Alkylating Agents on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Alkylation is the transfer of an 
 The SN2 mechanism is not available for aryl substituents, where the trajectory to attack the carbon atom would be inside the ring. Thus only reactions catalyzed by organometallic catalysts are possible.
The SN2 mechanism is not available for aryl substituents, where the trajectory to attack the carbon atom would be inside the ring. Thus only reactions catalyzed by organometallic catalysts are possible.
R-OH + R'-X -> R-O-R'
When the alkylating agent is an alkyl halide, the conversion is called the Ph-O- + Me2-SO4 -> Ph-O-Me + Me-SO4-
:(with as a
 Electrophilic alkylating agents deliver the equivalent of an alkyl
Electrophilic alkylating agents deliver the equivalent of an alkyl
 Electrophilic alkylations use
Electrophilic alkylations use C2H4 + CH3CO2H -> CH3CO2C2H5
 In
In

 In a conventional
In a conventional
Macrogalleria page on polycarbonate production
* {{Authority control Industrial processes Oil refining Organic reactions Chemical processes
alkyl
In organic chemistry, an alkyl group is an alkane missing one hydrogen.
The term ''alkyl'' is intentionally unspecific to include many possible substitutions.
An acyclic alkyl has the general formula of . A cycloalkyl is derived from a cycloalk ...
group from one molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioch ...
to another. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation
A carbocation is an ion with a positively charged carbon atom. Among the simplest examples are the methenium , methanium and vinyl cations. Occasionally, carbocations that bear more than one positively charged carbon atom are also encountere ...
, a free radical
A daughter category of ''Ageing'', this category deals only with the biological aspects of ageing.
Ageing
Ailments of unknown cause
Biogerontology
Biological processes
Causes of death
Cellular processes
Gerontology
Life extension
Metabo ...
, a carbanion
In organic chemistry, a carbanion is an anion in which carbon is trivalent (forms three bonds) and bears a formal negative charge (in at least one significant resonance form).
Formally, a carbanion is the conjugate base of a carbon acid:
:R3C ...
, or a carbene
In organic chemistry, a carbene is a molecule containing a neutral carbon atom with a valence of two and two unshared valence electrons. The general formula is or where the R represents substituents or hydrogen atoms.
The term "carbene" ma ...
(or their equivalents). Alkylating agents are reagent
In chemistry, a reagent ( ) or analytical reagent is a substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, or test if one occurs. The terms ''reactant'' and ''reagent'' are often used interchangeably, but reactant specifies a ...
s for effecting alkylation. Alkyl groups can also be removed in a process known as dealkylation. Alkylating agents are often classified according to their nucleophilic
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are ...
or electrophilic
In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively charged, have an atom that carri ...
character.
In oil refining contexts, alkylation refers to a particular alkylation of isobutane
Isobutane, also known as ''i''-butane, 2-methylpropane or methylpropane, is a chemical compound with molecular formula HC(CH3)3. It is an isomer of butane. Isobutane is a colourless, odourless gas.
It is the simplest alkane with a tertiary carbon a ...
with olefins. For upgrading of petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
, alkylation produces a premium blending stock for gasoline.
In medicine, alkylation of DNA is used in chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherap ...
to damage the DNA of cancer cells. Alkylation is accomplished with the class of drugs called alkylating antineoplastic agent
An alkylating antineoplastic agent is an alkylating agent used in cancer treatment that attaches an alkyl group (CnH2n+1) to DNA.
The alkyl group is attached to the guanine base of DNA, at the number 7 nitrogen atom of the purine ring.
Since ...
s.
Nucleophilic alkylating agents
Nucleophilic alkylating agents deliver the equivalent of analkyl
In organic chemistry, an alkyl group is an alkane missing one hydrogen.
The term ''alkyl'' is intentionally unspecific to include many possible substitutions.
An acyclic alkyl has the general formula of . A cycloalkyl is derived from a cycloalk ...
anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
(carbanion
In organic chemistry, a carbanion is an anion in which carbon is trivalent (forms three bonds) and bears a formal negative charge (in at least one significant resonance form).
Formally, a carbanion is the conjugate base of a carbon acid:
:R3C ...
). The formal "alkyl anion" attacks an electrophile
In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively charged, have an atom that carries ...
, forming a new covalent bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms ...
between the alkyl group and the electrophile. The counterion, which is a cation such as lithium, can be removed and washed away in the work-up. Examples include the use of organometallic compound
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and s ...
s such as Grignard (organomagnesium), organolithium
In organometallic chemistry
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, ...
, organocopper
Organocopper compounds is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to copper chemical bond. Organocopper chemistry is the study of organocopper compounds describing their physical properties, synthesis and reactions. They a ...
, and organosodium
Organosodium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to sodium chemical bond. The application of organosodium compounds in chemistry is limited in part due to competition from organolithium compounds, which are ...
reagents. These compounds typically can add to an electron-deficient carbon atom such as at a carbonyl group
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups. A compound containing a ...
. Nucleophilic alkylating agents can displace halide
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a fluor ...
substituents on a carbon atom through the SN2
The SN2 reaction is a type of reaction mechanism that is common in organic chemistry. In this mechanism, one bond is broken and one bond is formed in a concerted way, i.e., in one step. The name SN2 refers to the Hughes-Ingold symbol of the ...
mechanism. With a catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
, they also alkylate alkyl and aryl halides, as exemplified by Suzuki couplings.
 The SN2 mechanism is not available for aryl substituents, where the trajectory to attack the carbon atom would be inside the ring. Thus only reactions catalyzed by organometallic catalysts are possible.
The SN2 mechanism is not available for aryl substituents, where the trajectory to attack the carbon atom would be inside the ring. Thus only reactions catalyzed by organometallic catalysts are possible.
Alkylation by carbon electrophiles
C-alkylation
C-alkylation is a process for the formation of carbon-carbon bonds. The largest example of this takes place in thealkylation unit
An alkylation unit (alky) is one of the conversion processes used in petroleum refineries. It is used to convert isobutane and low-molecular-weight alkenes (primarily a mixture of propene and butene) into alkylate, a high octane gasoline componen ...
s of petrochemical plants, which convert low-molecular-weight alkenes
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond.
Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, an ...
into high octane gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic co ...
components. Electron-rich species such as phenol
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it req ...
s are also commonly alkylated to produce a variety of products; examples include linear alkylbenzene
Linear alkylbenzenes (sometimes also known as LABs) are a family of organic compounds with the formula C6H5CnH2n+1. Typically, ''n'' lies between 10 and 16, although generally supplied as a tighter cut, such as C12-C15, C12-C13 and C10-C13, for de ...
s used in the production of surfactants
Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension between two liquids, between a gas and a liquid, or interfacial tension between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsion#Emulsifiers , ...
like LAS, or butylated phenols like BHT, which are used as antioxidant
Antioxidants are compounds that inhibit oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce free radicals. This can lead to polymerization and other chain reactions. They are frequently added to industrial products, such as fuels and lubricant ...
s. This can be achieved using either acid catalysts like Amberlyst
An ion-exchange resin or ion-exchange polymer is a resin or polymer that acts as a medium for ion exchange. It is an insoluble matrix (or support structure) normally in the form of small (0.25–1.43 mm radius) microbeads, usually white or y ...
, or Lewis acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any sp ...
s like aluminium. On a laboratory scale the Friedel–Crafts reaction
The Friedel–Crafts reactions are a set of reactions developed by Charles Friedel and James Crafts in 1877 to attach substituents to an aromatic ring. Friedel–Crafts reactions are of two main types: alkylation reactions and acylation reacti ...
uses alkyl halide
The haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are alkanes containing one or more halogen substituents. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely ...
s, as these are often easier to handle than their corresponding alkenes, which tend to be gasses. The reaction is catalysed by aluminium trichloride
Aluminium chloride, also known as aluminium trichloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It forms hexahydrate with the formula , containing six water molecules of hydration. Both are colourless crystals, but samples are often conta ...
. This approach is rarely used industrially as alkyl halides are more expensive than alkenes.
N-and P-alkylation
N- and P-alkylation are important processes for the formation of carbon-nitrogen and carbon-phosphorus bonds. Amines are readily alkylated. The rate of alkylation follows the order tertiary amine < secondary amine < primary amine. Typical alkylating agents are alkyl halides. Industry often relies ongreen chemistry
Green chemistry, also called sustainable chemistry, is an area of chemistry and chemical engineering focused on the design of products and processes that minimize or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances. While environmental che ...
methods involving alkylation of amines with alcohols, the byproduct being water. Hydroamination
In organic chemistry, hydroamination is the addition of an bond of an amine across a carbon-carbon multiple bond of an alkene, alkyne, diene, or allene. In the ideal case, hydroamination is atom economical and green. Amines are common in fine ...
is another green method for N-alkylation.
In the Menshutkin reaction
In organic chemistry, the Menshutkin reaction converts a tertiary amine into a quaternary ammonium salt by reaction with an alkyl halide. Similar reactions occur when tertiary phosphines are treated with alkyl halides.
The reaction is the meth ...
, a tertiary amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such ...
is converted into a quaternary ammonium salt
In chemistry, quaternary ammonium cations, also known as quats, are positively charged polyatomic ions of the structure , R being an alkyl group or an aryl group. Unlike the ammonium ion () and the primary, secondary, or tertiary ammonium cations ...
by reaction with an alkyl halide
The haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are alkanes containing one or more halogen substituents. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely ...
. Similar reactions occur when tertiary phosphines are treated with alkyl halides, the products being phosphonium salts.
S-alkylation
Thiol
In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl gro ...
s are readily alkylated to give thioether
In organic chemistry, an organic sulfide (British English sulphide) or thioether is an organosulfur functional group with the connectivity as shown on right. Like many other sulfur-containing compounds, volatile sulfides have foul odors. A sul ...
s via the thiol-ene reaction
In organosulfur chemistry, the thiol-ene reaction (also alkene hydrothiolation) is an organic reaction between a thiol () and an alkene () to form a thioether (). This reaction was first reported in 1905, but it gained prominence in the late 1990s ...
. The reaction is typically conducted in the presence of a base or using the conjugate base of the thiol. Thioethers undergo alkylation to give sulfonium ions.
O-alkylation
Alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
s alkylate to give ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be c ...
s:
:Williamson ether synthesis
The Williamson ether synthesis is an organic reaction, forming an ether from an organohalide and a deprotonated alcohol (alkoxide). This reaction was developed by Alexander Williamson in 1850. Typically it involves the reaction of an alkoxide io ...
.
Alcohols are also good alkylating agents in the presence of suitable acid catalysts. For example, most methyl amines are prepared by alkylation of ammonia with methanol. The alkylation of phenols is particularly straightforward since it is subject to fewer competing reactions.
:spectator ion
A spectator ion is an ion that exists as a reactant and a product in a chemical equation. A spectator ion can, therefore, be observed in the reaction of aqueous solutions of sodium carbonate and copper(II) sulfate but does not affect the equilibr ...
)
More complex alkylation of a alcohols and phenols involve ethoxylation
Ethoxylation is a chemical reaction in which ethylene oxide adds to a substrate. It is the most widely practiced alkoxylation, which involves the addition of epoxides to substrates.
In the usual application, alcohols and phenols are converted in ...
. Ethylene oxide
Ethylene oxide is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula . It is a cyclic ether and the simplest epoxide: a three-membered Ring (chemistry), ring consisting of one oxygen atom and two carbon atoms. Ethylene oxide is a colorless a ...
is the alkylating group in this reaction.
Oxidative addition to metals
In the process calledoxidative addition
Oxidative addition and reductive elimination are two important and related classes of reactions in organometallic chemistry. Oxidative addition is a process that increases both the oxidation state and coordination number of a metal centre. Oxidat ...
, low-valent metals often react with alkylating agents to give metal alkyls. This reaction is one step in the Cativa process
The Cativa process is a method for the production of acetic acid by the carbonylation of methanol. The technology, which is similar to the Monsanto process, was developed by BP Chemicals and is under license by BP Plc. The process is based on an ...
for the synthesis of acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component ...
from methyl iodide. Many cross coupling reaction
In organic chemistry, a cross-coupling reaction is a reaction where two fragments are joined together with the aid of a metal catalyst. In one important reaction type, a main group organometallic compound of the type R-M (R = organic fragment, M = ...
s proceed via oxidative addition as well.
Electrophilic alkylating agents
 Electrophilic alkylating agents deliver the equivalent of an alkyl
Electrophilic alkylating agents deliver the equivalent of an alkyl cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
. Alkyl halides are typical alkylating agents. Trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate
Trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate is the organic compound with the formula . (It is sometimes called "Meerwein's salt" after Hans Meerwein.Meerwein's salt classically referred to triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate. However, in recent years, the t ...
and triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate
Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate is the organic oxonium compound with the formula CH3CH2)3OF4. It is often called Meerwein's reagent or Meerwein's salt after its discoverer Hans Meerwein. Also well known and commercially available is the rela ...
are particularly strong electrophiles due to their overt positive charge and an inert leaving group (dimethyl or diethyl ether). Dimethyl sulfate
Dimethyl sulfate (DMS) is a chemical compound with formula (CH3O)2SO2. As the diester of methanol and sulfuric acid, its formula is often written as ( CH3)2 SO4 or Me2SO4, where CH3 or Me is methyl. Me2SO4 is mainly used as a methylating agent ...
is intermediate in electrophilicity.
Methylation with diazomethane
Diazomethane
Diazomethane is the chemical compound CH2N2, discovered by German chemist Hans von Pechmann in 1894. It is the simplest diazo compound. In the pure form at room temperature, it is an extremely sensitive explosive yellow gas; thus, it is almost u ...
is a popular methylating agent
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group on a substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replacing a hydrogen atom. These t ...
in the laboratory, but it is too hazardous (explosive gas with a high acute toxicity) to be employed on an industrial scale without special precautions. Use of diazomethane has been significantly reduced by the introduction of the safer and equivalent reagent trimethylsilyldiazomethane
Trimethylsilyldiazomethane is the organosilicon compound with the formula (CH3)3SiCHN2. It is classified as a diazo compound. Trimethylsilyldiazomethane is a commercially available reagent used in organic chemistry as a methylating agent and as ...
.
Hazards
Electrophilic, soluble alkylating agents are often toxic and carcinogenic, due to their tendency to alkylate DNA. This mechanism of toxicity is relevant to the function of anti-cancer drugs in the form ofalkylating antineoplastic agents
Alkylation is the transfer of an alkyl group from one molecule to another. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene (or their equivalents). Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting a ...
. Some chemical weapons
A chemical weapon (CW) is a specialized Ammunition, munition that uses chemicals chemical engineering, formulated to inflict death or harm on humans. According to the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW), this can be an ...
such as mustard gas
Mustard gas or sulfur mustard is a chemical compound belonging to a family of cytotoxic and blister agents known as mustard agents. The name ''mustard gas'' is technically incorrect: the substance, when dispersed, is often not actually a gas, b ...
(sulfide of dichloroethyl) function as alkylating agents. Alkylated DNA either does not coil or uncoil properly, or cannot be processed by information-decoding enzymes.
Catalysts
Lewis acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any sp ...
s and Brønsted acids, sometimes both. Classically, Lewis acids, e.g., aluminium trichloride
Aluminium chloride, also known as aluminium trichloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It forms hexahydrate with the formula , containing six water molecules of hydration. Both are colourless crystals, but samples are often conta ...
, are employed when the alkyl halide are used. Brønsted acids are used when alkylating with olefins. Typical catalysts are zeolites, i.e. solid acid catalysts, and sulfuric acid. Silicotungstic acid is used to manufacture ethyl acetate
Ethyl acetate ( systematically ethyl ethanoate, commonly abbreviated EtOAc, ETAC or EA) is the organic compound with the formula , simplified to . This colorless liquid has a characteristic sweet smell (similar to pear drops) and is used in glues ...
by the alkylation of acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component ...
by ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds).
Ethylene i ...
:
:In biology
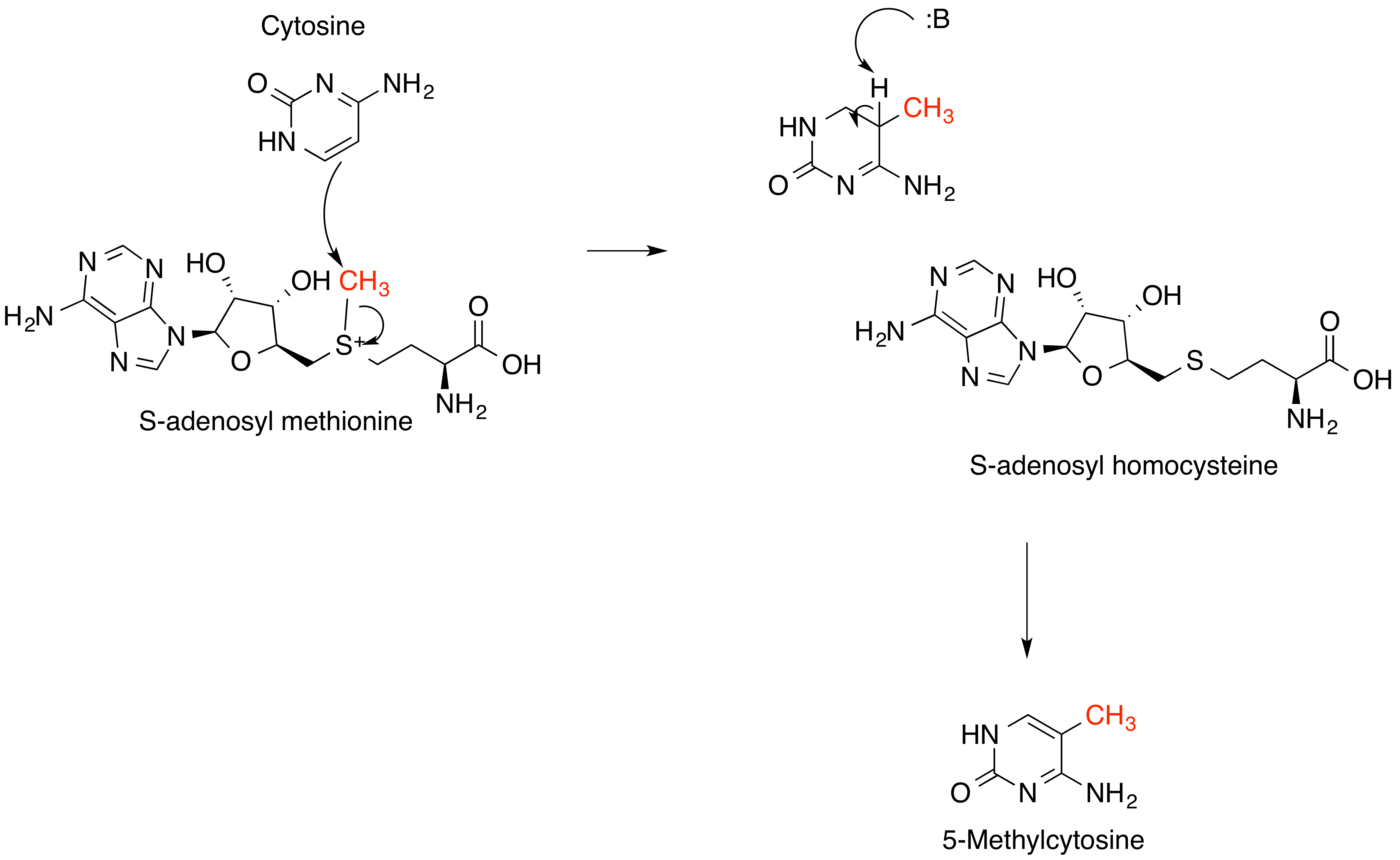
Methylation is the most common type of alkylation. Methylation in nature is often effected byvitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. It is one of eight B vitamins. It is required by animals, which use it as a cofactor in DNA synthesis, in both fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. It ...
- and radical-SAM
''S''-Adenosyl methionine (SAM), also known under the commercial names of SAMe, SAM-e, or AdoMet, is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation. Although these anabolic reactions occur throug ...
-based enzymes.
 In
In methanogenesis
Methanogenesis or biomethanation is the formation of methane coupled to energy conservation by microbes known as methanogens. Organisms capable of producing methane for energy conservation have been identified only from the domain Archaea, a group ...
, coenzyme M
Coenzyme M is a coenzyme required for methyl-transfer reactions in the metabolism of archaeal methanogens, and in the metabolism of other substrates in bacteria. It is also a necessary cofactor in the metabolic pathway of alkene-oxidizing bacteria. ...
is methylated by tetrahydromethanopterin
Tetrahydromethanopterin (THMPT, ) is a coenzyme in methanogenesis. It is the carrier of the C1 group as it is reduced to the methyl level, before transferring to the coenzyme M.
Tetrahydrosarcinapterin (THSPT, ) is a modified form of THMPT, wh ...
.
Commodity chemicals
Several commodity chemicals are produced by alkylation. Included are several fundamental benzene-based feedstocks such asethylbenzene
Ethylbenzene is an organic compound with the formula . It is a highly flammable, colorless liquid with an odor similar to that of gasoline. This monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon is important in the petrochemical industry as an reaction intermedia ...
(precursor to styrene
Styrene () is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH=CH2. This derivative of benzene is a colorless oily liquid, although aged samples can appear yellowish. The compound evaporates easily and has a sweet smell, although high concen ...
), cumene
Cumene (isopropylbenzene) is an organic compound that contains a benzene ring with an isopropyl substituent. It is a constituent of crude oil and refined fuels. It is a flammable colorless liquid that has a boiling point of 152 °C. Near ...
(precursor to phenol
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it req ...
and acetone
Acetone (2-propanone or dimethyl ketone), is an organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest and smallest ketone (). It is a colorless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odour.
Acetone is miscib ...
), linear alkylbenzene sulfonate
Alkylbenzene sulfonates are a class of anionic surfactants, consisting of a hydrophilic sulfonate head-group and a hydrophobic alkylbenzene tail-group. Along with sodium laureth sulfate, they are one of the oldest and most widely used synthetic ...
s (for detergents).
Gasoline production
 In a conventional
In a conventional oil refinery
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refined into useful products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, asphalt base, fuel oils, heating oil, kerosene, lique ...
, isobutane
Isobutane, also known as ''i''-butane, 2-methylpropane or methylpropane, is a chemical compound with molecular formula HC(CH3)3. It is an isomer of butane. Isobutane is a colourless, odourless gas.
It is the simplest alkane with a tertiary carbon a ...
is alkylated with low-molecular-weight alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond.
Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, an ...
s (primarily a mixture of propene
Propylene, also known as propene, is an unsaturated organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CH=CH2. It has one double bond, and is the second simplest member of the alkene class of hydrocarbons. It is a colorless gas with a faint petro ...
and butene
Butene, also known as butylene, is an alkene with the formula . The word ''butene'' may refer to any of the individual compounds. They are colourless gases that are present in crude oil as a minor constituent in quantities that are too small for ...
) in the presence of a Brønsted acid catalyst, which can include solid acid
Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and plasma). The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount of kinetic energy. A solid is characterized by structural ...
s (zeolites). The catalyst protonates the alkenes (propene, butene) to produce carbocation
A carbocation is an ion with a positively charged carbon atom. Among the simplest examples are the methenium , methanium and vinyl cations. Occasionally, carbocations that bear more than one positively charged carbon atom are also encountere ...
s, which alkylate isobutane. The product, called "alkylate", is composed of a mixture of high-octane
Octane is a hydrocarbon and an alkane with the chemical formula , and the condensed structural formula . Octane has many structural isomers that differ by the amount and location of branching in the carbon chain. One of these isomers, 2,2,4-Tri ...
, branched-chain paraffin Paraffin may refer to:
Substances
* Paraffin wax, a white or colorless soft solid that is used as a lubricant and for other applications
* Liquid paraffin (drug), a very highly refined mineral oil used in cosmetics and for medical purposes
* Alkan ...
ic hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ex ...
s (mostly isoheptane
2-Methylhexane ( C7 H16, also known as isoheptane, ethylisobutylmethane) is an isomer of heptane. It is structurally a hexane molecule with a methyl group attached to its second carbon atom. It exists in most commercially available heptane merchan ...
and isooctane
2,2,4-Trimethylpentane, also known as isooctane or iso-octane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)3CCH2CH(CH3)2. It is one of several isomers of octane (C8H18). This particular isomer is the standard 100 point on the octane rating sc ...
). Alkylate is a premium gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic co ...
blending stock because it has exceptional antiknock properties and is clean burning. Alkylate is also a key component of avgas
Avgas (aviation gasoline, also known as aviation spirit in the UK) is an aviation fuel used in aircraft with spark-ignited internal combustion engines. ''Avgas'' is distinguished from conventional gasoline (petrol) used in motor vehicles, w ...
. By combining fluid catalytic cracking, polymerization, and alkylation, refineries can obtain a gasoline yield of 70 percent. The widespread use of sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
and hydrofluoric acid
Hydrofluoric acid is a Solution (chemistry), solution of hydrogen fluoride (HF) in water. Solutions of HF are colourless, acidic and highly Corrosive substance, corrosive. It is used to make most fluorine-containing compounds; examples include th ...
in refineries poses significant environmental risks. Ionic liquid
An ionic liquid (IL) is a salt in the liquid state. In some contexts, the term has been restricted to salts whose melting point is below a specific temperature, such as . While ordinary liquids such as water and gasoline are predominantly made of ...
s are used in place of the older generation of strong Bronsted acids.
Dealkylation
Complementing alkylation reactions are the reverse, dealkylations. Prevalent areether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be c ...
dealkylations.
See also
*Hydrodealkylation
Hydrodealkylation is a chemical reaction that often involves reacting an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as toluene, in the presence of hydrogen gas to form a simpler aromatic hydrocarbon devoid of functional groups. An example is the conversion of 1,2, ...
*Transalkylation
In organic chemistry, transalkylation is a chemical reaction involving the transfer of an alkyl group from one organic compound to another. The reaction is used for the transfer of methyl and ethyl groups between benzene rings. This is of particul ...
*Alkynylation
In organic chemistry, alkynylation is an addition reaction in which a terminal alkyne () is added to a carbonyl group () to form an Alpha and beta carbon, α-alkynyl alcohol (chemistry), alcohol ().
When the acetylide is formed from acetylene () ...
*Friedel–Crafts reaction
The Friedel–Crafts reactions are a set of reactions developed by Charles Friedel and James Crafts in 1877 to attach substituents to an aromatic ring. Friedel–Crafts reactions are of two main types: alkylation reactions and acylation reacti ...
* :Alkylating agents
** :Ethylating agents
** :Methylating agents
References
External links
Macrogalleria page on polycarbonate production
* {{Authority control Industrial processes Oil refining Organic reactions Chemical processes