|
Ethoxylation
Ethoxylation is a chemical reaction in which ethylene oxide adds to a substrate. It is the most widely practiced alkoxylation, which involves the addition of epoxides to substrates. In the usual application, alcohols and phenols are converted into R(OC2H4)nOH where n ranges from 1 to 10. Such compounds are called alcohol ethoxylates. Alcohol ethoxylates are often converted to related species called ethoxysulfates. Alcohol ethoxylates and ethoxysulfates are surfactants, used widely in cosmetic and other commercial products. The process is of great industrial significance with more than 2,000,000 metric tons of various ethoxylates produced worldwide in 1994. Production The process was developed at the Ludwigshafen laboratories of IG Farben by Conrad Schöller and during the 1930s. Alcohol ethoxylates Industrial ethoxylation is primarily performed upon fatty alcohols in order to generate fatty alcohol ethoxylates (FAE's), which are a common form of nonionic surfactant (e.g. octa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylene Oxide
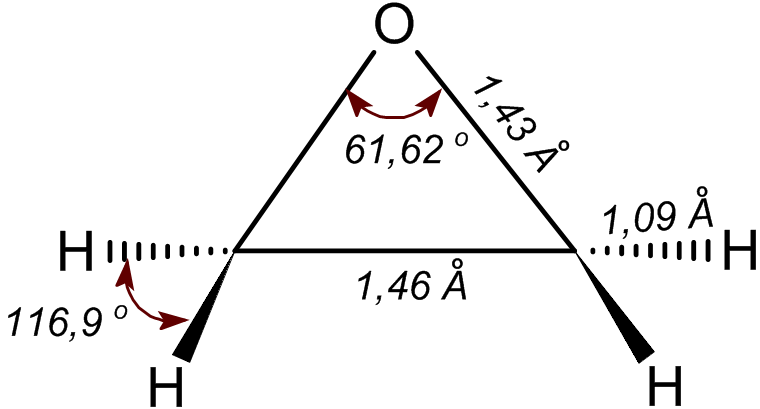
Ethylene oxide is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula . It is a cyclic ether and the simplest epoxide: a three-membered Ring (chemistry), ring consisting of one oxygen atom and two carbon atoms. Ethylene oxide is a colorless and flammable gas with a faintly sweet odor. Because it is a strained ring, ethylene oxide easily participates in a number of addition reactions that result in ring-opening. Ethylene oxide is isomeric with acetaldehyde and with vinyl alcohol. Ethylene oxide is industrially produced by oxidation of ethylene in the presence of silver catalyst. The reactivity that is responsible for many of ethylene oxide's hazards also makes it useful. Although too dangerous for direct household use and generally unfamiliar to consumers, ethylene oxide is used for making many consumer products as well as non-consumer chemicals and intermediates. These products include detergents, thickeners, solvents, plastics, and various organic chemicals such as ethylene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (chemistry), products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anionic Surfactant
Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension between two liquids, between a gas and a liquid, or interfacial tension between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsifiers, foaming agents, or dispersants. The word "surfactant" is a blend of ''surface-active agent'', coined . Agents that increase surface tension are "surface active" in the literal sense but are not called surfactants as their effect is opposite to the common meaning. A common example of surface tension increase is salting out: by adding an inorganic salt to an aqueous solution of a weakly polar substance, the substance will precipitate. The substance may itself be a surfactant – this is one of the reasons why many surfactants are ineffective in sea water. Composition and structure Surfactants are usually organic compounds that are amphiphilic, meaning each molecule contains both a hydrophilic "water-seeking" group (the ''head''), and a hydrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organosulfate
Organosulfates are a class of organic compounds sharing a common functional group with the structure R-O-SO3−. The SO4 core is a sulfate group and the R group is any organic residue. All organosulfates are formally esters derived from alcohols and sulfuric acid, although many are not prepared in this way. Many sulfate esters are used in detergents, and some are useful reagents. Alkyl sulfates consist of a hydrophobic hydrocarbon chain, a polar sulfate group (containing an anion) and either a cation or amine to neutralize the sulfate group. Examples include: sodium lauryl sulfate (also known as sulfuric acid mono dodecyl ester sodium salt) and related potassium and ammonium salts. Applications Alkyl sulfates are commonly used as an anionic surfactant in liquid soaps and detergents used to clean wool, as surface cleaners, and as active ingredients in laundry detergents, shampoos and conditioners. They can also be found in household products such as toothpaste, antacids, cosmeti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defoamer
A defoamer or an anti-foaming agent is a chemical additive that reduces and hinders the formation of foam in industrial process liquids. The terms anti-foam agent and defoamer are often used interchangeably. Strictly speaking, defoamers eliminate existing foam and anti-foamers prevent the formation of further foam. Commonly used agents are insoluble oils, polydimethylsiloxanes and other silicones, certain alcohols, stearates and glycols. The additive is used to prevent formation of foam or is added to break a foam already formed. In industrial processes, foams pose serious problems. They cause defects on surface coatings and prevent the efficient filling of containers. A variety of chemical formulae are available to prevent formation of foams. Properties Generally a defoamer is insoluble in the foaming medium and has surface active properties. An essential feature of a defoamer product is a low viscosity and a facility to spread rapidly on foamy surfaces. It has affinity to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poloxamer
Poloxamers are nonionic triblock copolymers composed of a central hydrophobic chain of polyoxypropylene (poly(propylene oxide)) flanked by two hydrophilic chains of polyoxyethylene (poly(ethylene oxide)). The word was coined by BASF inventor, Irving Schmolka, who received the patent for these materials in 1973. Poloxamers are also known by the trade names Pluronic, Kolliphor (pharma grade), and Synperonic. Because the lengths of the polymer blocks can be customized, many different poloxamers exist that have slightly different properties. For the generic term ''poloxamer'', these copolymers are commonly named with the letter ''P'' (for poloxamer) followed by three digits: the first two digits multiplied by 100 give the approximate molecular mass of the polyoxypropylene core, and the last digit multiplied by 10 gives the percentage polyoxyethylene content (e.g. P407 = poloxamer with a polyoxypropylene molecular mass of 4000 g/mol and a 70% polyoxyethylene content). For the Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Block Copolymer
In polymer chemistry, a copolymer is a polymer derived from more than one species of monomer. The polymerization of monomers into copolymers is called copolymerization. Copolymers obtained from the copolymerization of two monomer species are sometimes called ''bipolymers''. Those obtained from three and four monomers are called ''terpolymers'' and ''quaterpolymers'', respectively. Copolymers can be characterized by a variety of techniques such as NMR spectroscopy and size-exclusion chromatography to determine the molecular size, weight, properties, and composition of the material. Commercial copolymers include acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), styrene/butadiene co-polymer (SBR), nitrile rubber, styrene-acrylonitrile, styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) and ethylene-vinyl acetate, all of which are formed by chain-growth polymerization. Another production mechanism is step-growth polymerization, which is used to produce the nylon-12/6/66 copolymer of nylon 12, nylon 6 and nylon 66 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propylene Oxide
Propylene oxide is an acutely toxic and carcinogenic organic compound with the molecular formula CH3CHCH2O. This colourless volatile liquid with an odour similar to ether, is produced on a large scale industrially. Its major application is its use for the production of polyether polyols for use in making polyurethane plastics. It is a chiral epoxide, although it is commonly used as a racemic mixture. This compound is sometimes called 1,2-propylene oxide to distinguish it from its isomer 1,3-propylene oxide, better known as oxetane. Production Industrial production of propylene oxide starts from propylene. Two general approaches are employed, one involving hydrochlorination and the other involving oxidation. In 2005, about half of the world production was through chlorohydrin technology and one half via oxidation routes. The latter approach is growing in importance. Hydrochlorination route The traditional route proceeds via the conversion of propene to propylene chlorohydrin a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Production Volume Chemicals Programme
High production volume chemicals (HPV chemicals) are produced or imported into the United States in quantities of 1 million pounds or 500 tons per year. In OECD countries, HPV chemicals are defined as being produced at levels greater than 1,000 metric tons per producer/importer per year in at least one member country/region. A list of HPV chemicals serves as an overall priority list, from which chemicals are selected to gather data for a screening information dataset (SIDS), for testing and for initial hazard assessment. History OECD countries including EU In 1987, member countries of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development decided to investigate existing chemicals. In 1991, they agreed to begin by focusing on High production volume (HPV) chemicals, where production volume was used as a surrogate for data on occupational, consumer, and environmental exposure. Each country agreed to "sponsor" the assessment of a proportion of the HPV chemicals. Countries also a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narrow-range Ethoxylate
Narrow-range ethoxylates (NREs) in chemistry are fatty alcohol polyglycol ethers with a narrow homolog distribution and are known nonionic surfactants. They can be produced industrially, for example, by the addition of ethylene oxide onto fatty alcohols in the presence of suitable catalysts (layer compounds which have been calcined or hydrophobized with fatty acids).Reviews on this subject are presented, for example, by M. Cox in '' J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc.'' 67, 599 (1990) and by H. Hensen et al. in Seifen-Ole-Fette-Wachse, 117, 592 (1991). This process can also be carried out on a variety of other hydrophobes and using different alkoxylating compounds (e.g., propylene oxide and butylene oxide) by modifying the catalyst properties. Example An ethoxylation reaction proceeds under an inert atmosphere with an amount of heat depending on the starting material. The reaction proceeds via the epoxide (in this case ethylene oxide) ring opening and activation of the nucleophile, ring, or comb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repeat Unit
In polymer chemistry, a repeat unit or repeating unit (or mer) is a part of a polymer whose repetition would produce the complete polymer chain (except for the end-groups) by linking the repeat units together successively along the chain, like the beads of a necklace. A repeat unit is sometimes called a mer (or mer unit). "Mer" originates from the Greek word ''meros'', which means "a part". The word polymer derives its meaning from this, which means "many mers". A repeat unit (mer) is not to be confused with the term monomer, which refers to the small molecule from which a polymer is synthesized.Callister, William D. (2007). ''Materials science and engineering : an introduction'' (7th ed.) New York : John Wiley & Sons. One of the simplest repeat units is that of the addition polymer polyvinyl chloride, - H2-CHClsub>n-, whose repeat unit is - H2-CHCl. In this case the repeat unit has the same atoms as the monomer vinyl chloride CH2=CHCl. When the polymer is formed, the C=C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Alcohols
A primary alcohol is an alcohol in which the hydroxy group In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy ... is bonded to a primary carbon atom. It can also be defined as a molecule containing a “–CH2OH” group. In contrast, a secondary alcohol has a formula “–CHROH” and a tertiary alcohol has a formula “–CR2OH”, where “R” indicates a carbon-containing group. Examples of primary alcohols include ethanol and n-Butanol, 1-butanol. Methanol is also generally regarded as a primary alcohol, including the 1911 edition of the Encyclopædia Britannica,. See also * Alcohol (chemistry), Alcohol (especially Nomenclature section for discussion on Secondary and Tertiary alcohols.) * Oxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids References Primary alcohols, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |