|
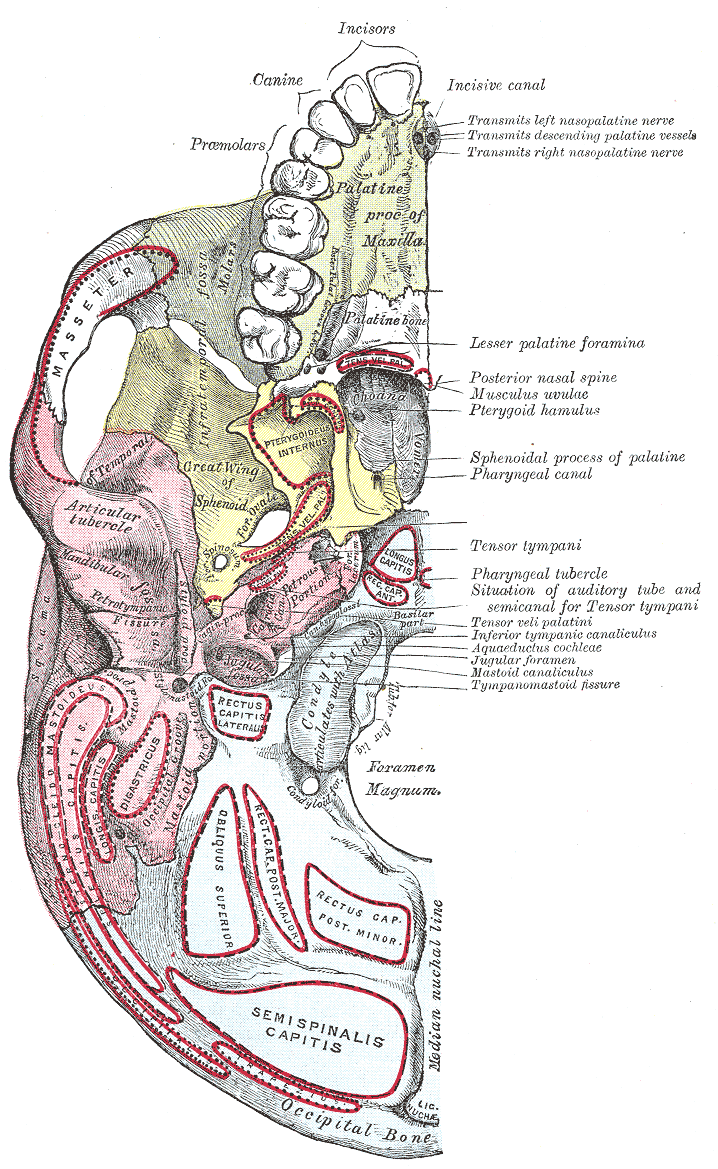
Petro-occipital Fissure
This grooved surface of the foramen magnum is separated on either side from the petrous portion of the temporal bone by the petro-occipital fissure, which is occupied in the fresh state by a plate of cartilage; the fissure is continuous behind with the jugular foramen, and its margins are grooved for the inferior petrosal sinus The inferior petrosal sinuses are two small sinuses situated on the inferior border of the petrous part of the temporal bone, one on each side. Each inferior petrosal sinus drains the cavernous sinus into the internal jugular vein. Structure The .... References External links * Bones of the head and neck {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Of The Skull
The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most inferior area of the skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the calvaria. Structure Structures found at the base of the skull are for example: Bones There are five bones that make up the base of the skull: *Ethmoid bone * Sphenoid bone * Occipital bone *Frontal bone *Temporal bone Sinuses *Occipital sinus * Superior sagittal sinus *Superior petrosal sinus Foramina of the skull * Foramen cecum *Optic foramen *Foramen lacerum *Foramen rotundum * Foramen magnum * Foramen ovale *Jugular foramen *Internal auditory meatus *Mastoid foramen *Sphenoidal emissary foramen *Foramen spinosum Sutures *Frontoethmoidal suture *Sphenofrontal suture *Sphenopetrosal suture *Sphenoethmoidal suture * Petrosquamous suture *Sphenosquamosal suture Other *Sphenoidal lingula *Subarcuate fossa *Dorsum sellae *Jugular process *Petro-occipital fissure *Condylar canal * Jugular tubercle * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrous Part Of The Temporal Bone
The petrous part of the temporal bone is pyramid-shaped and is wedged in at the base of the skull between the sphenoid and occipital bones. Directed medially, forward, and a little upward, it presents a base, an apex, three surfaces, and three angles, and houses in its interior, the components of the inner ear. The petrous portion is among the most basal elements of the skull and forms part of the endocranium. Petrous comes from the Latin word ''petrosus'', meaning "stone-like, hard". It is one of the densest bones in the body. The petrous bone is important for studies of ancient DNA from skeletal remains, as it tends to contain extremely well-preserved DNA. Base The base is fused with the internal surfaces of the squamous and mastoid parts. Apex The apex, which is rough and uneven, is received into the angular interval between the posterior border of the great wing of the sphenoid bone and the basilar part of the occipital bone; it presents the anterior or internal openin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Bone
The temporal bones are situated at the sides and base of the skull, and lateral to the temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex. The temporal bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples, and house the structures of the ears. The lower seven cranial nerves and the major vessels to and from the brain traverse the temporal bone. Structure The temporal bone consists of four parts— the squamous, mastoid, petrous and tympanic parts. The squamous part is the largest and most superiorly positioned relative to the rest of the bone. The zygomatic process is a long, arched process projecting from the lower region of the squamous part and it articulates with the zygomatic bone. Posteroinferior to the squamous is the mastoid part. Fused with the squamous and mastoid parts and between the sphenoid and occipital bones lies the petrous part, which is shaped like a pyramid. The tympanic part is relatively small and lies inferior to the squamous part, anterior to the mast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occipital Bone
The occipital bone () is a neurocranium, cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the cerebrum. At the base of skull in the occipital bone, there is a large oval opening called the foramen magnum, which allows the passage of the spinal cord. Like the other cranial bones, it is classed as a flat bone. Due to its many attachments and features, the occipital bone is described in terms of separate parts. From its front to the back is the basilar part of occipital bone, basilar part, also called the basioccipital, at the sides of the foramen magnum are the lateral parts of occipital bone, lateral parts, also called the exoccipitals, and the back is named as the squamous part of occipital bone, squamous part. The basilar part is a thick, somewhat quadrilateral piece in front of the foramen magnum and directed towards the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foramen Magnum
The foramen magnum ( la, great hole) is a large, oval-shaped opening in the occipital bone of the skull. It is one of the several oval or circular openings (foramina) in the base of the skull. The spinal cord, an extension of the medulla oblongata, passes through the foramen magnum as it exits the cranial cavity. Apart from the transmission of the medulla oblongata and its membranes, the foramen magnum transmits the vertebral arteries, the anterior and posterior spinal arteries, the tectorial membranes and alar ligaments. It also transmits the accessory nerve into the skull. The foramen magnum is a very important feature in bipedal mammals. One of the attributes of a biped's foramen magnum is a forward shift of the anterior border of the cerebellar tentorium; this is caused by the shortening of the cranial base. Studies on the foramen magnum position have shown a connection to the functional influences of both posture and locomotion. The forward shift of the foramen magnum i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck and the bronchial tubes, and the intervertebral discs. In other taxa, such as chondrichthyans, but also in cyclostomes, it may constitute a much greater proportion of the skeleton. It is not as hard and rigid as bone, but it is much stiffer and much less flexible than muscle. The matrix of cartilage is made up of glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, collagen fibers and, sometimes, elastin. Because of its rigidity, cartilage often serves the purpose of holding tubes open in the body. Examples include the rings of the trachea, such as the cricoid cartilage and carina. Cartilage is composed of specialized cells called chondrocytes that produce a large amount of collagenous extracellular matrix, abundant ground substance that is rich in pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jugular Foramen
A jugular foramen is one of the two (left and right) large foramina (openings) in the base of the skull, located behind the carotid canal. It is formed by the temporal bone and the occipital bone. It allows many structures to pass, including the inferior petrosal sinus, three cranial nerves, the sigmoid sinus, and meningeal arteries. Structure The jugular foramen is formed in front by the petrous portion of the temporal bone, and behind by the occipital bone. It is generally slightly larger on the right side than on the left side. Contents The jugular foramen may be subdivided into three compartments, each with their own contents. * The ''anterior'' compartment transmits the inferior petrosal sinus. * The ''intermediate'' compartment transmits the glossopharyngeal nerve, the vagus nerve, and the accessory nerve. * The ''posterior'' compartment transmits the sigmoid sinus (becoming the internal jugular vein), and some meningeal branches from the occipital artery and ascending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Petrosal Sinus
The inferior petrosal sinuses are two small sinuses situated on the inferior border of the petrous part of the temporal bone, one on each side. Each inferior petrosal sinus drains the cavernous sinus into the internal jugular vein. Structure The inferior petrosal sinus is situated in the inferior petrosal sulcus, formed by the junction of the petrous part of the temporal bone with the basilar part of the occipital bone. It begins below and behind the cavernous sinus and, passing through the anterior part of the jugular foramen, ends in the superior bulb of the internal jugular vein. Function The inferior petrosal sinus receives the internal auditory veins and also veins from the medulla oblongata, pons, and under surface of the cerebellum. Additional images File:Gray568.png, Sagittal section of the skull, showing the sinuses of the dura. See also * Dural venous sinuses * Inferior petrosal sinus sampling Inferior petrosal sinus sampling (or IPSS), is a diagnostic medical p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |