Ankara ( , ; ), historically known as Ancyra and Angora, is the
capital of
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
. Located in the
central part of
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The r ...
, the city has a population of 5.1 million in its urban center and over 5.7 million in
Ankara Province
Ankara Province ( tr, , ) is a province of Turkey with the capital city Ankara.
Demographics
History
The site of the modern city has been home to settlements by many historic Anatolian civilizations in antiquity and classical times, in ...
,
making it Turkey's
second-largest city after
Istanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, ...
.
Serving as the capital of the ancient
Celt
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
ic state of
Galatia (280–64 BC), and later of the
Roman province with the
same name (25 BC–7th century), the city is very old, with various
Hattian,
Hittite,
Lydia
Lydia ( Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish provin ...
n,
Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empire ...
n,
Galatian,
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
,
Persian,
Roman,
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
, and
Ottoman archeological sites. The Ottomans made the city the capital first of the
Anatolia Eyalet (1393 – late 15th century) and then the
Angora Vilayet
The Vilayet of Angora ( ota, ولايت آنقره, Vilâyet-i Ankara) or Ankara was a first-level administrative division (vilayet) of the Ottoman Empire, centered on the city of Angora (Ankara) in north-central Anatolia, which included most of ...
(1867–1922). The historical center of Ankara is a rocky hill rising over the left bank of the
Ankara River, a tributary of the
Sakarya River
The Sakarya (Sakara River, tr, Sakarya Irmağı; gr, Σαγγάριος, translit=Sangarios; Latin: ''Sangarius'') is the third longest river in Turkey. It runs through the region known in ancient times as Phrygia. It was considered one of th ...
. The hill remains crowned by the ruins of
Ankara Castle. Although few of its outworks have survived, there are well-preserved examples of
Roman and
Ottoman architecture
Ottoman architecture is the architectural style that developed under the Ottoman Empire. It first emerged in northwestern Anatolia in the late 13th century and developed from earlier Seljuk Turkish architecture, with influences from Byzantine a ...
throughout the city, the most remarkable being the 20 BC
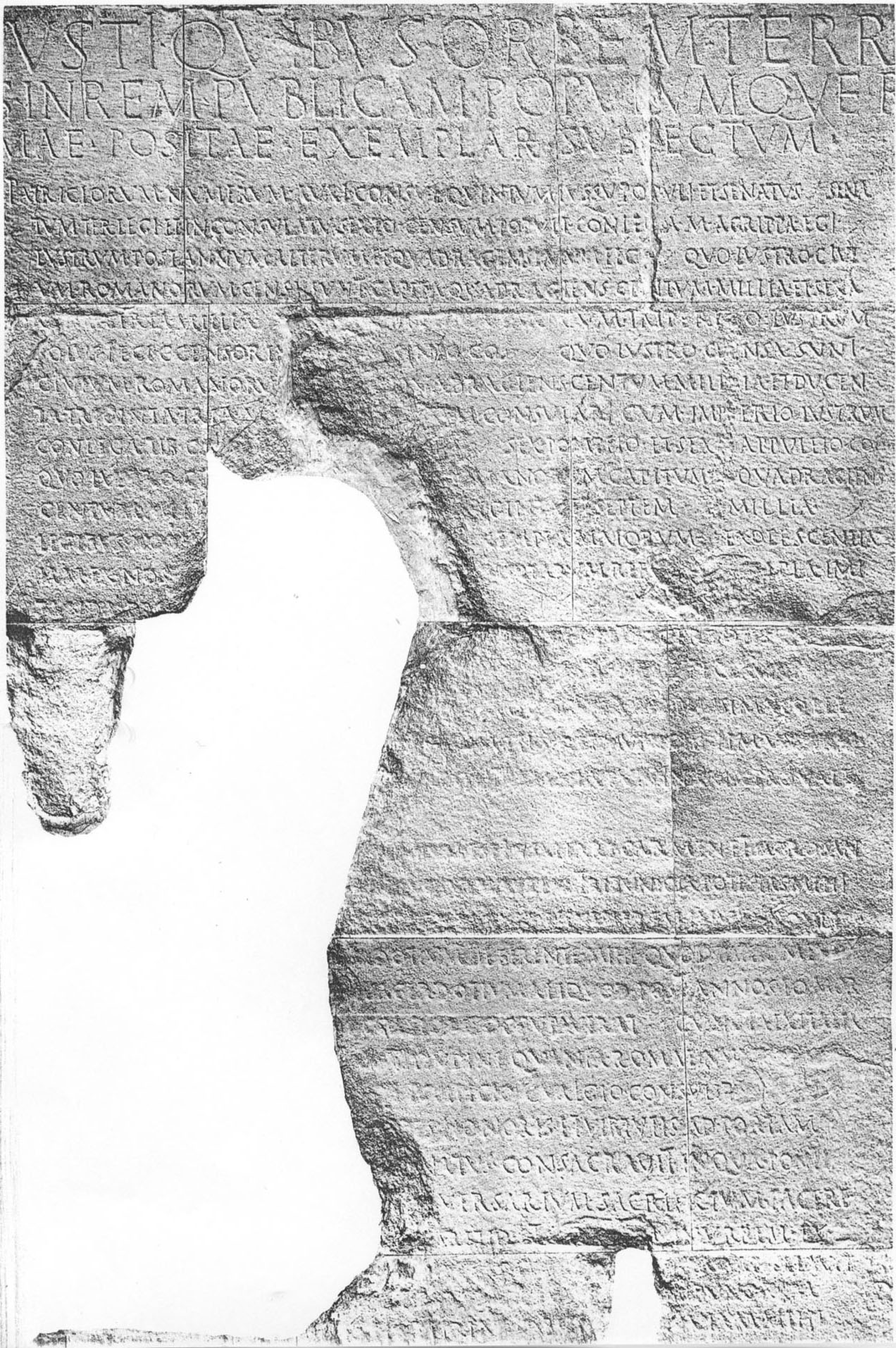
Temple of Augustus and Rome that boasts the
Monumentum Ancyranum, the inscription recording the ''
Res Gestae Divi Augusti''.
On 23 April 1920, the
Grand National Assembly of Turkey
The Grand National Assembly of Turkey ( tr, ), usually referred to simply as the TBMM or Parliament ( tr, or ''Parlamento''), is the unicameral Turkish legislature. It is the sole body given the legislative prerogatives by the Turkish Consti ...
was established in Ankara, which became the headquarters of the
Turkish National Movement
The Turkish National Movement ( tr, Türk Ulusal Hareketi) encompasses the political and military activities of the Turkish revolutionaries that resulted in the creation and shaping of the modern Republic of Turkey, as a consequence of the defe ...
during the
Turkish War of Independence
The Turkish War of Independence "War of Liberation", also known figuratively as ''İstiklâl Harbi'' "Independence War" or ''Millî Mücadele'' "National Struggle" (19 May 1919 – 24 July 1923) was a series of military campaigns waged by th ...
. Ankara became the new Turkish capital upon the establishment of the Republic on 29 October 1923, succeeding in this role as the former Turkish capital Istanbul following the
fall of the Ottoman Empire
The dissolution of the Ottoman Empire (1908–1922) began with the Young Turk Revolution which restored the constitution of 1876 and brought in multi-party politics with a two-stage electoral system for the Ottoman parliament. At the same tim ...
. The
government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government ...
is a prominent employer, but Ankara is also an important commercial and industrial city located at the center of Turkey's road and railway networks. The city gave its name to the
Angora wool shorn from
Angora rabbits, the long-haired
Angora goat (the source of
mohair
Mohair (pronounced ) is a fabric or yarn made from the hair of the Angora goat. (This should not be confused with Angora wool, which is made from the fur of the Angora rabbit.) Both durable and resilient, mohair is notable for its high lus ...
), and the
Angora cat. The area is also known for its pears, honey and
muscat grapes. Although situated in one of the driest regions of Turkey and surrounded mostly by
steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslan ...
vegetation (except for the forested areas on the southern periphery), Ankara can be considered a
green city in terms of green areas per inhabitant, at per head.
Etymology

The orthography of the name Ankara has varied over the ages. It has been identified with the
Hittite cult center ''Ankuwaš'',
although this remains a matter of debate.
[Gorny, Ronald L. "Zippalanda and Ankuwa: The Geography of Central Anatolia in the Second Millennium B.C." ''The Journal of the American Oriental Society''. Vol. 117 (1997).] In classical antiquity and during the medieval period, the city was known as ''Ánkyra'' (,
"
anchor
An anchor is a device, normally made of metal , used to secure a vessel to the bed of a body of water to prevent the craft from drifting due to wind or current. The word derives from Latin ''ancora'', which itself comes from the Greek ...
") in
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and ''Ancyra'' in
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
; the
Galatian Celtic name was probably a similar variant. Following its annexation by the
Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
in 1073, the city became known in many European languages as ''Angora''; it was also known in
Ottoman Turkish
Ottoman Turkish ( ota, لِسانِ عُثمانى, Lisân-ı Osmânî, ; tr, Osmanlı Türkçesi) was the standardized register of the Turkish language used by the citizens of the Ottoman Empire (14th to 20th centuries CE). It borrowed exten ...
as ''Engürü''. The form "Angora" is preserved in the names of breeds of many different kinds of animals, and in the names of several locations in the US (see
Angora).
History

The region's history can be traced back to the
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
Hattic civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
C ...
, which was succeeded in the 2nd millennium BC by the
Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian people who played an important role in establishing first a kingdom in Kussara (before 1750 BC), then the Kanesh or Nesha kingdom (c. 1750–1650 BC), and next an empire centered on Hattusa in north-cent ...
, in the 10th century BC by the
Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empire ...
ns, and later by the
Lydia
Lydia ( Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish provin ...
ns,
Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkme ...
ns,
Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, Albania, Greeks in Italy, ...
,
Galatians,
Romans,
Byzantines, and
Turks (the
Seljuk Sultanate of Rûm, the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
and finally republican
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
).
Ancient history

The oldest settlements in and around the city center of Ankara belonged to the
Hattic civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
C ...
which existed during the
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
and was gradually absorbed c. 2000 – 1700 BC by the
Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, ...
Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian people who played an important role in establishing first a kingdom in Kussara (before 1750 BC), then the Kanesh or Nesha kingdom (c. 1750–1650 BC), and next an empire centered on Hattusa in north-cent ...
. The city grew significantly in size and importance under the
Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empire ...
ns starting around 1000 BC, and experienced a large expansion following the mass migration from
Gordion, (the capital of
Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empire ...
), after an earthquake which severely damaged that city around that time. In Phrygian tradition, King
Midas was venerated as the founder of Ancyra, but
Pausanias mentions that the city was actually far older, which accords with present archeological knowledge.
Phrygian rule was succeeded first by
Lydia
Lydia ( Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish provin ...
n and later by
Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkme ...
n rule, though the strongly Phrygian character of the peasantry remained, as evidenced by the gravestones of the much later Roman period. Persian sovereignty lasted until the Persians' defeat at the hands of
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
who conquered the city in 333 BC. Alexander came from
Gordion to Ankara and stayed in the city for a short period. After his death at
Babylon in 323 BC and the subsequent division of his empire among his generals, Ankara, and its environs fell into the share of
Antigonus Antigonus or Antigonos ( grc, Ἀντίγονος), a Greek name meaning "comparable to his father" or "worthy of his father", may refer to:
Rulers
* Three Macedonian kings of the Antigonid dynasty that succeeded Alexander the Great:
** Antigon ...
.
Another important expansion took place under the
Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, Albania, Greeks in Italy, ...
of
Pontos who came there around 300 BC and developed the city as a trading center for the commerce of goods between the
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, ...
ports and Crimea to the north; Assyria, Cyprus, and Lebanon to the south; and Georgia, Armenia and Persia to the east. By that time the city also took its name Ἄγκυρα (''Ánkyra'', meaning ''
anchor
An anchor is a device, normally made of metal , used to secure a vessel to the bed of a body of water to prevent the craft from drifting due to wind or current. The word derives from Latin ''ancora'', which itself comes from the Greek ...
'' in
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
) which, in slightly modified form, provides the modern name of ''Ankara''.
Celtic history

In 278 BC, the city, along with the rest of central Anatolia, was occupied by a
Celt
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
ic group, the
Galatians, who were the first to make Ankara one of their main tribal centers, the headquarters of the
Tectosages tribe. Other centers were
Pessinus, today's Ballıhisar, for the
Trocmi tribe, and
Tavium, to the east of Ankara, for the
Tolistobogii tribe. The city was then known as ''Ancyra''. The Celtic element was probably relatively small in numbers; a warrior aristocracy which ruled over
Phrygian-speaking peasants. However, the
Celtic language
The Celtic languages (usually , but sometimes ) are a group of related languages descended from Proto-Celtic. They form a branch of the Indo-European language family. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edwar ...
continued to be spoken in Galatia for many centuries. At the end of the 4th century,
St. Jerome, a native of Dalmatia, observed that the language spoken around Ankara was very similar to that being spoken in the northwest of the Roman world near
Trier
Trier ( , ; lb, Tréier ), formerly known in English as Trèves ( ;) and Triers (see also names in other languages), is a city on the banks of the Moselle in Germany. It lies in a valley between low vine-covered hills of red sandstone in the ...
.
Roman history


The city was subsequently passed under the control of the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
. In 25 BC, Emperor
Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
raised it to the status of a ''
polis
''Polis'' (, ; grc-gre, πόλις, ), plural ''poleis'' (, , ), literally means "city" in Greek. In Ancient Greece, it originally referred to an administrative and religious city center, as distinct from the rest of the city. Later, it also ...
'' and made it the capital city of the
Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
of
Galatia.
Ankara is famous for the ''
Monumentum Ancyranum'' (''Temple of Augustus and Rome'') which contains the official record of the ''Acts of Augustus'', known as the ''
Res Gestae Divi Augusti'', an inscription cut in marble on the walls of this temple. The ruins of Ancyra still furnish today valuable
bas-relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term '' relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that th ...
s, inscriptions and other architectural fragments. Two other Galatian tribal centers,
Tavium near
Yozgat
Yozgat is a city and the capital district of Yozgat Province in the Central Anatolia Region of Turkey. According to 2019 census, population of the district is 421,200 of which 106,280 live in the city of Yozgat.
History
The first surveys were ...
, and
Pessinus (Balhisar) to the west, near Sivrihisar, continued to be reasonably important settlements in the Roman period, but it was Ancyra that grew into a grand metropolis.

An estimated 200,000 people lived in Ancyra in good times during the Roman Empire, a far greater number than was to be the case from after the fall of the Roman Empire until the early 20th century. The small
Ankara River ran through the center of the Roman town. It has now been covered and diverted, but it formed the northern boundary of the old town during the Roman, Byzantine and Ottoman periods. Çankaya, the rim of the majestic hill to the south of the present city center, stood well outside the Roman city, but may have been a summer resort. In the 19th century, the remains of at least one
Roman villa
A Roman villa was typically a farmhouse or country house built in the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, sometimes reaching extravagant proportions.
Typology and distribution
Pliny the Elder (23–79 AD) distinguished two kinds of villas ...
or large house were still standing not far from where the Çankaya Presidential Residence stands today. To the west, the Roman city extended until the area of the Gençlik Park and Railway Station, while on the southern side of the hill, it may have extended downwards as far as the site presently occupied by
Hacettepe University. It was thus a sizeable city by any standards and much larger than the Roman towns of
Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only durin ...
or
Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Gr ...
.
Ancyra's importance rested on the fact that it was the junction point where the roads in northern Anatolia running north–south and east–west intersected, giving it major strategic importance for Rome's eastern frontier.
The great imperial road running east passed through Ankara and a succession of emperors and their armies came this way. They were not the only ones to use the Roman highway network, which was equally convenient for invaders. In the second half of the 3rd century, Ancyra was invaded in rapid succession by the
Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Euro ...
coming from the west (who rode far into the heart of
Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Re ...
, taking slaves and pillaging) and later by the
Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Wester ...
s. For about a decade, the town was one of the western outposts of one of Palmyrean empress
Zenobia in the
Syrian Desert
The Syrian Desert ( ar, بادية الشام ''Bādiyat Ash-Shām''), also known as the North Arabian Desert, the Jordanian steppe, or the Badiya, is a region of desert, semi-desert and steppe covering of the Middle East, including parts of so ...
, who took advantage of a period of weakness and disorder in the Roman Empire to set up a short-lived state of her own.
The town was reincorporated into the Roman Empire under Emperor
Aurelian
Aurelian ( la, Lucius Domitius Aurelianus; 9 September 214 October 275) was a Roman emperor, who reigned during the Crisis of the Third Century, from 270 to 275. As emperor, he won an unprecedented series of military victories which reunited ...
in 272. The
tetrarchy
The Tetrarchy was the system instituted by Roman emperor Diocletian in 293 AD to govern the ancient Roman Empire by dividing it between two emperors, the ''augusti'', and their juniors colleagues and designated successors, the '' caesares'' ...
, a system of multiple (up to four) emperors introduced by
Diocletian (284–305), seems to have engaged in a substantial program of rebuilding and of road construction from Ancyra westwards to Germe and
Dorylaeum (now
Eskişehir
Eskişehir ( , ; from "old" and "city") is a city in northwestern Turkey and the capital of the Eskişehir Province. The urban population of the city is 898,369 with a metropolitan population of 797,708. The city is located on the banks of the ...
).
In its heyday, Roman Ancyra was a large market and trading center but it also functioned as a major administrative capital, where a high official ruled from the city's Praetorium, a large administrative palace or office. During the 3rd century, life in Ancyra, as in other Anatolian towns, seems to have become somewhat militarized in response to the invasions and instability of the town.
Byzantine history
The city is well known during the 4th century as a center of Christian activity (see also
below
Below may refer to:
*Earth
* Ground (disambiguation)
* Soil
* Floor
* Bottom (disambiguation)
* Less than
*Temperatures below freezing
* Hell or underworld
People with the surname
* Ernst von Below (1863–1955), German World War I general
* Fr ...
), due to frequent imperial visits, and through the letters of the pagan scholar
Libanius
Libanius ( grc-gre, Λιβάνιος, Libanios; ) was a teacher of rhetoric of the Sophist school in the Eastern Roman Empire. His prolific writings make him one of the best documented teachers of higher education in the ancient world and a crit ...
.
Bishop
Marcellus of Ancyra and
Basil of Ancyra were active in the theological controversies of their day, and the city was the site of no fewer than three church synods in
314
__NOTOC__
Year 314 ( CCCXIV) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Rufius and Annianus (or, less frequently, year 1067 ''Ab ...
, 358 and 375, the latter two in favor of
Arianism
Arianism ( grc-x-koine, Ἀρειανισμός, ) is a Christological doctrine first attributed to Arius (), a Christian presbyter from Alexandria, Egypt. Arian theology holds that Jesus Christ is the Son of God, who was begotten by G ...
.

The city was visited by Emperor
Constans I (r. 337–350) in 347 and 350,
Julian
Julian may refer to:
People
* Julian (emperor) (331–363), Roman emperor from 361 to 363
* Julian (Rome), referring to the Roman gens Julia, with imperial dynasty offshoots
* Saint Julian (disambiguation), several Christian saints
* Julian (give ...
(r. 361–363) during his Persian campaign in 362, and Julian's successor
Jovian (r. 363–364) in winter 363/364 (he entered his
consulship
A consul held the highest elected political office of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC), and ancient Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the '' cursus honorum'' (an ascending sequence of public offices to which polit ...
while in the city). After Jovian's death soon after,
Valentinian I
Valentinian I ( la, Valentinianus; 32117 November 375), sometimes called Valentinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 364 to 375. Upon becoming emperor, he made his brother Valens his co-emperor, giving him rule of the eastern provinces. Vale ...
(r. 364–375) was acclaimed emperor at Ancyra, and in the next year his brother
Valens
Valens ( grc-gre, Ουάλης, Ouálēs; 328 – 9 August 378) was Roman emperor from 364 to 378. Following a largely unremarkable military career, he was named co-emperor by his elder brother Valentinian I, who gave him the eastern half o ...
(r. 364–378) used Ancyra as his base against the usurper
Procopius
Procopius of Caesarea ( grc-gre, Προκόπιος ὁ Καισαρεύς ''Prokópios ho Kaisareús''; la, Procopius Caesariensis; – after 565) was a prominent late antique Greek scholar from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman ge ...
.
When the province of Galatia was divided sometime in 396/99, Ancyra remained the civil capital of Galatia I, as well as its ecclesiastical center (
metropolitan see
Metropolitan may refer to:
* Metropolitan area, a region consisting of a densely populated urban core and its less-populated surrounding territories
* Metropolitan borough, a form of local government district in England
* Metropolitan county, a typ ...
).
Emperor
Arcadius
Arcadius ( grc-gre, Ἀρκάδιος ; 377 – 1 May 408) was Roman emperor from 383 to 408. He was the eldest son of the ''Augustus'' Theodosius I () and his first wife Aelia Flaccilla, and the brother of Honorius (). Arcadius ruled the e ...
(r. 383–408) frequently used the city as his summer residence, and some information about the ecclesiastical affairs of the city during the early 5th century is found in the works of
Palladius of Galatia
Palladius of Galatia ( el, Παλλάδιος Γαλατίας) was a Christian chronicler and the bishop of Helenopolis in Bithynia. He was a devoted disciple of Saint John Chrysostom. He is best remembered for his work, the ''Lausiac History.'' ...
and Nilus of Ancyra.
In 479, the rebel
Marcian attacked the city, without being able to capture it.
In 610/11,
Comentiolus, brother of Emperor
Phocas
Phocas ( la, Focas; grc-gre, Φωκάς, Phōkás; 5475 October 610) was Eastern Roman emperor from 602 to 610. Initially, a middle-ranking officer in the Eastern Roman army, Phocas rose to prominence as a spokesman for dissatisfied soldie ...
(r. 602–610), launched his own unsuccessful rebellion in the city against
Heraclius
Heraclius ( grc-gre, Ἡράκλειος, Hērákleios; c. 575 – 11 February 641), was Eastern Roman emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the exarch of Africa, led a revolt ...
(r. 610–641).
Ten years later, in 620 or more likely 622, it was captured by the
Sassanid Persia
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th cen ...
ns during the
Byzantine–Sassanid War of 602–628. Although the city returned to Byzantine hands after the end of the war, the
Persian presence left traces in the city's archeology, and likely began the process of its transformation from a
late antique city to a medieval fortified settlement.
In 654, the city, also known in Arabic sources as ''Qalat as-Salasil'' ("fortress of the chains"), was captured for the first time by the
Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
of the
Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate ( ar, اَلْخِلَافَةُ ٱلرَّاشِدَةُ, al-Khilāfah ar-Rāšidah) was the first caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was ruled by the first four successive caliphs of Muhammad after hi ...
, under
Muawiyah, the future founder of the
Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
.
At about the same time, the
themes were established in Anatolia, and Ancyra became capital of the
Opsician Theme, which was the largest and most important theme until it was split up under Emperor
Constantine V
Constantine V ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντῖνος, Kōnstantīnos; la, Constantinus; July 718 – 14 September 775), was Byzantine emperor from 741 to 775. His reign saw a consolidation of Byzantine security from external threats. As an able ...
(r. 741–775); Ancyra then became the capital of the new
Bucellarian Theme
The Bucellarian Theme ( el, Βουκελλάριον θέμα, ''Boukellarion thema''), more properly known as the Theme of the Bucellarians ( el, θέμα Βουκελλαρίων, ''thema Boukellariōn'') was a Byzantine theme (a military-civil ...
.
The city was captured at least temporarily by the Umayyad prince
Maslama ibn Hisham in 739/40, the last of the Umayyads' territorial gains from the Byzantine Empire. Ancyra was attacked without success by
Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttal ...
forces in 776 and in 798/99. In 805, Emperor
Nikephoros I
Nikephoros I or Nicephorus I ( gr, Νικηφόρος; 750 – 26 July 811) was Byzantine emperor from 802 to 811. Having served Empress Irene as '' genikos logothetēs'', he subsequently ousted her from power and took the throne himself. In r ...
(r. 802–811) strengthened its fortifications, a fact which probably saved it from sack during the
large-scale invasion of Anatolia by Caliph
Harun al-Rashid
Abu Ja'far Harun ibn Muhammad al-Mahdi ( ar
, أبو جعفر هارون ابن محمد المهدي) or Harun ibn al-Mahdi (; or 766 – 24 March 809), famously known as Harun al-Rashid ( ar, هَارُون الرَشِيد, translit=Hārūn ...
in the next year.
Arab sources report that Harun and his successor
al-Ma'mun
Abu al-Abbas Abdallah ibn Harun al-Rashid ( ar, أبو العباس عبد الله بن هارون الرشيد, Abū al-ʿAbbās ʿAbd Allāh ibn Hārūn ar-Rashīd; 14 September 786 – 9 August 833), better known by his regnal name Al-Ma'm ...
(r. 813–833) took the city, but this information is later invention. In 838, however, during the
Amorium campaign, the armies of Caliph
al-Mu'tasim (r. 833–842) converged and met at the city; abandoned by its inhabitants, Ancara was razed to the ground, before the Arab armies went on to besiege and destroy
Amorium reaching as far as
Smyrna
Smyrna ( ; grc, Σμύρνη, Smýrnē, or , ) was a Greek city located at a strategic point on the Aegean coast of Anatolia. Due to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence, and its good inland connections, Smyrna rose to promi ...
.
In 859, Emperor
Michael III (r. 842–867) came to the city during a campaign against the Arabs, and ordered its fortifications restored.
In 872, the city was menaced, but not taken, by the
Paulicians under
Chrysocheir.
The last Arab raid to reach the city was undertaken in 931, by the Abbasid governor of
Tarsus,
Thamal al-Dulafi Thamal al-Dulafi ( ar, ثمل الدلفي, Thamal al-Dulafī; ) was an Abbasid military commander and longtime governor (''wali'' or ''amir'') of Tarsus and the borderlands with the Byzantine Empire in Cilicia (). A former Dulafid slave, he comman ...
, but the city again was not captured.
Ecclesiastical history

Early Christian martyrs of Ancyra, about whom little is known, included Proklos and Hilarios who were natives of the otherwise unknown nearby village of Kallippi, and suffered repression under the emperor
Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presid ...
(98–117). In the 280s we hear of Philumenos, a Christian corn merchant from southern Anatolia, being captured and martyred in Ankara, and Eustathius.
As in other Roman towns, the reign of
Diocletian marked the culmination of the persecution of the Christians. In 303, Ancyra was one of the towns where the co-emperors Diocletian and his deputy
Galerius
Gaius Galerius Valerius Maximianus (; 258 – May 311) was Roman emperor from 305 to 311. During his reign he campaigned, aided by Diocletian, against the Sasanian Empire, sacking their capital Ctesiphon in 299. He also campaigned across the D ...
launched their anti-Christian persecution. In Ancyra, their first target was the 38-year-old Bishop of the town, whose name was Clement. Clement's life describes how he was taken to Rome, then sent back, and forced to undergo many interrogations and hardship before he, and his brother, and various companions were put to death. The remains of the church of
St. Clement can be found today in a building just off Işıklar Caddesi in the Ulus district. Quite possibly this marks the site where Clement was originally buried. Four years later, a doctor of the town named Plato and his brother Antiochus also became celebrated martyrs under Galerius.
Theodotus of Ancyra is also venerated as a saint.
However, the persecution proved unsuccessful and in 314 Ancyra was the center of
an important council of the
early church
Early Christianity (up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325) spread from the Levant, across the Roman Empire, and beyond. Originally, this progression was closely connected to already established Jewish centers in the Holy Land and the Je ...
; its 25 disciplinary canons constitute one of the most important documents in the early history of the administration of the
Sacrament of Penance
The Sacrament of Penance (also commonly called the Sacrament of Reconciliation or Confession) is one of the seven sacraments of the Catholic Church (known in Eastern Christianity as sacred mysteries), in which the faithful are absolved from ...
. The synod also considered ecclesiastical policy for the reconstruction of the
Christian Church
In ecclesiology, the Christian Church is what different Christian denominations conceive of as being the true body of Christians or the original institution established by Jesus. "Christian Church" has also been used in academia as a synonym f ...
after the persecutions, and in particular the treatment of ''
lapsi''—Christians who had given in to forced
paganism
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Judaism. ...
(sacrifices) to avoid
martyrdom during these persecutions.
Though paganism was probably tottering in Ancyra in Clement's day, it may still have been the majority religion. Twenty years later, Christianity and
monotheism
Monotheism is the belief that there is only one deity, an all-supreme being that is universally referred to as God. Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxf ...
had taken its place. Ancyra quickly turned into a Christian city, with a life dominated by monks and priests and theological disputes. The town council or senate gave way to the bishop as the main local figurehead. During the middle of the 4th century, Ancyra was involved in the complex theological disputes over the nature of Christ, and a form of
Arianism
Arianism ( grc-x-koine, Ἀρειανισμός, ) is a Christological doctrine first attributed to Arius (), a Christian presbyter from Alexandria, Egypt. Arian theology holds that Jesus Christ is the Son of God, who was begotten by G ...
seems to have originated there.
In 362–363, Emperor Julian passed through Ancyra on his way to an ill-fated campaign against the Persians, and according to Christian sources, engaged in a persecution of various holy men.
The stone base for a statue, with an inscription describing Julian as "Lord of the whole world from the British Ocean to the barbarian nations", can still be seen, built into the eastern side of the inner circuit of the walls of Ankara Castle. The Column of Julian which was erected in honor of the emperor's visit to the city in 362 still stands today. In 375, Arian bishops met at Ancyra and deposed several bishops, among them
St. Gregory of Nyssa.
In the late 4th century, Ancyra became something of an imperial
holiday resort. After
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
became the
East Roman capital, emperors in the 4th and 5th centuries would retire from the humid summer weather on the
Bosporus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, Βόσπορος ; tr, İstanbul Boğazı 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''Boğaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern T ...
to the drier mountain atmosphere of Ancyra.
Theodosius II
Theodosius II ( grc-gre, Θεοδόσιος, Theodosios; 10 April 401 – 28 July 450) was Roman emperor for most of his life, proclaimed ''augustus'' as an infant in 402 and ruling as the eastern Empire's sole emperor after the death of his ...
(408–450) kept his court in Ancyra in the summers. Laws issued in Ancyra testify to the time they spent there.

The
Metropolis of Ancyra
The Metropolis of Ancyra ( gr, Μητρόπολις Ἀγκύρας) was a Christian (Eastern Orthodox after the East–West Schism) bishopric in Ancyra (modern Ankara, Turkey) and metropolitan see of Galatia Prima. The see survived the Seljuk T ...
continued to be a residential
see of the
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops vi ...
until the 20th century, with about 40,000 faithful, mostly Turkish-speaking, but that situation ended as a result of the 1923
Convention Concerning the Exchange of Greek and Turkish Populations. The earlier
Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenians in the Ottoman Empire, Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was ...
put an end to the residential eparchy of Ancyra of the
Armenian Catholic Church
, native_name_lang = hy
, image = St Elie - St Gregory Armenian Catholic Cathedral.jpg
, imagewidth = 260px
, alt =
, caption = Cathedral of Saint Elias and Saint Gregory the Illumina ...
, which had been established in 1850.
[Bull ''Universi Dominici gregis''](_blank)
, in Giovanni Domenico Mansi, ''Sacrorum Conciliorum Nova et Amplissima Collectio'', vol. XL, coll. 779–780[F. Tournebize, v. ''II. Ancyre, évêché arménien catholique'', i]
''Dictionnaire d'Histoire et de Géographie ecclésiastiques''
, vol. II, Paris 1914, coll. 1543–1546 It is also a titular metropolis of the
Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople
The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople ( el, Οἰκουμενικὸν Πατριαρχεῖον Κωνσταντινουπόλεως, translit=Oikoumenikón Patriarkhíon Konstantinoupóleos, ; la, Patriarchatus Oecumenicus Constanti ...
.
Both the Ancient Byzantine Metropolitan archbishopric and the 'modern' Armenian eparchy are now listed by the
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
as
titular see
A titular see in various churches is an episcopal see of a former diocese that no longer functions, sometimes called a "dead diocese". The ordinary or hierarch of such a see may be styled a "titular metropolitan" (highest rank), "titular archbis ...
s, with separate
apostolic successions.
Seljuk and Ottoman history

After the
Battle of Manzikert
The Battle of Manzikert or Malazgirt was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Seljuk Empire on 26 August 1071 near Manzikert, theme of Iberia (modern Malazgirt in Muş Province, Turkey). The decisive defeat of the Byzantine army and ...
in 1071, the
Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
overran much of Anatolia. By 1073, the Turkish settlers had reached the vicinity of Ancyra, and the city was captured shortly after, at the latest by the time of the rebellion of
Nikephoros Melissenos
Nikephoros Melissenos ( el, Νικηφόρος Μελισσηνός, – 17 November 1104), Latinized as Nicephorus Melissenus, was a Byzantine general and aristocrat. Of distinguished lineage, he served as a governor and general in the Balkans ...
in 1081.
In 1101, when the
Crusade under
Raymond IV of Toulouse
Raymond IV, Count of Toulouse ( 1041 – 28 February 1105), sometimes called Raymond of Saint-Gilles or Raymond I of Tripoli, was a powerful noble in southern France and one of the leaders of the First Crusade (1096–1099). He was the Count o ...
arrived, the city had been under
Danishmend control for some time. The Crusaders captured the city, and handed it over to the Byzantine emperor
Alexios I Komnenos
Alexios I Komnenos ( grc-gre, Ἀλέξιος Κομνηνός, 1057 – 15 August 1118; Latinized Alexius I Comnenus) was Byzantine emperor from 1081 to 1118. Although he was not the first emperor of the Komnenian dynasty, it was during ...
(r. 1081–1118).
Byzantine rule did not last long, and the city was captured by the Seljuk
Sultanate of Rum
fa, سلجوقیان روم ()
, status =
, government_type = Hereditary monarchy Triarchy (1249–1254)Diarchy (1257–1262)
, year_start = 1077
, year_end = 1308
, p1 = B ...
at some unknown point; in 1127, it returned to Danishmend control until 1143, when the Seljuks of Rum retook it.
After the
Battle of Köse Dağ in 1243, in which the
Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
defeated the Seljuks, most of Anatolia became part of the dominion of the Mongols. Taking advantage of Seljuk decline, a semi-religious cast of craftsmen and trade people named ''
Ahiler'' chose Angora as their independent city-state in 1290.
Orhan I
Orhan Ghazi ( ota, اورخان غازی; tr, Orhan Gazi, also spelled Orkhan, 1281 – March 1362) was the second bey of the Ottoman Beylik from 1323/4 to 1362. He was born in Söğüt, as the son of Osman I.
In the early stages of his ...
, the second
Bey of the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, captured the city in 1356.
Timur
Timur ; chg, ''Aqsaq Temür'', 'Timur the Lame') or as ''Sahib-i-Qiran'' ( 'Lord of the Auspicious Conjunction'), his epithet. ( chg, ''Temür'', 'Iron'; 9 April 133617–19 February 1405), later Timūr Gurkānī ( chg, ''Temür Kür ...
defeated
Bayezid I at the
Battle of Ankara in 1402 and took the city, but in 1403 Angora was again under Ottoman control.
The
Levant Company
The Levant Company was an English chartered company formed in 1592. Elizabeth I of England approved its initial charter on 11 September 1592 when the Venice Company (1583) and the Turkey Company (1581) merged, because their charters had expired ...
maintained a factory in the town from 1639 to 1768. In the 19th century, its population was estimated at 20,000 to 60,000. It was sacked by
Egyptians under
Ibrahim Pasha in 1832.
From 1867 to 1922, the city served as the capital of the
Angora Vilayet
The Vilayet of Angora ( ota, ولايت آنقره, Vilâyet-i Ankara) or Ankara was a first-level administrative division (vilayet) of the Ottoman Empire, centered on the city of Angora (Ankara) in north-central Anatolia, which included most of ...
, which included most of ancient Galatia.
Prior to
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, the town had a
British consulate
A consulate is the office of a consul. A type of diplomatic mission, it is usually subordinate to the state's main representation in the capital of that foreign country (host state), usually an embassy (or, only between two Commonwealth count ...
and a population of around 28,000, roughly of whom were Christian.
Turkish republican capital

Following the
Ottoman defeat in
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, the Ottoman capital
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
(modern Istanbul) and much of
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The r ...
was occupied by the Allies, who planned to share these lands between
Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ...
,
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
,
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wit ...
,
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
and the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, leaving for the Turks the core piece of land in central Anatolia. In response, the leader of the Turkish nationalist movement,
Mustafa Kemal Atatürk
Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, or Mustafa Kemal Pasha until 1921, and Ghazi Mustafa Kemal from 1921 until 1934 ( 1881 – 10 November 1938) was a Turkish field marshal, revolutionary statesman, author, and the founding father of the Rep ...
, established the headquarters of his
resistance movement
A resistance movement is an organized effort by some portion of the civil population of a country to withstand the legally established government or an occupying power and to disrupt civil order and stability. It may seek to achieve its objective ...
in Angora in 1920. After the
Turkish War of Independence
The Turkish War of Independence "War of Liberation", also known figuratively as ''İstiklâl Harbi'' "Independence War" or ''Millî Mücadele'' "National Struggle" (19 May 1919 – 24 July 1923) was a series of military campaigns waged by th ...
was won and the
Treaty of Sèvres was superseded by the
Treaty of Lausanne (1923), the Turkish nationalists replaced the Ottoman Empire with the
Republic of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula i ...
on 29 October 1923. A few days earlier, Angora had officially replaced Constantinople as the new Turkish capital city, on 13 October 1923,
and Republican officials declared that the city's name is Ankara.
After Ankara became the capital of the newly founded Republic of Turkey, new development divided the city into an old section, called ''Ulus'', and a new section, called ''Yenişehir''. Ancient buildings reflecting Roman, Byzantine, and Ottoman history and narrow winding streets mark the old section. The new section, now centered on
Kızılay Square, has the trappings of a more modern city: wide streets, hotels, theaters, shopping malls, and high-rises.

Government offices and foreign embassies are also located in the new section. Ankara has experienced a phenomenal growth since it was made Turkey's capital in 1923, when it was "a small town of no importance". In 1924, the year after the government had moved there, Ankara had about 35,000 residents. By 1927 there were 44,553 residents and by 1950 the population had grown to 286,781. Ankara continued to grow rapidly during the latter half of the 20th century and eventually outranked
Izmir as Turkey's second-largest city, after
Istanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, ...
. Ankara's urban population reached 4,587,558 in 2014, while the population of
Ankara Province
Ankara Province ( tr, , ) is a province of Turkey with the capital city Ankara.
Demographics
History
The site of the modern city has been home to settlements by many historic Anatolian civilizations in antiquity and classical times, in ...
reached 5,150,072 in 2015.
After 1930, it became known officially in Western languages as Ankara. After the late 1930s the public stopped using the name "Angora".
The
Presidential Palace of Turkey is situated in Ankara. This building serves as the main residence of the president.
Economy and infrastructure

Ankara has long been a productive agricultural region in Anatolia. In the Ottoman period, Ankara was well known for producing grain, cotton, and fruits.
The city has exported
mohair
Mohair (pronounced ) is a fabric or yarn made from the hair of the Angora goat. (This should not be confused with Angora wool, which is made from the fur of the Angora rabbit.) Both durable and resilient, mohair is notable for its high lus ...
(from the
Angora goat) and
Angora wool (from the
Angora rabbit) internationally for centuries. In the 19th century, the city also exported substantial amounts of
goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of ...
and cat skins,
gum
Gum may refer to:
Types of gum
* Adhesive
* Bubble gum
* Chewing gum
* Gum (botany), sap or other resinous material associated with certain species of the plant kingdom
** Gum arabic, made from the sap of ''Acacia senegal'', an Old World tree s ...
,
wax,
honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of plants (primar ...
, berries, and
madder root
''Rubia'' is the type genus of the Rubiaceae family of flowering plants, which also contains coffee. It contains around 80 species of perennial scrambling or climbing herbs and subshrubs native to the Old World. The genus and its best-known spe ...
. It was connected to
Istanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, ...
by railway before the
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fig ...
, continuing to export mohair, wool, berries, and
grain
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit ( caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and legu ...
.

The
Central Anatolia Region
The Central Anatolia Region ( tr, İç Anadolu Bölgesi) is a geographical region of Turkey. The largest city in the region is Ankara. Other big cities are Konya, Kayseri, Eskişehir, Sivas, and Aksaray.
Located in Central Turkey, it is bo ...
is one of the primary locations of grape and
wine production in Turkey, and Ankara is particularly famous for its
Kalecik Karası
Kalecik Karası is a Turkish grape variety and a Turkish wine produced from this grape. This grape and wine are called by the name of area, the Kalecik district of Ankara Province, Turkey. Kalecik Karası grows successfully near Kalecik. In its ...
and
Muscat grapes
The Muscat family of grapes includes over 200 grape varieties belonging to the ''Vitis vinifera'' species that have been used in wine production and as raisin and table grapes around the globe for many centuries. Their Wine color, colors range ...
; and its
Kavaklıdere wine, which is produced in the
Kavaklıdere neighborhood within the
Çankaya district of the city. Ankara is also famous for its pears. Another renowned natural product of Ankara is its indigenous type of
honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of plants (primar ...
(''Ankara Balı'') which is known for its light color and is mostly produced by the
Atatürk Forest Farm and Zoo
Atatürk Forest Farm and Zoo ( tr, Atatürk Orman Çiftliği ve Hayvanat Bahçesi, in short ''AOÇ'') is an expansive recreational farming area, which houses a zoo, several small agricultural farms, greenhouses, restaurants, a dairy farm and a bre ...
in the Gazi district, and by other facilities in the Elmadağ, Çubuk and Beypazarı districts.
Çubuk-1 and
Çubuk-2 dams on the Çubuk Brook in Ankara were among the first dams constructed in the Turkish Republic.

Ankara is the center of the state-owned and private Turkish
defence
Defense or defence may refer to:
Tactical, martial, and political acts or groups
* Defense (military), forces primarily intended for warfare
* Civil defense, the organizing of civilians to deal with emergencies or enemy attacks
* Defense indust ...
and
aerospace
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and astrona ...
companies, where the industrial plants and headquarters of the
Turkish Aerospace Industries,
MKE,
ASELSAN,
HAVELSAN,
ROKETSAN,
FNSS,
Nurol Makina, and numerous other firms are located. Exports to foreign countries from these defense and aerospace firms have steadily increased in the past decades. The
IDEF in Ankara is one of the largest international expositions of the global
arms industry
The arms industry, also known as the arms trade, is a global industry which manufactures and sells weapons and military technology. It consists of a commercial industry involved in the research and development, engineering, production, and ...
. A number of the global
automotive companies also have production facilities in Ankara, such as the German bus and truck manufacturer
MAN SE
MAN SE (abbreviation of ''Maschinenfabrik Augsburg- Nürnberg'', ) was a manufacturing and engineering company based in Munich, Germany. Its primary output was commercial vehicles and diesel engines through its MAN Truck & Bus and MAN Latin Ame ...
. Ankara hosts the
OSTIM Industrial Zone, Turkey's largest
industrial park
An industrial park (also known as industrial estate, trading estate) is an area zoned and planned for the purpose of industrial development. An industrial park can be thought of as a more "heavyweight" version of a business park or office park ...
.
A large percentage of the complicated employment in Ankara is provided by the state institutions; such as the
ministries, subministries, and other administrative bodies of the Turkish government. There are also many foreign citizens working as diplomats or clerks in the
embassies
A diplomatic mission or foreign mission is a group of people from a state or organization present in another state to represent the sending state or organization officially in the receiving or host state. In practice, the phrase usually deno ...
of their respective countries.
Geography

Geographically, Ankara is located in the middle of the
Kızılırmak and
Sakarya Sakarya may refer to:
Places
* Sakarya Province, in Turkey
** Sakarya (electoral district)
** Sakarya University
* Sakarya (continent), a small continent 90 million years ago
* Sakarya River, in Turkey
* Sakarya, Polatlı, a village in Ankara Pro ...
rivers, and the
Sakarya River
The Sakarya (Sakara River, tr, Sakarya Irmağı; gr, Σαγγάριος, translit=Sangarios; Latin: ''Sangarius'') is the third longest river in Turkey. It runs through the region known in ancient times as Phrygia. It was considered one of th ...
forms its border with
Eskişehir
Eskişehir ( , ; from "old" and "city") is a city in northwestern Turkey and the capital of the Eskişehir Province. The urban population of the city is 898,369 with a metropolitan population of 797,708. The city is located on the banks of the ...
in the west. Ankara shares its borders with
Bolu and
Çankırı in the north;
Konya
Konya () is a major city in central Turkey, on the southwestern edge of the Central Anatolian Plateau, and is the capital of Konya Province. During antiquity and into Seljuk times it was known as Iconium (), although the Seljuks also called it D ...
in the south and
Kırıkkale in the east.
Ankara and
its province are located in the
Central Anatolia Region
The Central Anatolia Region ( tr, İç Anadolu Bölgesi) is a geographical region of Turkey. The largest city in the region is Ankara. Other big cities are Konya, Kayseri, Eskişehir, Sivas, and Aksaray.
Located in Central Turkey, it is bo ...
of Turkey. The Çubuk Brook flows through the city center of Ankara. It is connected in the western suburbs of the city to the
Ankara River, which is a
tributary
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainag ...
of the
Sakarya River
The Sakarya (Sakara River, tr, Sakarya Irmağı; gr, Σαγγάριος, translit=Sangarios; Latin: ''Sangarius'') is the third longest river in Turkey. It runs through the region known in ancient times as Phrygia. It was considered one of th ...
.
Climate
Ankara has a
cold semi-arid climate (
Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, nota ...
: ''BSk'').
[ ] Under the
Trewartha climate classification
The Trewartha climate classification (TCC) or the Köppen–Trewartha climate classification (KTC) is a climate classification system first published by American geographer Glenn Thomas Trewartha in 1966. It is a modified version of the Köpp ...
, Ankara has a temperate
humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freez ...
(''Dc''). Due to its elevation and inland location, Ankara has cold and snowy winters, and hot and dry summers. Rainfall occurs mostly during the spring and autumn. The city lies in
USDA
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, rural economic development, and food. It aims to meet the needs of com ...
Hardiness zone
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most wide ...
7b, and its annual average precipitation is fairly low at , nevertheless precipitation can be observed throughout the year. Monthly mean temperatures range from in January to in July, with an annual mean of .
[
]
Demographics
 Ankara had a population of 75,000 in 1927. As of 2019, the population of the Ankara Province was 5,639,076. When Ankara became the capital of the Republic of Turkey in 1923, it was designated as a planned city for 500,000 future inhabitants. During the 1920s, 1930s and 1940s, the city grew in a planned and orderly pace. However, from the 1950s onward, the city grew much faster than envisioned, because unemployment and poverty forced people to migrate from the countryside into the city in order to seek a better standard of living. As a result, many illegal houses called gecekondu were built around the city, causing the unplanned and uncontrolled urban landscape of Ankara, as not enough planned housing could be built fast enough. Although precariously built, the vast majority of them have electricity, running water and modern household amenities.
Nevertheless, many of these gecekondus have been replaced by huge public housing projects in the form of
Ankara had a population of 75,000 in 1927. As of 2019, the population of the Ankara Province was 5,639,076. When Ankara became the capital of the Republic of Turkey in 1923, it was designated as a planned city for 500,000 future inhabitants. During the 1920s, 1930s and 1940s, the city grew in a planned and orderly pace. However, from the 1950s onward, the city grew much faster than envisioned, because unemployment and poverty forced people to migrate from the countryside into the city in order to seek a better standard of living. As a result, many illegal houses called gecekondu were built around the city, causing the unplanned and uncontrolled urban landscape of Ankara, as not enough planned housing could be built fast enough. Although precariously built, the vast majority of them have electricity, running water and modern household amenities.
Nevertheless, many of these gecekondus have been replaced by huge public housing projects in the form of tower block
A tower block, high-rise, apartment tower, residential tower, apartment block, block of flats, or office tower is a tall building, as opposed to a low-rise building and is defined differently in terms of height depending on the jurisdicti ...
s such as Elvankent, Eryaman and Güzelkent; and also as mass housing compounds for military and civil service accommodation. Although many gecekondus still remain, they too are gradually being replaced by mass housing compounds, as empty land plots in the city of Ankara for new construction projects are becoming impossible to find.
Çorum and Yozgat, which are located in Central Anatolia and whose population is decreasing, are the provinces with the highest net migration to Ankara. About one third of the Central Anatolia population of 15,608,868 people resides in Ankara.
The literacy rate in the whole province for people who are 15 years old or older is 98.18% according to 2020 TÜİK data. Ankara Province also has the highest percentage of tertiary education
Tertiary education, also referred to as third-level, third-stage or post-secondary education, is the educational level following the completion of secondary education. The World Bank, for example, defines tertiary education as including univer ...
graduates in Turkey with 29.08% of the population having either an undergraduate, master's or doctor's degree.
Transportation

 The ''Electricity, Gas, Bus General Directorate'' (EGO) operates the Ankara Metro and other forms of public transportation. Ankara is served by a
The ''Electricity, Gas, Bus General Directorate'' (EGO) operates the Ankara Metro and other forms of public transportation. Ankara is served by a suburban rail
Commuter rail, or suburban rail, is a passenger rail transport service that primarily operates within a metropolitan area, connecting commuters to a central city from adjacent suburbs or commuter towns. Generally commuter rail systems are ...
named Ankaray (A1) and three subway
Subway, Subways, The Subway, or The Subways may refer to:
Transportation
* Subway, a term for underground rapid transit rail systems
* Subway (underpass), a type of walkway that passes underneath an obstacle
* Subway (George Bush Interconti ...
lines (M1, M2, M3) of the Ankara Metro with about 300,000 total daily commuters, while an additional subway line (M4) is under construction. A long gondola lift with four stations connects the district of Şentepe to the Yenimahalle metro station.
The Ankara Central Station is a major rail hub in Turkey. The Turkish State Railways operates passenger train service from Ankara to other major cities, such as: Istanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, ...
, Eskişehir
Eskişehir ( , ; from "old" and "city") is a city in northwestern Turkey and the capital of the Eskişehir Province. The urban population of the city is 898,369 with a metropolitan population of 797,708. The city is located on the banks of the ...
, Balıkesir
Balıkesir () is a city in Turkey and is the capital city of Balıkesir Province. Balıkesir is located in the Marmara region of Turkey and has a population of 338,936. Between 1341–1922, it was the capital of Karasi.
History
Close to ...
, Kütahya, İzmir
İzmir ( , ; ), also spelled Izmir, is a metropolitan city in the western extremity of Anatolia, capital of the province of the same name. It is the third most populous city in Turkey, after Istanbul and Ankara and the second largest urban aggl ...
, Kayseri, Adana
Adana (; ; ) is a major city in southern Turkey. It is situated on the Seyhan River, inland from the Mediterranean Sea. The administrative seat of Adana province, it has a population of 2.26 million.
Adana lies in the heart of Cilicia, ...
, Kars
Kars (; ku, Qers; ) is a city in northeast Turkey and the capital of Kars Province. Its population is 73,836 in 2011. Kars was in the ancient region known as ''Chorzene'', (in Greek Χορζηνή) in classical historiography ( Strabo), part of ...
, Elazığ
Elazığ () is a city in the Eastern Anatolia region of Turkey, and the administrative centre of Elazığ Province and Elazığ District. It is located in the uppermost Euphrates valley. The plain on which the city extends has an altitude of . ...
, Malatya
Malatya ( hy, Մալաթիա, translit=Malat'ya; Syro-Aramaic ܡܠܝܛܝܢܐ Malīṭīná; ku, Meletî; Ancient Greek: Μελιτηνή) is a large city in the Eastern Anatolia region of Turkey and the capital of Malatya Province. The city ...
, Diyarbakır
Diyarbakır (; ; ; ) is the largest Kurdish-majority city in Turkey. It is the administrative center of Diyarbakır Province.
Situated around a high plateau by the banks of the Tigris river on which stands the historic Diyarbakır Fortress, ...
, Karabük, Zonguldak and Sivas
Sivas (Latin and Greek: ''Sebastia'', ''Sebastea'', Σεβάστεια, Σεβαστή, ) is a city in central Turkey and the seat of Sivas Province.
The city, which lies at an elevation of in the broad valley of the Kızılırmak river, is ...
. Commuter rail also runs between the stations of Sincan and Kayaş. On 13 March 2009, the new Yüksek Hızlı Tren (YHT) high-speed rail service began operation between Ankara and Eskişehir. On 23 August 2011, another YHT high-speed line commercially started its service between Ankara and Konya. On 25 July 2014, the Ankara–Istanbul high-speed line of YHT entered service.
Esenboğa International Airport, located in the north-east of the city, is Ankara's main airport.
Ankara public transportation statistics
The average amount of time people spend commuting on public transit in Ankara on a weekday is 71 minutes. 17% of public transit passengers, ride for more than two hours every day. The average amount of time people wait at a stop or station for public transit is sixteen minutes, while 28% of users wait for over twenty minutes on average every day. The average distance people usually ride in a single trip with public transit is , while 27% travel for over in a single direction.
Politics

 Since 8 April 2019, the Mayor of Ankara is Mansur Yavaş from the Republican People's Party (CHP), who won the mayoral election in 2019.
Ankara is politically a triple battleground between the ruling conservative AK Party, the opposition Kemalist center-left Republican People's Party (CHP) and the nationalist far-right MHP. The province of Ankara is divided into 25 districts. The CHP's key and almost only political stronghold in Ankara lies within the central area of Çankaya, which is the city's most populous district. While the CHP has always gained between 60 and 70% of the vote in Çankaya since 2002, political support elsewhere throughout Ankara is minimal. The high population within Çankaya, as well as Yenimahalle to an extent, has allowed the CHP to take overall second place behind the AK Party in both local and general elections, with the MHP a close third, despite the fact that the MHP is politically stronger than the CHP in almost every other district. Overall, the AK Party enjoys the most support throughout the city. The electorate of Ankara thus tend to vote in favor of the political right, far more so than the other main cities of
Since 8 April 2019, the Mayor of Ankara is Mansur Yavaş from the Republican People's Party (CHP), who won the mayoral election in 2019.
Ankara is politically a triple battleground between the ruling conservative AK Party, the opposition Kemalist center-left Republican People's Party (CHP) and the nationalist far-right MHP. The province of Ankara is divided into 25 districts. The CHP's key and almost only political stronghold in Ankara lies within the central area of Çankaya, which is the city's most populous district. While the CHP has always gained between 60 and 70% of the vote in Çankaya since 2002, political support elsewhere throughout Ankara is minimal. The high population within Çankaya, as well as Yenimahalle to an extent, has allowed the CHP to take overall second place behind the AK Party in both local and general elections, with the MHP a close third, despite the fact that the MHP is politically stronger than the CHP in almost every other district. Overall, the AK Party enjoys the most support throughout the city. The electorate of Ankara thus tend to vote in favor of the political right, far more so than the other main cities of Istanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, ...
and İzmir
İzmir ( , ; ), also spelled Izmir, is a metropolitan city in the western extremity of Anatolia, capital of the province of the same name. It is the third most populous city in Turkey, after Istanbul and Ankara and the second largest urban aggl ...
. In retrospect, the 2013–14 protests against the AK Party government were particularly strong in Ankara, proving to be fatal on multiple occasions. The city suffered from a series of terrorist attacks in 2015 and 2016, most notably on 10 October 2015; 17 February 2016; 13 March 2016; and 15 July 2016.
Melih Gökçek was the Metropolitan Mayor of Ankara between 1994 and 2017. Initially elected in the 1994 local elections, he was re-elected in 1999
File:1999 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The funeral procession of King Hussein of Jordan in Amman; the 1999 İzmit earthquake kills over 17,000 people in Turkey; the Columbine High School massacre, one of the first major school s ...
, 2004
2004 was designated as an International Year of Rice by the United Nations, and the International Year to Commemorate the Struggle Against Slavery and its Abolition (by UNESCO).
Events January
* January 3 – Flash Airlines Flight 60 ...
and 2009. In the 2014 local elections, Gökçek stood for a fifth term. The MHP's metropolitan mayoral candidate for the 2009 local elections, Mansur Yavaş, stood as the CHP's candidate against Gökçek in 2014. In a heavily controversial election, Gökçek was declared the winner by just 1% ahead of Yavaş amid allegations of systematic electoral fraud. With the Supreme Electoral Council and courts rejecting his appeals, Yavaş declared his intention to take the irregularities to the European Court of Human Rights
The European Court of Human Rights (ECHR or ECtHR), also known as the Strasbourg Court, is an international court of the Council of Europe which interprets the European Convention on Human Rights. The court hears applications alleging that a ...
. Although Gökçek was inaugurated for a fifth term, most election observers believe that Yavaş was the winner of the election. Gökçek resigned on 28 October 2017 and was replaced by the former mayor of Sincan district, Mustafa Tuna; who was succeeded by Mansur Yavaş of the CHP, the current Mayor of Ankara, elected in 2019.
Main sights
Ancient/archeological sites


Ankara Citadel
The foundations of the Ankara castle and citadel were laid by the Galatians on a prominent lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock ( magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or ...
outcrop (), and the rest was completed by the Romans. The Byzantines and Seljuks further made restorations and additions. The area around and inside the citadel, being the oldest part of Ankara, contains many fine examples of traditional architecture. There are also recreational areas to relax. Many restored traditional Turkish houses inside the citadel area have found new life as restaurants, serving local cuisine.
The citadel was depicted in various Turkish banknotes during 1927–1952 and 1983–1989.
Roman Theater
The remains, the stage, and the backstage of the Roman theater can be seen outside the castle. Roman statues that were found here are exhibited in the Museum of Anatolian Civilizations. The seating area is still under excavation.
Temple of Augustus and Rome
The Augusteum, now known as the Temple of Augustus and Rome, was built 25 20 BC following the conquest of Central Anatolia by the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
. Ancyra then formed the capital of the new province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outsi ...
of Galatia. After the death of Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
in AD 14, a copy of the text of the '' Res Gestae Divi Augusti'' (the '' Monumentum Ancyranum'') was inscribed on the interior of the temple's ' in Latin and a Greek translation on an exterior wall of the '. The temple on the ancient acropolis of Ancyra was enlarged in the 2nd century and converted into a church in the 5th century. It is located in the Ulus quarter of the city. It was subsequently publicized by the Austrian ambassador Ogier Ghiselin de Busbecq
Ogier Ghiselin de Busbecq (1522 in Comines – 29 October 1592 in Saint-Germain-sous-Cailly; la, Augerius Gislenius Busbequius), sometimes Augier Ghislain de Busbecq, was a 16th-century Flemish writer, herbalist and diplomat in the employ ...
in the 16th century.
Roman Baths
The Roman Baths of Ankara
The Roman Baths of Ankara are the ruined remains of an ancient Roman bath complex in Ankara, Turkey, which were uncovered by excavations carried out in 1937–1944, and have subsequently been opened to the public as an open-air museum.
History
Th ...
have all the typical features of a classical Roman bath complex: a '' frigidarium'' (cold room), a ''tepidarium
The tepidarium was the warm (''tepidus'') bathroom of the Roman baths heated by a hypocaust or underfloor heating system. The speciality of a tepidarium is the pleasant feeling of constant radiant heat which directly affects the human body from ...
'' (warm room) and a '' caldarium'' (hot room). The baths were built during the reign of the Roman emperor Caracalla
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Lucius Septimius Bassianus, 4 April 188 – 8 April 217), better known by his nickname "Caracalla" () was Roman emperor from 198 to 217. He was a member of the Severan dynasty, the elder son of Emperor ...
in the early 3rd century to honor Asclepios, the God of Medicine. Today, only the basement and first floors remain. It is situated in the Ulus quarter.
Roman Road
The Roman Road of Ankara
The Roman Road of Ankara or Cardo Maximus is an ancient Roman road in Ankara, the capital of Turkey. The road was found in 1995 by Turkish archaeologist Cevdet Bayburtluoğlu. It is long and wide. Many ancient artifacts were discovered during ...
or ''Cardo Maximus'' was found in 1995 by Turkish archeologist Cevdet Bayburtluoğlu. It is long and wide. Many ancient artifacts were discovered during the excavations along the road and most of them are displayed at the Museum of Anatolian Civilizations.
Column of Julian
The Column of Julian or Julianus, now in the Ulus district, was erected in honor of the Roman emperor Julian the Apostate
Julian ( la, Flavius Claudius Julianus; grc-gre, Ἰουλιανός ; 331 – 26 June 363) was Roman emperor from 361 to 363, as well as a notable philosopher and author in Greek. His rejection of Christianity, and his promotion of Neoplat ...
's visit to Ancyra in 362.
Mosques
Kocatepe Mosque
Kocatepe Mosque is the largest mosque in the city. Located in the Kocatepe quarter, it was constructed between 1967 and 1987 in classical Ottoman style with four minarets. Its size and prominent location have made it a landmark for the city.
Ahmet Hamdi Akseki Mosque
Ahmet Hamdi Akseki Mosque is located near the Presidency of Religious Affairs on the Eskişehir
Eskişehir ( , ; from "old" and "city") is a city in northwestern Turkey and the capital of the Eskişehir Province. The urban population of the city is 898,369 with a metropolitan population of 797,708. The city is located on the banks of the ...
Road. Built in the Turkish neoclassical style, it is one of the largest new mosques in the city, completed and opened in 2013. It can accommodate 6 thousand people during general prayers, and up to 30 thousand people during funeral prayers. The mosque was decorated with Anatolian Seljuk style patterns.
Yeni (Cenab Ahmet) Mosque
It is the largest Ottoman mosque in Ankara and was built by the famous architect Sinan in the 16th century. The mimber (pulpit) and mihrap (prayer niche) are of white marble, and the mosque itself is of Ankara stone, an example of very fine workmanship.
Hacı Bayram Mosque
 This mosque, in the Ulus quarter next to the Temple of Augustus, was built in the early 15th century in Seljuk style by an unknown architect. It was subsequently restored by architect
This mosque, in the Ulus quarter next to the Temple of Augustus, was built in the early 15th century in Seljuk style by an unknown architect. It was subsequently restored by architect Mimar Sinan
Mimar Sinan ( ota, معمار سينان, translit=Mi'mâr Sinân, , ) ( 1488–1490 – 17 July 1588) also known as Koca Mi'mâr Sinân Âğâ, ("Sinan Agha the Grand Architect" or "Grand Sinan") was the chief Ottoman architect ( tr, l ...
in the 16th century, with Kütahya tiles being added in the 18th century. The mosque was built in honor of Hacı Bayram-ı Veli
Haji Bayram Veli or Wali ( ar, الحاج بيرم ولي) (1352–1430) was an Ottoman poet, Sufi saint, and the founder of the Bayrami Order.Levine, Lynn A. (editor) (2006) "Hacı Bayram Mosque (Hacı Bayram Camii)" ''Frommer's Turkey'' ...
, whose tomb is next to the mosque, two years before his death (1427–28). The usable space inside this mosque is on the first floor and on the second floor.
Ahi Elvan Mosque
It was founded in the Ulus quarter near the Ankara Citadel and was constructed by the Ahi fraternity during the late 14th and early 15th centuries. The finely carved walnut mimber (pulpit) is of particular interest.
Alâeddin Mosque
The Alâeddin Mosque is the oldest mosque in Ankara. It has a carved
Carving is the act of using tools to shape something from a material by scraping away portions of that material. The technique can be applied to any material that is solid enough to hold a form even when pieces have been removed from it, and ...
walnut
A walnut is the edible seed of a drupe of any tree of the genus '' Juglans'' (family Juglandaceae), particularly the Persian or English walnut, '' Juglans regia''.
Although culinarily considered a "nut" and used as such, it is not a tru ...
mimber
A minbar (; sometimes romanized as ''mimber'') is a pulpit in a mosque where the imam (leader of prayers) stands to deliver sermons (, ''khutbah''). It is also used in other similar contexts, such as in a Hussainiya where the speaker sits and lec ...
, the inscription on which records that the mosque was completed in early AH 574 (which corresponds to the summer of 1178 AD) and was built by the Seljuk prince Muhiddin Mesud Şah (died 1204), the Bey of Ankara, who was the son of the Anatolian Seljuk sultan Kılıç Arslan II (reigned 1156–1192.)
Modern monuments
Victory Monument
The '' Victory Monument'' (Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
: '' Zafer Anıtı'') was crafted by Austrian sculptor Heinrich Krippel in 1925 and was erected in 1927 at Ulus Square. The monument is made of marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite. Marble is typically not foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorpho ...
and bronze and features an equestrian statue
An equestrian statue is a statue of a rider mounted on a horse, from the Latin ''eques'', meaning ' knight', deriving from ''equus'', meaning 'horse'. A statue of a riderless horse is strictly an equine statue. A full-sized equestrian statue is ...
of Mustafa Kemal Atatürk
Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, or Mustafa Kemal Pasha until 1921, and Ghazi Mustafa Kemal from 1921 until 1934 ( 1881 – 10 November 1938) was a Turkish field marshal, revolutionary statesman, author, and the founding father of the Rep ...
, who wears a Republic era modern military uniform, with the rank Field Marshal
Field marshal (or field-marshal, abbreviated as FM) is the most senior military rank, ordinarily senior to the general officer ranks. Usually, it is the highest rank in an army and as such few persons are appointed to it. It is considered a ...
.
Statue of Atatürk
Located at Zafer(Victory) Square (Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
: ''Zafer Meydanı''), the marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite. Marble is typically not foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorpho ...
and bronze statue was crafted by the renowned Italian sculptor Pietro Canonica in 1927 and depicts a standing Atatürk who wears a Republic era modern military uniform, with the rank Field Marshal
Field marshal (or field-marshal, abbreviated as FM) is the most senior military rank, ordinarily senior to the general officer ranks. Usually, it is the highest rank in an army and as such few persons are appointed to it. It is considered a ...
.
Monument to a Secure, Confident Future
This monument, located in Güven Park near Kızılay Square, was erected in 1935 and bears Atatürk's advice to his people: "Turk! Be proud, work hard, and believe in yourself." (There is debate on whether or not Atatürk actually said "Use your mind"(Turkish: öğün) instead of "Be proud"(Turkish: övün))
The monument was depicted on the reverse of the Turkish 5 lira banknote of 1937–1952 and of the 1000 lira banknotes of 1939–1946.
Hatti Monument
Erected in 1978 at Sıhhiye Square
Sıhhıye Square ( tr, Sıhhiye Meydanı) is a square in Ankara, Turkey. "''Sıhhiye''" is a Turkish word for "Health". Because the former main building of the Ministry of Health was facing Sıhhiye Square from the east.
Formerly, it was also ca ...
, this impressive monument symbolizes the Hatti Hatti may refer to
*Hatti (; Assyrian ) in Bronze Age Anatolia:
**the area of Hattusa, roughly delimited by the Halys bend
**the Hattians of the 3rd and 2nd millennia BC
**the Hittites of ''ca'' 1400–1200 BC
**the areas to the west of the Euphrat ...
Sun Disc (which was later adopted by the Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian people who played an important role in establishing first a kingdom in Kussara (before 1750 BC), then the Kanesh or Nesha kingdom (c. 1750–1650 BC), and next an empire centered on Hattusa in north-cent ...
) and commemorates Anatolia's earliest known civilization. The Hatti Sun Disc has been used in the previous logo of Ankara Metropolitan Municipality. It was also used in the previous logo of the Ministry of Culture & Tourism.
Inns
Suluhan

Suluhan
Suluhan is a historical caravanserai (''han'') in Ankara, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula ...
is a historical Inn in Ankara. It is also called the ''Hasanpaşa Han''. It is about southeast of Ulus Square and situated in the Hacıdoğan neighborhood. According to the ''vakfiye'' (inscription) of the building, the Ottoman era ''han'' was commissioned by Hasan Pasha, a regional beylerbey, and was constructed between 1508 and 1511, during the final years of the reign of Sultan Bayezid II
Bayezid II ( ota, بايزيد ثانى, Bāyezīd-i s̱ānī, 3 December 1447 – 26 May 1512, Turkish: ''II. Bayezid'') was the eldest son and successor of Mehmed II, ruling as Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1481 to 1512. During his reign, Ba ...
.
Çengelhan Rahmi Koç Museum
Çengelhan Rahmi Koç Museum is a museum of industrial technology situated in Çengel Han, an Ottoman era Inn which was completed in 1523, during the early years of the reign of Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent
Suleiman I ( ota, سليمان اول, Süleyman-ı Evvel; tr, I. Süleyman; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the West and Suleiman the Lawgiver ( ota, قانونى سلطان سليمان, Ḳ ...
. The exhibits include industrial/technological artifacts from the 1850s onwards. There are also sections about Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, the founder of modern Turkey; Vehbi Koç, Rahmi Koç's father and one of the first industrialists of Turkey, and Ankara city.
Shopping
 Foreign visitors to Ankara usually like to visit the old shops in ''Çıkrıkçılar Yokuşu'' (Weavers' Road) near Ulus, where myriad things ranging from traditional fabrics, hand-woven carpets and leather products can be found at bargain prices. ''Bakırcılar Çarşısı'' (Bazaar of Coppersmiths) is particularly popular, and many interesting items, not just of copper, can be found here like jewelry, carpets, costumes, antiques and embroidery. Up the hill to the castle gate, there are many shops selling a huge and fresh collection of spices,
Foreign visitors to Ankara usually like to visit the old shops in ''Çıkrıkçılar Yokuşu'' (Weavers' Road) near Ulus, where myriad things ranging from traditional fabrics, hand-woven carpets and leather products can be found at bargain prices. ''Bakırcılar Çarşısı'' (Bazaar of Coppersmiths) is particularly popular, and many interesting items, not just of copper, can be found here like jewelry, carpets, costumes, antiques and embroidery. Up the hill to the castle gate, there are many shops selling a huge and fresh collection of spices, dried fruit
Dried fruit is fruit from which the majority of the original water content has been removed either naturally, through sun drying, or through the use of specialized dryers or dehydrators. Dried fruit has a long tradition of use dating back to th ...
s, nuts, and other produce.
 Modern shopping areas are mostly found in Kızılay, or on Tunalı Hilmi Avenue, including the modern mall of Karum (named after the ancient
Modern shopping areas are mostly found in Kızılay, or on Tunalı Hilmi Avenue, including the modern mall of Karum (named after the ancient Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the As ...
n merchant colonies called ''Kârum'' that were established in central Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The r ...
at the beginning of the 2nd millennium BC) which is located towards the end of the Avenue; and in Çankaya, the quarter with the highest elevation in the city. Atakule Tower next to Atrium Mall in Çankaya has views over Ankara and also has a revolving restaurant
A revolving restaurant or rotating restaurant is usually a tower restaurant eating space designed to rest atop a broad circular revolving platform that operates as a large turntable. The building remains stationary and the diners are carried on ...
at the top. The symbol of the Armada Shopping Mall is an anchor
An anchor is a device, normally made of metal , used to secure a vessel to the bed of a body of water to prevent the craft from drifting due to wind or current. The word derives from Latin ''ancora'', which itself comes from the Greek ...
, and there's a large anchor monument at its entrance, as a reference to the ancient Greek name of the city, Ἄγκυρα (Ánkyra), which means anchor. Likewise, the anchor monument is also related with the Spanish name of the mall, Armada, which means naval fleet
A fleet or naval fleet is a large formation of warships – the largest formation in any navy – controlled by one leader. A fleet at sea is the direct equivalent of an army on land.
Purpose
In the modern sense, fleets are usually, but not n ...
.
As Ankara started expanding westward in the 1970s, several modern, suburbia-style developments and mini-cities began to rise along the western highway, also known as the Eskişehir
Eskişehir ( , ; from "old" and "city") is a city in northwestern Turkey and the capital of the Eskişehir Province. The urban population of the city is 898,369 with a metropolitan population of 797,708. The city is located on the banks of the ...
Road. The ''Armada'', ''CEPA'' and ''Kentpark'' malls on the highway, the ''Galleria'', ''Arcadium'' and ''Gordion'' in Ümitköy, and a huge mall, ''Real'' in Bilkent Center, offer North American and European style shopping opportunities (these places can be reached through the Eskişehir Highway.) There is also the newly expanded ''ANKAmall
ANKAmall is the second largest shopping centre in Turkey after Cevahir Mall from İstanbul. It is located in Ankara
Ankara ( , ; ), historically known as Ancyra and Angora, is the capital of Turkey. Located in the central part of Anatoli ...
'' at the outskirts, on the Istanbul Highway, which houses most of the well-known international brands. This mall is the largest throughout the Ankara region. In 2014, a few more shopping malls were open in Ankara. They are ''Next Level'' and ''Taurus'' on the Boulevard of Mevlana (also known as Konya
Konya () is a major city in central Turkey, on the southwestern edge of the Central Anatolian Plateau, and is the capital of Konya Province. During antiquity and into Seljuk times it was known as Iconium (), although the Seljuks also called it D ...
Road).
Culture
The arts




Turkish State Opera and Ballet
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and m ...
, the national directorate of opera and ballet companies of Turkey, has its headquarters in Ankara, and serves the city with three venues:
* Ankara Opera House (''Opera Sahnesi'', also known as ''Büyük Tiyatro'') is the largest of the three venues for opera and ballet in Ankara.
Music
Ankara is host to five classical music orchestras:
* Presidential Symphony Orchestra (Turkish Presidential Symphony Orchestra)
* Bilkent Symphony Orchestra (BSO) is a major symphony orchestra of Turkey.
*Hacettepe Symphony Orchestra The Hacettepe Symphony Orchestra (''Hacettepe Senfoni Orkestrası'') is an orchestra based in Ankara, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country ...
was founded in 2003 and directed by Erol Erdinç
*Başkent Oda Orkestrası (Chamber Orchestra of the Capital)
There are four concert halls in the city:
* CSO Concert Hall
*Bilkent Concert Hall
Bilkent is a district in Ankara, Turkey, with the postal code 06800 where Bilkent University
Bilkent University ( tr, Bilkent Üniversitesi) is a private university located in Ankara, Turkey. It was founded by Prof. İhsan Doğramacı in 1984, w ...
is a performing arts center in Ankara. It is located in the Bilkent University campus.
*MEB Şura Salonu MEB Şura Salonu also known as Festival Hall is a concert hall in Ankara. It is noted for its tango
Tango is a partner dance and social dance that originated in the 1880s along the Río de la Plata, the natural border between Argentina and Urug ...
(also known as the Festival Hall), It is noted for its tango performances.
* Çankaya Çağdaş Sanatlar Merkezi Concert Hall was founded in 1994.
The city has been host to several well-established, annual theater, music, film festivals:
*Ankara International Music Festival Ankara International Music Festival ( tr, Ankara Uluslararası Müzik Festivali) is a music festival held annually in Ankara, Turkey. In addition to Turkish artists, performers from many countries have participated in the festival.
The annual festiv ...
, a music festival organized in the Turkish capital presenting classical music and ballet programs.
Ankara also has a number of concert venues such as ''Eskiyeni'', '' IF Performance Hall'', '' Jolly Joker'', ''Kite'', ''Nefes Bar'', and ''Route'', which host the live performances and events of popular musicians.
Theater
The Turkish State Theatres
The Turkish State Theatres ( tr, Devlet Tiyatroları - DT) is the official directorate of the national theatre companies in Turkey. It is bound to the Ministry of Culture and Tourism and financed by the state to promote performed arts and enhance t ...
also has its head office in Ankara and runs the following stages in the city:
*125. Yıl Çayyolu Sahnesi
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. I ...
* Büyük Tiyatro,
* Küçük Tiyatro,
*Şinasi Sahnesi Şinasi is the Turkish spelling of the Persian name (شناسی), also transliterated as ''Shinasi''. Today, it is commonly used as a male given name.
Given name
* İbrahim Şinasi (1826–1871), Ottoman author, playwright, and journalist
* Şinasi ...
,
*Akün Sahnesi
The Turkish State Theatres ( tr, Devlet Tiyatroları - DT) is the official directorate of the national theatre companies in Turkey. It is bound to the Ministry of Culture and Tourism and financed by the state to promote performed arts and enhance t ...
,
*Altındağ Tiyatrosu
Altındağ is a metropolitan district of Ankara Province in the Central Anatolia region of Turkey, part of the city of Ankara. According to the 2000 census, the population of the district is 407,101, of which 400,023 live in the urban center of A ...
,
* İrfan Şahinbaş Atölye Sahnesi,
* Oda Tiyatrosu,
* Mahir Canova Sahnesi,
*Muhsin Ertuğrul Sahnesi
Muhsin (also spelled Mohsen, Mohsin, Mehsin, or Muhsen, ar, محسن) is a masculine Arabic given name. The first person known to have the name "Muhsin" was Muhsin bin Ali, the son of Ali ibn Abi Talib and Fatimah bint Muhammad.
Islamic term
I ...
.
In addition, the city is served by several private theater companies, among which Ankara Sanat Tiyatrosu
Ankara ( , ; ), historically known as Ancyra and Angora, is the list of national capitals, capital of Turkey. Located in the Central Anatolia Region, central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5.1 million in its urban center ...
, who have their own stage in the city center, is a notable example.
Museums
There are about 50 museums in the city.
Museum of Anatolian Civilizations
The Museum of Anatolian Civilizations (''Anadolu Medeniyetleri Müzesi'') is situated at the entrance of the Ankara Castle. It is an old 15th century bedesten (covered bazaar) that has been restored and now houses a collection of Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός '' palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone to ...
, Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several part ...
, Hatti Hatti may refer to
*Hatti (; Assyrian ) in Bronze Age Anatolia:
**the area of Hattusa, roughly delimited by the Halys bend
**the Hattians of the 3rd and 2nd millennia BC
**the Hittites of ''ca'' 1400–1200 BC
**the areas to the west of the Euphrat ...
, Hittite, Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empire ...
n, Urartian and Roman works as well as a major section dedicated to Lydia
Lydia ( Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish provin ...
n treasures.
Anıtkabir
 Anıtkabir is located on an imposing hill, which forms the ''Anıttepe'' quarter of the city, where the mausoleum of
Anıtkabir is located on an imposing hill, which forms the ''Anıttepe'' quarter of the city, where the mausoleum of Mustafa Kemal Atatürk
Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, or Mustafa Kemal Pasha until 1921, and Ghazi Mustafa Kemal from 1921 until 1934 ( 1881 – 10 November 1938) was a Turkish field marshal, revolutionary statesman, author, and the founding father of the Rep ...
, founder of the Republic of Turkey, stands. Completed in 1953, it is an impressive fusion of ancient and modern architectural styles. An adjacent museum houses a wax statue of Atatürk, his writings, letters and personal items, as well as an exhibition of photographs recording important moments in his life and during the establishment of the Republic. Anıtkabir is open every day, while the adjacent museum is open every day except Mondays.
Ankara Ethnography Museum
Ankara Ethnography Museum (''Etnoğrafya Müzesi'') is located opposite to the Ankara Opera House on Talat Paşa Boulevard, in the Ulus district. There is a fine collection of folkloric items, as well as artifacts from the Seljuk and Ottoman periods. In front of the museum building, there is a marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite. Marble is typically not foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorpho ...
and bronze equestrian statue
An equestrian statue is a statue of a rider mounted on a horse, from the Latin ''eques'', meaning ' knight', deriving from ''equus'', meaning 'horse'. A statue of a riderless horse is strictly an equine statue. A full-sized equestrian statue is ...
of Mustafa Kemal Atatürk
Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, or Mustafa Kemal Pasha until 1921, and Ghazi Mustafa Kemal from 1921 until 1934 ( 1881 – 10 November 1938) was a Turkish field marshal, revolutionary statesman, author, and the founding father of the Rep ...
(who wears a Republic era modern military uniform, with the rank Field Marshal
Field marshal (or field-marshal, abbreviated as FM) is the most senior military rank, ordinarily senior to the general officer ranks. Usually, it is the highest rank in an army and as such few persons are appointed to it. It is considered a ...
) which was crafted in 1927 by the renowned Italian sculptor Pietro Canonica.
State Art and Sculpture Museum
 The State Art and Sculpture Museum (''Resim-Heykel Müzesi'') which opened to the public in 1980 is close to the Ethnography Museum and houses a rich collection of Turkish art from the late 19th century to the present day. There are also galleries which host guest exhibitions.
The State Art and Sculpture Museum (''Resim-Heykel Müzesi'') which opened to the public in 1980 is close to the Ethnography Museum and houses a rich collection of Turkish art from the late 19th century to the present day. There are also galleries which host guest exhibitions.
Cer Modern
Cer Modern is the modern-arts museum of Ankara, inaugurated on 1 April 2010. It is situated in the renovated building of the historic TCDD Cer Atölyeleri, formerly a workshop of the Turkish State Railways. The museum incorporates the largest exhibition hall in Turkey. The museum holds periodic exhibitions of modern and contemporary art as well as hosting other contemporary arts events.
War of Independence Museum
 The War of Independence Museum (''Kurtuluş Savaşı Müzesi'') is located on Ulus Square. It was originally the first Parliament building (TBMM) of the Republic of Turkey. The War of Independence was planned and directed here as recorded in various photographs and items presently on exhibition. In another display,
The War of Independence Museum (''Kurtuluş Savaşı Müzesi'') is located on Ulus Square. It was originally the first Parliament building (TBMM) of the Republic of Turkey. The War of Independence was planned and directed here as recorded in various photographs and items presently on exhibition. In another display, wax figure
A wax sculpture is a depiction made using a waxy substance. Often these are effigies, usually of a notable individual, but there are also death masks and scenes with many figures, mostly in relief.
The properties of beeswax make it an exc ...
s of former presidents of the Republic of Turkey are on exhibit.
Mehmet Akif Literature Museum Library
The Mehmet Akif Literature Museum Library
The Mehmet Akif Ersoy Literature Museum Library ( tr, Mehmet Akif Ersoy Edebiyat Müze Kütüphanesi) is a literary museum and archive dedicated to Turkish literature and named after the poet Mehmet Âkif Ersoy (1873–1936), the Turkish poet of ...
is an important literary museum and archive opened in 2011 and dedicated to Mehmet Akif Ersoy (1873–1936), the poet of the Turkish National Anthem
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
.
TCDD Open Air Steam Locomotive Museum
The TCDD Open Air Steam Locomotive Museum is an open-air museum
An open-air museum (or open air museum) is a museum that exhibits collections of buildings and artifacts out-of-doors. It is also frequently known as a museum of buildings or a folk museum.
Definition
Open air is “the unconfined atmosphere� ...
which traces the history of steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the loco ...
s.
Ankara Aviation Museum
Ankara Aviation Museum (''Hava Kuvvetleri Müzesi Komutanlığı'') is located near the Istanbul Road in Etimesgut. The museum opened to the public in September 1998. It is home to various missiles, avionics, aviation materials and aircraft that have served in the Turkish Air Force
The Turkish Air Force ( tr, ) is the aerial warfare service branch of the Turkish Armed Forces. The Turkish Air Force can trace its origins back to June 1911 when it was founded by the Ottoman Empire, however, the air force as it is known t ...
(e.g. combat aircraft such as the F-86 Sabre, F-100 Super Sabre
The North American F-100 Super Sabre is an American supersonic jet fighter aircraft that served with the United States Air Force (USAF) from 1954 to 1971 and with the Air National Guard (ANG) until 1979. The first of the Century Series of ...
, F-102 Delta Dagger
The Convair F-102 Delta Dagger was an American interceptor aircraft designed and manufactured by Convair.
Built as part of the backbone of the United States Air Force's air defenses in the late 1950s, it entered service in 1956. Its main purpos ...
, F-104 Starfighter, F-5 Freedom Fighter, F-4 Phantom
The McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II is an American tandem two-seat, twin-engine, all-weather, long-range supersonic jet interceptor and fighter-bomber originally developed by McDonnell Aircraft for the United States Navy.Swanborough and Bo ...
; and cargo planes such as the Transall C-160.) Also a Hungarian MiG-21
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-21 (russian: Микоян и Гуревич МиГ-21; NATO reporting name: Fishbed) is a supersonic jet fighter and interceptor aircraft, designed by the Mikoyan-Gurevich Design Bureau in the Soviet Union. Its nickn ...
, a Pakistani MiG-19
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-19 (russian: Микоян и Гуревич МиГ-19; NATO reporting name: Farmer) is a Soviet second generation, single-seat, twinjet fighter aircraft, the world's first mass-produced supersonic aircraft. It was ...
, and a Bulgarian MiG-17
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-17 (russian: Микоян и Гуревич МиГ-17; NATO reporting name: Fresco) is a high-subsonic fighter aircraft produced in the Soviet Union from 1952 and was operated by air forces internationally. The MiG-17 ...
are on display at the museum.
METU Science and Technology Museum
The METU Science and Technology Museum
METU Science and Technology Museum ( tr, ODTÜ Bilim ve Teknoloji Müzesi) is a museum established within the campus of the Middle East Technical University, Ankara,
Turkey. The museum is aimed to present the modern technological tools as well as ...
(''ODTÜ Bilim ve Teknoloji Müzesi'') is located inside the Middle East Technical University
Middle East Technical University (commonly referred to as METU; in Turkish, ''Orta Doğu Teknik Üniversitesi'', ODTÜ) is a public technical university located in Ankara, Turkey. The university emphasizes research and education in engineering a ...
campus.
Sports
 As with all other cities of Turkey, football is the most popular sport in Ankara. The city has two football clubs competing in the Turkish Süper Lig: Ankaragücü, founded in 1910, is the oldest club in Ankara and is associated with Ankara's military arsenal manufacturing company MKE. They were the
As with all other cities of Turkey, football is the most popular sport in Ankara. The city has two football clubs competing in the Turkish Süper Lig: Ankaragücü, founded in 1910, is the oldest club in Ankara and is associated with Ankara's military arsenal manufacturing company MKE. They were the Turkish Cup
The Turkish Cup (Turkish: ''Türkiye Kupası'') is a football cup competition in Turkish football, run by the Turkish Football Federation since 1962. During a brief sponsorship period with Fortis, its sponsored name was ''Fortis Türkiye Kupası ...
winners in 1972 and 1981. Gençlerbirliği, founded in 1923, are known as the ''Ankara Gale'' or the ''Poppies'' because of their colors: red and black. They were the Turkish Cup winners in 1987 and 2001. Gençlerbirliği's B team, Hacettepe S.K.
Hacettepe Spor Kulübü ( en, Hacettepe Sports Club), commonly known as Hacettepe, is a Turkish professional football club located in Ankara.
History
Hacettepe Spor Kulübü was founded as Sanayi Barbarosspor in 1949. The club played in third ...
(formerly known as Gençlerbirliği OFTAŞ) played in the Süper Lig but currently plays in the TFF Second League
TFF 2. Lig (Turkish Football Federation Second League), is the third level in the Turkish football league system. It was founded in the 2001–02 season with the name of ''Turkish Second League Category B'' as a continuation of the then second le ...
. A fourth team, Büyükşehir Belediye Ankaraspor, played in the Süper Lig until 2010, when they were expelled. The club was reconstituted in 2014 as Osmanlıspor but have since returned to their old identity as Ankaraspor. Ankaraspor currently play in the TFF First League
The TFF 1. Lig, officially known as Spor Toto 1. Lig for sponsorship reasons, is the second level of the Turkish football league system. The league was founded in 2001 as the ''Turkish Second League Category A'' after the reorganization of the ...
at the Osmanlı Stadium in the Sincan district of Yenikent, outside the city center. Keçiörengücü also currently play in the TFF First League
The TFF 1. Lig, officially known as Spor Toto 1. Lig for sponsorship reasons, is the second level of the Turkish football league system. The league was founded in 2001 as the ''Turkish Second League Category A'' after the reorganization of the ...
.
Ankara has a large number of minor teams, playing at regional levels. In the TFF Second League
TFF 2. Lig (Turkish Football Federation Second League), is the third level in the Turkish football league system. It was founded in the 2001–02 season with the name of ''Turkish Second League Category B'' as a continuation of the then second le ...
: Mamak FK in Mamak, Ankara Demirspor in Çankaya, Etimesgut Belediyespor in Etimesgut; in the TFF Third League
TFF 3. Lig (Turkish Football Federation Third League) is the fourth level in the Turkish football league system. It was founded in 2001–02 season as a continuation of then third level division Turkish Third Football League.Turkish Third Footb ...
: Çankaya FK in Keçiören; AltındağsporAmateur League
A sports league is a group of sports teams or individual athletes that compete against each other and gain points in a specific sport. At its simplest, it may be a local group of amateur athletes who form teams among themselves and compete on week ...
: Turanspor in Etimesgut, Türk Telekomspor owned by the phone company in Yenimahalle, Çubukspor in Çubuk, and Bağlumspor in Keçiören.
In the Turkish Basketball League
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and ...
, Ankara is represented by Türk Telekom, whose home is the Ankara Arena, and CASA TED Kolejliler, whose home is the TOBB Sports Hall.
Halkbank Ankara is the leading domestic powerhouse in men's volleyball, having won many championships and cups in the Turkish Men's Volleyball League and even the CEV Cup
The CEV Cup is the second tier official competition for men's Volleyball clubs of Europe. The competition takes place every year.
Until 2000, it was the CEV Cup Winners' Cup. In 2000 it was renamed CEV Top Teams Cup and in 2007 it was renamed ...
in 2013.
Ankara Buz Pateni Sarayı is where the ice skating
Ice skating is the self-propulsion and gliding of a person across an ice surface, using metal-bladed ice skates. People skate for various reasons, including recreation (fun), exercise, competitive sports, and commuting. Ice skating may be per ...
and ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an Ice rink, ice skating rink with Ice hockey rink, lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two o ...
competitions take place in the city.
There are many popular spots for skateboarding which is active in the city since the 1980s. Skaters in Ankara usually meet in the park near the Grand National Assembly of Turkey
The Grand National Assembly of Turkey ( tr, ), usually referred to simply as the TBMM or Parliament ( tr, or ''Parlamento''), is the unicameral Turkish legislature. It is the sole body given the legislative prerogatives by the Turkish Consti ...
.
The 2012-built THF Sport Hall hosts the Handball Super League and Women's Handball Super League matches scheduled in Ankara.
Parks

 Ankara has many parks and open spaces mainly established in the early years of the Republic and well maintained and expanded thereafter. The most important of these parks are: Gençlik Parkı (houses an
Ankara has many parks and open spaces mainly established in the early years of the Republic and well maintained and expanded thereafter. The most important of these parks are: Gençlik Parkı (houses an amusement park
An amusement park is a park that features various attractions, such as rides and games, as well as other events for entertainment purposes. A theme park is a type of amusement park that bases its structures and attractions around a central ...
with a large pond for rowing), the Botanical garden
A botanical garden or botanic gardenThe terms ''botanic'' and ''botanical'' and ''garden'' or ''gardens'' are used more-or-less interchangeably, although the word ''botanic'' is generally reserved for the earlier, more traditional gardens, an ...
, Seğmenler Park, Anayasa Park, Kuğulu Park
Kuğulu Park (''Swan Park'') is a public park in a part of town(referred to as Tunalı by locals) in the Çankaya district of Ankara, Turkey. The park is known for its swans (a symbol of Ankara), but also has ducks and geese. Its pond was renov ...
(famous for the swans received as a gift from the Chinese government), Abdi İpekçi Park, Esertepe Parkı
Esertepe Park (literally ''Esertepe Park'') is a public park in Ankara, Turkey.
Geography
The park is at the northern part of Ankara. Its altitude changes between and , which makes it one of the highest points in Ankara. It is surrounded by hi ...
, Güven Park (see above for the monument), Kurtuluş Park (has an ice-skating rink), Altınpark
Altınpark (literally Golden Park) is a public park in Ankara, Turkey Geography
Altınpark is in Altındağ district of Ankara, situated on the way connecting Ankara to Ankara airport. The park area is
History
Up to 1977, the park area was ...
(also a prominent exposition/fair area), Harikalar Diyarı (claimed to be Biggest Park of Europe inside city borders) and Göksu Park. Dikmen Vadisi
Dikmen Vadisi (literally "Dikmen Valley") is a popular recreation and picnic area in Ankara, Turkey.
Location
The valley is a dried-up stream bed at Dikmen quarter in Çankaya ilçe (district) of Ankara. It is oriented north to east direction b ...
(Dikmen Valley) is a park and recreation area situated in Çankaya district.
Gençlik Park was depicted on the reverse of the Turkish 100 lira banknotes of 1952–1976.
Atatürk Forest Farm and Zoo
Atatürk Forest Farm and Zoo ( tr, Atatürk Orman Çiftliği ve Hayvanat Bahçesi, in short ''AOÇ'') is an expansive recreational farming area, which houses a zoo, several small agricultural farms, greenhouses, restaurants, a dairy farm and a bre ...
(''Atatürk Orman Çiftliği'') is an expansive recreational farming area which houses a zoo, several small agricultural farms, greenhouse
A greenhouse (also called a glasshouse, or, if with sufficient heating, a hothouse) is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic conditions are grown.These ...
s, restaurants, a dairy farm and a brewery. It is a pleasant place to spend a day with family, be it for having picnics, hiking, biking or simply enjoying good food and nature. There is also an exact replica of the house where Atatürk was born in 1881, in Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its Thessaloniki metropolitan area, metropolitan area, and the capi ...
, Greece. Visitors to the "Çiftlik" (farm) as it is affectionately called by Ankarans, can sample such famous products of the farm such as old-fashioned beer and ice cream
Ice cream is a sweetened frozen food typically eaten as a snack or dessert. It may be made from milk or cream and is flavoured with a sweetener, either sugar or an alternative, and a spice, such as cocoa or vanilla, or with fruit such as ...
, fresh dairy product
Dairy products or milk products, also known as lacticinia, are food products made from (or containing) milk. The most common dairy animals are cow, water buffalo, nanny goat, and ewe. Dairy products include common grocery store food items in ...
s and meat rolls/kebabs made on charcoal, at a traditional restaurant (''Merkez Lokantası'', Central Restaurant), cafés and other establishments scattered around the farm.
Education
Universities
Ankara is noted, within Turkey, for the multitude of universities it is home to. These include the following, several of them being among the most reputable in the country:
*Ankara University
Ankara University ( tr, Ankara Üniversitesi) is a public university in Ankara, the capital city of Turkey. It was the first higher education institution founded in Turkey after the formation of the republic in 1923.
The university has 40 vo ...
* Atılım University
* Başkent University
* Bilkent University
*Çankaya University
Çankaya University ( tr, Çankaya Üniversitesi) is a private university in Ankara, Turkey. It was established on July 9, 1997, by the Sıtkı Alp Education Foundation. The university began its teaching in the Fall 1997 semester. Sıtkı Al ...
* Gazi University
* Gülhane Military Medical Academy
* Hacettepe University
*Middle East Technical University
Middle East Technical University (commonly referred to as METU; in Turkish, ''Orta Doğu Teknik Üniversitesi'', ODTÜ) is a public technical university located in Ankara, Turkey. The university emphasizes research and education in engineering a ...
* TED University
* TOBB University of Economics and Technology
* Turkish Aeronautical Association University
* Turkish Military Academy
*Turkish National Police Academy
The Turkish National Police Academy ( tr, Ulusal Polis Akademisi) is a public institution of higher education in Ankara, Turkey dedicated to the training of police officers. It was founded in 1937 and has offered a four-year undergraduate program ...
* Ufuk University
*Yıldırım Beyazıt University
Yıldırım is a Turkish word meaning "lightning" and may refer to:
People
Given name
*Ali Yıldırım Koç (born 1967), Turkish businessman and member of the Koç family
*Yıldırım Akbulut (1935–2021), Turkish politician
*Yıldırım Aktun ...
Fauna
Angora cat
 Ankara is home to a world-famous domestic
Ankara is home to a world-famous domestic cat breed
The following list of cat breeds includes only domestic cat breeds and domestic and wild hybrids. The list includes established breeds recognized by various cat registries, new and experimental breeds, landraces being established as standardize ...
– the Turkish Angora
The Turkish Angora ( tr, Ankara kedisi, "Ankara cat") is a breed of domestic cat. Turkish Angoras are one of the ancient, natural breeds of cat, having originated in central Anatolia (modern-day Turkey, Ankara region). The breed has been docume ...
, called ''Ankara kedisi'' (Ankara cat) in Turkish. Turkish Angoras are one of the ancient, naturally occurring cat breeds, having originated in Ankara and its surrounding region in central Anatolia.
They mostly have a white, silky, medium to long length coat, no undercoat and a fine bone structure. There seems to be a connection between the Angora Cats and Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
, and the Turkish Angora is also a distant cousin of the Turkish Van. Although they are known for their shimmery white coat, there are more than twenty varieties including black, blue and reddish fur. They come in tabby and tabby-white, along with smoke varieties, and are in every color other than pointed, lavender, and cinnamon (all of which would indicate breeding to an outcross.)
Eyes may be blue, green, or amber, or even one blue and one amber or green. The W gene which is responsible for the white coat and blue eye is closely related to the hearing ability, and the presence of a blue eye can indicate that the cat is deaf to the side the blue eye is located. However, a great many blue and odd-eyed white cats have normal hearing, and even deaf cats lead a very normal life if kept indoors.
Ears are pointed and large, eyes are almond shaped and the head is massive with a two plane profile. Another characteristic is the tail, which is often kept parallel to the back.
Angora goat
 The Angora goat () is a breed of
The Angora goat () is a breed of domestic goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of t ...
that originated in Ankara and its surrounding region in central Anatolia.Abdülmecid I
Abdulmejid I ( ota, عبد المجيد اول, ʿAbdü'l-Mecîd-i evvel, tr, I. Abdülmecid; 25 April 182325 June 1861) was the 31st Sultan of the Ottoman Empire and succeeded his father Mahmud II on 2 July 1839. His reign was notable for the ...
in appreciation for his services and advice on the raising of cotton.
The fleece taken from an Angora goat is called mohair
Mohair (pronounced ) is a fabric or yarn made from the hair of the Angora goat. (This should not be confused with Angora wool, which is made from the fur of the Angora rabbit.) Both durable and resilient, mohair is notable for its high lus ...
. A single goat produces between of hair per year. Angoras are shorn twice a year, unlike sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus ''Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated sh ...
, which are shorn only once. Angoras have high nutritional requirements due to their rapid hair growth. A poor quality diet will curtail mohair development. The United States, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
, and South Africa are the top producers of mohair.
For a long period of time, Angora goats were bred for their white coat. In 1998, the Colored Angora Goat Breeders Association was set up to promote breeding of colored Angoras. Today, Angora goats produce white, black (deep black to greys and silver), red (the color fades significantly as the goat gets older), and brownish fiber.
Angora goats were depicted on the reverse of the Turkish 50 lira banknotes of 1938–1952.
Angora rabbit
 The Angora rabbit () is a variety of domestic rabbit bred for its long, soft hair. The Angora is one of the oldest types of domestic rabbit, originating in Ankara and its surrounding region in central Anatolia, along with the Angora cat and Angora goat. The rabbits were popular pets with French royalty in the mid-18th century, and spread to other parts of Europe by the end of the century. They first appeared in the United States in the early 20th century. They are bred largely for their long Angora wool, which may be removed by shearing, combing, or plucking (gently pulling loose wool.)
Angoras are bred mainly for their wool because it is silky and soft. They have a humorous appearance, as they oddly resemble a fur ball. Most are calm and docile but should be handled carefully. Grooming is necessary to prevent the fiber from matting and felting on the rabbit. A condition called "wool block" is common in Angora rabbits and should be treated quickly. Sometimes they are shorn in the summer as the long fur can cause the rabbits to overheat.
The Angora rabbit () is a variety of domestic rabbit bred for its long, soft hair. The Angora is one of the oldest types of domestic rabbit, originating in Ankara and its surrounding region in central Anatolia, along with the Angora cat and Angora goat. The rabbits were popular pets with French royalty in the mid-18th century, and spread to other parts of Europe by the end of the century. They first appeared in the United States in the early 20th century. They are bred largely for their long Angora wool, which may be removed by shearing, combing, or plucking (gently pulling loose wool.)
Angoras are bred mainly for their wool because it is silky and soft. They have a humorous appearance, as they oddly resemble a fur ball. Most are calm and docile but should be handled carefully. Grooming is necessary to prevent the fiber from matting and felting on the rabbit. A condition called "wool block" is common in Angora rabbits and should be treated quickly. Sometimes they are shorn in the summer as the long fur can cause the rabbits to overheat.
International relations
Twin towns and sister cities
Ankara is twinned
Twinning (making a twin of) may refer to:
* In biology and agriculture, producing two offspring (i.e., twins) at a time, or having a tendency to do so;
* Twin towns and sister cities, towns and cities involved in town twinning
* Twinning inst ...
with:
* Seoul
Seoul (; ; ), officially known as the Seoul Special City, is the Capital city, capital and largest metropolis of South Korea.Before 1972, Seoul was the ''de jure'' capital of the North Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea ...
, South Korea (since 1971)Islamabad
Islamabad (; ur, , ) is the capital city of Pakistan. It is the country's ninth-most populous city, with a population of over 1.2 million people, and is federally administered by the Pakistani government as part of the Islamabad Capita ...
, Pakistan (since 1982)
* Kuala Lumpur
, anthem = ''Maju dan Sejahtera''
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, pushpin_map = Malaysia#Southeast Asia#Asia
, pushpin_map_caption =
, coordinates =
, sub ...
, Malaysia (since 1984)
* Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
, China (since 1990)
* Amman, Jordan (since 1992)
* Bishkek
Bishkek ( ky, Бишкек), ), formerly Pishpek and Frunze, is the capital and largest city of Kyrgyzstan. Bishkek is also the administrative centre of the Chüy Region. The region surrounds the city, although the city itself is not part of ...
, Kyrgyzstan (since 1992)
* Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population ...
, Hungary (since 1992)
* Khartoum
Khartoum or Khartum ( ; ar, الخرطوم, Al-Khurṭūm, din, Kaartuɔ̈m) is the capital of Sudan. With a population of 5,274,321, its metropolitan area is the largest in Sudan. It is located at the confluence of the White Nile, flowing n ...
, Sudan (since 1992)
* Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
, Russia (since 1992)
* Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. ...
, Bulgaria (since 1992)
* Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center. , Cuba (since 1993)
* Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the List of European cities by populat ...
, Ukraine (since 1993)
* Ashgabat
Ashgabat or Asgabat ( tk, Aşgabat, ; fa, عشقآباد, translit='Ešqābād, formerly named Poltoratsk ( rus, Полтора́цк, p=pəltɐˈratsk) between 1919 and 1927), is the capital and the largest city of Turkmenistan. It lies ...
, Turkmenistan (since 1994)
* Kuwait City, Kuwait (since 1994)
* Sarajevo
Sarajevo ( ; cyrl, Сарајево, ; ''see names in other languages'') is the capital and largest city of Bosnia and Herzegovina, with a population of 275,524 in its administrative limits. The Sarajevo metropolitan area including Sarajev ...
, Bosnia and Herzegovina (since 1994)
* Tirana
Tirana ( , ; aln, Tirona) is the capital and largest city of Albania. It is located in the centre of the country, enclosed by mountains and hills with Dajti rising to the east and a slight valley to the northwest overlooking the Adriatic Sea ...
, Albania (since 1995)Tbilisi
Tbilisi ( ; ka, თბილისი ), in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis ( ), is the capital and the largest city of Georgia, lying on the banks of the Kura River with a population of approximately 1.5 million p ...
, Georgia (since 1996)Bashkortostan
The Republic of Bashkortostan or Bashkortostan ( ba, Башҡортостан Республикаһы, Bashqortostan Respublikahy; russian: Республика Башкортостан, Respublika Bashkortostan),; russian: Респу́блик� ...
, Russia (since 1997)
* Alanya, Turkey
* Bucharest
Bucharest ( , ; ro, București ) is the capital and largest city of Romania, as well as its cultural, industrial, and financial centre. It is located in the southeast of the country, on the banks of the Dâmbovița River, less than north ...
, Romania (since 1998)
* Hanoi
Hanoi or Ha Noi ( or ; vi, Hà Nội ) is the capital and second-largest city of Vietnam. It covers an area of . It consists of 12 urban districts, one district-leveled town and 17 rural districts. Located within the Red River Delta, Hanoi i ...
, Vietnam (since 1998)
* Manama
Manama ( ar, المنامة ', Bahrani pronunciation: ) is the capital and largest city of Bahrain, with an approximate population of 200,000 people as of 2020. Long an important trading center in the Persian Gulf, Manama is home to a very d ...
, Bahrain (since 2000)
* Mogadishu
Mogadishu (, also ; so, Muqdisho or ; ar, مقديشو ; it, Mogadiscio ), locally known as Xamar or Hamar, is the capital and most populous city of Somalia. The city has served as an important port connecting traders across the Indian Oc ...
, Somalia (since 2000)
* Santiago
Santiago (, ; ), also known as Santiago de Chile, is the capital and largest city of Chile as well as one of the largest cities in the Americas. It is the center of Chile's most densely populated region, the Santiago Metropolitan Region, who ...
, Chile (since 2000)
* Astana
Astana, previously known as Akmolinsk, Tselinograd, Akmola, and most recently Nur-Sultan, is the capital city of Kazakhstan.
The city lies on the banks of the Ishim River in the north-central part of Kazakhstan, within the Akmola Region, tho ...
, Kazakhstan (since 2001)
* Dushanbe
Dushanbe ( tg, Душанбе, ; ; russian: Душанбе) is the capital and largest city of Tajikistan. , Dushanbe had a population of 863,400 and that population was largely Tajik. Until 1929, the city was known in Russian as Dyushambe (ru ...
, Tajikistan (since 2003)
* Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Ac ...
, Afghanistan (since 2003)
* Ulan Bator
Ulaanbaatar (; mn, Улаанбаатар, , "Red Hero"), previously anglicized as Ulan Bator, is the capital and most populous city of Mongolia. It is the coldest capital city in the world, on average. The municipality is located in north c ...
, Mongolia (since 2003)
* Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo met ...
, Egypt (since 2004)
* Chișinău, Moldova (since 2004)Sana'a
Sanaa ( ar, صَنْعَاء, ' , Yemeni Arabic: ; Old South Arabian: 𐩮𐩬𐩲𐩥 ''Ṣnʿw''), also spelled Sana'a or Sana, is the capital and largest city in Yemen and the centre of Sanaa Governorate. The city is not part of the Gove ...
, Yemen (since 2004)
* Tashkent, Uzbekistan (since 2004)
* Pristina, Kosovo (since 2005)
* Kazan, Tatarstan, Russia (since 2005)
* Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo (since 2005)
* Addis Ababa, Ethiopia (since 2006)
* Minsk, Belarus (since 2007)
Partner cities
* Skopje, North Macedonia (since 1995)
See also
* Angora cat
* Angora goat
* Angora rabbit
*Ankara Agreement
* Ankara Arena
*Ankara Central railway station, Ankara Central Station
*Esenboğa International Airport, Ankara Esenboğa International Airport
* Ankara Metro
*Ankara Province
Ankara Province ( tr, , ) is a province of Turkey with the capital city Ankara.
Demographics
History
The site of the modern city has been home to settlements by many historic Anatolian civilizations in antiquity and classical times, in ...
*Ankara University
Ankara University ( tr, Ankara Üniversitesi) is a public university in Ankara, the capital city of Turkey. It was the first higher education institution founded in Turkey after the formation of the republic in 1923.
The university has 40 vo ...
*ATO Congresium
* Basil of Ancyra
*Battle of Ancyra
* Battle of Ankara
*Clement of Ancyra
*Gemellus of Ancyra
*History of Ankara
*List of hospitals in Ankara Province
*List of mayors of Ankara
*List of municipalities in Ankara Province
*List of districts of Ankara
*List of people from Ankara
*List of tallest buildings in Ankara
* Marcellus of Ancyra
* Monumentum Ancyranum
*Nilus of Sinai, Nilus of Ancyra
*Roman Baths of Ankara
The Roman Baths of Ankara are the ruined remains of an ancient Roman bath complex in Ankara, Turkey, which were uncovered by excavations carried out in 1937–1944, and have subsequently been opened to the public as an open-air museum.
History
Th ...
*Synod of Ancyra
*Theodotus of Ancyra (bishop)
*Theodotus of Ancyra (martyr)
*Timeline of Ankara
*Treaty of Ankara (disambiguation)
*Victory Monument (Ankara)
Notes
References
*
*
*
43
ilişki durumu evli izle
Attribution
*
*
Further reading
*
External links
Governorate of Ankara
Municipality of Ankara
Ankara Development Agency
Esenboğa International Airport
*
{{Authority control
Ankara,
Capitals in Asia
Populated places in Ankara Province
 The orthography of the name Ankara has varied over the ages. It has been identified with the Hittite cult center ''Ankuwaš'', although this remains a matter of debate.Gorny, Ronald L. "Zippalanda and Ankuwa: The Geography of Central Anatolia in the Second Millennium B.C." ''The Journal of the American Oriental Society''. Vol. 117 (1997). In classical antiquity and during the medieval period, the city was known as ''Ánkyra'' (, "
The orthography of the name Ankara has varied over the ages. It has been identified with the Hittite cult center ''Ankuwaš'', although this remains a matter of debate.Gorny, Ronald L. "Zippalanda and Ankuwa: The Geography of Central Anatolia in the Second Millennium B.C." ''The Journal of the American Oriental Society''. Vol. 117 (1997). In classical antiquity and during the medieval period, the city was known as ''Ánkyra'' (, " The region's history can be traced back to the
The region's history can be traced back to the  The oldest settlements in and around the city center of Ankara belonged to the Hattic
The oldest settlements in and around the city center of Ankara belonged to the Hattic  In 278 BC, the city, along with the rest of central Anatolia, was occupied by a
In 278 BC, the city, along with the rest of central Anatolia, was occupied by a 
 The city was subsequently passed under the control of the
The city was subsequently passed under the control of the  An estimated 200,000 people lived in Ancyra in good times during the Roman Empire, a far greater number than was to be the case from after the fall of the Roman Empire until the early 20th century. The small Ankara River ran through the center of the Roman town. It has now been covered and diverted, but it formed the northern boundary of the old town during the Roman, Byzantine and Ottoman periods. Çankaya, the rim of the majestic hill to the south of the present city center, stood well outside the Roman city, but may have been a summer resort. In the 19th century, the remains of at least one
An estimated 200,000 people lived in Ancyra in good times during the Roman Empire, a far greater number than was to be the case from after the fall of the Roman Empire until the early 20th century. The small Ankara River ran through the center of the Roman town. It has now been covered and diverted, but it formed the northern boundary of the old town during the Roman, Byzantine and Ottoman periods. Çankaya, the rim of the majestic hill to the south of the present city center, stood well outside the Roman city, but may have been a summer resort. In the 19th century, the remains of at least one  Early Christian martyrs of Ancyra, about whom little is known, included Proklos and Hilarios who were natives of the otherwise unknown nearby village of Kallippi, and suffered repression under the emperor
Early Christian martyrs of Ancyra, about whom little is known, included Proklos and Hilarios who were natives of the otherwise unknown nearby village of Kallippi, and suffered repression under the emperor  The
The  After the
After the  Following the Ottoman defeat in
Following the Ottoman defeat in  Government offices and foreign embassies are also located in the new section. Ankara has experienced a phenomenal growth since it was made Turkey's capital in 1923, when it was "a small town of no importance". In 1924, the year after the government had moved there, Ankara had about 35,000 residents. By 1927 there were 44,553 residents and by 1950 the population had grown to 286,781. Ankara continued to grow rapidly during the latter half of the 20th century and eventually outranked Izmir as Turkey's second-largest city, after
Government offices and foreign embassies are also located in the new section. Ankara has experienced a phenomenal growth since it was made Turkey's capital in 1923, when it was "a small town of no importance". In 1924, the year after the government had moved there, Ankara had about 35,000 residents. By 1927 there were 44,553 residents and by 1950 the population had grown to 286,781. Ankara continued to grow rapidly during the latter half of the 20th century and eventually outranked Izmir as Turkey's second-largest city, after  Ankara has long been a productive agricultural region in Anatolia. In the Ottoman period, Ankara was well known for producing grain, cotton, and fruits.
The city has exported
Ankara has long been a productive agricultural region in Anatolia. In the Ottoman period, Ankara was well known for producing grain, cotton, and fruits.
The city has exported  The
The  Ankara is the center of the state-owned and private Turkish
Ankara is the center of the state-owned and private Turkish  Geographically, Ankara is located in the middle of the Kızılırmak and
Geographically, Ankara is located in the middle of the Kızılırmak and  Ankara had a population of 75,000 in 1927. As of 2019, the population of the Ankara Province was 5,639,076. When Ankara became the capital of the Republic of Turkey in 1923, it was designated as a planned city for 500,000 future inhabitants. During the 1920s, 1930s and 1940s, the city grew in a planned and orderly pace. However, from the 1950s onward, the city grew much faster than envisioned, because unemployment and poverty forced people to migrate from the countryside into the city in order to seek a better standard of living. As a result, many illegal houses called gecekondu were built around the city, causing the unplanned and uncontrolled urban landscape of Ankara, as not enough planned housing could be built fast enough. Although precariously built, the vast majority of them have electricity, running water and modern household amenities.
Nevertheless, many of these gecekondus have been replaced by huge public housing projects in the form of
Ankara had a population of 75,000 in 1927. As of 2019, the population of the Ankara Province was 5,639,076. When Ankara became the capital of the Republic of Turkey in 1923, it was designated as a planned city for 500,000 future inhabitants. During the 1920s, 1930s and 1940s, the city grew in a planned and orderly pace. However, from the 1950s onward, the city grew much faster than envisioned, because unemployment and poverty forced people to migrate from the countryside into the city in order to seek a better standard of living. As a result, many illegal houses called gecekondu were built around the city, causing the unplanned and uncontrolled urban landscape of Ankara, as not enough planned housing could be built fast enough. Although precariously built, the vast majority of them have electricity, running water and modern household amenities.
Nevertheless, many of these gecekondus have been replaced by huge public housing projects in the form of 
 The ''Electricity, Gas, Bus General Directorate'' (EGO) operates the Ankara Metro and other forms of public transportation. Ankara is served by a
The ''Electricity, Gas, Bus General Directorate'' (EGO) operates the Ankara Metro and other forms of public transportation. Ankara is served by a 
 Since 8 April 2019, the Mayor of Ankara is Mansur Yavaş from the Republican People's Party (CHP), who won the mayoral election in 2019.
Ankara is politically a triple battleground between the ruling conservative AK Party, the opposition Kemalist center-left Republican People's Party (CHP) and the nationalist far-right MHP. The province of Ankara is divided into 25 districts. The CHP's key and almost only political stronghold in Ankara lies within the central area of Çankaya, which is the city's most populous district. While the CHP has always gained between 60 and 70% of the vote in Çankaya since 2002, political support elsewhere throughout Ankara is minimal. The high population within Çankaya, as well as Yenimahalle to an extent, has allowed the CHP to take overall second place behind the AK Party in both local and general elections, with the MHP a close third, despite the fact that the MHP is politically stronger than the CHP in almost every other district. Overall, the AK Party enjoys the most support throughout the city. The electorate of Ankara thus tend to vote in favor of the political right, far more so than the other main cities of
Since 8 April 2019, the Mayor of Ankara is Mansur Yavaş from the Republican People's Party (CHP), who won the mayoral election in 2019.
Ankara is politically a triple battleground between the ruling conservative AK Party, the opposition Kemalist center-left Republican People's Party (CHP) and the nationalist far-right MHP. The province of Ankara is divided into 25 districts. The CHP's key and almost only political stronghold in Ankara lies within the central area of Çankaya, which is the city's most populous district. While the CHP has always gained between 60 and 70% of the vote in Çankaya since 2002, political support elsewhere throughout Ankara is minimal. The high population within Çankaya, as well as Yenimahalle to an extent, has allowed the CHP to take overall second place behind the AK Party in both local and general elections, with the MHP a close third, despite the fact that the MHP is politically stronger than the CHP in almost every other district. Overall, the AK Party enjoys the most support throughout the city. The electorate of Ankara thus tend to vote in favor of the political right, far more so than the other main cities of 

 This mosque, in the Ulus quarter next to the Temple of Augustus, was built in the early 15th century in Seljuk style by an unknown architect. It was subsequently restored by architect
This mosque, in the Ulus quarter next to the Temple of Augustus, was built in the early 15th century in Seljuk style by an unknown architect. It was subsequently restored by architect 
 Modern shopping areas are mostly found in Kızılay, or on Tunalı Hilmi Avenue, including the modern mall of Karum (named after the ancient
Modern shopping areas are mostly found in Kızılay, or on Tunalı Hilmi Avenue, including the modern mall of Karum (named after the ancient 



 Anıtkabir is located on an imposing hill, which forms the ''Anıttepe'' quarter of the city, where the mausoleum of
Anıtkabir is located on an imposing hill, which forms the ''Anıttepe'' quarter of the city, where the mausoleum of  The State Art and Sculpture Museum (''Resim-Heykel Müzesi'') which opened to the public in 1980 is close to the Ethnography Museum and houses a rich collection of Turkish art from the late 19th century to the present day. There are also galleries which host guest exhibitions.
The State Art and Sculpture Museum (''Resim-Heykel Müzesi'') which opened to the public in 1980 is close to the Ethnography Museum and houses a rich collection of Turkish art from the late 19th century to the present day. There are also galleries which host guest exhibitions.
 The War of Independence Museum (''Kurtuluş Savaşı Müzesi'') is located on Ulus Square. It was originally the first Parliament building (TBMM) of the Republic of Turkey. The War of Independence was planned and directed here as recorded in various photographs and items presently on exhibition. In another display,
The War of Independence Museum (''Kurtuluş Savaşı Müzesi'') is located on Ulus Square. It was originally the first Parliament building (TBMM) of the Republic of Turkey. The War of Independence was planned and directed here as recorded in various photographs and items presently on exhibition. In another display,  As with all other cities of Turkey, football is the most popular sport in Ankara. The city has two football clubs competing in the Turkish Süper Lig: Ankaragücü, founded in 1910, is the oldest club in Ankara and is associated with Ankara's military arsenal manufacturing company MKE. They were the
As with all other cities of Turkey, football is the most popular sport in Ankara. The city has two football clubs competing in the Turkish Süper Lig: Ankaragücü, founded in 1910, is the oldest club in Ankara and is associated with Ankara's military arsenal manufacturing company MKE. They were the 
 Ankara has many parks and open spaces mainly established in the early years of the Republic and well maintained and expanded thereafter. The most important of these parks are: Gençlik Parkı (houses an
Ankara has many parks and open spaces mainly established in the early years of the Republic and well maintained and expanded thereafter. The most important of these parks are: Gençlik Parkı (houses an  Ankara is home to a world-famous domestic
Ankara is home to a world-famous domestic  The Angora rabbit () is a variety of domestic rabbit bred for its long, soft hair. The Angora is one of the oldest types of domestic rabbit, originating in Ankara and its surrounding region in central Anatolia, along with the Angora cat and Angora goat. The rabbits were popular pets with French royalty in the mid-18th century, and spread to other parts of Europe by the end of the century. They first appeared in the United States in the early 20th century. They are bred largely for their long Angora wool, which may be removed by shearing, combing, or plucking (gently pulling loose wool.)
Angoras are bred mainly for their wool because it is silky and soft. They have a humorous appearance, as they oddly resemble a fur ball. Most are calm and docile but should be handled carefully. Grooming is necessary to prevent the fiber from matting and felting on the rabbit. A condition called "wool block" is common in Angora rabbits and should be treated quickly. Sometimes they are shorn in the summer as the long fur can cause the rabbits to overheat.
The Angora rabbit () is a variety of domestic rabbit bred for its long, soft hair. The Angora is one of the oldest types of domestic rabbit, originating in Ankara and its surrounding region in central Anatolia, along with the Angora cat and Angora goat. The rabbits were popular pets with French royalty in the mid-18th century, and spread to other parts of Europe by the end of the century. They first appeared in the United States in the early 20th century. They are bred largely for their long Angora wool, which may be removed by shearing, combing, or plucking (gently pulling loose wool.)
Angoras are bred mainly for their wool because it is silky and soft. They have a humorous appearance, as they oddly resemble a fur ball. Most are calm and docile but should be handled carefully. Grooming is necessary to prevent the fiber from matting and felting on the rabbit. A condition called "wool block" is common in Angora rabbits and should be treated quickly. Sometimes they are shorn in the summer as the long fur can cause the rabbits to overheat.