
(DME)
* EGPWS
* Flight director
Flight controllers are personnel who aid space flight by working in such Mission Control Centers as NASA's Mission Control Center or ESA's European Space Operations Centre. Flight controllers work at computer consoles and use telemetry to mon ...
, FD
* Fog
Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. Reprint from Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud usually resembling stratus, and is heavily influ ...
* George Vernon Holloman – the pilot who made first automated landing
* Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
(GPS)
* HUD
Hud or HUD may refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Hud'' (1963 film), a 1963 film starring Paul Newman
* ''Hud'' (1986 film), a 1986 Norwegian film
* ''HUD'' (TV program), or ''Heads Up Daily'', a Canadian e-sports television program
Places
* Hud, Fa ...
* Instrument flight rules
In aviation, instrument flight rules (IFR) is one of two sets of regulations governing all aspects of civil aviation aircraft operations; the other is visual flight rules (VFR).
The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration's (FAA) ''Instrument Fly ...
(IFR)
* Local Area Augmentation System
The local-area augmentation system (LAAS) is an all-weather aircraft landing system based on real-time differential correction of the GPS signal. Local reference receivers located around the airport send data to a central location at the airpor ...
(LAAS)
* Localizer performance with vertical guidance (LPV)
* Lorenz beam The Lorenz beam was a blind-landing radio navigation system developed by C. Lorenz AG in Berlin. The first system had been installed in 1932 at Berlin-Tempelhof Central Airport, followed by Dübendorf in Switzerland (1934) and others all over the ...
* Microwave landing system
The microwave landing system (MLS) is an all-weather, precision radio guidance system intended to be installed at large airports to assist aircraft in landing, including 'blind landings'. MLS enables an approaching aircraft to determine when it ...
(MLS)
* Non-directional beacon
A non-directional beacon (NDB) or non-directional radio beacon is a radio beacon which does not include directional information. Radio beacons are radio transmitters at a known location, used as an aviation or marine navigational aid. NDB are ...
(NDB)
* Precision approach radar
Precision approach radar (PAR) is a type of radar guidance system designed to provide lateral and vertical guidance to an aircraft pilot for landing, until the landing threshold is reached. Controllers monitoring the PAR displays observe each airc ...
(PAR)
* Space modulation
{{Modulation techniques
Space modulation is a radio amplitude modulation technique used in instrument landing systems (ILS) that incorporates the use of multiple antennas fed with various radio frequency powers and phases to create different dep ...
* Transponder landing system (TLS)
* Visual flight rules
In aviation, visual flight rules (VFR) are a set of regulations under which a pilot operates an aircraft in weather conditions generally clear enough to allow the pilot to see where the aircraft is going. Specifically, the weather must be better ...
(VFR)
* VHF omnidirectional range
Very high frequency omnirange station (VOR) is a type of short-range radio navigation system for aircraft, enabling aircraft with a receiving unit to determine its position and stay on course by receiving radio signals transmitted by a network ...
(VOR)
* Wide Area Augmentation System
The Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS) is an air navigation aid developed by the Federal Aviation Administration to augment the Global Positioning System (GPS), with the goal of improving its accuracy, integrity, and availability. Essential ...
(WAAS)
Notes
References
* ICAO Annex 10 Volume 1, Radio Navigation Aids, Fifth Edition — July 1996Aeronautical Information Manual
FAA – February 11, 2010
Digital Terminal Procedures
FAA – May 2010
External links
– U.S. Centennial of Flight Commission
"Happy Landings In Fog", June 1933, Popular Mechanics
article on the early system setup in the USA.
ILS Tutorial Animations
Website dedicated to the description of ILS
ILS Tutorial Animation
- Illustrates and describes how ILS navigation signals are displayed on board of an aircraft in various positions, which may occur during a safe approach for landing.
* {{Authority control 1929 in aviation Navigational aids Aircraft landing systems Avionics Radio navigation Radio stations and systems ITU Runway safety Types of final approach (aviation)