A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a
medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to rev ...
technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called
radiographer
Radiographers, also known as radiologic technologists, diagnostic radiographers and medical radiation technologists are healthcare professionals who specialize in the imaging of human anatomy for the diagnosis and treatment of pathology. Radi ...
s or radiology technologists.
CT scanners use a rotating
X-ray tube
An X-ray tube is a vacuum tube that converts electrical input power into X-rays. The availability of this controllable source of X-rays created the field of radiography, the imaging of partly opaque objects with penetrating radiation. In contrast ...
and a row of detectors placed in a
gantry
A gantry is an overhead bridge-like structure supporting equipment such as a crane, signals, or cameras.
Devices and structures
*Gantry (medical), cylindrical scanner assembly used for medical 3D-imaging or treatment
*Gantry (transport), an over ...
to measure X-ray
attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple
X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using
tomographic reconstruction
Tomographic reconstruction is a type of multidimensional inverse problem where the challenge is to yield an estimate of a specific system from a finite number of projections. The mathematical basis for tomographic imaging was laid down by Johann ...
algorithms to produce
tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom
magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
(MRI) is
contraindicated
In medicine, a contraindication is a condition that serves as a reason not to take a certain medical treatment due to the harm that it would cause the patient. Contraindication is the opposite of indication, which is a reason to use a certain tre ...
.
Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in
medical diagnosis
Medical diagnosis (abbreviated Dx, Dx, or Ds) is the process of determining which disease or condition explains a person's symptoms and signs. It is most often referred to as diagnosis with the medical context being implicit. The information re ...
, it can also be used to form images of non-living objects. The 1979
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accord ...
was awarded jointly to South African-American physicist
Allan MacLeod Cormack
Allan MacLeod Cormack (February 23, 1924 ŌĆō May 7, 1998) was a South African American physicist who won the 1979 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine (along with Godfrey Hounsfield) for his work on X-ray computed tomography (CT).
Early life a ...
and British electrical engineer
Godfrey Hounsfield
Sir Godfrey Newbold Hounsfield (28 August 1919 ŌĆō 12 August 2004) was an English electrical engineer who shared the 1979 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine with Allan MacLeod Cormack for his part in developing the diagnostic technique of X ...
"for the development of computer-assisted tomography".
Types
On the basis of image acquisition and procedures, various type of scanners are available in the market.
Sequential CT
Sequential CT, also known as step-and-shoot CT, is a type of scanning method in which the CT table moves stepwise. The table increments to a particular location and then stops which is followed by the
X-ray tube
An X-ray tube is a vacuum tube that converts electrical input power into X-rays. The availability of this controllable source of X-rays created the field of radiography, the imaging of partly opaque objects with penetrating radiation. In contrast ...
rotation and acquisition of a slice. The table then increments again, and another slice is taken. The table movement stops while taking slices. This results in an increased time of scanning.
Spiral CT
Spinning tube, commonly called
spiral CT
X-ray computed tomography operates by using an X-ray generator that rotates around the object; X-ray detectors are positioned on the opposite side of the circle from the X-ray source.
A visual representation of the raw data obtained is called ...
, or helical CT, is an imaging technique in which an entire
X-ray tube
An X-ray tube is a vacuum tube that converts electrical input power into X-rays. The availability of this controllable source of X-rays created the field of radiography, the imaging of partly opaque objects with penetrating radiation. In contrast ...
is spun around the central axis of the area being scanned. These are the dominant type of scanners on the market because they have been manufactured longer and offer a lower cost of production and purchase. The main limitation of this type of CT is the bulk and inertia of the equipment (X-ray tube assembly and detector array on the opposite side of the circle) which limits the speed at which the equipment can spin. Some designs use two X-ray sources and detector arrays offset by an angle, as a technique to improve temporal resolution.
Electron beam tomography
Electron beam tomography
Electron beam computed tomography (EBCT) is a specific form of computed tomography (CT) in which the X-ray tube is not mechanically spun in order to rotate the source of X-ray photons. This different design was explicitly developed to better im ...
(EBT) is a specific form of CT in which a large enough X-ray tube is constructed so that only the path of the
electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no kn ...
s, travelling between the
cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. A conventional current describes the direction in whi ...
and
anode
An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic is ...
of the X-ray tube, are spun using
deflection coils. This type had a major advantage since sweep speeds can be much faster, allowing for less blurry imaging of moving structures, such as the heart and arteries. Fewer scanners of this design have been produced when compared with spinning tube types, mainly due to the higher cost associated with building a much larger X-ray tube and detector array and limited anatomical coverage.
Dual Energy CT
Dual Energy CT, also known as Spectral CT, is an advancement of Computed Tomography in which two energies are used to create two sets of data. A Dual Energy CT may employ Dual source, Single source with dual detector layer, Single source with energy switching methods to get two different sets of data.
#Dual source CT is an advanced scanner with a two X-ray tube detector system, unlike conventional single tube systems. These two detector systems are mounted on a single gantry at 90┬░ in the same plane.
Dual Source CT scanners allow fast scanning with higher temporal resolution by acquiring a full CT slice in only half a rotation. Fast imaging reduces motion blurring at high heart rates and potentially allowing for shorter breath-hold time. This is particularly useful for ill patients having difficulty holding their breath or unable to take heart-rate lowering medication.
#Single Source with Energy switching is another mode of Dual energy CT in which a single tube is operated at two different energies by switching the energies frequently.
CT perfusion imaging

CT perfusion imaging is a specific form of CT to assess flow through
blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away ...
s whilst injecting a
contrast agent
A contrast agent (or contrast medium) is a substance used to increase the contrast of structures or fluids within the body in medical imaging. Contrast agents absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound, which is different from radiop ...
.
Blood flow, blood transit time, and organ blood volume, can all be calculated with reasonable
sensitivity and specificity
''Sensitivity'' and ''specificity'' mathematically describe the accuracy of a test which reports the presence or absence of a condition. Individuals for which the condition is satisfied are considered "positive" and those for which it is not are ...
.
This type of CT may be used on the
heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide t ...
, although sensitivity and specificity for detecting abnormalities are still lower than for other forms of CT. This may also be used on the
brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a v ...
, where CT perfusion imaging can often detect poor brain perfusion well before it is detected using a conventional spiral CT scan.
This is better for
stroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functionin ...
diagnosis than other CT types.
PET CT

Positron emission tomographyŌĆōcomputed tomography is a hybrid CT modality which combines, in a single gantry, a
positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in Metabolism, metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including bl ...
(PET) scanner and an X-ray computed tomography (CT) scanner, to acquire sequential images from both devices in the same session, which are combined into a single superposed (
co-registered) image. Thus,
functional imaging
Functional imaging (or physiological imaging) is a medical imaging technique of detecting or measuring changes in metabolism, blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption.
As opposed to structural imaging, functional imaging center ...
obtained by PET, which depicts the spatial distribution of metabolic or biochemical activity in the body can be more precisely aligned or correlated with anatomic imaging obtained by CT scanning.
PET-CT gives both anatomical and functional details of an organ under examination and is helpful in detecting different type of cancers.
Medical use
Since its introduction in the 1970s, CT has become an important tool in
medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to rev ...
to supplement conventional
X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
imaging and
medical ultrasonography
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly medical imaging, imaging techniques) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic ultrasound, therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal ...
. It has more recently been used for
preventive medicine
Preventive healthcare, or prophylaxis, consists of measures taken for the purposes of disease prevention.Hugh R. Leavell and E. Gurney Clark as "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life, and promoting physical and mental hea ...
or
screening
Screening may refer to:
* Screening cultures, a type a medical test that is done to find an infection
* Screening (economics), a strategy of combating adverse selection (includes sorting resumes to select employees)
* Screening (environmental), a ...
for disease, for example,
CT colonography
Virtual colonoscopy (VC, also called CT colonography or CT pneumocolon) is the use of CT scanning or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to produce two- and three-dimensional images of the colon (large intestine), from the lowest part, the rectum, ...
for people with a high risk of
colon cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel mo ...
, or full-motion heart scans for people with a high risk of heart disease. Several institutions offer
full-body scans for the general population although this practice goes against the advice and official position of many professional organizations in the field primarily due to the
radiation dose
Ionizing radiation (or ionising radiation), including nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have sufficient energy to ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel ...
applied.
The use of CT scans has increased dramatically over the last two decades in many countries.
An estimated 72 million scans were performed in the United States in 2007 and more than 80 million in 2015.
Head

CT scanning of the head is typically used to detect
infarction
Infarction is tissue death (necrosis) due to inadequate blood supply to the affected area. It may be caused by artery blockages, rupture, mechanical compression, or vasoconstriction. The resulting lesion is referred to as an infarct
(from the ...
(
stroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functionin ...
),
tumors
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
,
calcification
Calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts in a body tissue. It normally occurs in the formation of bone, but calcium can be deposited abnormally in soft tissue,Miller, J. D. Cardiovascular calcification: Orbicular origins. ''Nature Mat ...
s,
haemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagi ...
, and bone
trauma
Trauma most often refers to:
* Major trauma, in physical medicine, severe physical injury caused by an external source
* Psychological trauma, a type of damage to the psyche that occurs as a result of a severely distressing event
*Traumatic i ...
. Of the above,
hypodense
Radiodensity (or radiopacity) is opacity to the radio wave and X-ray portion of the electromagnetic spectrum: that is, the relative inability of those kinds of electromagnetic radiation to pass through a particular material. Radiolucency or hypo ...
(dark) structures can indicate
edema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's Tissue (biology), tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels t ...
and infarction, hyperdense (bright) structures indicate calcifications and haemorrhage and bone trauma can be seen as disjunction in bone windows. Tumors can be detected by the swelling and anatomical distortion they cause, or by surrounding edema. CT scanning of the head is also used in CT-
guided stereotactic surgery
Stereotactic surgery is a minimally invasive form of surgical intervention that makes use of a three-dimensional coordinate system to locate small targets inside the body and to perform on them some action such as ablation, biopsy, lesion, injec ...
and
radiosurgery
Radiosurgery is surgery using radiation, that is, the destruction of precisely selected areas of tissue using ionizing radiation rather than excision with a blade. Like other forms of radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy), it is usually u ...
for treatment of intracranial tumors,
arteriovenous malformation
Arteriovenous malformation is an abnormal connection between arteries and veins, bypassing the capillary system. This vascular anomaly is widely known because of its occurrence in the central nervous system (usually cerebral AVM), but can appea ...
s, and other surgically treatable conditions using a device known as the
N-localizer
The N-localizer is a device that enables guidance of stereotactic surgery or radiosurgery using tomographic images that are obtained via computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or positron emission tomography (PET). The N-local ...
.
Neck
Contrast CT
Contrast CT, or contrast enhanced computed tomography (CECT), is X-ray computed tomography (CT) using radiocontrast. Radiocontrasts for X-ray CT are generally iodine-based types. This is useful to highlight structures such as blood vessels that ...
is generally the initial study of choice for
neck mass
A neck mass or neck lump is an ambiguous mass found in the neck area. There are many different possible causes, including congenital conditions like branchial anomalies and thyroglossal duct cysts.
Workup
Workup of a neck mass includes a medical ...
es in adults.
[ This topic last updated: Dec 04, 2017.] CT of the thyroid plays an important role in the evaluation of
thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer is cancer that develops from the tissues of the thyroid gland. It is a disease in which cells grow abnormally and have the potential to spread to other parts of the body. Symptoms can include swelling or a lump in the neck. C ...
.
CT scan often incidentally finds thyroid abnormalities, and so is often the preferred investigation modality for thyroid abnormalities.
Lungs
A CT scan can be used for detecting both acute and chronic changes in the
lung parenchyma
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ or structure such as a tumour. In zoology it is the name for the tissue that fills the interior of flatworms.
Etymology
The term ''parenchyma'' is New Latin from the word ŽĆ ...
, the tissue of the
lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
s. It is particularly relevant here because normal two-dimensional X-rays do not show such defects. A variety of techniques are used, depending on the suspected abnormality. For evaluation of chronic interstitial processes such as
emphysema
Emphysema, or pulmonary emphysema, is a lower respiratory tract disease, characterised by air-filled spaces ( pneumatoses) in the lungs, that can vary in size and may be very large. The spaces are caused by the breakdown of the walls of the alve ...
, and
fibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is a pathological wound healing in which connective tissue replaces normal parenchymal tissue to the extent that it goes unchecked, leading to considerable tissue remodelling and the formation of perma ...
, thin sections with high spatial frequency reconstructions are used; often scans are performed both on inspiration and expiration. This special technique is called
high resolution CT
High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) is a type of computed tomography (CT) with specific techniques to enhance image resolution. It is used in the diagnosis of various health problems, though most commonly for lung disease, by assessing t ...
that produces a sampling of the lung, and not continuous images.
Bronchial wall thickening can be seen on lung CTs and generally (but not always) implies inflammation of the
bronchi
A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi pronounced (BRAN-KAI) to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. ...
.
An
incidentally found nodule in the absence of symptoms (sometimes referred to as an
incidentaloma
In medical or research imaging, an incidental imaging finding (also called an incidentaloma) is an unanticipated finding which is not related to the original diagnostic inquiry. As with other types of incidental medical findings, they may represen ...
) may raise concerns that it might represent a tumor, either
benign
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse.
Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malign ...
or
malignant
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse.
Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not s ...
. Perhaps persuaded by fear, patients and doctors sometimes agree to an intensive schedule of CT scans, sometimes up to every three months and beyond the recommended guidelines, in an attempt to do surveillance on the nodules.
[, which cites
*
*
*
*] However, established guidelines advise that patients without a prior history of cancer and whose solid nodules have not grown over a two-year period are unlikely to have any malignant cancer.
For this reason, and because no research provides supporting evidence that intensive surveillance gives better outcomes, and because of risks associated with having CT scans, patients should not receive CT screening in excess of those recommended by established guidelines.
Angiography
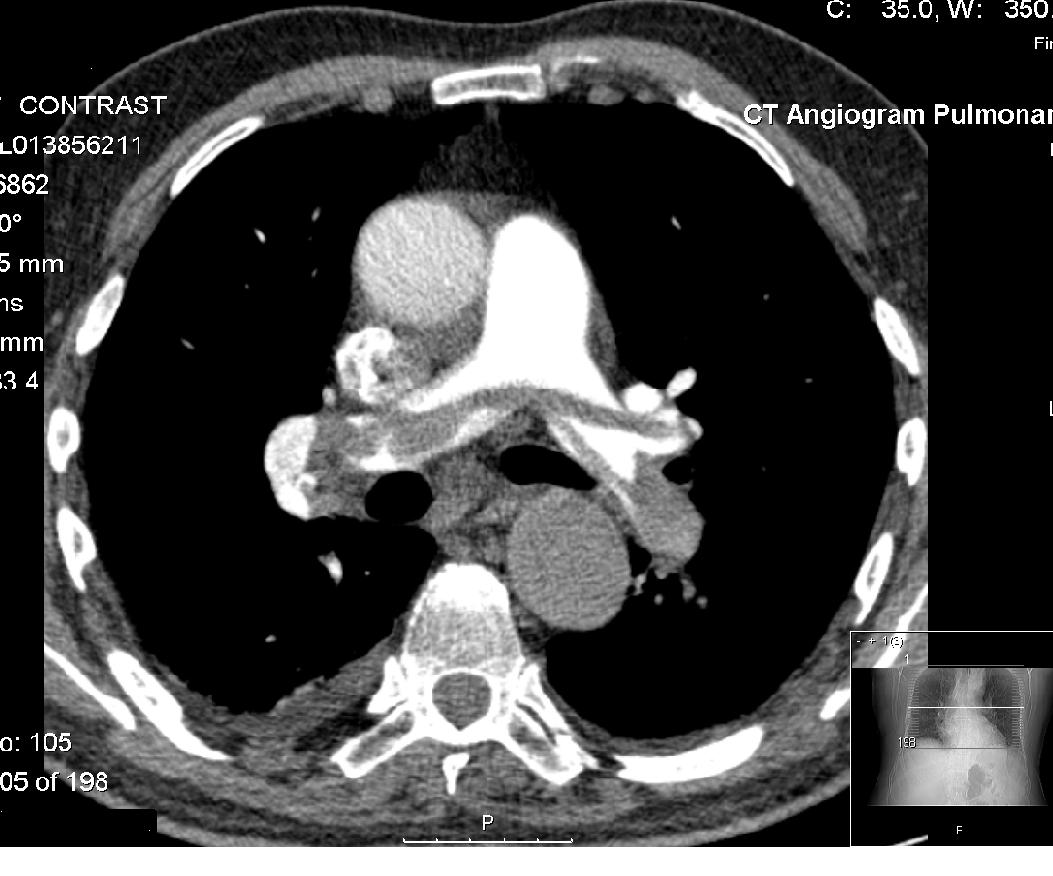
Computed tomography angiography
Computed tomography angiography (also called CT angiography or CTA) is a computed tomography technique used for angiographyŌĆöthe visualization of arteries and veinsŌĆöthroughout the human body. Using contrast injected into the blood vessels, im ...
(CTA) is a type of
contrast CT
Contrast CT, or contrast enhanced computed tomography (CECT), is X-ray computed tomography (CT) using radiocontrast. Radiocontrasts for X-ray CT are generally iodine-based types. This is useful to highlight structures such as blood vessels that ...
to visualize the
arteries
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pul ...
and
vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated b ...
s throughout the body. This ranges from arteries serving the
brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a v ...
to those bringing blood to the
lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
s,
kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood ...
s,
arm
In human anatomy, the arm refers to the upper limb in common usage, although academically the term specifically means the upper arm between the glenohumeral joint (shoulder joint) and the elbow joint. The distal part of the upper limb between the ...
s and
leg
A leg is a weight-bearing and animal locomotion, locomotive anatomical structure, usually having a columnar shape. During locomotion, legs function as "extensible struts". The combination of movements at all joints can be modeled as a single ...
s. An example of this type of exam is
CT pulmonary angiogram
A CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA) is a medical diagnostic test that employs computed tomography (CT) angiography to obtain an image of the pulmonary arteries. Its main use is to diagnose pulmonary embolism (PE). It is a preferred choice of imaging i ...
(CTPA) used to diagnose
pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an pulmonary artery, artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include dyspnea, shortness of breath, chest pain p ...
(PE). It employs computed tomography and an
iodine-based contrast agent to obtain an image of the
pulmonary arteries
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and t ...
.
Cardiac
A CT scan of the heart is performed to gain knowledge about cardiac or coronary anatomy. Traditionally, cardiac CT scans are used to detect, diagnose, or follow up
coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic pla ...
.
More recently CT has played a key role in the fast-evolving field of
transcatheter structural heart interventions, more specifically in the transcatheter repair and replacement of heart valves.
The main forms of cardiac CT scanning are:
*
Coronary CT angiography
Coronary CT angiography (CTA or CCTA) is the use of computed tomography (CT) angiography to assess the coronary arteries of the heart. The patient receives an intravenous injection of radiocontrast and then the heart is scanned using a high spee ...
(CCTA): the use of CT to assess the
coronary arteries
The coronary arteries are the arterial blood vessels of coronary circulation, which transport oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. The heart requires a continuous supply of oxygen to function and survive, much like any other tissue or organ of ...
of the
heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide t ...
. The subject receives an
intravenous injection
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutri ...
of
radiocontrast
Radiocontrast agents are substances used to enhance the visibility of internal structures in X-ray-based imaging techniques such as computed tomography (contrast CT), projectional radiography, and fluoroscopy. Radiocontrast agents are typically io ...
, and then the heart is scanned using a high-speed CT scanner, allowing radiologists to assess the extent of occlusion in the coronary arteries, usually to diagnose coronary artery disease.
*
Coronary CT calcium scan: also used for the assessment of severity of coronary artery disease. Specifically, it looks for calcium deposits in the coronary arteries that can narrow arteries and increase the risk of a heart attack.
A typical coronary CT calcium scan is done without the use of radiocontrast, but it can possibly be done from contrast-enhanced images as well.
To better visualize the anatomy, post-processing of the images is common.
Most common are multiplanar reconstructions (MPR) and
volume rendering
In scientific visualization and computer graphics, volume rendering is a set of techniques used to display a 2D projection of a 3D discretely sampled data set, typically a 3D scalar field.
A typical 3D data set is a group of 2D slice images ...
. For more complex anatomies and procedures, such as heart valve interventions, a true
3D reconstruction
In computer vision and computer graphics, 3D reconstruction is the process of capturing the shape and appearance of real objects.
This process can be accomplished either by active or passive methods. If the model is allowed to change its shape i ...
or a 3D print is created based on these CT images to gain a deeper understanding.
Abdomen and pelvis
CT is an accurate technique for diagnosis of
abdominal
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. ...
diseases like
Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea (which may be bloody if inflammation is severe), fever, abdominal distension ...
, GIT bleeding, and diagnosis and staging of cancer, as well as follow-up after cancer treatment to assess response. It is commonly used to investigate
acute abdominal pain
An acute abdomen refers to a sudden, severe abdominal pain. It is in many cases a medical emergency, requiring urgent and specific diagnosis. Several causes need immediate surgical treatment.
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis o ...
.
Non-enhanced computed tomography is today the gold standard for diagnosing
urinary stones. The size, volume and density of stones can be estimated to help clinicians guide further treatment; size is especially important in predicting spontaneous passage of a stone.
Axial skeleton and extremities
For the
axial skeleton
The axial skeleton is the part of the skeleton that consists of the bones of the head and trunk (anatomy), trunk of a vertebrate. In the human skeleton, it consists of 80 bones and is composed of six parts; the human skull, skull (22 bones), als ...
and
extremities, CT is often used to image complex
fractures
Fracture is the separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displa ...
, especially ones around joints, because of its ability to reconstruct the area of interest in multiple planes. Fractures, ligamentous injuries, and
dislocations
In materials science, a dislocation or Taylor's dislocation is a linear crystallographic defect or irregularity within a crystal structure that contains an abrupt change in the arrangement of atoms. The movement of dislocations allow atoms to sl ...
can easily be recognized with a 0.2 mm resolution. With modern dual-energy CT scanners, new areas of use have been established, such as aiding in the diagnosis of
gout
Gout ( ) is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by recurrent attacks of a red, tender, hot and swollen joint, caused by deposition of monosodium urate monohydrate crystals. Pain typically comes on rapidly, reaching maximal intensit ...
.
Biomechanical use
CT is used in
biomechanics
Biomechanics is the study of the structure, function and motion of the mechanical aspects of biological systems, at any level from whole organisms to organs, cells and cell organelles, using the methods of mechanics. Biomechanics is a branch of ...
to quickly reveal the geometry, anatomy,
density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''Žü'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematical ...
and
elastic moduli
An elastic modulus (also known as modulus of elasticity) is the unit of measurement of an object's or substance's resistance to being deformed elastically (i.e., non-permanently) when a stress is applied to it. The elastic modulus of an object is ...
of biological tissues.
Other uses
Industrial use
Industrial CT scanning
Industrial computed tomography (CT) scanning is any computer-aided tomographic process, usually X-ray computed tomography, that uses irradiation to produce three-dimensional internal and external representations of a scanned object. Industrial CT ...
(industrial computed tomography) is a process which uses X-ray equipment to produce 3D representations of components both externally and internally. Industrial CT scanning has been used in many areas of industry for internal inspection of components. Some of the key uses for CT scanning have been flaw detection, failure analysis, metrology, assembly analysis, image-based finite element methods and reverse engineering applications. CT scanning is also employed in the imaging and conservation of museum artifacts.
Aviation security
CT scanning has also found an application in transport security (predominantly
airport security
Airport security includes the techniques and methods used in an attempt to protect passengers, staff, aircraft, and airport property from malicious harm, crime, terrorism, and other threats.
Aviation security is a combination of measures and hum ...
) where it is currently used in a materials analysis context for explosives detection
CTX (explosive-detection device) The CTX (Computer Tomography X-ray) is an explosive detection device, a family of x-ray devices developed by InVision Technologies in 1990 that uses CAT scans and sophisticated image processing software to automatically screen checked baggage for e ...
and is also under consideration for automated baggage/parcel security scanning using
computer vision
Computer vision is an interdisciplinary scientific field that deals with how computers can gain high-level understanding from digital images or videos. From the perspective of engineering, it seeks to understand and automate tasks that the hum ...
based object recognition algorithms that target the detection of specific threat items based on 3D appearance (e.g. guns, knives, liquid containers).
Its usage in airport security pioneered at
Shannon Airport
Shannon Airport ( ga, Aerfort na Sionainne) is an international airport located in County Clare in the Republic of Ireland. It is adjacent to the Shannon Estuary and lies halfway between Ennis and Limerick. The airport is the third busiest ai ...
in March 2022 has ended the ban on liquids over 100 ml there, a move that
Heathrow Airport
Heathrow Airport (), called ''London Airport'' until 1966 and now known as London Heathrow , is a major international airport in London, England. It is the largest of the six international airports in the London airport system (the others be ...
plans for a full roll-out on 1 December 2022 and the TSA spent $781.2 million on an order for over 1,000 scanners, ready to go live in the summer.
Geological use
X-ray CT is used in geological studies to quickly reveal materials inside a drill core. Dense minerals such as pyrite and barite appear brighter and less dense components such as clay appear dull in CT images.
Cultural heritage use
X-ray CT and
micro-CT
X-ray microtomography, like tomography and X-ray computed tomography, uses X-rays to create cross-sections of a physical object that can be used to recreate a virtual model (3D model) without destroying the original object. The prefix ''micro-'' ...
can also be used for the conservation and preservation of objects of cultural heritage. For many fragile objects, direct research and observation can be damaging and can degrade the object over time. Using CT scans, conservators and researchers are able to determine the material composition of the objects they are exploring, such as the position of ink along the layers of a scroll, without any additional harm. These scans have been optimal for research focused on the workings of the
Antikythera mechanism
The Antikythera mechanism ( ) is an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek hand-powered orrery, described as the oldest example of an analogue computer used to predict astronomy, astronomical positions and eclipses decades in advance. It could also be ...
or the text hidden inside the charred outer layers of the
En-Gedi Scroll
The En-Gedi Scroll is an ancient Hebrew parchment found in 1970 at Ein Gedi, Israel. Radiocarbon testing dates the scroll to the third or fourth century CE (210ŌĆō390 CE), although paleographical considerations suggest that the scrolls may date b ...
. However, they are not optimal for every object subject to these kinds of research questions, as there are certain artifacts like the
Herculaneum papyri
The Herculaneum papyri are more than 1,800 papyri found in the Herculaneum Villa of the Papyri, in the 18th century, carbonized by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in AD 79.
The papyri, containing a number of Greek philosophical texts, come fro ...
in which the material composition has very little variation along the inside of the object. After scanning these objects, computational methods can be employed to examine the insides of these objects, as was the case with the virtual unwrapping of the
En-Gedi scroll
The En-Gedi Scroll is an ancient Hebrew parchment found in 1970 at Ein Gedi, Israel. Radiocarbon testing dates the scroll to the third or fourth century CE (210ŌĆō390 CE), although paleographical considerations suggest that the scrolls may date b ...
and the
Herculaneum papyri
The Herculaneum papyri are more than 1,800 papyri found in the Herculaneum Villa of the Papyri, in the 18th century, carbonized by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in AD 79.
The papyri, containing a number of Greek philosophical texts, come fro ...
. Micro-CT has also proved useful for analyzing more recent artifacts such as still-sealed historic correspondence that employed the technique of
letterlocking
Letterlocking is the act of folding and securing a written message (such as a letter) on papyrus, parchment, or paper, without requiring it to be contained in an envelope or packet. It is a traditional method of document security that utilizes fol ...
(complex folding and cuts) that provided a "tamper-evident locking mechanism". Further examples of use cases in archaeology is imaging the contents of sarcophagi or ceramics.
Recently, CWI in Amsterdam has collaborated with Rijksmuseum to investigate art object inside details in the framework called IntACT.
Micro organism research
Varied types of fungus can degrade wood to different degrees, one Belgium research group has been used X-ray CT 3 dimension with sub-micron resolution unveiled fungi can penetrate micropores of 0.6 ╬╝m under certain conditions.
Timber sawmill
Sawmills use industrial CT scanners to detect round defects, for instance knots, to improve total value of timber productions. Most sawmills are planning to incorporate this robust detection tool to improve productivity in the long run, however initial investment cost is high.
Interpretation of results
Presentation
The result of a CT scan is a volume of
voxel
In 3D computer graphics, a voxel represents a value on a regular grid in three-dimensional space. As with pixels in a 2D bitmap, voxels themselves do not typically have their position (i.e. coordinates) explicitly encoded with their values. Ins ...
s, which may be presented to a human observer by various methods, which broadly fit into the following categories:
*Slices (of varying thickness). Thin slice is generally regarded as planes representing a thickness of less than 3
mm.
Thick slice is generally regarded as planes representing a thickness between 3 mm and 5 mm.
*Projection, including
maximum intensity projection
In scientific visualization, a maximum intensity projection (MIP) is a method for 3D data that projects in the visualization plane the voxels with maximum intensity that fall in the way of parallel rays traced from the viewpoint to the plane of p ...
and ''average intensity projection''
*
Volume rendering
In scientific visualization and computer graphics, volume rendering is a set of techniques used to display a 2D projection of a 3D discretely sampled data set, typically a 3D scalar field.
A typical 3D data set is a group of 2D slice images ...
(VR)
Technically, all volume renderings become projections when viewed on a
2-dimensional display, making the distinction between projections and volume renderings a bit vague. The epitomes of volume rendering models feature a mix of for example coloring and shading in order to create realistic and observable representations.
Two-dimensional CT images are conventionally rendered so that the view is as though looking up at it from the patient's feet.
Hence, the left side of the image is to the patient's right and vice versa, while anterior in the image also is the patient's anterior and vice versa. This left-right interchange corresponds to the view that physicians generally have in reality when positioned in front of patients.
Grayscale
Pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device.
In most digital display devices, pixels are the smal ...
s in an image obtained by CT scanning are displayed in terms of relative
radiodensity
Radiodensity (or radiopacity) is opacity to the radio wave and X-ray portion of the electromagnetic spectrum: that is, the relative inability of those kinds of electromagnetic radiation to pass through a particular material. Radiolucency or hypod ...
. The pixel itself is displayed according to the mean
attenuation
In physics, attenuation (in some contexts, extinction) is the gradual loss of flux intensity through a medium. For instance, dark glasses attenuate sunlight, lead attenuates X-rays, and water and air attenuate both light and sound at variable att ...
of the tissue(s) that it corresponds to on a scale from +3,071 (most attenuating) to ŌłÆ1,024 (least attenuating) on the
Hounsfield scale The Hounsfield scale , named after Sir Godfrey Hounsfield, is a quantitative scale for describing radiodensity. It is frequently used in CT scans, where its value is also termed CT number.
Definition
The Hounsfield unit (HU) scale is a linear tran ...
. A
pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device.
In most digital display devices, pixels are the smal ...
is a two dimensional unit based on the matrix size and the field of view. When the CT slice thickness is also factored in, the unit is known as a
voxel
In 3D computer graphics, a voxel represents a value on a regular grid in three-dimensional space. As with pixels in a 2D bitmap, voxels themselves do not typically have their position (i.e. coordinates) explicitly encoded with their values. Ins ...
, which is a three-dimensional unit. Water has an attenuation of 0
Hounsfield units The Hounsfield scale , named after Sir Godfrey Hounsfield, is a quantitative scale for describing radiodensity. It is frequently used in CT scans, where its value is also termed CT number.
Definition
The Hounsfield unit (HU) scale is a linear tran ...
(HU), while air is ŌłÆ1,000 HU, cancellous bone is typically +400 HU, and cranial bone can reach 2,000 HU. The attenuation of metallic implants depends on the atomic number of the element used: Titanium usually has an amount of +1000 HU, iron steel can completely block the X-ray and is, therefore, responsible for well-known line-artifacts in computed tomograms. Artifacts are caused by abrupt transitions between low- and high-density materials, which results in data values that exceed the dynamic range of the processing electronics.
Windowing
CT data sets have a very high
dynamic range
Dynamic range (abbreviated DR, DNR, or DYR) is the ratio between the largest and smallest values that a certain quantity can assume. It is often used in the context of signals, like sound and light. It is measured either as a ratio or as a base-1 ...
which must be reduced for display or printing. This is typically done via a process of "windowing", which maps a range (the "window") of pixel values to a grayscale ramp. For example, CT images of the brain are commonly viewed with a window extending from 0 HU to 80 HU. Pixel values of 0 and lower, are displayed as black; values of 80 and higher are displayed as white; values within the window are displayed as a gray intensity proportional to position within the window. The window used for display must be matched to the X-ray density of the object of interest, in order to optimize the visible detail. Window width and window level parameters are used to control the windowing of a scan.
Multiplanar reconstruction and projections

Multiplanar reconstruction (MPR) is the process of converting data from one
anatomical plane
An anatomical plane is a hypothetical plane used to transect the body, in order to describe the location of structures or the direction of movements. In human and animal anatomy, three principal planes are used:
* The sagittal plane or lateral ...
(usually
transverse
Transverse may refer to:
*Transverse engine, an engine in which the crankshaft is oriented side-to-side relative to the wheels of the vehicle
*Transverse flute, a flute that is held horizontally
* Transverse force (or ''Euler force''), the tangen ...
) to other planes. It can be used for thin slices as well as projections. Multiplanar reconstruction is possible as present CT scanners provide almost
isotropic
Isotropy is uniformity in all orientations; it is derived . Precise definitions depend on the subject area. Exceptions, or inequalities, are frequently indicated by the prefix ' or ', hence ''anisotropy''. ''Anisotropy'' is also used to describe ...
resolution.
MPR is used almost in every scan. The spine is frequently examined with it. An image of the spine in axial plane can only show one vertebral bone at a time and cannot show its relation with other vertebral bones. By reformatting the data in other planes, visualization of the relative position can be achieved in sagittal and coronal plane.
New software allows the reconstruction of data in non-orthogonal (oblique) planes, which help in the visualization of organs which are not in orthogonal planes. It is better suited for visualization of the anatomical structure of the bronchi as they do not lie orthogonal to the direction of the scan.
Curved-plane reconstruction (or curved planar reformation = CPR) is performed mainly for the evaluation of vessels. This type of reconstruction helps to straighten the bends in a vessel, thereby helping to visualize a whole vessel in a single image or in multiple images. After a vessel has been "straightened", measurements such as cross-sectional area and length can be made. This is helpful in preoperative assessment of a surgical procedure.
For 2D projections used in
radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radia ...
for quality assurance and planning of
external beam radiotherapy
External beam radiotherapy (EBRT) is the most common form of radiotherapy (radiation therapy). The patient sits or lies on a couch and an external source of ionizing radiation is pointed at a particular part of the body. In contrast to brachyt ...
, including digitally reconstructed radiographs, see
Beam's eye view Beam's eye view (abbreviated BEV) is an imaging technique used in radiation therapy for quality assurance and planning of external beam radiotherapy (EBRT). These are primarily used to ensure that the relative orientation of the patient and the trea ...
.
Volume rendering

A threshold value of radiodensity is set by the operator (e.g., a level that corresponds to bone). With the help of
edge detection
Edge detection includes a variety of mathematical methods that aim at identifying edges, curves in a digital image at which the image brightness changes sharply or, more formally, has discontinuities. The same problem of finding discontinuitie ...
image processing algorithms a 3D model can be constructed from the initial data and displayed on screen. Various thresholds can be used to get multiple models, each anatomical component such as muscle, bone and cartilage can be differentiated on the basis of different colours given to them. However, this mode of operation cannot show interior structures.
Surface rendering is limited technique as it displays only the surfaces that meet a particular threshold density, and which are towards the viewer. However, In volume rendering, transparency, colours and
shading
Shading refers to the depiction of depth perception in 3D models (within the field of 3D computer graphics) or illustrations (in visual art) by varying the level of darkness. Shading tries to approximate local behavior of light on the object's ...
are used which makes it easy to present a volume in a single image. For example, Pelvic bones could be displayed as semi-transparent, so that, even viewing at an oblique angle one part of the image does not hide another.
Image quality

Dose versus image quality
An important issue within radiology today is how to reduce the radiation dose during CT examinations without compromising the image quality. In general, higher radiation doses result in higher-resolution images,
while lower doses lead to increased image noise and unsharp images. However, increased dosage raises the adverse side effects, including the risk of
radiation-induced cancer
Exposure to ionizing radiation is known to increase the future incidence of cancer, particularly leukemia. The mechanism by which this occurs is well understood, but quantitative models predicting the level of risk remain controversial. The most wi ...
ŌĆō a four-phase abdominal CT gives the same radiation dose as 300 chest X-rays. Several methods that can reduce the exposure to ionizing radiation during a CT scan exist.
[Barkan, O; Weill, J; Averbuch, A; Dekel, S]
"Adaptive Compressed Tomography Sensing"
. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2013 (pp. 2195ŌĆō2202).
# New software technology can significantly reduce the required radiation dose. New
iterative
Iteration is the repetition of a process in order to generate a (possibly unbounded) sequence of outcomes. Each repetition of the process is a single iteration, and the outcome of each iteration is then the starting point of the next iteration. ...
tomographic reconstruction
Tomographic reconstruction is a type of multidimensional inverse problem where the challenge is to yield an estimate of a specific system from a finite number of projections. The mathematical basis for tomographic imaging was laid down by Johann ...
algorithms (''e.g.'',
iterative Sparse Asymptotic Minimum Variance) could offer
super-resolution
Super-resolution imaging (SR) is a class of techniques that enhance (increase) the resolution of an imaging system. In optical SR the diffraction limit of systems is transcended, while in geometrical SR the resolution of digital imaging sensors i ...
without requiring higher radiation dose.
# Individualize the examination and adjust the radiation dose to the body type and body organ examined. Different body types and organs require different amounts of radiation.
# Higher resolution is not always suitable, such as detection of small pulmonary masses.
Artifacts
Although images produced by CT are generally faithful representations of the scanned volume, the technique is susceptible to a number of
artifacts, such as the following:
;: Streaks are often seen around materials that block most X-rays, such as metal or bone. Numerous factors contribute to these streaks: under sampling, photon starvation, motion, beam hardening, and
Compton scatter
Compton scattering, discovered by Arthur Holly Compton, is the scattering of a high frequency photon after an interaction with a charged particle, usually an electron. If it results in a decrease in energy (increase in wavelength) of the photon ...
. This type of artifact commonly occurs in the posterior fossa of the brain, or if there are metal implants. The streaks can be reduced using newer reconstruction techniques.
Approaches such as metal artifact reduction (MAR) can also reduce this artifact.
MAR techniques include spectral imaging, where CT images are taken with
photons
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they alway ...
of different energy levels, and then synthesized into
monochromatic
A monochrome or monochromatic image, object or color scheme, palette is composed of one color (or lightness, values of one color). Images using only Tint, shade and tone, shades of grey are called grayscale (typically digital) or Black and wh ...
images with special software such as GSI (Gemstone Spectral Imaging).
;Partial volume effect: This appears as "blurring" of edges. It is due to the scanner being unable to differentiate between a small amount of high-density material (e.g., bone) and a larger amount of lower density (e.g., cartilage). The reconstruction assumes that the X-ray attenuation within each voxel is homogeneous; this may not be the case at sharp edges. This is most commonly seen in the z-direction (craniocaudal direction), due to the conventional use of highly
anisotropic
Anisotropy () is the property of a material which allows it to change or assume different properties in different directions, as opposed to isotropy. It can be defined as a difference, when measured along different axes, in a material's physic ...
voxels, which have a much lower out-of-plane resolution, than in-plane resolution. This can be partially overcome by scanning using thinner slices, or an isotropic acquisition on a modern scanner.
;Ring artifact: Probably the most common mechanical artifact, the image of one or many "rings" appears within an image. They are usually caused by the variations in the response from individual elements in a two dimensional X-ray detector due to defect or miscalibration.
Ring artifacts can largely be reduced by intensity normalization, also referred to as flat field correction.
Remaining rings can be suppressed by a transformation to polar space, where they become linear stripes.
A comparative evaluation of ring artefact reduction on X-ray tomography images showed that the method of Sijbers and Postnov can effectively suppress ring artefacts.
;Noise: This appears as grain on the image and is caused by a low signal to noise ratio. This occurs more commonly when a thin slice thickness is used. It can also occur when the power supplied to the X-ray tube is insufficient to penetrate the anatomy.
;Windmill: Streaking appearances can occur when the detectors intersect the reconstruction plane. This can be reduced with filters or a reduction in pitch.
;Beam hardening: This can give a "cupped appearance" when grayscale is visualized as height. It occurs because conventional sources, like X-ray tubes emit a polychromatic spectrum. Photons of higher
photon energy
Photon energy is the energy carried by a single photon. The amount of energy is directly proportional to the photon's electromagnetic frequency and thus, equivalently, is inversely proportional to the wavelength. The higher the photon's frequency, ...
levels are typically attenuated less. Because of this, the mean energy of the spectrum increases when passing the object, often described as getting "harder". This leads to an effect increasingly underestimating material thickness, if not corrected. Many algorithms exist to correct for this artifact. They can be divided into mono- and multi-material methods.
Advantages
CT scanning has several advantages over traditional
two-dimensional
In mathematics, a plane is a Euclidean (flat), two-dimensional surface that extends indefinitely. A plane is the two-dimensional analogue of a point (zero dimensions), a line (one dimension) and three-dimensional space. Planes can arise as s ...
medical
radiography
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeut ...
. First, CT eliminates the superimposition of images of structures outside the area of interest. Second, CT scans have greater
image resolution
Image resolution is the detail an image holds. The term applies to digital images, film images, and other types of images. "Higher resolution" means more image detail.
Image resolution can be measured in various ways. Resolution quantifies how ...
, enabling examination of finer details. CT can distinguish between
tissues that differ in radiographic
density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''Žü'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematical ...
by 1% or less. Third, CT scanning enables multiplanar reformatted imaging: scan data can be visualized in the
transverse (or axial),
coronal, or
sagittal
The sagittal plane (; also known as the longitudinal plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into right and left sections. It is perpendicular to the transverse and coronal planes. The plane may be in the center of the body and divid ...
plane, depending on the diagnostic task.
The improved resolution of CT has permitted the development of new investigations. For example, CT
angiography
Angiography or arteriography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is performe ...
avoids the invasive insertion of a
catheter
In medicine, a catheter (/╦łk├”╬Ė╔Öt╔Ör/) is a thin tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. Cath ...
. CT scanning can perform a
virtual colonoscopy
Virtual colonoscopy (VC, also called CT colonography or CT pneumocolon) is the use of CT scanning or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to produce two- and three-dimensional images of the colon (large intestine), from the lowest part, the rectum, ...
with greater accuracy and less discomfort for the patient than a traditional
colonoscopy
Colonoscopy () or coloscopy () is the endoscopic examination of the large bowel and the distal part of the small bowel with a CCD camera or a fiber optic camera on a flexible tube passed through the anus. It can provide a visual diagnosis (''e. ...
.
Virtual colonography is far more accurate than a
barium enema
A lower gastrointestinal series is a medical procedure used to examine and diagnose problems with the human colon of the large intestine. Radiographs (X-ray pictures) are taken while barium sulfate, a radiocontrast agent, fills the colon via an ...
for detection of tumors and uses a lower radiation dose.
CT is a moderate-to-high
radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'', such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visi ...
diagnostic technique. The radiation dose for a particular examination depends on multiple factors: volume scanned, patient build, number and type of scan protocol, and desired resolution and image quality. Two helical CT scanning parameters, tube current and pitch, can be adjusted easily and have a profound effect on radiation. CT scanning is more accurate than two-dimensional radiographs in evaluating anterior interbody fusion, although they may still over-read the extent of fusion.
Adverse effects
Cancer
The
radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'', such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visi ...
used in CT scans can damage body cells, including
DNA molecules, which can lead to
radiation-induced cancer
Exposure to ionizing radiation is known to increase the future incidence of cancer, particularly leukemia. The mechanism by which this occurs is well understood, but quantitative models predicting the level of risk remain controversial. The most wi ...
.
The radiation doses received from CT scans is variable. Compared to the lowest dose X-ray techniques, CT scans can have 100 to 1,000 times higher dose than conventional X-rays.
[Redberg, Rita F., and Smith-Bindman, Rebecca]
"We Are Giving Ourselves Cancer"
, ''New York Times'', January 30, 2014 However, a lumbar spine X-ray has a similar dose as a head CT. Articles in the media often exaggerate the relative dose of CT by comparing the lowest-dose X-ray techniques (chest X-ray) with the highest-dose CT techniques. In general, a routine abdominal CT has a radiation dose similar to three years of average
background radiation
Background radiation is a measure of the level of ionizing radiation present in the environment at a particular location which is not due to deliberate introduction of radiation sources.
Background radiation originates from a variety of sources ...
.
Large scale population-based studies have consistently demonstrated that low dose radiation from CT scans has impacts on cancer incidence in a variety of cancers.
For example, in a large population-based cohort it was found that up to 4% of brain cancers were caused by CT scan radiation.
Some experts project that in the future, between three and five percent of all cancers would result from medical imaging.
An Australian study of 10.9 million people reported that the increased incidence of cancer after CT scan exposure in this cohort was mostly due to irradiation. In this group, one in every 1,800 CT scans was followed by an excess cancer. If the lifetime risk of developing cancer is 40% then the absolute risk rises to 40.05% after a CT. The risks of CT scan radiation are especially important in patients undergoing recurrent CT scans within a short time span of one to five years.
Some experts note that CT scans are known to be "overused," and "there is distressingly little evidence of better health outcomes associated with the current high rate of scans."
On the other hand, a recent paper analyzing the data of patients who received high
cumulative dose
Cumulative dose is the total dose resulting from repeated exposures of ionizing radiation to an occupationally exposed worker to the same portion of the body, or to the whole body, over a period of time.
In medicine, the total amount of a drug or ...
s showed a high degree of appropriate use.
This creates an important issue of cancer risk to these patients. Moreover, a highly significant finding that was previously unreported is that some patients received >100 mSv dose from CT scans in a single day,
which counteracts existing criticisms some investigators may have on the effects of protracted versus acute exposure.
There are contrarian views and the debate is ongoing. Some studies have shown that publications indicating an increased risk of cancer from typical doses of body CT scans are plagued with serious methodological limitations and several highly improbable results, concluding that no evidence indicates such low doses cause any long-term harm.
One study estimated that as many as 0.4% of cancers in the United States resulted from CT scans, and that this may have increased to as much as 1.5 to 2% based on the rate of CT use in 2007.
Others dispute this estimate, as there is no consensus that the low levels of radiation used in CT scans cause damage. Lower radiation doses are used in many cases, such as in the investigation of renal colic.
A person's age plays a significant role in the subsequent risk of cancer.
Estimated lifetime cancer mortality risks from an abdominal CT of a one-year-old is 0.1%, or 1:1000 scans.
The risk for someone who is 40 years old is half that of someone who is 20 years old with substantially less risk in the elderly.
The
International Commission on Radiological Protection
The International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) is an independent, international, non-governmental organization, with the mission to protect people, animals, and the environment from the harmful effects of ionising radiation. Its r ...
estimates that the risk to a fetus being exposed to 10
mGy
The gray (symbol: Gy) is the unit of ionizing radiation dose in the International System of Units (SI), defined as the absorption of one joule of radiation energy per kilogram of matter.
It is used as a unit of the radiation quantity absorbed do ...
(a unit of radiation exposure) increases the rate of cancer before 20 years of age from 0.03% to 0.04% (for reference a CT pulmonary angiogram exposes a fetus to 4 mGy).
A 2012 review did not find an association between medical radiation and cancer risk in children noting however the existence of limitations in the evidences over which the review is based. CT scans can be performed with different settings for lower exposure in children with most manufacturers of CT scans as of 2007 having this function built in.
Furthermore, certain conditions can require children to be exposed to multiple CT scans.
Current recommendations are to inform patients of the risks of CT scanning.
However, employees of imaging centers tend not to communicate such risks unless patients ask.
Contrast reactions
In the United States half of CT scans are
contrast CT
Contrast CT, or contrast enhanced computed tomography (CECT), is X-ray computed tomography (CT) using radiocontrast. Radiocontrasts for X-ray CT are generally iodine-based types. This is useful to highlight structures such as blood vessels that ...
s using intravenously injected
radiocontrast agent
Radiocontrast agents are substances used to enhance the visibility of internal structures in X-ray-based imaging techniques such as computed tomography (contrast CT), projectional radiography, and fluoroscopy. Radiocontrast agents are typically io ...
s.
The most common reactions from these agents are mild, including nausea, vomiting, and an itching rash. Severe life-threatening reactions may rarely occur.
Overall reactions occur in 1 to 3% with
nonionic contrast and 4 to 12% of people with
ionic contrast.
Skin rashes may appear within a week to 3% of people.
The old
radiocontrast agent
Radiocontrast agents are substances used to enhance the visibility of internal structures in X-ray-based imaging techniques such as computed tomography (contrast CT), projectional radiography, and fluoroscopy. Radiocontrast agents are typically io ...
s caused
anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a serious, potentially fatal allergic reaction and medical emergency that is rapid in onset and requires immediate medical attention regardless of use of emergency medication on site. It typically causes more than one of the follow ...
in 1% of cases while the newer, low-osmolar agents cause reactions in 0.01ŌĆō0.04% of cases.
Death occurs in about 2 to 30 people per 1,000,000 administrations, with newer agents being safer.
There is a higher risk of mortality in those who are female, elderly or in poor health, usually secondary to either anaphylaxis or
acute kidney injury
Acute kidney injury (AKI), previously called acute renal failure (ARF), is a sudden decrease in kidney function that develops within 7 days, as shown by an increase in serum creatinine or a decrease in urine output, or both.
Causes of AKI are cla ...
.
The contrast agent may induce
contrast-induced nephropathy
Contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) is a purported form of kidney damage in which there has been recent exposure to medical imaging contrast material without another clear cause for the acute kidney injury.
Despite extensive speculation, the actua ...
.
This occurs in 2 to 7% of people who receive these agents, with greater risk in those who have preexisting
kidney failure
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as eit ...
,
preexisting
diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
, or reduced intravascular volume. People with mild kidney impairment are usually advised to ensure full hydration for several hours before and after the injection. For moderate kidney failure, the use of
iodinated contrast
Iodinated contrast is a form of intravenous radiocontrast agent containing iodine, which enhances the visibility of vascular structures and organs during radiographic procedures. Some pathologies, such as cancer, have particularly improved visibil ...
should be avoided; this may mean using an alternative technique instead of CT. Those with severe
kidney failure
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as eit ...
requiring
dialysis Dialysis may refer to:
*Dialysis (chemistry), a process of separating molecules in solution
**Electrodialysis, used to transport salt ions from one solution to another through an ion-exchange membrane under the influence of an applied electric pote ...
require less strict precautions, as their kidneys have so little function remaining that any further damage would not be noticeable and the dialysis will remove the contrast agent; it is normally recommended, however, to arrange dialysis as soon as possible following contrast administration to minimize any adverse effects of the contrast.
In addition to the use of intravenous contrast, orally administered contrast agents are frequently used when examining the abdomen. These are frequently the same as the intravenous contrast agents, merely diluted to approximately 10% of the concentration. However, oral alternatives to iodinated contrast exist, such as very dilute (0.5ŌĆō1% w/v)
barium sulfate
Barium sulfate (or sulphate) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ba SO4. It is a white crystalline solid that is odorless and insoluble in water. It occurs as the mineral barite, which is the main commercial source of barium an ...
suspensions. Dilute barium sulfate has the advantage that it does not cause allergic-type reactions or kidney failure, but cannot be used in patients with suspected bowel perforation or suspected bowel injury, as leakage of barium sulfate from damaged bowel can cause fatal
peritonitis
Peritonitis is inflammation of the localized or generalized peritoneum, the lining of the inner wall of the abdomen and cover of the abdominal organs. Symptoms may include severe pain, swelling of the abdomen, fever, or weight loss. One part or ...
.
Side effects from
contrast agent
A contrast agent (or contrast medium) is a substance used to increase the contrast of structures or fluids within the body in medical imaging. Contrast agents absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound, which is different from radiop ...
s, administered
intravenously
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrie ...
in some CT scans, might impair
kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood ...
performance in patients with
kidney disease
Kidney disease, or renal disease, technically referred to as nephropathy, is damage to or disease of a kidney. Nephritis is an inflammatory kidney disease and has several types according to the location of the inflammation. Inflammation can ...
, although this risk is now believed to be lower than previously thought.
Scan dose
The table reports average radiation exposures; however, there can be a wide variation in radiation doses between similar scan types, where the highest dose could be as much as 22 times higher than the lowest dose.
A typical plain film X-ray involves radiation dose of 0.01 to 0.15 mGy, while a typical CT can involve 10ŌĆō20 mGy for specific organs, and can go up to 80 mGy for certain specialized CT scans.
For purposes of comparison, the world average dose rate from naturally occurring sources of
background radiation
Background radiation is a measure of the level of ionizing radiation present in the environment at a particular location which is not due to deliberate introduction of radiation sources.
Background radiation originates from a variety of sources ...
is 2.4
mSv
mSv or MSV may refer to:
* Maize streak virus, a plant disease
* Medium-speed vehicle, US category
* Medium Systems Vehicle, a class of fictional artificially intelligent starship in The Culture universe of late Scottish author Iain Banks
* Mill ...
per year, equal for practical purposes in this application to 2.4 mGy per year.
While there is some variation, most people (99%) received less than 7 mSv per year as background radiation. Medical imaging as of 2007 accounted for half of the radiation exposure of those in the United States with CT scans making up two thirds of this amount.
In the United Kingdom it accounts for 15% of radiation exposure.
The average radiation dose from medical sources is Ōēł0.6 mSv per person globally as of 2007.
Those in the nuclear industry in the United States are limited to doses of 50 mSv a year and 100 mSv every 5 years.
Lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
is the main material used by radiography personnel for
shielding against scattered X-rays.
Radiation dose units
The radiation dose reported in the
gray or mGy unit is proportional to the amount of energy that the irradiated body part is expected to absorb, and the physical effect (such as DNA
double strand breaks
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA da ...
) on the cells' chemical bonds by X-ray radiation is proportional to that energy.
The
sievert
The sievert (symbol: SvNot be confused with the sverdrup or the svedberg, two non-SI units that sometimes use the same symbol.) is a unit in the International System of Units (SI) intended to represent the stochastic health risk of ionizing radi ...
unit is used in the report of the
effective dose. The sievert unit, in the context of CT scans, does not correspond to the actual radiation dose that the scanned body part absorbs but to another radiation dose of another scenario, the whole body absorbing the other radiation dose and the other radiation dose being of a magnitude, estimated to have the same probability to induce cancer as the CT scan. Thus, as is shown in the table above, the actual radiation that is absorbed by a scanned body part is often much larger than the effective dose suggests. A specific measure, termed the
computed tomography dose index (CTDI), is commonly used as an estimate of the radiation absorbed dose for tissue within the scan region, and is automatically computed by medical CT scanners.
The
equivalent dose
Equivalent dose is a dose quantity '' H '' representing the stochastic health effects of low levels of ionizing radiation on the human body which represents the probability of radiation-induced cancer and genetic damage. It is derived from the ...
is the effective dose of a case, in which the whole body would actually absorb the same radiation dose, and the sievert unit is used in its report. In the case of non-uniform radiation, or radiation given to only part of the body, which is common for CT examinations, using the local equivalent dose alone would overstate the biological risks to the entire organism.
Effects of radiation
Most adverse health effects of radiation exposure may be grouped in two general categories:
*deterministic effects (harmful tissue reactions) due in large part to the killing/malfunction of cells following high doses;
*stochastic effects, i.e., cancer and heritable effects involving either cancer development in exposed individuals owing to mutation of somatic cells or heritable disease in their offspring owing to mutation of reproductive (germ) cells.
The added lifetime risk of developing cancer by a single abdominal CT of 8 mSv is estimated to be 0.05%, or 1 one in 2,000.
Because of increased susceptibility of fetuses to radiation exposure, the radiation dosage of a CT scan is an important consideration in the choice of
medical imaging in pregnancy
Medical imaging in pregnancy may be indicated because of pregnancy complications, intercurrent diseases or routine prenatal care.
Options
Options for medical imaging in pregnancy include the following:
*Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) without ...
.
Excess doses
In October, 2009, the US
Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respon ...
(FDA) initiated an investigation of brain perfusion CT (PCT) scans, based on
radiation burn
A radiation burn is a damage to the skin or other biological tissue and organs as an effect of radiation. The radiation types of greatest concern are thermal radiation, radio frequency energy, ultraviolet light and ionizing radiation.
The most ...
s caused by incorrect settings at one particular facility for this particular type of CT scan. Over 200 patients were exposed to radiation at approximately eight times the expected dose for an 18-month period; over 40% of them lost patches of hair. This event prompted a call for increased CT quality assurance programs. It was noted that "while unnecessary radiation exposure should be avoided, a medically needed CT scan obtained with appropriate acquisition parameter has benefits that outweigh the radiation risks."
Similar problems have been reported at other centers.
These incidents are believed to be due to
human error
Human error refers to something having been done that was " not intended by the actor; not desired by a set of rules or an external observer; or that led the task or system outside its acceptable limits".Senders, J.W. and Moray, N.P. (1991) Human ...
.
Procedure
CT scan procedure varies according to the type of the study and the organ being imaged. The patient is made to lie on the CT table and the centering of the table is done according to the body part. The IV line is established in case of contrast-enhanced CT. After selecting proper and rate of contrast from the pressure injector, the scout is taken to localize and plan the scan. Once the plan is selected, the contrast is given. The raw data is processed according to the study and proper windowing is done to make scans easy to diagnose.
Preparation
Patient preparation may vary according to the type of scan. The general patient preparation includes.
# Signing the
informed consent
Informed consent is a principle in medical ethics and medical law, that a patient must have sufficient information and understanding before making decisions about their medical care. Pertinent information may include risks and benefits of treatme ...
.
# Removal of metallic objects and jewelry from the region of interest.
# Changing to the hospital gown according to hospital protocol.
#
Checking of kidney function, especially
creatinine
Creatinine (; ) is a breakdown product of creatine phosphate from muscle and protein metabolism. It is released at a constant rate by the body (depending on muscle mass).
Biological relevance
Serum creatinine (a blood measurement) is an import ...
and
urea
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two amino groups (ŌĆō) joined by a carbonyl functional group (ŌĆōC(=O)ŌĆō). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid.
Urea serves an important r ...
levels (in case of
CECT
CECT is one of the many brands of cellular phones manufactured in China. CECT offers unauthorized clones or replicas of the Apple Inc. iPhone and various Nokia cell phones manufactured in China and sold at a fraction of the price of the origi ...
).
Mechanism
Computed tomography operates by using an
X-ray generator
An X-ray generator is a device that produces X-rays. Together with an X-ray detector, it is commonly used in a variety of applications including medicine, X-ray fluorescence, electronic assembly inspection, and measurement of material thickness ...
that rotates around the object;
X-ray detector
X-ray detectors are devices used to measure the flux, spatial distribution, spectrum, and/or other properties of X-rays.
Detectors can be divided into two major categories: imaging detectors (such as photographic plates and X-ray film (photograp ...
s are positioned on the opposite side of the circle from the X-ray source. As the X-rays pass through the patient, they are attenuated differently by various tissues according to the tissue density. A visual representation of the raw data obtained is called a sinogram, yet it is not sufficient for interpretation. Once the scan data has been acquired, the data must be processed using a form of
tomographic reconstruction
Tomographic reconstruction is a type of multidimensional inverse problem where the challenge is to yield an estimate of a specific system from a finite number of projections. The mathematical basis for tomographic imaging was laid down by Johann ...
, which produces a series of cross-sectional images. These cross-sectional images are made up of small units of pixels or voxels.
Pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device.
In most digital display devices, pixels are the smal ...
s in an image obtained by CT scanning are displayed in terms of relative
radiodensity
Radiodensity (or radiopacity) is opacity to the radio wave and X-ray portion of the electromagnetic spectrum: that is, the relative inability of those kinds of electromagnetic radiation to pass through a particular material. Radiolucency or hypod ...
. The pixel itself is displayed according to the mean
attenuation
In physics, attenuation (in some contexts, extinction) is the gradual loss of flux intensity through a medium. For instance, dark glasses attenuate sunlight, lead attenuates X-rays, and water and air attenuate both light and sound at variable att ...
of the tissue(s) that it corresponds to on a scale from +3,071 (most attenuating) to ŌłÆ1,024 (least attenuating) on the
Hounsfield scale The Hounsfield scale , named after Sir Godfrey Hounsfield, is a quantitative scale for describing radiodensity. It is frequently used in CT scans, where its value is also termed CT number.
Definition
The Hounsfield unit (HU) scale is a linear tran ...
. A
pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device.
In most digital display devices, pixels are the smal ...
is a two dimensional unit based on the matrix size and the field of view. When the CT slice thickness is also factored in, the unit is known as a
voxel
In 3D computer graphics, a voxel represents a value on a regular grid in three-dimensional space. As with pixels in a 2D bitmap, voxels themselves do not typically have their position (i.e. coordinates) explicitly encoded with their values. Ins ...
, which is a three-dimensional unit.
Water has an attenuation of 0
Hounsfield units The Hounsfield scale , named after Sir Godfrey Hounsfield, is a quantitative scale for describing radiodensity. It is frequently used in CT scans, where its value is also termed CT number.
Definition
The Hounsfield unit (HU) scale is a linear tran ...
(HU), while air is ŌłÆ1,000 HU, cancellous bone is typically +400 HU, and cranial bone can reach 2,000 HU or more (os temporale) and can cause
artifacts. The attenuation of metallic implants depends on the atomic number of the element used: Titanium usually has an amount of +1000 HU, iron steel can completely extinguish the X-ray and is, therefore, responsible for well-known line-artifacts in computed tomograms. Artifacts are caused by abrupt transitions between low- and high-density materials, which results in data values that exceed the dynamic range of the processing electronics. Two-dimensional CT images are conventionally rendered so that the view is as though looking up at it from the patient's feet.
[Computerized Tomography chapter](_blank)
at University of Connecticut Health Center
UConn Health (formerly known as the UConn Health Center) is the branch of the University of Connecticut that oversees clinical care, advanced biomedical research, and academic education in medicine. The main branch is located in Farmington, Connect ...
. Hence, the left side of the image is to the patient's right and vice versa, while anterior in the image also is the patient's anterior and vice versa. This left-right interchange corresponds to the view that physicians generally have in reality when positioned in front of patients.
Initially, the images generated in CT scans were in the
transverse
Transverse may refer to:
*Transverse engine, an engine in which the crankshaft is oriented side-to-side relative to the wheels of the vehicle
*Transverse flute, a flute that is held horizontally
* Transverse force (or ''Euler force''), the tangen ...
(axial)
anatomical plane
An anatomical plane is a hypothetical plane used to transect the body, in order to describe the location of structures or the direction of movements. In human and animal anatomy, three principal planes are used:
* The sagittal plane or lateral ...
, perpendicular to the long axis of the body. Modern scanners allow the scan data to be reformatted as images in other
planes.
Digital geometry processing can generate a
three-dimensional
Three-dimensional space (also: 3D space, 3-space or, rarely, tri-dimensional space) is a geometric setting in which three values (called ''parameters'') are required to determine the position of an element (i.e., point). This is the informal ...
image of an object inside the body from a series of two-dimensional
radiographic
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeut ...
images taken by
rotation around a fixed axis
Rotation around a fixed axis is a special case of rotational motion. The fixed-axis hypothesis excludes the possibility of an axis changing its orientation and cannot describe such phenomena as wobbling or precession. According to Euler's rota ...
.
These cross-sectional images are widely used for medical
diagnosis
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " cause and effect". In systems engin ...
and
therapy
A therapy or medical treatment (often abbreviated tx, Tx, or Tx) is the attempted remediation of a health problem, usually following a medical diagnosis.
As a rule, each therapy has indications and contraindications. There are many different ...
.
Contrast
Contrast media
A contrast agent (or contrast medium) is a substance used to increase the contrast of structures or fluids within the body in medical imaging. Contrast agents absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound, which is different from radio ...
used for X-ray CT, as well as for
plain film X-ray, are called
radiocontrast
Radiocontrast agents are substances used to enhance the visibility of internal structures in X-ray-based imaging techniques such as computed tomography (contrast CT), projectional radiography, and fluoroscopy. Radiocontrast agents are typically io ...
s. Radiocontrasts for CT are, in general, iodine-based. This is useful to highlight structures such as blood vessels that otherwise would be difficult to delineate from their surroundings. Using contrast material can also help to obtain functional information about tissues. Often, images are taken both with and without radiocontrast.
History
The history of X-ray computed tomography goes back to at least 1917 with the mathematical theory of the
Radon transform
In mathematics, the Radon transform is the integral transform which takes a function ''f'' defined on the plane to a function ''Rf'' defined on the (two-dimensional) space of lines in the plane, whose value at a particular line is equal to the l ...
.
In October 1963,
William H. Oldendorf
William Henry Oldendorf (March 27, 1925 ŌĆō December 14, 1992) was an American neurologist, physician, researcher, medical pioneer, founding member of the American Society for Neuroimaging (ASN), and originator of the technique of computed tomog ...
received a U.S. patent for a "radiant energy apparatus for investigating selected areas of interior objects obscured by dense material".
The first commercially viable CT scanner was invented by
Godfrey Hounsfield
Sir Godfrey Newbold Hounsfield (28 August 1919 ŌĆō 12 August 2004) was an English electrical engineer who shared the 1979 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine with Allan MacLeod Cormack for his part in developing the diagnostic technique of X ...
in 1972.
It is often claimed that revenues from the sales of The Beatles' records in the 1960s helped fund the development of the first CT scanner at EMI. The first production X-ray CT machines were in fact called EMI scanners.
Etymology
The word ''tomography'' is derived from the
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
'slice' and 'to write'. Computed tomography was originally known as the "EMI scan" as it was developed in the early 1970s at a research branch of
EMI
EMI Group Limited (originally an initialism for Electric and Musical Industries, also referred to as EMI Records Ltd. or simply EMI) was a British transnational conglomerate founded in March 1931 in London. At the time of its break-up in 201 ...
, a company best known today for its music and recording business. It was later known as ''computed axial tomography'' (''CAT'' or ''CT scan'') and ''body section r├Čntgenography''.
The term ''CAT scan'' is no longer in technical use because current CT scans enable for multiplanar reconstructions. This makes ''CT scan'' the most appropriate term, which is used by
radiologist
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiatio ...
s in common vernacular as well as in textbooks and scientific papers.
In
Medical Subject Headings
Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) is a comprehensive controlled vocabulary for the purpose of indexing journal articles and books in the life sciences. It serves as a thesaurus that facilitates searching. Created and updated by the United States N ...
(MeSH), ''computed axial tomography'' was used from 1977 to 1979, but the current indexing explicitly includes ''X-ray'' in the title.
The term
''sinogram'' was introduced by Paul Edholm and Bertil Jacobson in 1975.
Society and culture
Campaigns
In response to increased concern by the public and the ongoing progress of best practices, the Alliance for Radiation Safety in Pediatric Imaging was formed within the
Society for Pediatric Radiology. In concert with the
American Society of Radiologic Technologists
The American Society of Radiologic Technologists (ASRT), located in Albuquerque, New Mexico, is a professional membership association for medical imaging technologists, radiation therapists, and radiologic science students.
ASRT members may spec ...
, the
American College of Radiology The American College of Radiology (ACR), founded in 1923, is a professional medical society representing nearly 40,000 diagnostic radiologists, radiation oncologists, interventional radiologists, nuclear medicine physicians and medical physicists.
...
and the
American Association of Physicists in Medicine
The American Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM) is a scientific, educational, and professional organization of Medical Physicists. In 2011, it absorbed the American College of Medical Physics
Their headquarters are located at 1631 Princ ...
, the Society for Pediatric Radiology developed and launched the Image Gently Campaign which is designed to maintain high-quality imaging studies while using the lowest doses and best radiation safety practices available on pediatric patients. This initiative has been endorsed and applied by a growing list of various professional medical organizations around the world and has received support and assistance from companies that manufacture equipment used in Radiology.
Following upon the success of the ''Image Gently'' campaign, the American College of Radiology, the Radiological Society of North America, the American Association of Physicists in Medicine and the American Society of Radiologic Technologists have launched a similar campaign to address this issue in the adult population called ''Image Wisely''.
The
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
and
International Atomic Energy Agency
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was established in 1957 ...
(IAEA) of the United Nations have also been working in this area and have ongoing projects designed to broaden best practices and lower patient radiation dose.
Prevalence
Use of CT has increased dramatically over the last two decades.
An estimated 72 million scans were performed in the United States in 2007,
accounting for close to half of the total per-capita dose rate from radiologic and nuclear medicine procedures. Of the CT scans, six to eleven percent are done in children,
an increase of seven to eightfold from 1980.
Similar increases have been seen in Europe and Asia.
In Calgary, Canada, 12.1% of people who present to the emergency with an urgent complaint received a CT scan, most commonly either of the head or of the abdomen. The percentage who received CT, however, varied markedly by the
emergency physician
An emergency physician (often called an "ER doctor" in the United States) is a physician who works at an emergency department to care for ill patients. The emergency physician is a specialist in advanced cardiac life support (advanced life suppo ...
who saw them from 1.8% to 25%. In the emergency department in the United States, CT or
MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
imaging is done in 15% of people who present with
injuries
An injury is any physiological damage to living tissue caused by immediate physical stress. An injury can occur intentionally or unintentionally and may be caused by blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, burning, toxic exposure, asphyxiation, or ...
as of 2007 (up from 6% in 1998).
The increased use of CT scans has been the greatest in two fields: screening of adults (screening CT of the lung in smokers, virtual colonoscopy, CT cardiac screening, and whole-body CT in asymptomatic patients) and CT imaging of children. Shortening of the scanning time to around 1 second, eliminating the strict need for the subject to remain still or be sedated, is one of the main reasons for the large increase in the pediatric population (especially for the diagnosis of
appendicitis
Appendicitis is inflammation of the appendix. Symptoms commonly include right lower abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and decreased appetite. However, approximately 40% of people do not have these typical symptoms. Severe complications of a rup ...
).
As of 2007, in the United States a proportion of CT scans are performed unnecessarily.
Some estimates place this number at 30%.
There are a number of reasons for this including: legal concerns, financial incentives, and desire by the public.
For example, some healthy people avidly pay to receive full-body CT scans as
screening
Screening may refer to:
* Screening cultures, a type a medical test that is done to find an infection
* Screening (economics), a strategy of combating adverse selection (includes sorting resumes to select employees)
* Screening (environmental), a ...
. In that case, it is not at all clear that the benefits outweigh the risks and costs. Deciding whether and how to treat
incidentaloma
In medical or research imaging, an incidental imaging finding (also called an incidentaloma) is an unanticipated finding which is not related to the original diagnostic inquiry. As with other types of incidental medical findings, they may represen ...
s is complex, radiation exposure is not negligible, and the money for the scans involves
opportunity cost
In microeconomic theory, the opportunity cost of a particular activity is the value or benefit given up by engaging in that activity, relative to engaging in an alternative activity. More effective it means if you chose one activity (for example ...
.
Manufacturers
Major manufacturers of CT scanning devices and equipment are:
*
GE Healthcare
GE HealthCare is a subsidiary of American multinational conglomerate General Electric incorporated in New York and headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. As of 2017, it is a manufacturer and distributor of diagnostic imaging agents and radiopharma ...
*
Siemens Healthineers
Siemens Healthineers AG (formerly Siemens Healthcare, Siemens Medical Solutions, Siemens Medical Systems) is a German medical device company. It is the parent company for several medical technology companies and is headquartered in Erlangen, Germ ...
*
Canon Medical Systems Corporation (formerly Toshiba Medical Systems)
*
Koninklijke Philips N.V.
Koninklijke Philips N.V. (), commonly shortened to Philips, is a Dutch multinational conglomerate corporation that was founded in Eindhoven in 1891. Since 1997, it has been mostly headquartered in Amsterdam, though the Benelux headquarters is ...
*
Fujifilm Healthcare (formerly Hitachi Medical Systems)
*
Neusoft Medical Systems
*
United Imaging
Research
Photon-counting computed tomography is a CT technique currently under development. Typical CT scanners use energy integrating detectors; photons are measured as a voltage on a capacitor which is proportional to the X-rays detected. However, this technique is susceptible to noise and other factors which can affect the linearity of the voltage to X-ray intensity relationship. Photon counting detectors (PCDs) are still affected by noise but it does not change the measured counts of photons. PCDs have several potential advantages, including improving signal (and contrast) to noise ratios, reducing doses, improving spatial resolution, and through use of several energies, distinguishing multiple contrast agents. PCDs have only recently become feasible in CT scanners due to improvements in detector technologies that can cope with the volume and rate of data required. As of February 2016, photon counting CT is in use at three sites. Some early research has found the dose reduction potential of photon counting CT for breast imaging to be very promising. In view of recent findings of high cumulative doses to patients from recurrent CT scans, there has been a push for scanning technologies and techniques that reduce ionising radiation doses to patients to sub-
milliSievert
The sievert (symbol: SvNot be confused with the sverdrup or the svedberg, two non-SI units that sometimes use the same symbol.) is a unit in the International System of Units (SI) intended to represent the stochastic health risk of ionizing radi ...
(sub-mSv in the literature) levels during the CT scan process, a goal that has been lingering.
See also
*
Barium sulfate suspension
Barium sulfate suspension, often simply called barium, is a contrast agent used during X-rays. Specifically it is used to improve visualization of the gastrointestinal tract (esophagus, stomach, intestines) on plain X-ray or computed tomograph ...
*
Cone beam computed tomography
Cone beam computed tomography (or CBCT, also referred to as C-arm CT, cone beam volume CT, flat panel CT or Digital Volume Tomography (DVT)) is a medical imaging technique consisting of X-ray computed tomography where the X-rays are divergent, fo ...
*
Dosimetry Radiation dosimetry in the fields of health physics and radiation protection is the measurement, calculation and assessment of the ionizing radiation dose absorbed by an object, usually the human body. This applies both internally, due to ingested o ...
*
Tomosynthesis
Tomosynthesis, also digital tomosynthesis (DTS), is a method for performing high-resolution limited-angle tomography at radiation dose levels comparable with projectional radiography. It has been studied for a variety of clinical applications, incl ...
*
Virtopsy
Virtopsy is a virtual alternative to a traditional autopsy, conducted with scanning and imaging technology. The name is a portmanteau of "virtual" and "autopsy" and is a trademark registered to Richard Dirnhofer (de), the former head of the Insti ...
*
X-ray microtomography
X-ray microtomography, like tomography and X-ray computed tomography, uses X-rays to create cross-sections of a physical object that can be used to recreate a virtual model ( 3D model) without destroying the original object. The prefix ''micro-' ...
*
Xenon-enhanced CT scanning
References
External links
Development of CT imagingĆöPPT by David Platten
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Computed Tomography
1972 introductions
Articles containing video clips
Diagnostic medical imaging
Medical tests
Multidimensional signal processing
Radiology
 CT perfusion imaging is a specific form of CT to assess flow through
CT perfusion imaging is a specific form of CT to assess flow through  Positron emission tomographyŌĆōcomputed tomography is a hybrid CT modality which combines, in a single gantry, a
Positron emission tomographyŌĆōcomputed tomography is a hybrid CT modality which combines, in a single gantry, a  CT scanning of the head is typically used to detect
CT scanning of the head is typically used to detect  Multiplanar reconstruction (MPR) is the process of converting data from one
Multiplanar reconstruction (MPR) is the process of converting data from one  A threshold value of radiodensity is set by the operator (e.g., a level that corresponds to bone). With the help of
A threshold value of radiodensity is set by the operator (e.g., a level that corresponds to bone). With the help of