Base Of The Skull on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most inferior area of the
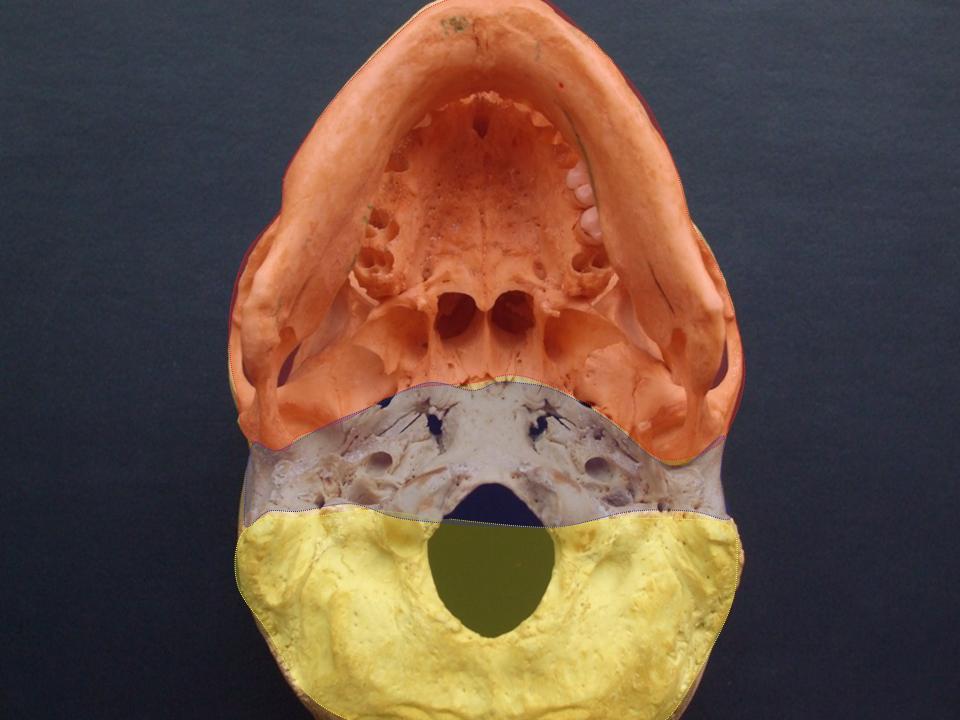
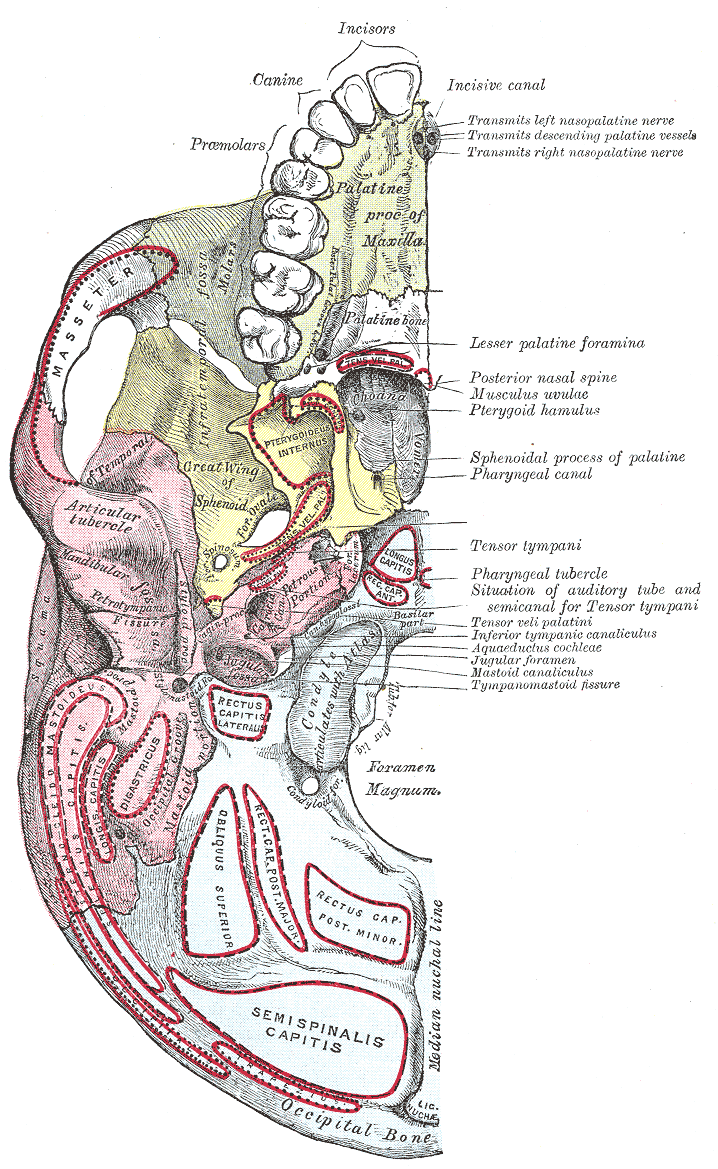 Structures found at the base of the skull are for example:
Structures found at the base of the skull are for example:


 *
*
File:Gray193.png , Base of the skull. Upper surface
File:Schädelbasis1.jpg, Base of skull
File:Base of skull 3.jpg, Base of skull - crista galli, cribriform plate and foramen cecum
File:Base of skull 11.jpg, Base of skull - sella turcica
File:Base of skull 24.jpg, The anterior, middle and posterior cranial fossa in different colors
{{Authority control
Skull
skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, th ...
. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the calvaria.
Structure
 Structures found at the base of the skull are for example:
Structures found at the base of the skull are for example:
Bones
There are five bones that make up the base of the skull: *Ethmoid bone
The ethmoid bone (; from grc, ἡθμός, hēthmós, sieve) is an unpaired bone in the skull that separates the nasal cavity from the brain. It is located at the roof of the nose, between the two orbits. The cubical bone is lightweight due to a ...
* Sphenoid bone
* Occipital bone
*Frontal bone
The frontal bone is a bone in the human skull. The bone consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, pa ...
*Temporal bone
The temporal bones are situated at the sides and base of the skull, and lateral to the temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex.
The temporal bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples, and house the structures of the ears. ...

Sinuses
*Occipital sinus
The occipital sinus is the smallest of the dural venous sinuses. It is usually unpaired, and is sometimes altogether absent. It is situated in the attached margin of the falx cerebelli. It commences near the foramen magnum, and ends by draining in ...
* Superior sagittal sinus
*Superior petrosal sinus
The superior petrosal sinus is one of the dural venous sinuses located beneath the brain. It receives blood from the cavernous sinus and passes backward and laterally to drain into the transverse sinus. The sinus receives superior petrosal veins, ...
Foramina of the skull
This article lists foramina that occur in the human body.
__TOC__
Skull
The human skull has numerous openings (foramina), through which cranial nerves, arteries, veins, and other structures pass. These foramina vary in size and number, with ...
* Foramen cecum
*Optic foramen
The ''optic foramen'' is the opening to the optic canal. The canal is located in the sphenoid bone; it is bounded medially by the body of the sphenoid and laterally by the lesser wing of the sphenoid.
The superior surface of the sphenoid bone is b ...
*Foramen lacerum
The foramen lacerum ( la, lacerated piercing) is a triangular hole in the base of skull. It is located between the sphenoid bone, the apex of the petrous part of the temporal bone, and the basilar part of the occipital bone.
Structure
The foram ...
*Foramen rotundum
The foramen rotundum is a circular hole in the sphenoid bone of the skull. It connects the middle cranial fossa and the pterygopalatine fossa. It allows for the passage of the maxillary nerve (V2), a branch of the trigeminal nerve.
Structure
T ...
* Foramen magnum
* Foramen ovale
*Jugular foramen
A jugular foramen is one of the two (left and right) large foramina (openings) in the base of the skull, located behind the carotid canal. It is formed by the temporal bone and the occipital bone. It allows many structures to pass, including the ...
*Internal auditory meatus
The internal auditory meatus (also meatus acusticus internus, internal acoustic meatus, internal auditory canal, or internal acoustic canal) is a canal within the petrous part of the temporal bone of the skull between the posterior cranial fossa ...
*Mastoid foramen
The mastoid foramen is a hole in the posterior border of the temporal bone. It transmits an emissary vein between the sigmoid sinus and the suboccipital venous plexus, and a small branch of the occipital artery, the posterior meningeal artery to ...
*Sphenoidal emissary foramen
In the base of the skull, in the great wings of the sphenoid bone, medial to the foramen ovale, a small aperture, the sphenoidal emissary foramen, may occasionally be seen (it is often absent) opposite the root of the pterygoid process. When pr ...
*Foramen spinosum
The foramen spinosum is a hole located in the greater wing of the sphenoid. It is located posterolateral to the foramen ovale and anterior to the sphenoidal spine. It allows the passage of the middle meningeal artery, middle meningeal vein and ...


Sutures
*Frontoethmoidal suture
The frontoethmoidal suture is the suture between the ethmoid bone and the frontal bone.
It is located in the anterior cranial fossa
The anterior cranial fossa is a depression in the floor of the cranial base which houses the projecting fronta ...
*Sphenofrontal suture
The sphenofrontal suture is the cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone
The frontal bone is a bone in the human skull. The bone consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamo ...
*Sphenopetrosal suture
The sphenopetrosal fissure (or sphenopetrosal suture) is the cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the petrous portion of the temporal bone.
It is in the middle cranial fossa
The middle cranial fossa, deeper than the anterior cranial fos ...
*Sphenoethmoidal suture
The sphenoethmoidal suture is the cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the ethmoid bone.
It is located in the anterior cranial fossa
The anterior cranial fossa is a depression in the floor of the cranial base which houses the projecting ...
* Petrosquamous suture
*Sphenosquamosal suture
The sphenosquamosal suture is a cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the squama of the temporal bone
The temporal bones are situated at the sides and base of the skull, and lateral to the temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex.
The te ...
Other
Sphenoidal lingula
Along the posterior part of the lateral margin of the carotid groove of the sphenoid bone, in the angle between the body and great wing, is a ridge of bone, called the lingula.
References
External links
*
Bones of the head and neck ...
*Subarcuate fossa
In the temporal bone at the sides of the skull, above and between the aquæductus vestibuli is an irregular depression which lodges a process of the dura mater and transmits a small vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals ...
*Dorsum sellae
The dorsum sellae is part of the sphenoid bone in the skull. Together with the basilar part of the occipital bone it forms the clivus.
In the sphenoid bone, the anterior boundary of the sella turcica is completed by two small eminences, one on ...
*Jugular process
The jugular process is a quadrilateral or triangular bony plate projecting lateralward from the posterior half of the occipital condyle; it is a part of the lateral part of the occipital bone.
The jugular process is excavated in front by the jugu ...
*Petro-occipital fissure
This grooved surface of the foramen magnum is separated on either side from the petrous portion of the temporal bone by the petro-occipital fissure, which is occupied in the fresh state by a plate of cartilage; the fissure is continuous behind wit ...
*Condylar canal
The condylar canal (or condyloid canal) is a canal in the condyloid fossa of the lateral parts of occipital bone behind the occipital condyle. Resection of the rectus capitis posterior major and minor muscles reveals the bony recess leading to t ...
* Jugular tubercle
*Tuberculum sellae
The tuberculum sellae (or the tubercle of the sella turcica) is a part of the sphenoid bone
The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the basilar part of ...
*Carotid groove
The carotid groove is an anatomical groove in the sphenoid bone located above the attachment of each great wing of the sphenoid bone. The groove is curved like the italic letter f, and lodges the internal carotid artery and the cavernous sinus
...
*Fossa hypophyseos
The sella turcica (Latin for 'Turkish saddle') is a saddle-shaped depression in the body of the sphenoid bone of the human skull and of the skulls of other hominids including chimpanzees, gorillas and orangutans. It serves as a cephalome ...
*Posterior clinoid processes
In the sphenoid bone, the anterior boundary of the sella turcica is completed by two small eminences, one on either side, called the anterior clinoid processes, while the posterior boundary is formed by a square-shaped plate of bone, the dorsum s ...
*Sigmoid sulcus
Sigmoid means resembling the lower-case Greek letter sigma (uppercase Σ, lowercase σ, lowercase in word-final position ς) or the Latin letter S. Specific uses include:
* Sigmoid function, a mathematical function
* Sigmoid colon, part of the l ...
*Internal occipital protuberance
Along the internal surface of the occipital bone, at the point of intersection of the four divisions of the cruciform eminence, is the internal occipital protuberance. Running transversely on either side is a groove for the transverse sinus
The ...
*Internal occipital crest
In the occipital bone, the lower division of the cruciate eminence is prominent, and is named the internal occipital crest; it bifurcates near the foramen magnum and gives attachment to the falx cerebelli; in the attached margin of this falx is th ...
*Ethmoidal spine
The superior surface of the body of the sphenoid bone (Fig. 145) presents in front a prominent spine, the ethmoidal spine, for articulation with the cribriform plate of the ethmoid; behind this is a smooth surface slightly raised in the middle lin ...
*Vestibular aqueduct
At the hinder part of the medial wall of the vestibule is the orifice of the vestibular aqueduct, which extends to the posterior surface of the petrous portion of the temporal bone.
It transmits a small vein, and contains a tubular prolongation ...
*Chiasmatic groove
The superior surface of the body of the sphenoid bone is bounded behind by a ridge, which forms the anterior border of a narrow, transverse groove, the chiasmatic groove (optic groove, prechiasmatic sulcus), above and behind which lies the optic c ...
*Middle clinoid process
The anterior boundary of the sella turcica is completed by two small eminences, one on either side, called the middle clinoid processes. It is found lateral to the sella turcica.
Etymology
Clinoid likely comes from the Greek root ''klinein'' or ...
*Groove for sigmoid sinus
Groove for Sigmoid Sinus is a groove in the posterior cranial fossa. It starts at lateral parts of occipital bone, curves around jugular process, and ends at posterior inferior angle of parietal bone. After that, groove for sigmoid sinus continues ...
*Trigeminal ganglion
A trigeminal ganglion (or Gasserian ganglion, or semilunar ganglion, or Gasser's ganglion) is the sensory ganglion at the base of each of the two trigeminal nerves (CN V), occupying a cavity ( Meckel's cave) in the dura mater, covering the trige ...
*Middle cranial fossa
The middle cranial fossa, deeper than the anterior cranial fossa, is narrow medially and widens laterally to the sides of the skull. It is separated from the posterior fossa by the clivus and the petrous crest.
It is bounded in front by the pos ...
*Anterior cranial fossa
The anterior cranial fossa is a depression in the floor of the cranial base which houses the projecting frontal lobes of the brain. It is formed by the orbital plates of the frontal, the cribriform plate of the ethmoid, and the small wings and fr ...
*Middle meningeal artery
The middle meningeal artery ('' la, arteria meningea media'') is typically the third branch of the first portion of the maxillary artery. After branching off the maxillary artery in the infratemporal fossa, it runs through the foramen spinosum t ...
*Cribriform plate
In mammalian anatomy, the cribriform plate (Latin for lit. ''sieve-shaped''), horizontal lamina or lamina cribrosa is part of the ethmoid bone. It is received into the ethmoidal notch of the frontal bone and roofs in the nasal cavities. It supp ...
*Posterior cranial fossa
The posterior cranial fossa is part of the cranial cavity, located between the foramen magnum and tentorium cerebelli. It contains the brainstem and cerebellum.
This is the most inferior of the fossae. It houses the cerebellum, medulla and pons. ...
*Nasociliary nerve
The nasociliary nerve is a branch of the ophthalmic nerve, itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It is intermediate in size between the other two branches of the ophthalmic nerve, the frontal nerve and lacrimal nerve.
Structure
The na ...
*Hypoglossal canal
The hypoglossal canal is a foramen in the occipital bone of the skull. It is hidden medially and superiorly to each occipital condyle. It transmits the hypoglossal nerve.
Structure
The hypoglossal canal lies in the epiphyseal junction between ...
Additional images