bronchial cancer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98ŌĆō99% of all lung cancers are
 A person suspected of having lung cancer will first have various imaging tests done to evaluate the presence, extent, and location of tumors. First, many
A person suspected of having lung cancer will first have various imaging tests done to evaluate the presence, extent, and location of tumors. First, many
 At diagnosis, lung cancers are classified based on the type of cells the tumor is derived from; tumors derived from different cells progress and respond to treatment differently. There are two main types of lung cancer, categorized by the size and appearance of the malignant cells seen by a
At diagnosis, lung cancers are classified based on the type of cells the tumor is derived from; tumors derived from different cells progress and respond to treatment differently. There are two main types of lung cancer, categorized by the size and appearance of the malignant cells seen by a
Diagram showing stage 1A and 1B lung cancer CRUK 197.svg, Stage IA and IB lung cancer
Diagram showing stage 2A lung cancer CRUK 213.svg, Stage IIA lung cancer
Diagram showing one option for stage 2Ba lung cancer CRUK 176.svg, Stage IIB lung cancer
Diagram showing one option for stage 2Bb lung cancer CRUK 177.svg, One option for stage IIB lung cancer, with T2b; but if tumor is within 2 cm of the
 For stage I and stage II NSCLC the first line of treatment is often surgical removal of the affected lobe of the lung. For those not well enough to tolerate full lobe removal, a smaller chunk of lung tissue can be removed by
For stage I and stage II NSCLC the first line of treatment is often surgical removal of the affected lobe of the lung. For those not well enough to tolerate full lobe removal, a smaller chunk of lung tissue can be removed by  Treatment for those with stage III NSCLC depends on the nature of their disease. Those with more limited spread may undergo surgery to have the tumor and affected lymph nodes removed, followed by chemotherapy and potentially radiotherapy. Those with particularly large tumors (T4) and those for whom surgery is impractical are treated with combination chemotherapy and radiotherapy along with the
Treatment for those with stage III NSCLC depends on the nature of their disease. Those with more limited spread may undergo surgery to have the tumor and affected lymph nodes removed, followed by chemotherapy and potentially radiotherapy. Those with particularly large tumors (T4) and those for whom surgery is impractical are treated with combination chemotherapy and radiotherapy along with the 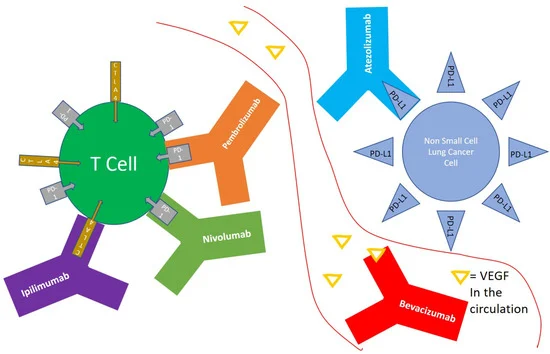
 Several treatments can be provided via bronchoscopy for the management of airway obstruction or bleeding. If an airway becomes obstructed by cancer growth, options include rigid bronchoscopy, balloon bronchoplasty, stenting, and microdebridement. Laser photosection involves the delivery of laser light inside the airway via a bronchoscope to remove the obstructing tumor.
Several treatments can be provided via bronchoscopy for the management of airway obstruction or bleeding. If an airway becomes obstructed by cancer growth, options include rigid bronchoscopy, balloon bronchoplasty, stenting, and microdebridement. Laser photosection involves the delivery of laser light inside the airway via a bronchoscope to remove the obstructing tumor.


 Cancer develops after
Cancer develops after
 Smoking prevention and
Smoking prevention and
carcinomas
Carcinoma is a malignancy that develops from epithelial cells. Specifically, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that arises from cells originating in the endodermal, mesoderm ...
), is a malignant lung tumor
Lung tumors are neoplastic lung nodules. These include:
Primary tumors of the lung/pulmonary system:
* Bronchial leiomyoma, a rare, benign tumor
* Lung cancer, the term commonly used to refer to ''carcinoma of the lung''
* Pulmonary carcinoid tu ...
characterized by uncontrolled cell growth
Cell growth refers to an increase in the total mass of a cell, including both cytoplasmic, nuclear and organelle volume. Cell growth occurs when the overall rate of cellular biosynthesis (production of biomolecules or anabolism) is greater than ...
in tissues of the lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malignant cells that originate as epithelial cells, or from tissues composed of epithelial cells. Other lung cancers, such as the rare sarcomas of the lung, are generated by the malignant transformation of connective tissues (i.e. nerve, fat, muscle, bone), which arise from mesenchymal cells. Lymphomas and melanomas (from lymphoid and melanocyte cell lineages) can also rarely result in lung cancer.
In time, this uncontrolled growth
Growth may refer to:
Biology
* Auxology, the study of all aspects of human physical growth
* Bacterial growth
* Cell growth
* Growth hormone, a peptide hormone that stimulates growth
* Human development (biology)
* Plant growth
* Secondary growth ...
can metastasize
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, ...
(spreading beyond the lung) either by direct extension, by entering the lymphatic circulation, or via hematogenous, bloodborne spread ŌĆō into nearby tissue or other, more distant parts of the body. Most cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
s that originate from within the lungs, known as primary lung cancers, are carcinomas
Carcinoma is a malignancy that develops from epithelial cells. Specifically, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that arises from cells originating in the endodermal, mesoderm ...
. The two main types are small-cell lung carcinoma
Small-cell carcinoma is a type of highly malignant cancer that most commonly arises within the lung, although it can occasionally arise in other body sites, such as the cervix, prostate, and gastrointestinal tract. Compared to non-small cell car ...
(SCLC) and non-small-cell lung carcinoma
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is any type of epithelial lung cancer other than small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC). NSCLC accounts for about 85% of all lung cancers. As a class, NSCLCs are relatively insensitive to chemotherapy, compared to sm ...
(NSCLC). The most common symptom
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showin ...
s are coughing (including coughing up blood
Hemoptysis is the coughing up of blood or blood-stained mucus from the bronchi, larynx, trachea, or lungs. In other words, it is the airway bleeding. This can occur with lung cancer, infections such as tuberculosis, bronchitis, or pneumonia, a ...
), weight loss, shortness of breath, and chest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with n ...
s.
The vast majority (85%) of cases of lung cancer are due to long-term tobacco smoking
Tobacco smoking is the practice of burning tobacco and ingesting the resulting smoke. The smoke may be inhaled, as is done with cigarettes, or simply released from the mouth, as is generally done with pipes and cigars. The practice is believed ...
. About 10ŌĆō15% of cases occur in people who have never smoked. These cases are often caused by a combination of genetic factors and exposure to radon
Radon is a chemical element with the symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colourless, odourless, tasteless noble gas. It occurs naturally in minute quantities as an intermediate step in the normal radioactive decay chains through ...
gas, asbestos
Asbestos () is a naturally occurring fibrous silicate mineral. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous crystals, each fibre being composed of many microscopic "fibrils" that can be released into the atmosphere b ...
, second-hand smoke
Passive smoking is the inhalation of tobacco smoke, called secondhand smoke (SHS), or environmental tobacco smoke (ETS), by persons other than the intended "active" smoker. It occurs when tobacco smoke enters an environment, causing its inhalat ...
, or other forms of air pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different types ...
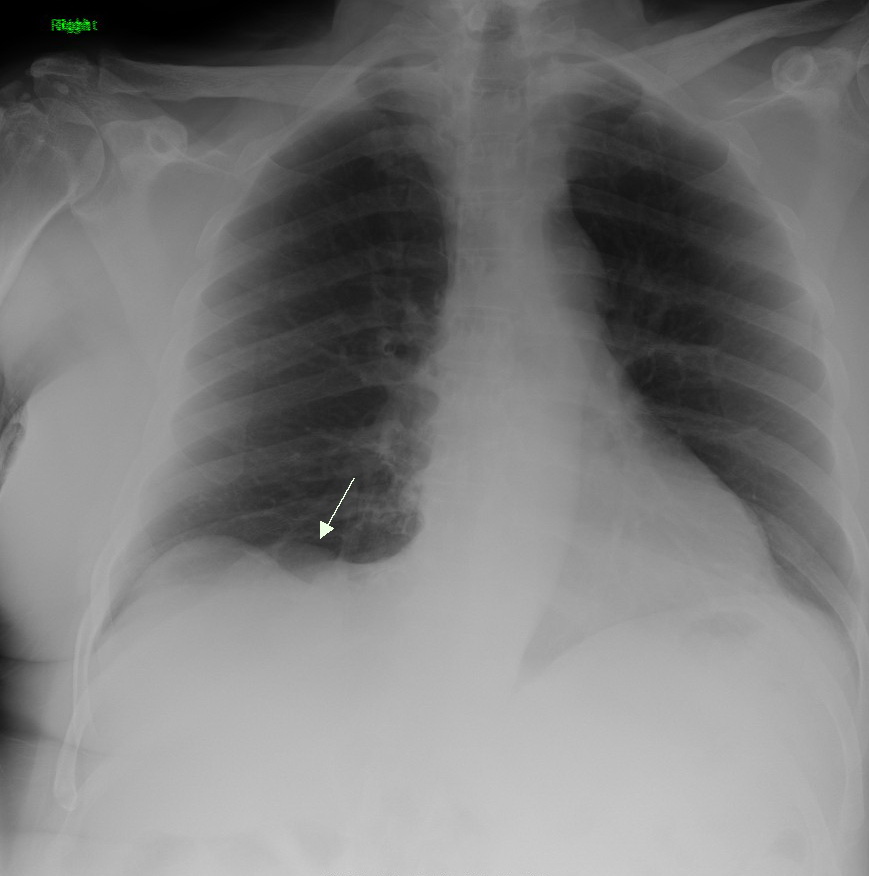
. Retrieved 2014-06-16 Lung cancer may be seen on chest radiograph
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in med ...
s and computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
(CT) scans. The diagnosis
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " cause and effect". In systems engin ...
is confirmed by biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a diseas ...
, which is usually performed by bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is an endoscopic technique of visualizing the inside of the airways for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. An instrument (bronchoscope) is inserted into the airways, usually through the nose or mouth, or occasionally through a trac ...
or CT-guidance.
The major method of prevention is the avoidance of risk factors, including smoking and air pollution. Treatment and long-term outcomes depend on the type of cancer, the stage
Stage or stages may refer to:
Acting
* Stage (theatre), a space for the performance of theatrical productions
* Theatre, a branch of the performing arts, often referred to as "the stage"
* ''The Stage'', a weekly British theatre newspaper
* Sta ...
(degree of spread), and the person's overall health. Most cases are not curable. Common treatments include surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgik─ō'' (composed of Žć╬Ą╬»Žü, "hand", and ß╝öŽü╬│╬┐╬Į, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pat ...
, chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherap ...
, and radiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radia ...
. NSCLC is sometimes treated with surgery, whereas SCLC usually responds better to chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Worldwide in 2020, lung cancer occurred in 2.2 million people and resulted in 1.8 million deaths. It is the most common cause of cancer-related death in both men and women. The most common age at diagnosis is 70 years. In most countries the five-year survival rate
The five-year survival rate is a type of survival rate for estimating the prognosis of a particular disease, normally calculated from the point of diagnosis. Lead time bias from earlier diagnosis can affect interpretation of the five-year surviva ...
is around 10 to 20%, while in Japan it is 33%, in Israel 27%, and in the Republic of Korea 25%. Outcomes typically are worse in the developing world.
Signs and symptoms
Early lung cancer often has no symptoms. When symptoms do arise they are often nonspecific respiratory problems ŌĆōcough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages that can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex following three pha ...
ing, shortness of breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing disc ...
, and/or chest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with n ...
ŌĆō that can differ from person to person. Those who experience coughing tend to report either a new cough, or an increase in the frequency or strength of a pre-existing cough. Around a quarter cough up blood, ranging from small streaks in the sputum
Sputum is mucus that is coughed up from the lower airways (the trachea and bronchi). In medicine, sputum samples are usually used for a naked eye examination, microbiological investigation of respiratory infections and cytological investigations ...
to large amounts. Around half of those diagnosed with lung cancer experience shortness of breath, while 25ŌĆō50% experience a dull, persistent chest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with n ...
that remains in the same location over time. In addition to respiratory symptoms, some experience systemic symptoms
Systemic fundamental to a predominant social, economic, or political practice. This refers to:
In medicine
In medicine, ''systemic'' means affecting the whole body, or at least multiple organ systems. It is in contrast with ''topical'' or ''loc ...
including loss of appetite
Anorexia is a medical term for a loss of appetite. While the term in non-scientific publications is often used interchangeably with anorexia nervosa, many possible causes exist for a loss of appetite, some of which may be harmless, while others i ...
, weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat (adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other conn ...
, general weakness, fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a body temperature, temperature above the human body temperature, normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, set point. There is not a single ...
, and night sweats
Night sweats, also referred to as nocturnal hyperhidrosis (Hyperhidrosis - a medical term for excessive sweating + nocturnal - night), is the repeated occurrence of excessive sweating during sleep. The person may or may not also perspire exces ...
.
Some less common symptoms suggest tumors in particular locations. Tumors in the thorax
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the cre ...
can cause breathing problems by obstructing the trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a Cartilage, cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends ...
or disrupting the nerve to the diaphragm
Diaphragm may refer to:
Anatomy
* Thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle between the thorax and the abdomen
* Pelvic diaphragm or pelvic floor, a pelvic structure
* Urogenital diaphragm or triangular ligament, a pelvic structure
Other
* Diap ...
, difficulty swallowing
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or liqu ...
by compressing the esophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the ...
, hoarseness
A hoarse voice, also known as dysphonia or hoarseness, is when the voice involuntarily sounds breathy, raspy, or strained, or is softer in volume or lower in pitch. A hoarse voice, can be associated with a feeling of unease or scratchiness in the ...
by disrupting the nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system.
A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the e ...
s of the larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about ...
, and Horner's syndrome
Horner's syndrome, also known as oculosympathetic paresis, is a combination of symptoms that arises when a group of nerves known as the sympathetic trunk is damaged. The signs and symptoms occur on the same side (ipsilateral) as it is a lesion o ...
by disrupting the sympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of th ...
. Horner's syndrome is also common in tumors at the top of the lung, known as Pancoast tumor
A Pancoast tumor is a tumor of the apex of the lung. It is a type of lung cancer defined primarily by its location situated at the top end of either the right or left lung. It typically spreads to nearby tissues such as the ribs and vertebrae. Most ...
s, which also cause shoulder pain that radiates down the little finger-side of the arm as well as destruction of the topmost rib
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs ( la, costae) are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the chest, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the ches ...
s. Swollen
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area ma ...
lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that inclu ...
s above the collarbone
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the right ...
can indicate a tumor that has spread within the chest. Tumors obstructing bloodflow to the heart can cause superior vena cava syndrome
Superior vena cava syndrome (SVCS), is a group of symptoms caused by obstruction of the superior vena cava ("SVC"), a short, wide vessel carrying circulating blood into the heart. The majority of cases are caused by malignant tumors within the m ...
, while tumors infiltrating the area around the heart can cause fluid buildup around the heart, arrythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast ŌĆō above 100 beats per minute in adults ...
, and heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, a ...
.
Around a third of people diagnosed with lung cancer have symptoms caused by metastases
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, ...
in sites distant from the lung. Lung cancer can metastasize anywhere in the body, with different symptoms depending on the location. Brain metastases can cause headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Headaches can occur as a result ...
, nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the ...
, vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the Human nose, nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like Food-poisoning, foo ...
, seizure
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with los ...
s, and neurological deficit
Neurology (from el, ╬Į╬Ąß┐”Žü╬┐╬Į (ne├╗ron), "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the brain, the spinal c ...
s. Bone metastases can cause pain, bone fracture
A bone fracture (abbreviated FRX or Fx, Fx, or #) is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of any bone in the body. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several fragments, known as a '' ...
s, and compression of the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the spi ...
. Metastasis into the bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoietic ce ...
can deplete blood cells and cause leukoerythroblastosis
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, th ...
(immature immune cells in the blood). Liver metastases can cause liver enlargement, pain in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, fever, and weight loss.
Lung tumors also often cause the release of body-altering hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required ...
s, which themselves cause unusual symptoms, called paraneoplastic syndrome
A paraneoplastic syndrome is a syndrome (a set of signs and symptoms) that is the consequence of a tumor in the body (usually a cancerous one), specifically due to the production of chemical signaling molecules (such as hormones or cytokines) by ...
s. Inappropriate hormone release can cause dramatic shifts in concentrations of blood minerals
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
. Most common is hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia, also spelled hypercalcaemia, is a high calcium (Ca2+) level in the blood serum. The normal range is 2.1ŌĆō2.6 mmol/L (8.8ŌĆō10.7 mg/dL, 4.3ŌĆō5.2 mEq/L), with levels greater than 2.6 mmol/L defined as hypercalcemi ...
caused by over-production of parathyroid hormone-related protein
Parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) is a proteinaceous hormone and a member of the parathyroid hormone family secreted by mesenchymal stem cells. It is occasionally secreted by cancer cells (for example, breast cancer, certain types of ...
or parathyroid hormone
Parathyroid hormone (PTH), also called parathormone or parathyrin, is a peptide hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands that regulates the serum calcium concentration through its effects on bone, kidney, and intestine.
PTH influences bone re ...
. Hypercalcemia can manifest as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, constipation, increased thirst, frequent urination
Frequent urination, or urinary frequency (sometimes called pollakiuria), is the need to urinate more often than usual. Diuretics are medications that increase urinary frequency. Nocturia is the need of frequent urination at night. The most common c ...
, and altered mental status. Those with lung cancer also commonly experience hypokalemia
Hypokalemia is a low level of potassium (K+) in the blood serum. Mild low potassium does not typically cause symptoms. Symptoms may include feeling tired, leg cramps, weakness, and constipation. Low potassium also increases the risk of an abno ...
due to inappropriate secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH; also adrenocorticotropin, corticotropin) is a polypeptide tropic hormone produced by and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. It is also used as a medication and diagnostic agent. ACTH is an important c ...
, as well as hyponatremia
Hyponatremia or hyponatraemia is a low concentration of sodium in the blood. It is generally defined as a sodium concentration of less than 135 mmol/L (135 mEq/L), with severe hyponatremia being below 120 mEq/L. Symptoms can be abs ...
due to overproduction of antidiuretic hormone
Human vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the AVP gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then travel ...
or atrial natriuretic peptide
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) or atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) is a natriuretic peptide hormone secreted from the cardiac atria that in humans is encoded by the NPPA gene. Natriuretic peptides (ANP, BNP, and CNP) are a family of hormone/pa ...
. Around a third of people with lung cancer develop nail clubbing
Nail clubbing, also known as digital clubbing or clubbing, is a deformity of the finger or toe nails associated with a number of diseases, mostly of the heart and lungs.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. ...
, while up to one in ten experience hypertrophic primary osteoarthropathy
Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy is a medical condition combining clubbing and periostitis of the small hand joints, especially the distal interphalangeal joints and the metacarpophalangeal joints. Distal expansion of the long bones as well as pain ...
. A variety of autoimmune disorders can arise as paraneoplastic syndromes in those with lung cancer, including LambertŌĆōEaton myasthenic syndrome
LambertŌĆōEaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) is a rare autoimmune disorder characterized by muscle weakness of the limbs.
Around 60% of those with LEMS have an underlying malignancy, most commonly small-cell lung cancer; it is therefore regarded ...
(which causes muscle weakness), sensory neuropathies
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, is a general term describing disease affecting the peripheral nerves, meaning nerves beyond the brain and spinal cord. Damage to peripheral nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland, or or ...
, muscle inflammation
Myositis is a rare disease that involves inflammation of the muscles. This can present with a variety of symptoms such as skin involvement (i.e., rashes), muscle weakness, and other organ involvement. Systemic symptoms such as weight loss, fatigue ...
, brain swelling, and autoimmune deterioration of cerebellum
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebel ...
, limbic system
The limbic system, also known as the paleomammalian cortex, is a set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, immediately beneath the medial temporal lobe of the cerebrum primarily in the forebrain.Schacter, Daniel L. 2012. ''Ps ...
, or brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is cont ...
. Up to 1 in 12 people with lung cancer have paraneoplastic clotting issues, including migratory venous thrombophlebitis
The Trousseau sign of malignancy or Trousseau's syndrome is a medical sign involving episodes of vessel inflammation due to blood clot (thrombophlebitis) which are recurrent or appearing in different locations over time (thrombophlebitis migrans o ...
, clots in the heart, and disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition in which blood clots form throughout the body, blocking small blood vessels. Symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, leg pain, problems speaking, or problems moving parts o ...
. Paraneoplastic syndromes involving the skin and kidneys are rare, each occurring in up to 1% of those with lung cancer.
Diagnosis

 A person suspected of having lung cancer will first have various imaging tests done to evaluate the presence, extent, and location of tumors. First, many
A person suspected of having lung cancer will first have various imaging tests done to evaluate the presence, extent, and location of tumors. First, many primary care provider
Primary care is the day-to-day healthcare given by a health care provider. Typically this provider acts as the first contact and principal point of continuing care for patients within a healthcare system, and coordinates other specialist care th ...
s perform a chest X-ray
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in med ...
to look for a mass inside the lung. The x-ray may reveal an obvious mass, the widening of the mediastinum
The mediastinum (from ) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagu ...
(suggestive of spread to lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that inclu ...
s there), atelectasis
Atelectasis is the collapse or closure of a lung resulting in reduced or absent gas exchange. It is usually unilateral, affecting part or all of one lung. It is a condition where the alveoli are deflated down to little or no volume, as distinct ...
(lung collapse), consolidation (pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity ...
), or pleural effusion
A pleural effusion is accumulation of excessive fluid in the pleural space, the potential space that surrounds each lung.
Under normal conditions, pleural fluid is secreted by the parietal pleural capillaries at a rate of 0.6 millilitre per kilog ...
; however, some lung tumors are not visible by X-ray. Next, many undergo computed tomography (CT) scanning, which can reveal the sizes and locations of tumors.
A definitive diagnosis of lung cancer requires a biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a diseas ...
of the suspected tissue be histologically
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single ...
examined for cancer cells. Bronchoscopic
Bronchoscopy is an endoscopy, endoscopic medical procedure, technique of visualizing the inside of the airways for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. An instrument (bronchoscope) is inserted into the airways, usually through the nose or mouth, o ...
or CT-guided biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a diseas ...
is often used to sample the tumor for histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", ŽĆ╬¼╬Ė╬┐Žé ''pathos'' "suffering", and -╬╗╬┐╬│╬»╬▒ '' -logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Spe ...
. Additionally, biopsy material of the original tumor or metastases are often tested for their molecular profile to determine eligibility for targeted therapies. Those who cannot undergo a more invasive biopsy procedure may instead have a liquid biopsy
A liquid biopsy, also known as fluid biopsy or fluid phase biopsy, is the sampling and analysis of non-solid biological tissue, primarily blood. Like traditional biopsy, this type of technique is mainly used as a diagnostic and monitoring tool for ...
taken (i.e. a sample of some body fluid) which may contain circulating tumor DNA
Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) is tumor-derived fragmented DNA in the bloodstream that is not associated with cells. ctDNA should not be confused with cell-free DNA (cfDNA), a broader term which describes DNA that is freely circulating in the bloo ...
that can be used for molecular testing.
Imaging is also used to assess the extent of cancer spread. Positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in Metabolism, metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including bl ...
(PET) scanning or combined PET-CT
Positron emission tomographyŌĆōcomputed tomography (better known as PET-CT or PET/CT) is a nuclear medicine technique which combines, in a single gantry, a positron emission tomography (PET) scanner and an x-ray computed tomography (CT) scann ...
scanning is often used to locate metastases in the body. Since PET scanning cannot be used in the brain, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network
National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) is an alliance of 32 cancer centers in the United States, most of which are designated by the National Cancer Institute (one of the U.S. National Institutes of Health) as comprehensive cancer centers. It ...
recommends magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
(MRI) ŌĆō or CT where MRI is unavailable ŌĆō to scan the brain for metastases in those with NSCLC and large tumors, or tumors that have spread to the nearby lymph nodes. When spread to lymph nodes or to a single site is suspected, the suspected metastasis is often biopsied using a minimally invasive needle biopsy technique ŌĆō typically using endobronchial ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
to guide a bronchoscope
Bronchoscopy is an endoscopic technique of visualizing the inside of the airways for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. An instrument (bronchoscope) is inserted into the airways, usually through the nose or mouth, or occasionally through a trac ...
equipped with transbronchial needle aspiration. Primary lung cancers most commonly metastasize to the brain, bones, liver, and adrenal gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which ...
s.
Lung cancer can often appear as a solitary pulmonary nodule
A lung nodule or pulmonary nodule is a relatively small focal density in the lung. A solitary pulmonary nodule (SPN) or coin lesion, is a mass in the lung smaller than three centimeters in diameter. A pulmonary micronodule has a diameter of less th ...
on a chest radiograph. However, the differential diagnosis
In healthcare, a differential diagnosis (abbreviated DDx) is a method of analysis of a patient's history and physical examination to arrive at the correct diagnosis. It involves distinguishing a particular disease or condition from others that p ...
is wide and many other diseases can also give this appearance, including metastatic cancer, hamartoma
A hamartoma is a mostly benign, local malformation of cells that resembles a neoplasm of local tissue but is usually due to an overgrowth of multiple aberrant cells, with a basis in a systemic genetic condition, rather than a growth descended fr ...
s, and infectious granuloma
A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such substances include infectious ...
s caused by tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in ...
, histoplasmosis
Histoplasmosis is a fungal infection caused by ''Histoplasma capsulatum''. Symptoms of this infection vary greatly, but the disease affects primarily the lungs. Occasionally, other organs are affected; called disseminated histoplasmosis, it can ...
, or coccidioidomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis (, ), commonly known as cocci, Valley fever, as well as California fever, desert rheumatism, or San Joaquin Valley fever, is a mammalian fungal disease caused by ''Coccidioides immitis'' or ''Coccidioides posadasii''. Coccidio ...
. Lung cancer can also be an incidental finding Incidental medical findings are previously undiagnosed medical or psychiatric conditions that are discovered unintentionally and during evaluation for a medical or psychiatric condition. Such findings may occur in a variety of settings, including ro ...
, as a solitary pulmonary nodule on a chest radiograph or CT scan done for an unrelated reason. Clinical practice guideline
Clinical may refer to: Healthcare
* Of or about a clinic, a healthcare facility
* Of or about the practice of medicine Other uses
* ''Clinical'' (film), a 2017 American horror thriller
See also
*
*
* Clinical chemistry, the analysis of bodily flu ...
s recommend specific frequencies (suggested intervals of time between tests) for pulmonary nodule surveillance. CT imaging is not suggested to be used for longer or more frequently than indicated in the clinical guidelines, as any additional surveillance
Surveillance is the monitoring of behavior, many activities, or information for the purpose of information gathering, influencing, managing or directing. This can include observation from a distance by means of electronic equipment, such as c ...
exposes people to increased radiation and is costly.
Classification
histopathologist
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", ŽĆ╬¼╬Ė╬┐Žé ''pathos'' "suffering", and -╬╗╬┐╬│╬»╬▒ ''-logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Spec ...
under a microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisibl ...
: small cell lung cancer
Small-cell carcinoma is a type of highly malignant cancer that most commonly arises within the lung, although it can occasionally arise in other body sites, such as the cervix, prostate, and gastrointestinal tract. Compared to non-small cell car ...
(SCLC; 15% of lung cancer diagnoses) and non-small-cell lung cancer
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is any type of epithelial lung cancer other than small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC). NSCLC accounts for about 85% of all lung cancers. As a class, NSCLCs are relatively insensitive to chemotherapy, compared to sm ...
(NSCLC; 85% of diagnoses). In SCLC, cancerous cells appear small with ill-defined boundaries, not much cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The ...
, many mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and Fungus, fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosi ...
, and have distinctive nuclei with granular-looking DNA and no visible nucleoli
The nucleolus (, plural: nucleoli ) is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis, which is the synthesis of ribosomes. The nucleolus also participates in the formation of sig ...
. Cells contain dense neurosecretory granules (vesicles
Vesicle may refer to:
; In cellular biology or chemistry
* Vesicle (biology and chemistry), a supramolecular assembly of lipid molecules, like a cell membrane
* Synaptic vesicle
; In human embryology
* Vesicle (embryology), bulge-like features o ...
containing neuroendocrine
Neuroendocrine cells are cells that receive neuronal input (through neurotransmitters released by nerve cells or neurosecretory cells) and, as a consequence of this input, release messenger molecules ( hormones) into the blood. In this way they b ...
hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required ...
s), which give this tumor an endocrine or paraneoplastic syndrome
A paraneoplastic syndrome is a syndrome (a set of signs and symptoms) that is the consequence of a tumor in the body (usually a cancerous one), specifically due to the production of chemical signaling molecules (such as hormones or cytokines) by ...
association. Most cases arise in the larger airways (primary and secondary bronchi
A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi pronounced (BRAN-KAI) to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. ...
). NSCLCs comprise a group of three cancer types: adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma (; plural adenocarcinomas or adenocarcinomata ) (AC) is a type of cancerous tumor that can occur in several parts of the body. It is defined as neoplasia of epithelial tissue that has glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or ...
, squamous-cell carcinoma
Squamous-cell carcinomas (SCCs), also known as epidermoid carcinomas, comprise a number of different types of cancer that begin in squamous cells. These cells form on the surface of the skin, on the lining of hollow organs in the body, and on the ...
, and large-cell carcinoma
Large-cell carcinoma (LCC, LCLC) is a heterogeneous group of undifferentiated malignant neoplasms that lack the cytologic and architectural features of small cell carcinoma and glandular or squamous differentiation. LCC is categorized as a type of ...
. Nearly 40% of lung cancers are adenocarcinomas, which usually come from peripheral lung tissue. Squamous-cell carcinoma causes about 30% of lung cancers. They typically occur close to large airways. A hollow cavity and associated cell death
Cell death is the event of a biological cell ceasing to carry out its functions. This may be the result of the natural process of old cells dying and being replaced by new ones, as in programmed cell death, or may result from factors such as dis ...
are commonly found at the center of the tumor. Less than 10% of lung cancers are large-cell carcinomas, so named because the cells are large, with excess cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The ...
, large nuclei, and conspicuous nucleoli
The nucleolus (, plural: nucleoli ) is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis, which is the synthesis of ribosomes. The nucleolus also participates in the formation of sig ...
.
Several lung cancer types are subclassified based on the growth characteristics of the cancer cells. Adenocarcinomas are classified as lepidic (growing along the surface of intact alveolar Alveolus (; pl. alveoli, adj. alveolar) is a general anatomical term for a concave cavity or pit.
Uses in anatomy and zoology
* Pulmonary alveolus, an air sac in the lungs
** Alveolar cell or pneumocyte
** Alveolar duct
** Alveolar macrophage
* ...
walls), acinar and papillary, or micropapillary and solid pattern. Lepidic adenocarcinomas tend to be least aggressive; micropapillary and solid pattern adenocarcinomas most aggressive.
In addition to examining cell morphology, biopsies are also often stained with immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the most common application of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to an ...
to confirm the diagnosis. SLCL is most often confirmed by the presence of chromogranin
Granin (chromogranin and secretogranin) is a protein family of regulated secretory proteins ubiquitously found in the cores of amine and peptide hormone and neurotransmitter dense-core secretory vesicles.
Function
Granins (chromogranins or sec ...
, synaptophysin
Synaptophysin, also known as the major synaptic vesicle protein p38, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SYP'' gene.
Genomics
The gene is located on the short arm of X chromosome (Xp11.23-p11.22). It is 12,406 bases in length and ...
, and CD56
Neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM), also called CD56, is a homophilic binding glycoprotein expressed on the surface of neurons, glia and skeletal muscle. Although CD56 is often considered a marker of neural lineage commitment due to its discove ...
. The presence of Napsin-A
Napsin-A is an aspartic proteinase that is encoded in humans by the NAPSA gene. The name napsin comes from ''n''ovel ''a''spartic ''p''roteinase of the pep''sin'' family.
The activation peptide of an aspartic proteinase acts as an inhibitor of ...
, TTF-1
NK2 homeobox 1 (NKX2-1), also known as thyroid transcription factor 1 (TTF-1), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''NKX2-1'' gene.
Function
Thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1) is a protein that regulates transcription of genes ...
, CK7, and CK20
Keratin 20, often abbreviated CK20, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KRT20'' gene.
Keratin 20 is a type I cytokeratin. It is a major cellular protein of mature enterocytes and goblet cells and is specifically found in the gastric ...
help confirm the subtype of lung carcinoma.
Around 10% of lung cancers are rarer types. These include mixes of the above subtypes like adenosquamous carcinoma
Adenosquamous carcinoma is a type of cancer that contains two types of cells: squamous cells (thin, flat cells that line certain organs) and gland-like cells. It has been associated with more aggressive characteristics when compared to adenocarcino ...
. Rare subtypes include carcinoid tumors
A carcinoid (also carcinoid tumor) is a slow-growing type of neuroendocrine tumor originating in the cells of the neuroendocrine system. In some cases, metastasis may occur. Carcinoid tumors of the midgut (jejunum, ileum, appendix, and cecum) ...
, bronchial gland carcinomas, and sarcomatoid carcinomas. A subtype of adenocarcinoma, the bronchioloalveolar carcinoma
Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) of the lung ŌĆöpreviously included in the category of "bronchioloalveolar carcinoma" (BAC)ŌĆöis a subtype of lung adenocarcinoma. It tends to arise in the distal bronchioles or alveoli and is defined by a non-invasive ...
, is more common in females who have not smoked tobacco.
Staging
Lungcancer staging
Cancer staging is the process of determining the extent to which a cancer has developed by growing and spreading. Contemporary practice is to assign a number from I to IV to a cancer, with I being an isolated cancer and IV being a cancer that ha ...
is an assessment of the degree of spread of the cancer from its original source. It is one of the factors affecting both the prognosis
Prognosis (Greek: ŽĆŽüŽī╬│╬ĮŽēŽā╬╣Žé "fore-knowing, foreseeing") is a medical term for predicting the likely or expected development of a disease, including whether the signs and symptoms will improve or worsen (and how quickly) or remain stabl ...
and the potential treatment of lung cancer.
SCLC is typically staged with a relatively simple system; cancers are scored as either "limited stage" or "extensive stage". Around a third of people are diagnosed at the limited stage, meaning cancer is confined to one side of the chest, within the scope of a single tolerable radiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radia ...
field. The other two thirds are diagnosed at the "extensive stage", with cancer spread to both sides of the chest, or to other parts of the body.
NSCLC ŌĆō and sometimes SCLC ŌĆō is typically staged with the American Joint Committee on Cancer {{Short description, Organization standardising cancer staging
The American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) is an organization best known for defining and popularizing cancer staging standards, officially the AJCC staging system.
The American Joi ...
's Tumor, Node, Metastasis (TNM) staging system. The size and extent of the tumor (T), spread to regional lymph nodes (N), and distant metastases (M) are scored individually, and combined to form "stage groups". Relatively small tumors are designated T1, which are subdivided by size: tumors Ōēż 1 centimeter
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the Electromagnetic spectrum, measured by the Metre and its deriveds scales. The Microwave are in-between 1 meter to 1 millimeter.
A centimetre (international spelling) or centimeter (American spellin ...
(cm) across are T1a; 1ŌĆō2 cm T1b; 2ŌĆō3 cm T1c. Tumors up to 5 cm across, or those that have spread to the visceral pleura
The pulmonary pleurae (''sing.'' pleura) are the two opposing layers of serous membrane overlying the lungs and the inside of the surrounding chest walls.
The inner pleura, called the visceral pleura, covers the surface of each lung and dips bet ...
(tissue covering the lung) or main bronchi
A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts Atmosphere of Earth, air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi pronounced (BRAN-KAI) to branch from the trachea at the Carina of trachea, carina are the right ma ...
, are desginated T2. T2a designates 3ŌĆō4 cm tumors; T2b 4ŌĆō5 cm tumors. T3 tumors are up to 7 cm across, have multiple nodules in the same lobe
Lobe may refer to:
People with the name
* Lobe (surname)
Science and healthcare
* Lobe (anatomy)
* Lobe, a large-scale structure of a radio galaxy
* Glacial lobe, a lobe-shaped glacier
* Lobation, a characteristic of the nucleus of certain biolo ...
of the lung, or invade the chest wall
The thoracic wall or chest wall is the boundary of the thoracic cavity.
Structure
The bone, bony human skeleton, skeletal part of the thoracic wall is the rib cage, and the rest is made up of muscle, skin, and fasciae.
The chest wall has 10 lay ...
, diaphragm (or the nerve that controls it), or area around the heart. Tumors that are larger than 7 cm, have nodules spread in different lobes of a lung, or invade the mediastinum
The mediastinum (from ) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagu ...
(center of the chest cavity), heart, largest blood vessels that supply the heart, trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a Cartilage, cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends ...
, esophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the ...
, or spine
Spine or spinal may refer to:
Science Biology
* Vertebral column, also known as the backbone
* Dendritic spine, a small membranous protrusion from a neuron's dendrite
* Thorns, spines, and prickles, needle-like structures in plants
* Spine (zoolog ...
are designated T4. Lymph node staging depends on the extent of local spread: with the cancer metastasized to no lymph nodes (N0), pulmonary or hilar nodes (along the bronchi) on the same side as the tumor (N1), mediastinal or subcarinal lymph nodes (in the middle of the lungs, N2), or lymph nodes on the opposite side of the lung from the tumor (N3). Metastases are staged as no metastases (M0), nearby metastases (M1a; the space around the lung or the heart, or the opposite lung), a single distant metastasis (M1b), or multiple metastases (M1c). These T, N, and M scores are combined to designate a "stage grouping" for the cancer. Cancers limited to smaller tumors are designated stage I. Those with larger tumors or spread to the nearest lymph nodes are stage II. Those with the largest tumors or extensive lymph node spread are stage III. Cancers that have metastasized are stage IV. Each stage is further subdivided based on the combination of T, N, and M scores. Around 40% of those diagnosed with NSCLC have stage IV disease at the time of diagnosis.
For both NSCLC and SCLC, the two general types of staging evaluations are clinical staging and surgical staging. Clinical staging is performed before definitive surgery. It is based on the results of imaging studies (such as CT scans and PET scans
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, r ...
) and biopsy results. Surgical staging is evaluated either during or after the operation. It is based on the combined results of surgical and clinical findings, including surgical sampling of thoracic lymph nodes.
carina
Carina may refer to:
Places
Australia
* Carina, Queensland, a suburb in Brisbane
* Carina Heights, Queensland, a suburb in Brisbane
* Carina, Victoria, a locality in Mildura
Serbia
* Carina, Ose─Źina, a village in the Kolubara District
...
, this is stage 3
Diagram 1 of 3 showing stage 3A lung cancer CRUK 008.svg, Stage IIIA lung cancer
Diagram 2 of 3 showing stage 3A lung cancer CRUK 014.svg, Stage IIIA lung cancer, if there is one feature from the list on each side
Diagram 3 of 3 showing stage 3A lung cancer CRUK 017.svg, Stage IIIA lung cancer
Diagram 1 of 2 showing stage 3B lung cancer CRUK 005.svg, Stage IIIB lung cancer
Diagram 2 of 2 showing stage 3B lung cancer CRUK 011.svg, Stage IIIB lung cancer
Diagram showing stage 4 lung cancer CRUK 232.svg, Stage IV lung cancer
Treatment
Treatment for lung cancer depends on the cancer's specific cell type, how far it hasspread
Spread may refer to:
Places
* Spread, West Virginia
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Spread'' (film), a 2009 film.
* ''$pread'', a quarterly magazine by and for sex workers
* "Spread", a song by OutKast from their 2003 album ''Speakerboxxx/T ...
, and the person's performance status
In medicine (oncology and other fields), performance status is an attempt to quantify cancer patients' general well-being and activities of daily life. This measure is used to determine whether they can receive chemotherapy, whether dose adjustment ...
. Common treatments for early stage cancers include surgical removal of the tumor, chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherap ...
, and radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radia ...
. For later stage cancers, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are combined with newer targeted molecular therapies and immune checkpoint inhibitor
Cancer immunotherapy (sometimes called immuno-oncology) is the stimulation of the immune system to treat cancer, improving on the immune system's natural ability to fight the disease. It is an application of the fundamental research of cancer im ...
s. All lung cancer treatment regimens are combined with lifestyle changes and palliative care
Palliative care (derived from the Latin root , or 'to cloak') is an interdisciplinary medical caregiving approach aimed at optimizing quality of life and mitigating suffering among people with serious, complex, and often terminal illnesses. Wit ...
to improve quality of life.
Small-cell lung cancer
Limited-stage SCLC is typically treated with a combination of chemotherapy and radiotherapy. For chemotherapy, theNational Comprehensive Cancer Network
National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) is an alliance of 32 cancer centers in the United States, most of which are designated by the National Cancer Institute (one of the U.S. National Institutes of Health) as comprehensive cancer centers. It ...
and American College of Chest Physicians
The American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) is a medical association in the United States consisting of physicians and non-physician specialists in the field of chest medicine, which includes pulmonology, critical care medicine, and sleep med ...
guidelines recommend four to six cycles of a platinum-based chemotherapeutic ŌĆō cisplatin
Cisplatin is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of cancers. These include testicular cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, breast cancer, bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, esophageal cancer, lung cancer, mesothelioma, br ...
or carboplatin
Carboplatin, sold under the trade name Paraplatin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of forms of cancer. This includes ovarian cancer, lung cancer, head and neck cancer, brain cancer, and neuroblastoma. It is used b ...
ŌĆō combined with either etoposide
Etoposide, sold under the brand name Vepesid among others, is a chemotherapy medication used for the treatments of a number of types of cancer including testicular cancer, lung cancer, lymphoma, leukemia, neuroblastoma, and ovarian cancer. It is ...
or irinotecan
Irinotecan, sold under the brand name Camptosar among others, is a medication used to treat colon cancer, and small cell lung cancer. For colon cancer it is used either alone or with fluorouracil. For small cell lung cancer it is used with cispl ...
. This is typically combined with thoracic radiation therapy ŌĆō 45 Gray
Grey (more common in British English) or gray (more common in American English) is an intermediate color between black and white. It is a neutral or achromatic color, meaning literally that it is "without color", because it can be composed o ...
(Gy) twice-daily ŌĆō alongside the first two chemotherapy cycles. First-line therapy causes remission in up to 80% of those who receive it; however most people relapse with chemotherapy-resistant disease. Those who relapse are given second-line chemotherapies. Topotecan
Topotecan, sold under the brand name Hycamtin among others, is a chemotherapeutic agent medication that is a topoisomerase inhibitor. It is a synthetic, water-soluble analog of the natural chemical compound camptothecin. It is used in the form o ...
and lurbinectedin
Lurbinectedin, sold under the brand name Zepzelca, is a medication used for the treatment of small cell lung cancer.
The most common side effects include leukopenia, lymphopenia, fatigue, anemia, neutropenia, increased creatinine, increased al ...
are approved by the US FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food s ...
for this purpose. Irinotecan
Irinotecan, sold under the brand name Camptosar among others, is a medication used to treat colon cancer, and small cell lung cancer. For colon cancer it is used either alone or with fluorouracil. For small cell lung cancer it is used with cispl ...
, paclitaxel
Paclitaxel (PTX), sold under the brand name Taxol among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes ovarian cancer, esophageal cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, cervical cancer ...
, docetaxel
Docetaxel (DTX or DXL), sold under the brand name Taxotere among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes breast cancer, head and neck cancer, stomach cancer, prostate cancer and non-small-ce ...
, vinorelbine
Vinorelbine (NVB), sold under the brand name Navelbine among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes breast cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. It is given by injection into a vein or by mou ...
, etoposide, and gemcitabine
Gemcitabine, with brand names including Gemzar, is a chemotherapy medication. It treats cancers including testicular cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, and bladder cancer. It is administered by i ...
are also sometimes used, and are similarly efficacious. Prophylactic cranial irradiation
Prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) is a technique used to combat the occurrence of metastasis to the brain in highly aggressive cancers that commonly metastasize to brain, most notably small-cell lung cancer. Radiation therapy is commonly use ...
can also reduce the risk of brain metastases and improve survival in those with limited-stage disease.
Similarly, extensive-stage SCLC is treated first with etoposide along with either cisplatin or carboplatin. Radiotherapy is used only to shrink tumors that are causing particularly severe symptoms. Combining standard chemotherapy with an immune checkpoint inhibitor
Cancer immunotherapy (sometimes called immuno-oncology) is the stimulation of the immune system to treat cancer, improving on the immune system's natural ability to fight the disease. It is an application of the fundamental research of cancer im ...
can improve survival for a minority of those affected, extending the average person's lifespan by around 2 months.
Non-small-cell lung cancer
 For stage I and stage II NSCLC the first line of treatment is often surgical removal of the affected lobe of the lung. For those not well enough to tolerate full lobe removal, a smaller chunk of lung tissue can be removed by
For stage I and stage II NSCLC the first line of treatment is often surgical removal of the affected lobe of the lung. For those not well enough to tolerate full lobe removal, a smaller chunk of lung tissue can be removed by wedge resection
Wedge resection is a surgical procedure to remove a triangle-shaped slice of tissue. It may be used to remove a tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm ...
or segmentectomy
Segmental resection (or segmentectomy) is a surgical procedure to remove part of an organ or gland, as a sub-type of a resection, which might involve removing the whole body part. It may also be used to remove a tumor and normal tissue around it. ...
surgery. Those with centrally located tumors and otherwise-healthy respiratory systems may have more extreme surgery to remove an entire lung (pneumonectomy
A pneumonectomy (or pneumectomy) is a surgical procedure to remove a lung first successfully done in 1933 by Dr. Evarts Graham. This is not to be confused with a lobectomy or segmentectomy, which only removes one part of the lung.
There are two ...
). Experienced thoracic surgeon
Cardiothoracic surgery is the field of medicine involved in surgical treatment of organs inside the thoracic cavity ŌĆö generally treatment of conditions of the heart (heart disease), lungs (lung disease), and other pleural or mediastinal struc ...
s, and a high-volume surgery clinic improve chances of survival. Those who are unable or unwilling to undergo surgery can instead receive radiation therapy. Stereotactic body radiation therapy
Stereotactic radiation therapy (SRT), also called stereotactic external-beam radiation therapy and stereotaxic radiation therapy, is a type of external radiation therapy that uses special equipment to position the patient and precisely deliver rad ...
is best practice, typically administered several times over 1ŌĆō2 weeks. Chemotherapy has little effect in those with stage I NSCLC, and may worsen disease outcomes in those with the earliest disease. In those with stage II disease, chemotherapy is usually initiated six to twelve weeks after surgery, with up to four cycles of cisplatin ŌĆō or carboplatin
Carboplatin, sold under the trade name Paraplatin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of forms of cancer. This includes ovarian cancer, lung cancer, head and neck cancer, brain cancer, and neuroblastoma. It is used b ...
in those with kidney problems, neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, is a general term describing disease affecting the peripheral nerves, meaning nerves beyond the brain and spinal cord. Damage to peripheral nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland, or o ...
, or hearing impairment
Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to acquire spoken l ...
ŌĆō combined with vinorelbine
Vinorelbine (NVB), sold under the brand name Navelbine among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes breast cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. It is given by injection into a vein or by mou ...
, pemetrexed
Pemetrexed, sold under the brand name Alimta among others, is a chemotherapy medication for the treatment of pleural mesothelioma and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)..
It is available as a generic medication.
Medical use
In February 2004, t ...
, gemcitabine, or docetaxel
Docetaxel (DTX or DXL), sold under the brand name Taxotere among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes breast cancer, head and neck cancer, stomach cancer, prostate cancer and non-small-ce ...
.
immunotherapy
Immunotherapy or biological therapy is the treatment of disease by activating or suppressing the immune system. Immunotherapies designed to elicit or amplify an immune response are classified as ''activation immunotherapies,'' while immunotherap ...
durvalumab
Durvalumab (trade name Imfinzi) is an FDA-approved immunotherapy for cancer, developed by Medimmune/AstraZeneca. It is a human immunoglobulin G1 kappa (IgG1╬║) monoclonal antibody that blocks the interaction of programmed cell death ligand 1 ...
. Combined chemotherapy and radiation enhances survival compared to chemotherapy followed by radiation, though the combination therapy comes with harsher side effects.
Those with stage IV disease are treated with combinations of pain medication, radiotherapy, immunotherapy, and chemotherapy. Many cases of advanced disease can be treated with targeted therapies depending on the genetic makeup of the cancerous cells. Up to 30% of tumors have mutations in the '' EGFR'' gene that result in an overactive EGFR protein; these can be treated with EGFR inhibitors osimertinib
Osimertinib, sold under the brand name Tagrisso, is a medication used to treat non-small-cell lung carcinomas with specific mutations. It is a third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
The most common side eff ...
, erlotinib
Erlotinib, sold under the brand name Tarceva among others, is a medication used to treat non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and pancreatic cancer. Specifically it is used for NSCLC with mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) Ō ...
, gefitinib
Gefitinib, sold under the brand name Iressa, is a medication used for certain breast, lung and other cancers. Gefitinib is an EGFR inhibitor, like erlotinib, which interrupts signaling through the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in targe ...
, afatinib
Afatinib, sold under the brand name Gilotrif among others, is a medication used to treat non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). It belongs to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor family of medications. It is taken by mouth.
It is mainly used to treat ...
, or dacomitinib
Dacomitinib, sold under the brand name Vizimpro, is a medication for the treatment of non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). It is a selective and irreversible inhibitor of EGFR.
Dacomitinib has advanced to several Phase III clinical trials. ...
ŌĆō with osimertinib known to be superior to erlotinib and gefitinib, and all superior to chemotherapy alone. Up to 7% of those with NSCLC harbor mutations that result in hyperactive ALK protein, which can be treated with ALK inhibitor
ALK inhibitors are anti-cancer drugs that act on tumours with variations of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) such as an EML4- ALK translocation. They fall under the category of tyrosine kinase inhibitors, which work by inhibiting proteins involved ...
s crizotinib
Crizotinib, sold under the brand name Xalkori among others, is an anti-cancer medication used for the treatment of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). It acts as an ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) and ROS1 (c-ros oncogene 1) inhibitor.
Med ...
, or its successors alectinib
Alectinib (INN, marketed as Alecensa) is an oral drug that blocks the activity of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and is used to treat non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). It was developed by Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Japan, which is part of th ...
, brigatinib
Brigatinib, sold under the brand name Alunbrig among others, is a small-molecule targeted cancer therapy being developed by Ariad Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Brigatinib acts as both an anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and epidermal growth factor re ...
, and ceritinib
Ceritinib (INN, trade name Zykadia , from Novartis) is a prescription-only drug used for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). It was developed by Novartis and received FDA approval for use in April 2014..Ceritinib is also sold un ...
. Those treated with ALK inhibitors who relapse can then be treated with the third-generation ALK inhibitor lorlatinib
Lorlatinib, sold under the brand name Lorbrena in the United States, Canada, and Japan, and Lorviqua in the European Union, is an anti-cancer drug developed by Pfizer. It is an orally administered inhibitor of ALK and ROS1, two enzymes that play ...
. Up to 5% with NSCLC have overactive MET, which can be inhibited with MET inhibitors capmatinib
Capmatinib, sold under the brand name Tabrecta, is a medication for the treatment of adults with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have a mutation that leads to the exon 14 skipping of the ''MET'' gene, which codes for th ...
or tepotinib
Tepotinib, sold under the brand name Tepmetko, is an anti-cancer medication used for the treatment of adults with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
The most common side effects include edema (build-up of fluid), nausea (feeling sick), low alb ...
. Targeted therapies are also available for some cancers with rare mutations. Cancers with hyperactive BRAF (around 2% of NSCLC) can be treated by dabrafenib
Dabrafenib, sold under the brand name Tafinlar & Rafinlar ( both by Novartis) among others, is a medication for the treatment of cancers associated with a mutated version of the gene BRAF. Dabrafenib acts as an inhibitor of the associated enzym ...
combined with the MEK inhibitor A MEK inhibitor is a chemical or drug that inhibits the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase enzymes MEK1 and/or MEK2.
They can be used to affect the MAPK/ERK pathway which is often overactive in some cancers. (See MAPK/ERK pathway#Clinical sign ...
trametinib
Trametinib, sold under the brand name Mekinist among others, is an anticancer medication used for the treatment of melanoma. It is a MEK inhibitor drug with anti-cancer activity. It inhibits MEK1 and MEK2.
Trametinib had good results for metast ...
; those with activated ROS1
Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase ROS is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ROS1'' gene.
Function
This proto-oncogene, highly expressed in a variety of tumor cell lines, belongs to the sevenless subfamily of tyrosine kinase ins ...
(around 1% of NSCLC) can be inhibited by crizotinib, lorlatinib, or entrectinib
Entrectinib, sold under the brand name Rozlytrek, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat ROS1-positive non-small cell lung cancer and NTRK fusion-positive solid tumors. It is a selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), of the tropomyosin r ...
; overactive NTRK
Trk receptors are a family of tyrosine kinases that regulates synaptic strength and plasticity in the mammalian nervous system. Trk receptors affect neuronal survival and differentiation through several signaling cascades. However, the activati ...
(<1% of NSCLC) by entrectinib or larotrectinib
Larotrectinib, sold under the brand name Vitrakvi, is a medication for the treatment of cancer. It is an inhibitor of tropomyosin kinase receptors TrkA, TrkB, and TrkC. It was discovered by Array BioPharma and licensed to Loxo Oncology in 2013. ...
; active RET (around 1% of NSCLC) by selpercatinib
Selpercatinib, sold under the brand name Retevmo among others, is a medication for the treatment of cancers in people whose tumors have an alteration (mutation or fusion) in a specific gene (RET (gene), RET which is short for "rearranged during ...
.
People whose NSCLC is not targetable by current molecular targeted therapies instead can be treated with combination chemotherapy plus immune checkpoint inhibitor
Cancer immunotherapy (sometimes called immuno-oncology) is the stimulation of the immune system to treat cancer, improving on the immune system's natural ability to fight the disease. It is an application of the fundamental research of cancer im ...
s, which prevent cancer cells from inactivating immune T cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
s. The chemotherapeutic agent of choice depends on the NSCLC subtype: cisplatin plus gemcitabine for squamous cell carcinoma, cisplatin plus pemetrexed for non-squamous cell carcinoma. Immune checkpoint inhibitors are most effective against cancers that express the protein PD-L1
Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) also known as cluster of differentiation 274 (CD274) or B7 homolog 1 (B7-H1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CD274'' gene.
Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is a 40kDa type 1 transmembrane protei ...
, but are sometimes effective in those that do not. Treatment with pembrolizumab
Pembrolizumab, sold under the brand name Keytruda, is a humanized antibody used in cancer immunotherapy that treats melanoma, lung cancer, head and neck cancer, Hodgkin lymphoma, stomach cancer, cervical cancer, and certain types of breast canc ...
, atezolizumab
Atezolizumab, sold under the brand name Tecentriq, is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat urothelial carcinoma, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), small cell lung cancer (SCLC), hepatocellular ...
, or combination nivolumab
Nivolumab, sold under the brand name Opdivo, is a medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes melanoma, lung cancer, malignant pleural mesothelioma, renal cell carcinoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, head and neck cancer, urotheli ...
plus ipilimumab
Ipilimumab, sold under the brand name Yervoy, is a monoclonal antibody medication that works to activate the immune system by targeting CTLA-4, a protein receptor that downregulates the immune system.
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) can recognize ...
are all superior to chemotherapy alone against tumors expressing PD-L1. Those who relapse on the above are treated with second-line chemotherapeutics docetaxel
Docetaxel (DTX or DXL), sold under the brand name Taxotere among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes breast cancer, head and neck cancer, stomach cancer, prostate cancer and non-small-ce ...
and ramucirumab
Ramucirumab (LY3009806, IMC-1121B, trade name Cyramza) is a fully human monoclonal antibody (IgG1) developed for the treatment of solid tumors. This drug was developed by ImClone Systems Inc. It was isolated from a native phage display library f ...
.

 Several treatments can be provided via bronchoscopy for the management of airway obstruction or bleeding. If an airway becomes obstructed by cancer growth, options include rigid bronchoscopy, balloon bronchoplasty, stenting, and microdebridement. Laser photosection involves the delivery of laser light inside the airway via a bronchoscope to remove the obstructing tumor.
Several treatments can be provided via bronchoscopy for the management of airway obstruction or bleeding. If an airway becomes obstructed by cancer growth, options include rigid bronchoscopy, balloon bronchoplasty, stenting, and microdebridement. Laser photosection involves the delivery of laser light inside the airway via a bronchoscope to remove the obstructing tumor.
Palliative care
Integrating palliative care (i.e. medical care focused on improving symptoms and lessening discomfort) into lung cancer treatment from the time of diagnosis improves the survival time and quality of life of those with lung cancer. Particularly common symptoms of lung cancer are shortness of breath and pain. Supplemental oxygen, improved airflow, re-orienting an effected person in bed, and low-dosemorphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a analgesic, pain medication, and is also commonly used recreational drug, recreationally, or to make ...
can all improve shortness of breath. Other causes of lung cancer-associated shortness of breath can be treated directly, such as antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
s for a lung infection, diuretic
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics in ...
s for pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema, also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive edema, liquid accumulation in the parenchyma, tissue and pulmonary alveolus, air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. It leads to impaired gas exchange and may cause hypoxemia an ...
, benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), sometimes called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, ...
s for anxiety, and steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and a ...
s for airway obstruction. Up to 92% of those with lung cancer report pain, either from tissue damage at the tumor site(s) or nerve damage. The World Health Organization (WHO) has developed a three-tiered system for managing cancer pain. For those with mild pain (tier one), the WHO recommends acetominophen
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. Common brand names include Tylenol (brand), Tylenol and Panadol (brand), Panadol.
At a standard dose, paracetamol only slightly decreases ...
or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
. Around a third of people experience moderate (tier two) or severe (tier three) pain, for which the WHO recommends opioid painkillers. Opioids are typically effective at easing nociceptive pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, ...
(pain caused by damage to various body tissues). Opioids are occasionally effective at easing neuropathic pain
Neuropathic pain is pain caused by damage or disease affecting the somatosensory system. Neuropathic pain may be associated with abnormal sensations called dysesthesia or pain from normally non-painful stimuli (allodynia). It may have continuous ...
(pain cauesd by nerve damage); Neuropathic agents such as anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs or recently as antiseizure drugs) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of b ...
s, tricyclic antidepressant
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are a class of medications that are used primarily as antidepressants, which is important for the management of depression. They are second-line drugs next to SSRIs. TCAs were discovered in the early 1950s and wer ...
s, and serotoninŌĆōnorepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
SerotoninŌĆōnorepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are a class of antidepressant drugs used to treat major depressive disorder (MDD), anxiety disorders, obsessiveŌĆōcompulsive disorder (OCD), social phobia, attention-deficit hyperactivity dis ...
s, are often used to ease neuropathic pain, either alone or in combination with opioids.
For both NSCLC and SCLC patients, smaller doses of radiation to the chest may be used for symptom control (palliative
Palliative care (derived from the Latin root , or 'to cloak') is an interdisciplinary medical caregiving approach aimed at optimizing quality of life and mitigating suffering among people with serious, complex, and often terminal illnesses. Wit ...
radiotherapy). With adequate physical fitness
Physical fitness is a state of health and well-being and, more specifically, the ability to perform aspects of Outline of sports, sports, occupations and daily activities. Physical fitness is generally achieved through proper nutrition, moderate ...
maintaining chemotherapy during lung cancer palliation offers 1.5 to 3 months of prolongation of survival, symptomatic relief, and an improvement in quality of life, with better results seen with modern agents.
Palliative care when added to usual cancer care benefits people even when they are still receiving chemotherapy. These approaches allow additional discussion of treatment options and provide opportunities to arrive at well-considered decisions. Palliative care may avoid unhelpful but expensive care not only at the end of life, but also throughout the course of the illness. For individuals who have more advanced disease, hospice care
Hospice care is a type of health care that focuses on the palliation of a terminally ill patient's pain and symptoms and attending to their emotional and spiritual needs at the end of life. Hospice care prioritizes comfort and quality of life by ...
may also be appropriate.
Noninvasive interventions
The most effective intervention for avoiding death from lung cancer is to stop smoking; even people who already have lung cancer are encouraged to stop smoking. There is no clear evidence whichsmoking cessation
Smoking cessation, usually called quitting smoking or stopping smoking, is the process of discontinuing tobacco smoking. Tobacco smoke contains nicotine, which is addictive and can cause dependence. As a result, nicotine withdrawal often make ...
program is most effective for people who have been diagnosed with lung cancer.
Some weak evidence suggests that certain supportive care interventions (noninvasive
Minimally invasive procedures (also known as minimally invasive surgeries) encompass surgical techniques that limit the size of incisions needed, thereby reducing wound healing time, associated pain, and risk of infection. Surgery by definition ...
) that focus on well-being for people with lung cancer may improve quality of life. Interventions such as nurse follow-ups, psychotherapy
Psychotherapy (also psychological therapy, talk therapy, or talking therapy) is the use of psychological methods, particularly when based on regular personal interaction, to help a person change behavior, increase happiness, and overcome pro ...
, psychosocial
The psychosocial approach looks at individuals in the context of the combined influence that psychological factors and the surrounding social environment have on their physical and mental wellness and their ability to function. This approach is ...
therapy, and educational programs may be beneficial, however, the evidence is not strong (further research is needed). Counseling
Counseling is the professional guidance of the individual by utilizing psychological methods especially in collecting case history data, using various techniques of the personal interview, and testing interests and aptitudes.
This is a list of co ...
may help people cope with emotional symptoms related to lung cancer. Reflexology
Reflexology, also known as zone therapy, is an alternative medical practice involving the application of pressure to specific points on the feet, ears, and hands. This is done using thumb, finger, and hand massage techniques without the use of ...
may be effective in the short-term, however more research is needed. No evidence has been found to suggest that nutritional interventions or exercise programs for a person with lung cancer result in an improvement in the quality of life that are relevant or last very long.
Exercise training may benefit people with NSCLC who are recovering from lung surgery. In addition, exercise training may benefit people with NSCLC who have received radiotherapy, chemotherapy, chemoradiotherapy, or palliative care. Exercise training before lung cancer surgery may also improve outcomes. It is unclear if exercise training or exercise programs are beneficial for people who have advanced lung cancer. A home-based component in a personalized physical rehabilitation
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patient ...
program may be useful for recovery. It is unclear if home-based prehabilitation (before surgery) leads to less adverse events or hospitalization time. Physical rehabilitation with a home-based component may improve recovery after treatment and overall lung health.
Prognosis
Around 19% of people diagnosed with lung cancer survive five years from diagnosis. Five-year survival is higher in women (22%) than men (16%); women tend to be diagnosed with less-advanced disease, and have better outcomes than men diagnosed at the same stage. In England and Wales, between 2013 and 2017, overallfive-year survival
The five-year survival rate is a type of survival rate for estimating the prognosis of a particular disease, normally calculated from the point of diagnosis. Lead time bias from earlier diagnosis can affect interpretation of the five-year surviva ...
for lung cancer was estimated at 13.8%. Outcomes are generally worse in the developing world
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
. In the US, people with medical insurance
Health insurance or medical insurance (also known as medical aid in South Africa) is a type of insurance that covers the whole or a part of the risk of a person incurring medical expenses. As with other types of insurance, risk is shared among ma ...
are more likely to have a better outcome.
Survival for lung cancer falls as the stage at diagnosis becomes more advanced; the English data suggest that around 70% of patients survive at least a year when diagnosed at the earliest stage, but this falls to just 14% for those diagnosed with the most advanced disease (stage IV).
SCLC is particularly aggressive. Most people treated for SCLC relapse and eventually develop chemotherapy-resistant cancer. The average person diagnosed with SCLC at the limited stage survives 12ŌĆō20 months from diagnosis; the average person diagnosed at the extensive stage survives around 12 months. 10ŌĆō15% of people with SCLC survive 5 years after diagnosis. Those with limited stage SCLC that goes into complete remission after chemotherapy and radiotherapy have a 50% chance of brain metastases developing within the next two years ŌĆō a chance reduced by prophylactic cranial irradiation.
For NSCLC, the best prognosis is achieved with complete surgical resection of stage-IA disease, with up to 70% five-year survival. The prognosis of patients with NSCLC improved significantly in the last years with the introduction of immunotherapy. 68ŌĆō92% of those diagnosed with stage I NSCLC survive at least 5 years after diagnosis, as do 53ŌĆō60% of those diagnosed with stage II NSCLC.
Several personal and disease factors are associated with improved outcomes. Those diagnosed at an earlier disease stage tend to have better prognoses, as do those diagnosed at a younger age. Those who smoke or experience weight loss as a symptom tend to have worse outcomes. Large/active metastases (by PET scan) and tumor mutations in ''KRAS'' are associated with reduced survival.

Experience
The uncertainty of lung cancer prognosis often causes stress, and makes future planning difficult, for those with lung cancer and their families. Those whose cancer goes into remission often experience fear of their cancer returning or progressing, associated with poor quality of life, negative mood, and functional impairment. This fear is exacerbated by frequent or prolonged surveillance imaging, and other reminders of cancer risks.Causes
genetic damage
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitos ...
to DNA and epigenetic
In biology, epigenetics is the study of stable phenotypic changes (known as ''marks'') that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix '' epi-'' ( "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "o ...
changes. Those changes affect the cell's normal functions, including cell proliferation
Cell proliferation is the process by which ''a cell grows and divides to produce two daughter cells''. Cell proliferation leads to an exponential increase in cell number and is therefore a rapid mechanism of tissue growth. Cell proliferation re ...
, programmed cell death (apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ß╝ĆŽĆŽīŽĆŽäŽēŽā╬╣Žé, ap├│pt┼Źsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes incl ...
), and DNA repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA dam ...
. As more damage accumulates, the risk for cancer increases.
Smoking
Tobacco smoking
Tobacco smoking is the practice of burning tobacco and ingesting the resulting smoke. The smoke may be inhaled, as is done with cigarettes, or simply released from the mouth, as is generally done with pipes and cigars. The practice is believed ...
is by far the major contributor to lung cancer, causing 80% to 90% of cases. Across the developed world, 90% of lung cancer deaths in men and 70% of those in women during 2000 were attributed to smoking. Cigarette smoke
Tobacco smoke is a sooty aerosol produced by the incomplete combustion of tobacco during the smoking of cigarettes and other tobacco products. Temperatures in burning cigarettes range from about 400 ┬░C between puffs to about 900 ┬░C d ...
contains at least 73 known carcinogens, including benzo 'a''yrene, NNK
Nicotine-derived nitrosamine ketone (NNK) is one of the key tobacco-specific nitrosamines derived from nicotine. It plays an important role in carcinogenesis. The conversion of nicotine to NNK entails opening of the pyrrolidine ring.
Synthesis a ...
, 1,3-butadiene
1,3-Butadiene () is the organic compound with the formula (CH2=CH)2. It is a colorless gas that is easily condensed to a liquid. It is important industrially as a precursor to synthetic rubber. The molecule can be viewed as the union of two viny ...
, and a radioactive isotope
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferr ...
of polonium ŌĆō polonium-210
Polonium-210 (210Po, Po-210, historically radium F) is an isotope of polonium. It undergoes alpha decay to stable 206Pb with a half-life of 138.376 days (about months), the longest half-life of all naturally occurring polonium isotopes. First i ...
. Vaping
An electronic cigarette is an electronic device that simulates tobacco smoking. It consists of an atomizer, a power source such as a battery, and a container such as a cartridge or tank. Instead of smoke, the user inhales vapor. As such ...
may be a risk factor for lung cancer, but less than that of cigarettes, and further research is necessary due to the length of time it can take for lung cancer to develop following an exposure to carcinogens.
Being around tobacoo smoke ŌĆō called passive smoking
Passive smoking is the inhalation of tobacco smoke, called secondhand smoke (SHS), or environmental tobacco smoke (ETS), by persons other than the intended "active" smoker. It occurs when tobacco smoke enters an environment, causing its inhalat ...
ŌĆō can also cause lung cancer. Living with a tobacco smoker increaes one's risk of developing lung cancer by 24%. An estimated 17% of lung cancer cases in those who do not smoke are caused by high levels of environmental tobacco smoke.
Cannabis smoke contains many of the same carcinogen
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substan ...
s as those found in tobacco smoke, but the effect of smoking cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: ''Cannabis sativa'', '' C. indica'', and '' C. ruderalis''. Alternatively ...
on lung cancer risk is not clear.
Other exposures
Exposure to a variety of other toxic chemicals ŌĆō typically encountered in certain occupations ŌĆō are associated with an increased risk of lung cancer. In all, occupational exposures to carcinogens are estimated to cause 9ŌĆō15% of lung cancers. A prominent example isasbestos
Asbestos () is a naturally occurring fibrous silicate mineral. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous crystals, each fibre being composed of many microscopic "fibrils" that can be released into the atmosphere b ...
, which causes lung cancer either directly or indirectly by inflamming the lung. Exposure to all commercially available forms of asbestos increase cancer risk, and cancer risk increases with time of exposure. Asbestos and cigarette smoking increase risk synergestically ŌĆō i.e. the risk of someone who smokes and has asbestos exposure dying from lung cancer is much higher than would be expected from adding the two risks together. Similarly, exposure to radon
Radon is a chemical element with the symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colourless, odourless, tasteless noble gas. It occurs naturally in minute quantities as an intermediate step in the normal radioactive decay chains through ...
, a naturally occurring breakdown product of the Earth's uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
, is associated with increased lung cancer risk. This is particularly true in underground miners, who have the greatest exposure; but also in indoor air in residential spaces. Like asbestos, cigarette smoking and radon exposure increase risk synergistically. Radon exposure is responsible for between 3% and 14% of lung cancer cases.
Several other chemicals encountered in various occupations are also associated with increased lung cancer risk including arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but ...
used in wood preservation
Wood easily degrades without sufficient preservation. Apart from structural wood preservation measures, there are a number of different chemical preservatives and processes (also known as "timber treatment", "lumber treatment" or "pressure treat ...
, pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are meant to control pests. This includes herbicide, insecticide, nematicide, molluscicide, piscicide, avicide, rodenticide, bactericide, insect repellent, animal repellent, microbicide, fungicide, and lampri ...
application, and some ore smelting
Smelting is a process of applying heat to ore, to extract a base metal. It is a form of extractive metallurgy. It is used to extract many metals from their ores, including silver, iron, copper, and other base metals. Smelting uses heat and a ch ...
; ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation (or ionising radiation), including nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have sufficient energy to ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel ...
encountered during uranium mining
Uranium mining is the process of extraction of uranium ore from the ground. Over 50 thousand tons of uranium were produced in 2019. Kazakhstan, Canada, and Australia were the top three uranium producers, respectively, and together account f ...
; vinyl chloride
Vinyl chloride is an organochloride with the formula H2C=CHCl. It is also called vinyl chloride monomer (VCM) or chloroethene. This colorless compound is an important industrial chemical chiefly used to produce the polymer polyvinyl chloride (PVC ...
in papermaking
Papermaking is the manufacture of paper and cardboard, which are used widely for printing, writing, and packaging, among many other purposes. Today almost all paper is made using industrial machinery, while handmade paper survives as a speciali ...
; beryllium
Beryllium is a chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with other elements to form mi ...
in jeweler
A bench jeweler is an artisan who uses a combination of skills to make and repair jewelry. Some of the more common skills that a bench jeweler might employ include antique restoration, silversmith, Goldsmith, stone setting, engraving, fabrica ...
s, ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain ...
s workers, missile technicians, and nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction or nuclear fusion reactions. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat from nu ...
workers; chromium
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and hardne ...
in stainless steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's corros ...
production, welding
Welding is a fabrication (metal), fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by using high heat to melt the parts together and allowing them to cool, causing Fusion welding, fusion. Welding is distinct from lower ...
, and hide tanning; nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow to ...
in electroplate
Electroplating, also known as electrochemical deposition or electrodeposition, is a process for producing a metal coating on a solid substrate through the reduction of cations of that metal by means of a direct electric current. The part to be ...
rs, glass workers, metal workers, welders, and those who make batteries, ceramics, and jewelry; and diesel exhaust
Diesel exhaust is the gaseous exhaust produced by a diesel type of internal combustion engine, plus any contained particulates. Its composition may vary with the fuel type or rate of consumption, or speed of engine operation (e.g., idling or at ...
encountered by miners.
Outdoor air pollutants, especially chemicals released from the burning of fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels m ...
s, increase the risk of lung cancer. Fine particulates
Particulates ŌĆō also known as atmospheric aerosol particles, atmospheric particulate matter, particulate matter (PM) or suspended particulate matter (SPM) ŌĆō are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspended in the air. The ter ...
(PM2.5) and sulfate aerosols
The term sulfate aerosols is used for a suspension of fine solid particles of a sulfate or tiny droplets of a solution of a sulfate or of sulfuric acid (hydrogen sulfate). They are produced by chemical reactions in the atmosphere from gaseous prec ...
, which may be released in traffic exhaust fumes
Exhaust gas or flue gas is emitted as a result of the combustion of fuels such as natural gas, gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, fuel oil, biodiesel blends, or coal. According to the type of engine, it is discharged into the atmosphere through an ...
, are associated with a slightly increased risk. For nitrogen dioxide, an incremental increase of 10 parts per billion increases the risk of lung cancer by 14%. Outdoor air pollution is estimated to cause 1ŌĆō2% of lung cancers.
Indoor air pollution from burning Wood fuel, wood, Charcoal-burning, charcoal, or crop residue for cooking and heating has also been linked to an increased risk of developing lung cancer. The International Agency for Research on Cancer has classified emission from household burning of coal and biomass as "carcinogenic" and "probably carcinogenic" respectively. This risk affects about 2.4 billion people worldwide, and it is believed to result in 1.5% of lung cancer deaths.
Genetics
About 8% of lung cancer cases are caused by heredity, inherited (genetic) factors. In relatives of people who are diagnosed with lung cancer, the risk is doubled, likely due to a polygenic disorder, combination of genes. Genetic polymorphism, Polymorphisms on chromosomes 5, 6, and 15 have been identified and are associated with an increased risk of lung cancer. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms of the genes encoding the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) ŌĆō ''CHRNA5'', ''CHRNA3'', and ''CHRNB4'' ŌĆō are of those associated with an increased risk of lung cancer, as well as ''RGS17'' ŌĆō a gene regulating G protein#Signaling, G-protein signaling. Newer genetic studies, have identified 18 susceptibility loci achieving genome-wide significance. These loci highlight a heterogeneity in genetic susceptibility across the histological subtypes of lung cancer, again identifying the cholinergic nicotinic receptors, e.g. CHRNA2.Pathogenesis
Similar to many other cancers, lung cancer is initiated by either the activation of oncogenes or the inactivation of tumor suppressor genes. Carcinogens cause mutations in these genes that induce the development of cancer. Mutations in the ''Ras (protein), K-ras'' proto-oncogene contribute to roughly 10ŌĆō30% of lung adenocarcinomas. Nearly 4% of non-small-cell lung carcinomas involve an EML4-ALK positive lung cancer, EML4-ALK tyrosine kinase fusion gene. The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) regulates cell proliferation,apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ß╝ĆŽĆŽīŽĆŽäŽēŽā╬╣Žé, ap├│pt┼Źsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes incl ...
, angiogenesis, and tumor invasion. Mutations and Amplification of DNA, amplification of EGFR are common in NSCLC, and they provide the basis for treatment with EGFR inhibitors. ''Her2/neu'' is affected less frequently. Other genes that are often mutated or amplified include ''c-MET'', ''NKX2-1'', ''LKB1'', ''PIK3CA'', and '' BRAF''.
Importantly, cancer cells develop resistance to oxidative stress, which enables them to withstand and exacerbate Inflammation, inflammatory conditions that inhibit the activity of the immune system against the tumor.
The Cell lineage, cell lines of origin are not fully understood. The mechanism may involve the abnormal activation of stem cells. In the proximal airways, stem cells that express keratin 5 are more likely to be affected, typically leading to Squamous cell lung carcinoma, squamous-cell lung carcinoma. In the middle airways, implicated stem cells include club cells and neuroepithelial cells that express uteroglobin, club-cell secretory protein. SCLC may originate from these cell lines or neuroendocrine cells, and it may express CD44. Metastasis of lung cancer requires EpithelialŌĆōmesenchymal transition, transition from Epithelium, epithelial to mesenchyme, mesenchymal cell type. This may occur through the activation of signaling pathways such as Protein kinase B, Akt/GSK3Beta, MAPK/ERK pathway, MEK-ERK, Fas receptor, Fas, and Par6.
The overwhelming majority of SCLCs have mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressors p53 and RB.
Prevention
 Smoking prevention and
Smoking prevention and smoking cessation
Smoking cessation, usually called quitting smoking or stopping smoking, is the process of discontinuing tobacco smoking. Tobacco smoke contains nicotine, which is addictive and can cause dependence. As a result, nicotine withdrawal often make ...
are effective ways of reducing the risk of lung cancer.
Smoking cessation
Those who smoke can reduce their lung cancer risk by quitting smoking ŌĆō the risk reduction is greater the longer a person goes without smoking. Self-help programs tend to have little influence on success of smoking cessation, whereas combined counseling and pharmacotherapy improve cessation rates. The U.S. FDA has approved antidepressant therapies and the nicotine replacement varenicline as first-line therapies to aid in smoking cessation. Clonidine and nortriptyline are recommended second-line therapies.Tobacco control
While in most countries industrial and domestic carcinogens have been identified and banned, tobacco smoking is still widespread. Eliminating tobacco smoking is a primary goal in the prevention of lung cancer, and smoking cessation is an important preventive tool in this process. Policy interventions to decreasepassive smoking
Passive smoking is the inhalation of tobacco smoke, called secondhand smoke (SHS), or environmental tobacco smoke (ETS), by persons other than the intended "active" smoker. It occurs when tobacco smoke enters an environment, causing its inhalat ...
in public areas such as restaurants and workplaces have become more common in many Western world, Western countries. Bhutan has had a complete smoking ban since 2005 while India introduced a ban on smoking in public in October 2008. The World Health Organization has called for governments to institute a total ban on tobacco advertising to prevent young people from taking up smoking. They assess that such bans have reduced tobacco consumption by 16% where instituted.
Screening
Some forms of population screening can allow for earlier detection and treatment of lung cancer cases, reducing deaths from lung cancer. In some trials, screening programs providing low-dose CT scans of individuals at high risk for lung cancer (i.e. people who smoke tobacco and are aged 55 to 74) reduced overall lung cancer mortality. The United States Preventive Services Task Force recommends yearly screening using low-dose CT in those who have a total smoking history of at least 30 pack-years and are between 55 and 80 years old.Other prevention strategies
The long-term use of supplemental vitamin A, B vitamins, vitamin D or vitamin E does not reduce the risk of lung cancer. Vitamin C supplementation might reduce the risk of lung cancer. Some studies have found vitamins A, B, and E may increase the risk of lung cancer in those who have a history of smoking. Some studies suggest that people who eat food with a higher proportion of vegetables and fruit tend to have a lower risk, but this may be due to confoundingwith the lower risk actually due to the association of a high fruit and vegetables diet with less smoking. Several rigorous studies have not demonstrated a clear association between diet and lung cancer risk, although meta-analysis that accounts for smoking status may show benefit from a healthy diet.Epidemiology
Worldwide, lung cancer is the most diagnosed type of cancer, and the leading cause of cancer death. In 2020, 2.2 million new cases were diagnosed, and 1.8 million people died from lung cancer, representing 18% of all cancer deaths. Lung cancer deaths are expected to rise globally to nearly 3 million annual deaths by 2035, due to high rates of tobacco use and aging populations. Lung cancer is rare in those younger than 40; from there cancer rates increase with age, stabilizing around age 80. The median age of a person diagnosed with lung cancer is 70; the median age of death is 72. Lung cancer incidence varies dramatically by geography and sex, with the highest rates in Micronesia, Polynesia, Europe, Asia, and North America; and lowest rates in Africa and Central America. Globally, around 8% of men and 6% of women develop lung cancer in their lifetimes. However, the ratio of lung cancer cases in men to women varies dramatically by geography, as high as nearly 12:1 in Belarus, to 1:1 in Brazil, likely due to differences in smoking patterns. In the United States, lung cancer remains the most common cause of cancer deaths, despite a nearly 50% decrease in the death rate from its peak in 1990. Lung cancer is the third-most common cancer in the UK (47,968 people were diagnosed with the disease in 2017), and it is the most common cause of cancer-related death (around 34,600 people died in 2018). In the US, lung cancer rates also vary by racial and ethnic group, with the highest rates in African Americans, and the lowest rates in Hispanics, Native American in the United States, Native Americans and Asian Americans. Also in the US, military veterans have a 25ŌĆō50% higher rate of lung cancer primarily due to higher rates of smoking. During World War II and the Korean War, asbestos also played a role, and Agent Orange may have caused some problems during the Vietnam War. Lung cancer risk is dramatically influenced by environmental exposure, namely cigarette smoking, as well as occupational risks in mining, shipbuilding, petroleum refining, and occupations that involve asbestos exposure. 85ŌĆō90% of lung cancer cases are in people who have smoked cigarettes, and 15% of smokers develop lung cancer. People who have a long history of smoking have the highest risk of developing lung cancer, with the risk increasing with duration of smoking. The incidence in men rose until the mid-1980s, and has declined since then. In women, the incidence rose until the late 1990s, and has since been stable. Non-smokers' risk of developing lung cancer is also influenced by tobacco smoking; secondhand smoke (i.e. being around tobacco smoke) increases risk of developing lung cancer around 30%, with risk correlated to duration of exposure. For every 3ŌĆō4 million cigarettes smoked, one lung cancer death can occur. The influence of "Big Tobacco" plays a significant role in smoking. Young nonsmokers who see Nicotine marketing, tobacco advertisements are more likely to smoke. The role of passive smoking is increasingly being recognized as a risk factor for lung cancer, resulting in policy interventions to decrease the undesired exposure of nonsmokers to others' tobacco smoke. From the 1960s, the rates of lung adenocarcinoma started to rise in relation to other kinds of lung cancer, partially due to the introduction of filter cigarettes. The use of filters removes larger particles from tobacco smoke, thus reducing deposition in larger airways. However, the smoker has to inhale more deeply to receive the same amount of nicotine, increasing particle deposition in small airways where adenocarcinoma tends to arise. Rates of lung adenocarcinoma continues to rise.History
Lung cancer was uncommon before the advent of cigarette smoking; it was not even recognized as a distinct disease until 1761. Different aspects of lung cancer were described further in 1810. Malignant lung tumors made up only 1% of all cancers seen at autopsy in 1878, but had risen to 10ŌĆō15% by the early 1900s. Case reports in the medical literature numbered only 374 worldwide in 1912, but a review of autopsies showed the incidence of lung cancer had increased from 0.3% in 1852 to 5.66% in 1952. In Germany in 1929, physician Fritz Lickint recognized the link between smoking and lung cancer, which led to an aggressive Anti-tobacco movement in Nazi Germany, antismoking campaign. The British Doctors Study, British Doctors' Study, published in the 1950s, was the first solid epidemiology, epidemiological evidence of the link between lung cancer and smoking. As a result, in 1964, the Surgeon General of the United States recommended smokers should stop smoking. The connection withradon
Radon is a chemical element with the symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colourless, odourless, tasteless noble gas. It occurs naturally in minute quantities as an intermediate step in the normal radioactive decay chains through ...
gas was first recognized among miners in the Ore Mountains (Germany), Ore Mountains near Schneeberg, Saxony. Silver has been mined there since 1470, and these mines are rich in uranium, with its accompanying radium and radon gas. Miners developed a disproportionate amount of lung disease, eventually recognized as lung cancer in the 1870s. Despite this discovery, mining continued into the 1950s, due to the USSR's demand for uranium. Radon was confirmed as a cause of lung cancer in the 1960s.
The first successful pneumonectomy
A pneumonectomy (or pneumectomy) is a surgical procedure to remove a lung first successfully done in 1933 by Dr. Evarts Graham. This is not to be confused with a lobectomy or segmentectomy, which only removes one part of the lung.
There are two ...
for lung cancer was performed in 1933. Palliative radiotherapy has been used since the 1940s. Radical radiotherapy, initially used in the 1950s, was an attempt to use larger radiation doses in patients with relatively early-stage lung cancer, but who were otherwise unfit for surgery. In 1997, CHART was seen as an improvement over conventional radical radiotherapy. With SCLC, initial attempts in the 1960s at surgical resection and radical radiotherapy were unsuccessful. In the 1970s, successful chemotherapy regimens were developed.
Research directions
The search for new treatment options continues. Many clinical trials involving radiotherapy, surgery, EGFR inhibitors, microtubule inhibitors and immunotherapy are currently underway. Research directions for lung cancer treatment includeimmunotherapy
Immunotherapy or biological therapy is the treatment of disease by activating or suppressing the immune system. Immunotherapies designed to elicit or amplify an immune response are classified as ''activation immunotherapies,'' while immunotherap ...
, which encourages the body's immune system to attack the tumor cells, epigenetics, and new combinations of chemotherapy and radiotherapy, both on their own and together. Many of these new treatments work through immune checkpoint blockade, disrupting cancer's ability to evade the immune system.
Ipilimumab blocks Signal transduction, signaling through a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor on T cells known as CTLA-4, which dampens down the immune system. It has been approved by the US U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Food and Drug Administration for treatment of melanoma, and is undergoing clinical trials for both NSCLC and SCLC.
Other immunotherapy treatments interfere with the binding of programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) protein with its ligand programmed cell death 1 ligand 1, PD-1 ligand 1 (PD-L1), and have been approved as first- and subsequent-line treatments for various subsets of lung cancers. Signaling through PD-1 inactivates T cells. Some cancer cells appear to exploit this by expressing PD-L1 in order to switch off T cells that might recognise them as a threat. Monoclonal antibodies targeting both PD-1 and PD-L1, such as pembrolizumab
Pembrolizumab, sold under the brand name Keytruda, is a humanized antibody used in cancer immunotherapy that treats melanoma, lung cancer, head and neck cancer, Hodgkin lymphoma, stomach cancer, cervical cancer, and certain types of breast canc ...
, nivolumab
Nivolumab, sold under the brand name Opdivo, is a medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes melanoma, lung cancer, malignant pleural mesothelioma, renal cell carcinoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, head and neck cancer, urotheli ...
, atezolizumab
Atezolizumab, sold under the brand name Tecentriq, is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat urothelial carcinoma, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), small cell lung cancer (SCLC), hepatocellular ...
, and durvalumab
Durvalumab (trade name Imfinzi) is an FDA-approved immunotherapy for cancer, developed by Medimmune/AstraZeneca. It is a human immunoglobulin G1 kappa (IgG1╬║) monoclonal antibody that blocks the interaction of programmed cell death ligand 1 ...
are currently in clinical trials for treatment for lung cancer.
Epigenetics is the study of small molecular modificationsor "tags"that bind to DNA and modify gene expression levels. Targeting these tags with drugs can kill cancer cells. Early-stage research in NSCLC using drugs aimed at epigenetic modifications shows that blocking more than one of these tags can kill cancer cells with fewer side effects. Studies also show that giving people these drugs before standard treatment can improve its effectiveness. Clinical trials are underway to evaluate how well these drugs kill lung cancer cells in humans. Several drugs that target epigenetic mechanisms are in development. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in development include valproic acid, vorinostat, belinostat, panobinostat, entinostat, and romidepsin. DNA methyltransferase inhibitors in development include decitabine, azacitidine, azacytidine, and hydralazine.
The TRACERx project is looking at how NSCLC develops and evolves, and how these tumors become resistant to treatment. The project will look at tumor samples from 850 people with NSCLC at various stages including diagnosis, after first treatment, post-treatment, and relapse. By studying samples at different points of tumor development, the researchers hope to identify the changes that drive tumor growth and resistance to treatment. The results of this project will help scientists and doctors gain a better understanding of NSCLC and potentially lead to the development of new treatments for the disease.
For lung cancer cases that develop resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) Kinase tyrosine-based inhibitory motif, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, new drugs are in development. EGFR inhibitors include erlotinib
Erlotinib, sold under the brand name Tarceva among others, is a medication used to treat non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and pancreatic cancer. Specifically it is used for NSCLC with mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) Ō ...
, gefitinib
Gefitinib, sold under the brand name Iressa, is a medication used for certain breast, lung and other cancers. Gefitinib is an EGFR inhibitor, like erlotinib, which interrupts signaling through the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in targe ...
, afatinib
Afatinib, sold under the brand name Gilotrif among others, is a medication used to treat non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). It belongs to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor family of medications. It is taken by mouth.
It is mainly used to treat ...
and icotinib (the last one is only available in China). An alternative signaling pathway, c-Met, can be inhibited by tivantinib and onartuzumab. New ALK inhibitors include crizotinib
Crizotinib, sold under the brand name Xalkori among others, is an anti-cancer medication used for the treatment of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). It acts as an ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) and ROS1 (c-ros oncogene 1) inhibitor.
Med ...
and ceritinib
Ceritinib (INN, trade name Zykadia , from Novartis) is a prescription-only drug used for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). It was developed by Novartis and received FDA approval for use in April 2014..Ceritinib is also sold un ...
. If the MAPK/ERK pathway is involved, the BRAF kinase inhibitor dabrafenib
Dabrafenib, sold under the brand name Tafinlar & Rafinlar ( both by Novartis) among others, is a medication for the treatment of cancers associated with a mutated version of the gene BRAF. Dabrafenib acts as an inhibitor of the associated enzym ...
and the MAPK/MEK inhibitor trametinib
Trametinib, sold under the brand name Mekinist among others, is an anticancer medication used for the treatment of melanoma. It is a MEK inhibitor drug with anti-cancer activity. It inhibits MEK1 and MEK2.
Trametinib had good results for metast ...
may be beneficial.
The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, PI3K pathway has been investigated as a target for lung cancer therapy. The most promising strategies for targeting this pathway seem to be selective inhibition of one or more members of the Class I PI 3-kinases, class I PI3Ks, and co-targeted inhibition of this pathway with others such as MEK.
Lung cancer stem cells are often resistant to conventional chemotherapy and radiotherapy. This may lead to relapse after treatment. New approaches target protein or glycoprotein markers that are specific to the stem cells. Such markers include CD133, CD90, ALDH1A1, CD44, and ABCG2. Cell signaling, Signaling pathways such as Hedgehog signaling pathway, Hedgehog, Wnt signaling pathway, Wnt, and Notch signaling pathway, Notch are often implicated in the self-renewal of stem cell lines. Thus, treatments targeting these pathways may help to prevent relapse.
See also
* Cancer recurrence#Lung cancer, Recurrence of lung cancerReferences
Cited
* * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Lung cancer Lung cancer, Causes of death Types of cancer Health effects of tobacco