|
Atelectasis
Atelectasis is the collapse or closure of a lung resulting in reduced or absent gas exchange. It is usually unilateral, affecting part or all of one lung. It is a condition where the alveoli are deflated down to little or no volume, as distinct from pulmonary consolidation, in which they are filled with liquid. It is often called a ''collapsed lung'', although that term may also refer to pneumothorax. It is a very common finding in chest X-rays and other radiological studies, and may be caused by normal exhalation or by various medical conditions. Although frequently described as a ''collapse of lung tissue'', atelectasis is not synonymous with a pneumothorax, which is a more specific condition that can cause atelectasis. Acute atelectasis may occur as a post-operative complication or as a result of surfactant deficiency. In premature babies, this leads to infant respiratory distress syndrome. The term uses combining forms of ''atel-'' + ''ectasis'', from el, ἀτελής, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atelectasis
Atelectasis is the collapse or closure of a lung resulting in reduced or absent gas exchange. It is usually unilateral, affecting part or all of one lung. It is a condition where the alveoli are deflated down to little or no volume, as distinct from pulmonary consolidation, in which they are filled with liquid. It is often called a ''collapsed lung'', although that term may also refer to pneumothorax. It is a very common finding in chest X-rays and other radiological studies, and may be caused by normal exhalation or by various medical conditions. Although frequently described as a ''collapse of lung tissue'', atelectasis is not synonymous with a pneumothorax, which is a more specific condition that can cause atelectasis. Acute atelectasis may occur as a post-operative complication or as a result of surfactant deficiency. In premature babies, this leads to infant respiratory distress syndrome. The term uses combining forms of ''atel-'' + ''ectasis'', from el, ἀτελής, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleural Effusion
A pleural effusion is accumulation of excessive fluid in the pleural space, the potential space that surrounds each lung. Under normal conditions, pleural fluid is secreted by the parietal pleural capillaries at a rate of 0.6 millilitre per kilogram weight per hour, and is cleared by lymphatic absorption leaving behind only 5–15 millilitres of fluid, which helps to maintain a functional vacuum between the parietal and visceral pleurae. Excess fluid within the pleural space can impair inspiration by upsetting the functional vacuum and hydrostatically increasing the resistance against lung expansion, resulting in a fully or partially collapsed lung. Various kinds of fluid can accumulate in the pleural space, such as serous fluid (hydrothorax), blood (hemothorax), pus (pyothorax, more commonly known as pleural empyema), chyle ( chylothorax), or very rarely urine (urinothorax). When unspecified, the term "pleural effusion" normally refers to hydrothorax. A pleural effusion can a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Surfactant
Pulmonary surfactant is a surface-active complex of phospholipids and proteins formed by type II alveolar cells. The proteins and lipids that make up the surfactant have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water. Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, t ... regions. By adsorption, adsorbing to the air-water Interface (chemistry), interface of pulmonary alveolus, alveoli, with hydrophilic head groups in the water and the hydrophobic tails facing towards the air, the main lipid component of surfactant, dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), reduces surface tension. As a medication, Pulmonary surfactant (medication), pulmonary surfactant is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, the most important medications needed in a basic health system. Function * To increase pulmonary com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
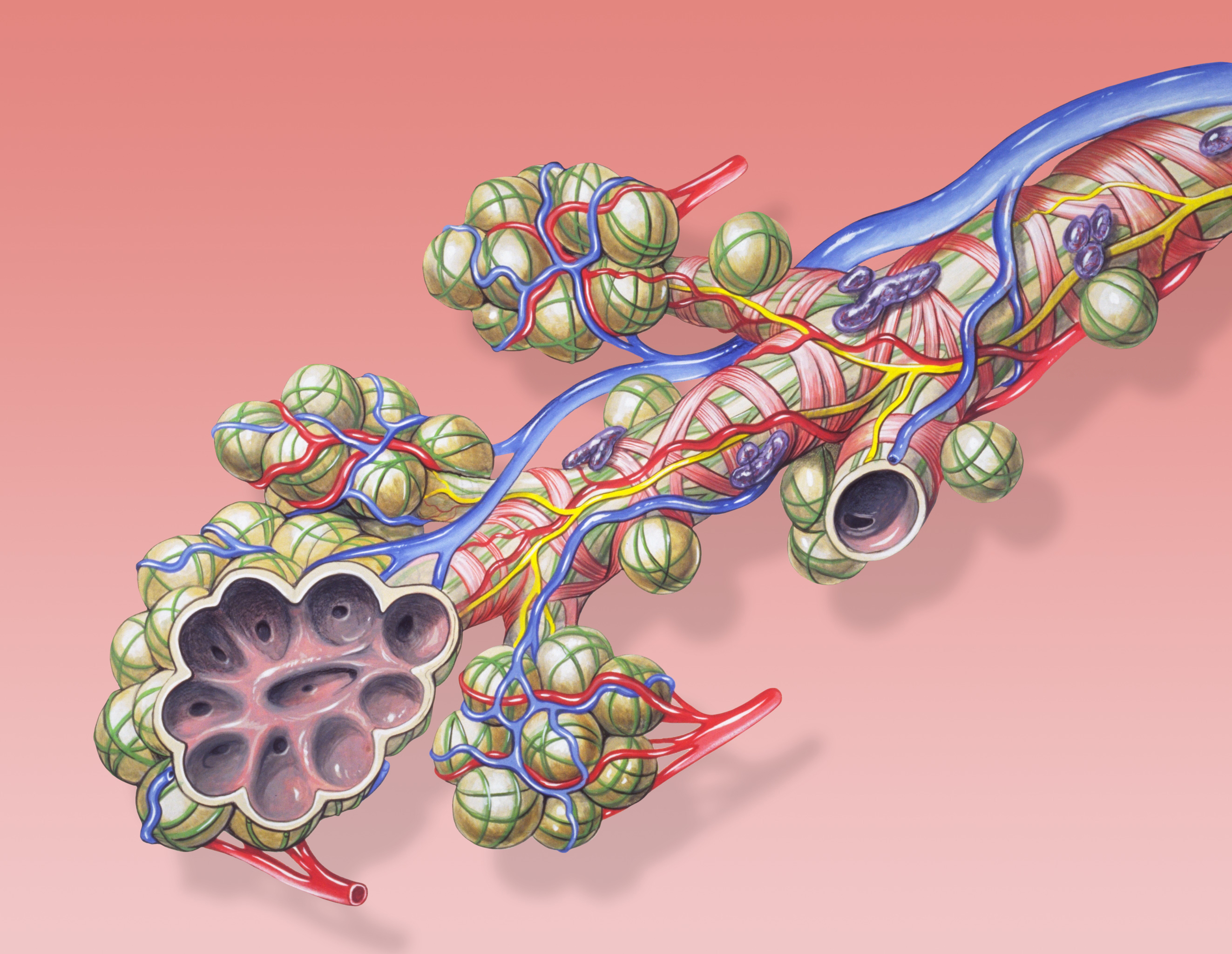
Pulmonary Alveolus
A pulmonary alveolus (plural: alveoli, from Latin ''alveolus'', "little cavity"), also known as an air sac or air space, is one of millions of hollow, distensible cup-shaped cavities in the lungs where oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide. Alveoli make up the functional tissue of the mammalian lungs known as the lung parenchyma, which takes up 90 percent of the total lung volume. Alveoli are first located in the respiratory bronchioles that mark the beginning of the respiratory zone. They are located sparsely in these bronchioles, line the walls of the alveolar ducts, and are more numerous in the blind-ended alveolar sacs. The acini are the basic units of respiration, with gas exchange taking place in all the alveoli present. The alveolar membrane is the gas exchange surface, surrounded by a network of capillaries. Across the membrane oxygen is diffused into the capillaries and carbon dioxide released from the capillaries into the alveoli to be breathed out. Alveoli are pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Surfactant
Pulmonary surfactant is a surface-active complex of phospholipids and proteins formed by type II alveolar cells. The proteins and lipids that make up the surfactant have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water. Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, t ... regions. By adsorption, adsorbing to the air-water Interface (chemistry), interface of pulmonary alveolus, alveoli, with hydrophilic head groups in the water and the hydrophobic tails facing towards the air, the main lipid component of surfactant, dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), reduces surface tension. As a medication, Pulmonary surfactant (medication), pulmonary surfactant is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, the most important medications needed in a basic health system. Function * To increase pulmonary com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectasis
Ectasia (), also called ectasis (), is dilation or distention of a tubular structure, either normal or Pathophysiology, pathophysiologic but usually the latter (except in atelectasis, where absence of ectasis is the problem). Specific conditions * Bronchiectasis, chronic dilatation of the bronchi * Duct ectasia of breast, a dilated milk duct. Duct ectasia syndrome is a synonym for nonpuerperal (unrelated to pregnancy and breastfeeding) mastitis. * Dural ectasia, dilation of the dural sac surrounding the spinal cord, usually in the very low back. * Pyelectasis, dilation of a part of the kidney, most frequently seen in prenatal ultrasounds. It usually resolves on its own. * Rete tubular ectasia, dilation of tubular structures in the testicles. It is usually found in older men. * Acral arteriolar ectasia * Keratoconus, Corneal ectasia (secondary keratoconus), a bulging of the cornea. ;Vascular ectasias * Most broadly, any abnormal dilatation of a blood vessel, including aneurysms * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chest X-ray
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in medicine. Like all methods of radiography, chest radiography employs ionizing radiation in the form of X-rays to generate images of the chest. The mean radiation dose to an adult from a chest radiograph is around 0.02 mSv (2 mrem) for a front view (PA, or posteroanterior) and 0.08 mSv (8 mrem) for a side view (LL, or latero-lateral). Together, this corresponds to a background radiation equivalent time of about 10 days. Medical uses Conditions commonly identified by chest radiography * Pneumonia * Pneumothorax * Interstitial lung disease * Heart failure * Bone fracture * Hiatal hernia Chest radiographs are used to diagnose many conditions involving the chest wall, including its bones, and also structures contained within the thoracic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumothorax
A pneumothorax is an abnormal collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve is formed by an area of damaged tissue, and the amount of air in the space between chest wall and lungs increases; this is called a tension pneumothorax. This can cause a steadily worsening oxygen shortage and low blood pressure. This leads to a type of shock called obstructive shock, which can be fatal unless reversed. Very rarely, both lungs may be affected by a pneumothorax. It is often called a "collapsed lung", although that term may also refer to atelectasis. A primary spontaneous pneumothorax is one that occurs without an apparent cause and in the absence of significant lung disease. A secondary spontaneous pneumothorax occurs in the presence of existing lung disease. Smoking increases the risk of primary spontaneous pneumothora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. water striders) to float on a water surface without becoming even partly submerged. At liquid–air interfaces, surface tension results from the greater attraction of liquid molecules to each other (due to cohesion) than to the molecules in the air (due to adhesion). There are two primary mechanisms in play. One is an inward force on the surface molecules causing the liquid to contract. Second is a tangential force parallel to the surface of the liquid. This ''tangential'' force is generally referred to as the surface tension. The net effect is the liquid behaves as if its surface were covered with a stretched elastic membrane. But this analogy must not be taken too far as the tension in an elastic membrane is dependent on the amount of deformation of the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inhalation
Inhalation (or Inspiration) happens when air or other gases enter the lungs. Inhalation of air Inhalation of air, as part of the cycle of breathing, is a vital process for all human life. The process is autonomic (though there are exceptions in some disease states) and does not need conscious control or effort. However, breathing can be consciously controlled or interrupted (within limits). Breathing allows oxygen (which humans and a lot of other species need for survival) to enter the lungs, from where it can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Other substances – accidental Examples of accidental inhalation includes inhalation of water (e.g. in drowning), smoke, food, vomitus and less common foreign substances (e.g. tooth fragments, coins, batteries, small toy parts, needles). Other substances – deliberate Recreational use Legal – helium, nitrous oxide ("laughing gas") Illegal – various gaseous, vaporised or aerosolized recreational drugs Medical use Diag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronchiole
The bronchioles or bronchioli (pronounced ''bron-kee-oh-lee'') are the smaller branches of the bronchial airways in the lower respiratory tract. They include the terminal bronchioles, and finally the respiratory bronchioles that mark the start of the respiratory zone delivering air to the gas exchanging units of the alveoli. The bronchioles no longer contain the cartilage that is found in the bronchi, or glands in their submucosa. Structure The pulmonary lobule is the portion of the lung ventilated by one bronchiole. Bronchioles are approximately 1 mm or less in diameter and their walls consist of ciliated cuboidal epithelium and a layer of smooth muscle. Bronchioles divide into even smaller bronchioles, called ''terminal'', which are 0.5 mm or less in diameter. Terminal bronchioles in turn divide into smaller respiratory bronchioles which divide into alveolar ducts. Terminal bronchioles mark the end of the conducting division of air flow in the respiratory system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. It was historically referred to as consumption due to the weight loss associated with the disease. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is spread from one person to the next through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with Latent TB do not spread the disease. Active infection occurs more often in people with HIV/AIDS and in those who smoke. Diagnosis of active TB is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |