Abbasid Governors Of Damascus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the
 The quarrel was taken up by Ibrahim's brother Abdallah, known by the name of Abu al-'Abbas as-Saffah, who defeated the Umayyads in 750 in the battle near the Great Zab and was subsequently proclaimed caliph. After this loss,
The quarrel was taken up by Ibrahim's brother Abdallah, known by the name of Abu al-'Abbas as-Saffah, who defeated the Umayyads in 750 in the battle near the Great Zab and was subsequently proclaimed caliph. After this loss,

 The first change made by the Abbasids under Al-Mansur was to move the empire's capital from
The first change made by the Abbasids under Al-Mansur was to move the empire's capital from


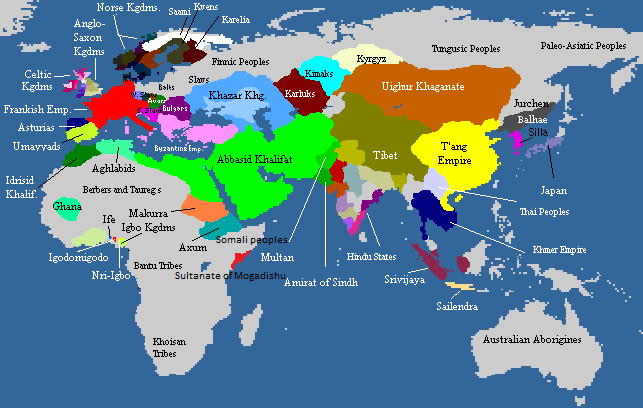 By the 870s, Egypt became autonomous under
By the 870s, Egypt became autonomous under  Outside Iraq, all the autonomous provinces slowly took on the characteristic of de facto states with hereditary rulers, armies, and revenues and operated under only nominal caliph suzerainty, which may not necessarily be reflected by any contribution to the treasury, such as the Soomro Emirs that had gained control of
Outside Iraq, all the autonomous provinces slowly took on the characteristic of de facto states with hereditary rulers, armies, and revenues and operated under only nominal caliph suzerainty, which may not necessarily be reflected by any contribution to the treasury, such as the Soomro Emirs that had gained control of
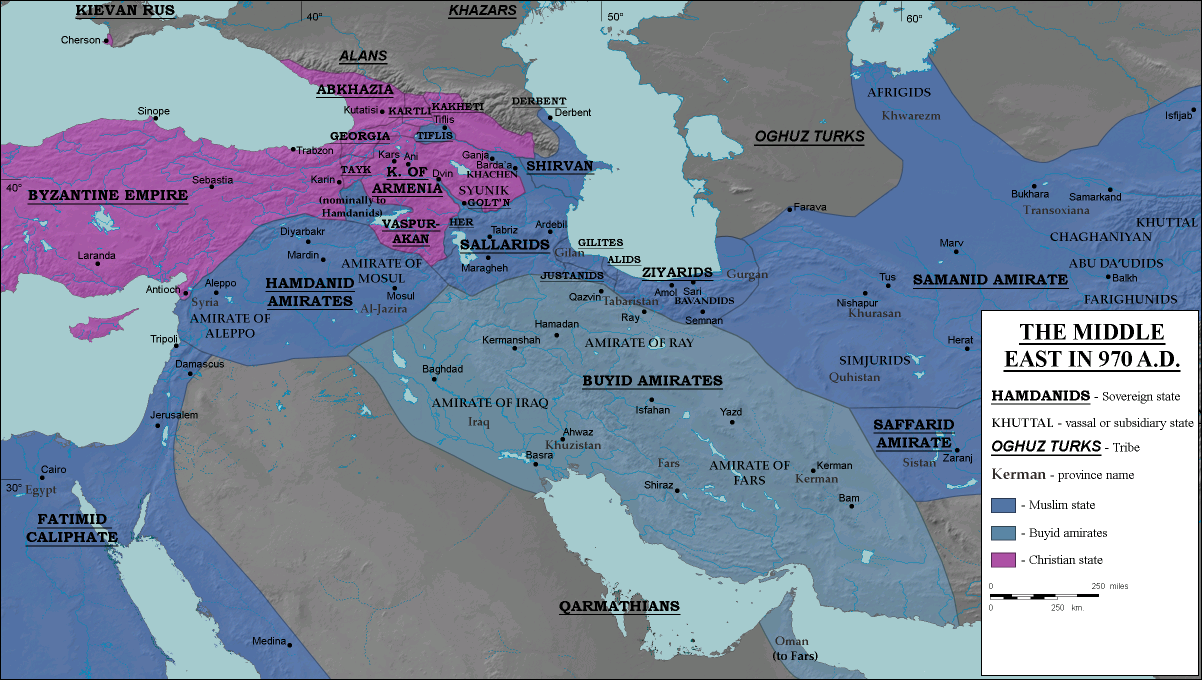 Despite the power of the Buyid amirs, the Abbasids retained a highly ritualized court in Baghdad, as described by the Buyid bureaucrat
Despite the power of the Buyid amirs, the Abbasids retained a highly ritualized court in Baghdad, as described by the Buyid bureaucrat
 While the Caliph al-Mustarshid was the first caliph to build an army capable of meeting a Seljuk army in battle, he was nonetheless defeated and assassinated in 1135. The Caliph al-Muqtafi was the first Abbasid Caliph to regain the full military independence of the Caliphate, with the help of his vizier Ibn Hubayra. After nearly 250 years of subjection to foreign dynasties, he successfully defended Baghdad against the Seljuqs in the
While the Caliph al-Mustarshid was the first caliph to build an army capable of meeting a Seljuk army in battle, he was nonetheless defeated and assassinated in 1135. The Caliph al-Muqtafi was the first Abbasid Caliph to regain the full military independence of the Caliphate, with the help of his vizier Ibn Hubayra. After nearly 250 years of subjection to foreign dynasties, he successfully defended Baghdad against the Seljuqs in the
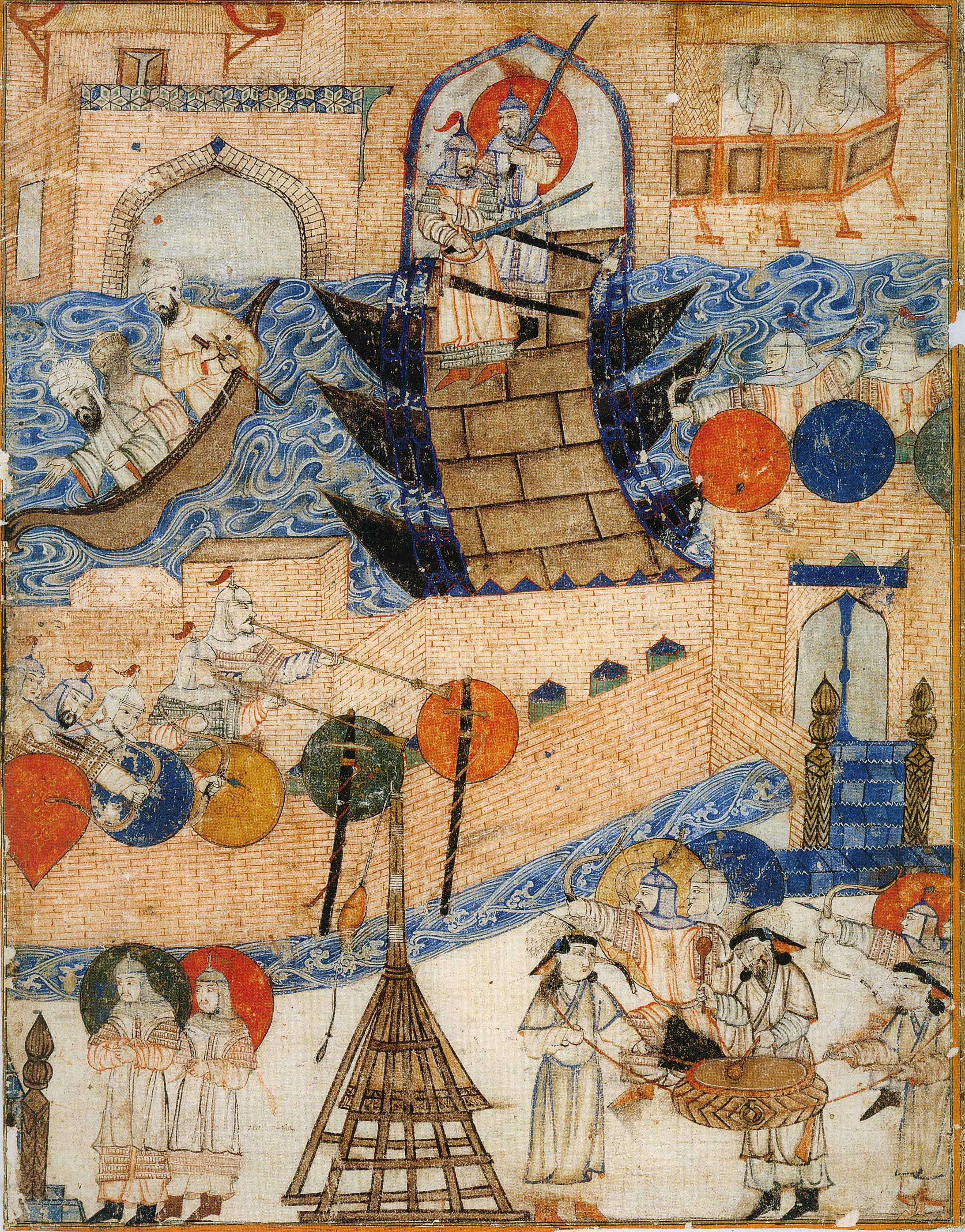 In 1206,
In 1206,
 The Abbasid historical period lasting to the
The Abbasid historical period lasting to the
 The reigns of Harun al-Rashid (786–809) and his successors fostered an age of great intellectual achievement. In large part, this was the result of the schismatic forces that had undermined the Umayyad regime, which relied on the assertion of the superiority of Arab culture as part of its claim to legitimacy, and the Abbasids' welcoming of support from non-Arab Muslims. It is well established that the Abbasid caliphs modeled their administration on that of the Sassanids. Harun al-Rashid's son,
The reigns of Harun al-Rashid (786–809) and his successors fostered an age of great intellectual achievement. In large part, this was the result of the schismatic forces that had undermined the Umayyad regime, which relied on the assertion of the superiority of Arab culture as part of its claim to legitimacy, and the Abbasids' welcoming of support from non-Arab Muslims. It is well established that the Abbasid caliphs modeled their administration on that of the Sassanids. Harun al-Rashid's son,  A number of medieval thinkers and scientists living under Islamic rule played a role in transmitting Islamic science to the Christian West. In addition, the period saw the recovery of much of the Alexandrian mathematical, geometric and astronomical knowledge, such as that of Euclid and Claudius Ptolemy. These recovered mathematical methods were later enhanced and developed by other Islamic scholars, notably by Persian scientists Al-Biruni and Abu Nasr Mansur.
Christians (particularly Nestorian Christians) contributed to the Arab Islamic Civilization during the Umayyads and the Abbasids by translating works of Greek philosophers to Syriac and afterwards to Arabic. Nestorians played a prominent role in the formation of Arab culture, with the
A number of medieval thinkers and scientists living under Islamic rule played a role in transmitting Islamic science to the Christian West. In addition, the period saw the recovery of much of the Alexandrian mathematical, geometric and astronomical knowledge, such as that of Euclid and Claudius Ptolemy. These recovered mathematical methods were later enhanced and developed by other Islamic scholars, notably by Persian scientists Al-Biruni and Abu Nasr Mansur.
Christians (particularly Nestorian Christians) contributed to the Arab Islamic Civilization during the Umayyads and the Abbasids by translating works of Greek philosophers to Syriac and afterwards to Arabic. Nestorians played a prominent role in the formation of Arab culture, with the  Arab scientist Ibn al-Haytham (Alhazen) developed an early scientific method in his ''
Arab scientist Ibn al-Haytham (Alhazen) developed an early scientific method in his ''
 As power shifted from the Umayyads to the Abbasids, the architectural styles changed also, from Greco-Roman tradition (which features elements of Hellenistic and Roman representative style) to Eastern tradition which retained their independent architectural traditions from Mesopotamia and Persia. The Abbasid architecture was particularly influenced by Sasanian architecture, which in turn featured elements present since ancient Mesopotamia. The Christian styles evolved into a style based more on the
As power shifted from the Umayyads to the Abbasids, the architectural styles changed also, from Greco-Roman tradition (which features elements of Hellenistic and Roman representative style) to Eastern tradition which retained their independent architectural traditions from Mesopotamia and Persia. The Abbasid architecture was particularly influenced by Sasanian architecture, which in turn featured elements present since ancient Mesopotamia. The Christian styles evolved into a style based more on the
 Early Abbasid painting has not survived in great quantities, and is sometimes harder to differentiate; however, Samarra provides good examples, as it was built by the Abbasids and abandoned 56 years later. The walls of the principal rooms of the palace that have been excavated show wall paintings and lively carved stucco dadoes. The style is obviously adopted with little variation from Sassanian art, bearing not only similar styles, with harems, animals, and dancing people, all enclosed in scrollwork, but the garments are also Persian.
Early Abbasid painting has not survived in great quantities, and is sometimes harder to differentiate; however, Samarra provides good examples, as it was built by the Abbasids and abandoned 56 years later. The walls of the principal rooms of the palace that have been excavated show wall paintings and lively carved stucco dadoes. The style is obviously adopted with little variation from Sassanian art, bearing not only similar styles, with harems, animals, and dancing people, all enclosed in scrollwork, but the garments are also Persian.
 Whereas painting and architecture were not areas of strength for the Abbasid dynasty, pottery was a different story. Islamic culture as a whole, and the Abbasids in particular, were at the forefront of new ideas and techniques. Some examples of their work were pieces engraved with decorations and then colored with yellow-brown, green, and purple glazes. Designs were diverse with geometric patterns, Kufic lettering, and arabesque scrollwork, along with rosettes, animals, birds, and humans. Abbasid pottery from the 8th and 9th centuries has been found throughout the region, as far as Cairo. These were generally made with a yellow clay and fired multiple times with separate glazes to produce metallic luster in shades of gold, brown, or red. By the 9th century, the potters had mastered their techniques and their decorative designs could be divided into two styles. The Persian style would show animals, birds, and humans, along with Kufic lettering in gold. Pieces excavated from
Whereas painting and architecture were not areas of strength for the Abbasid dynasty, pottery was a different story. Islamic culture as a whole, and the Abbasids in particular, were at the forefront of new ideas and techniques. Some examples of their work were pieces engraved with decorations and then colored with yellow-brown, green, and purple glazes. Designs were diverse with geometric patterns, Kufic lettering, and arabesque scrollwork, along with rosettes, animals, birds, and humans. Abbasid pottery from the 8th and 9th centuries has been found throughout the region, as far as Cairo. These were generally made with a yellow clay and fired multiple times with separate glazes to produce metallic luster in shades of gold, brown, or red. By the 9th century, the potters had mastered their techniques and their decorative designs could be divided into two styles. The Persian style would show animals, birds, and humans, along with Kufic lettering in gold. Pieces excavated from
 In technology, the Abbasids adopted
In technology, the Abbasids adopted  Engineers in the Abbasid caliphate made a number of innovative industrial uses of hydropower, and early industrial uses of tidal power, wind power, and petroleum (notably by distillation into kerosene). The industrial uses of watermills in the Islamic world date back to the 7th century, while horizontal-
Engineers in the Abbasid caliphate made a number of innovative industrial uses of hydropower, and early industrial uses of tidal power, wind power, and petroleum (notably by distillation into kerosene). The industrial uses of watermills in the Islamic world date back to the 7th century, while horizontal-
 The status and treatment of Jews, Christians, and non-Muslims in the Abbasid Caliphate was a complex and continually changing issue. Non-Muslims were called
The status and treatment of Jews, Christians, and non-Muslims in the Abbasid Caliphate was a complex and continually changing issue. Non-Muslims were called
 The standing army of the Muslims in Khorosan was overwhelmingly Arab. The unit organization of the Abbasids was designed with the goal of ethnic and racial equality among supporters. When Abu Muslim recruited officers along the Silk Road, he registered them based not on their tribal or ethno-national affiliations but on their current places of residence. The Cambridge History of Iran
The standing army of the Muslims in Khorosan was overwhelmingly Arab. The unit organization of the Abbasids was designed with the goal of ethnic and racial equality among supporters. When Abu Muslim recruited officers along the Silk Road, he registered them based not on their tribal or ethno-national affiliations but on their current places of residence. The Cambridge History of Iran
p. 62
Ed. Richard N. Frye. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1975. Under the Abbasids, Iranian peoples became better represented in the army and bureaucracy as compared to before. The Abbasid army was centred on the Khurasan
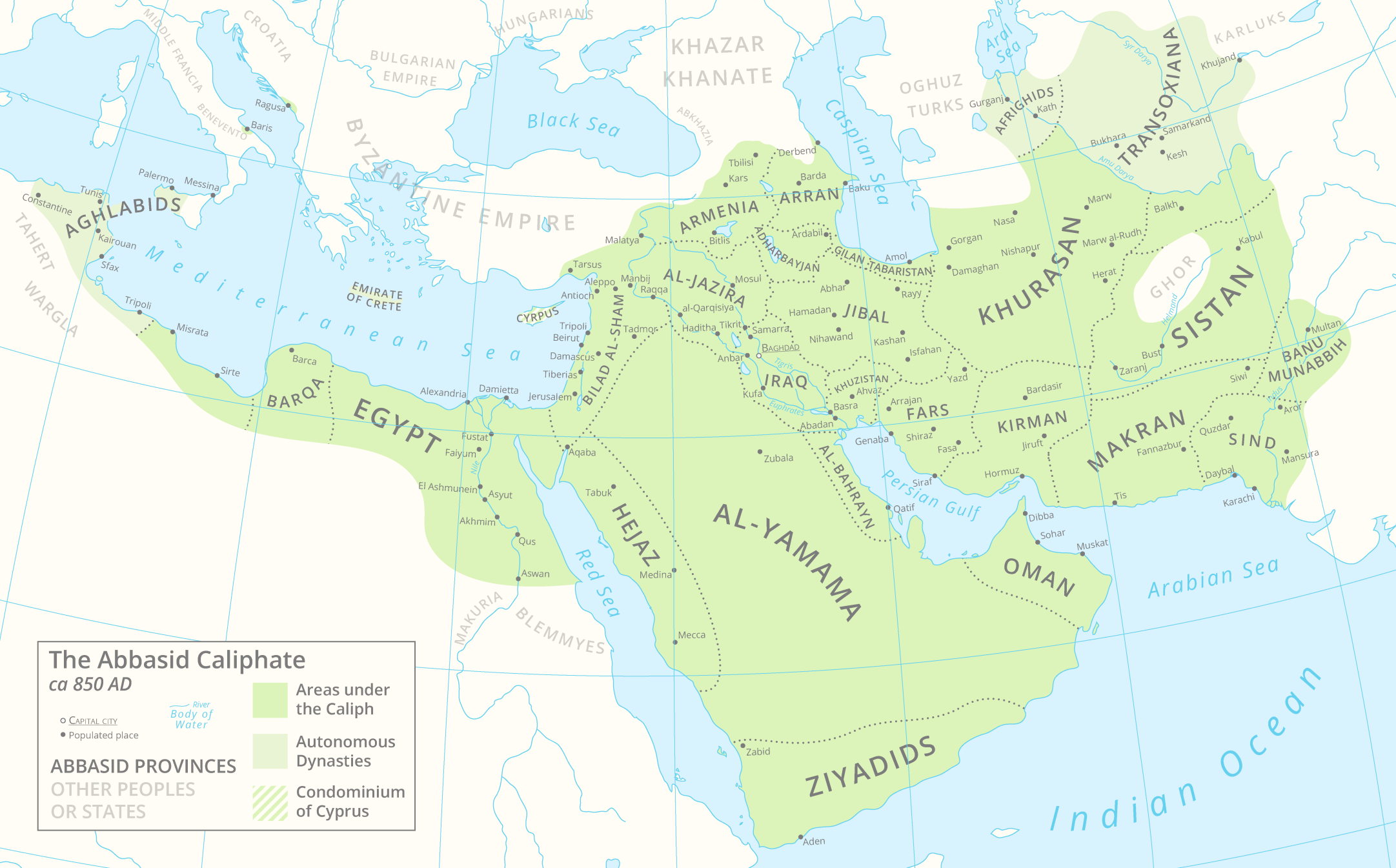 As a result of such a vast Empire, the caliphate was decentralized and divided into 24 provinces.
In keeping with Persian tradition, Harun's vizier enjoyed close to unchecked powers. Under Harun, a special "bureau of confiscation" was created. This governmental wing made it possible for the vizier to seize the property and riches of any corrupt governor or civil servant. In addition, it allowed governors to confiscate the estates of lower-ranking officials. Finally, the caliph could impose the same penalty on a vizier who fell from grace. As one later caliph put it: "The vizier is our representative throughout the land and amongst our subjects. Therefore, he who obeys him obeys us; and he who obeys us obeys God, and God shall cause him who obeys Him to enter paradise."
Every regional metropolis had a post office and hundreds of roads were paved in order to link the imperial capital with other cities and towns. The empire employed a system of relays to deliver mail. The central post office in Baghdad even had a map with directions that noted the distances between each town. The roads were provided with roadside inns, hospices, and wells and could reach eastward through Persia and Central Asia, to as far as China. The post office not only enhanced civil services but also served as intelligence for the caliph. Mailmen were employed as spies who kept an eye on local affairs.
Early in the days of the caliphate, the Barmakids took the responsibility of shaping the
As a result of such a vast Empire, the caliphate was decentralized and divided into 24 provinces.
In keeping with Persian tradition, Harun's vizier enjoyed close to unchecked powers. Under Harun, a special "bureau of confiscation" was created. This governmental wing made it possible for the vizier to seize the property and riches of any corrupt governor or civil servant. In addition, it allowed governors to confiscate the estates of lower-ranking officials. Finally, the caliph could impose the same penalty on a vizier who fell from grace. As one later caliph put it: "The vizier is our representative throughout the land and amongst our subjects. Therefore, he who obeys him obeys us; and he who obeys us obeys God, and God shall cause him who obeys Him to enter paradise."
Every regional metropolis had a post office and hundreds of roads were paved in order to link the imperial capital with other cities and towns. The empire employed a system of relays to deliver mail. The central post office in Baghdad even had a map with directions that noted the distances between each town. The roads were provided with roadside inns, hospices, and wells and could reach eastward through Persia and Central Asia, to as far as China. The post office not only enhanced civil services but also served as intelligence for the caliph. Mailmen were employed as spies who kept an eye on local affairs.
Early in the days of the caliphate, the Barmakids took the responsibility of shaping the
Islamic prophet
Prophets in Islam ( ar, الأنبياء في الإسلام, translit=al-ʾAnbiyāʾ fī al-ʾIslām) are individuals in Islam who are believed to spread God in Islam, God's message on Earth and to serve as models of ideal human behaviour. So ...
Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes its name. They ruled as caliphs for most of the caliphate from their capital in Baghdad in modern-day Iraq, after having overthrown the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 AH). The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph Al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad, near the ancient Babylonian capital city of Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
. Baghdad became the center of science, culture and invention
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition, idea or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a machine, product, or process for increasing efficiency or lowering cost. It may also be an entirely new concept. If an i ...
in what became known as the Golden Age of Islam
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
. This, in addition to housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom
The House of Wisdom ( ar, بيت الحكمة, Bayt al-Ḥikmah), also known as the Grand Library of Baghdad, refers to either a major Abbasid public academy and intellectual center in Baghdad or to a large private library belonging to the Abba ...
, as well as a multiethnic and multi-religious environment, garnered it a worldwide reputation as the "Center of Learning".
The Abbasid period was marked by dependence on Persian bureaucrats (such as the Barmakid family) for governing the territories as well as an increasing inclusion of non-Arab Muslims in the '' ummah'' (Muslim community). Persian customs were broadly adopted by the ruling elite, and they began patronage of artists and scholars. Despite this initial cooperation, the Abbasids of the late 8th century had alienated both non-Arab '' mawali'' (clients) and Persian bureaucrats. They were forced to cede authority over al-Andalus (current Spain and Portugal) to the Umayyads in 756, Morocco to the Idrisids in 788, Ifriqiya
Ifriqiya ( '), also known as al-Maghrib al-Adna ( ar, المغرب الأدنى), was a medieval historical region comprising today's Tunisia and eastern Algeria, and Tripolitania (today's western Libya). It included all of what had previously ...
and Sicily to the Aghlabids
The Aghlabids ( ar, الأغالبة) were an Arab dynasty of emirs from the Najdi tribe of Banu Tamim, who ruled Ifriqiya and parts of Southern Italy, Sicily, and possibly Sardinia, nominally on behalf of the Abbasid Caliph, for about a cen ...
in 800, Khorasan
Khorasan may refer to:
* Greater Khorasan, a historical region which lies mostly in modern-day northern/northwestern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
* Khorasan Province, a pre-2004 province of Ira ...
and Transoxiana to the Samanid
The Samanid Empire ( fa, سامانیان, Sāmāniyān) also known as the Samanian Empire, Samanid dynasty, Samanid amirate, or simply as the Samanids) was a Persianate Sunni Muslim empire, of Iranian dehqan origin. The empire was centred in Kho ...
s and Persia to the Saffarids in the 870s, and Egypt to the Isma'ili- Shia caliphate of the Fatimids in 969.
The political power of the caliphs was limited with the rise of the Iranian Buyids and the Seljuq Turks, who captured Baghdad in 945 and 1055, respectively. Although Abbasid leadership over the vast Islamic empire was gradually reduced to a ceremonial religious function in much of the Caliphate, the dynasty retained control of its Mesopotamian
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
domain during the rule of Caliph Al-Muqtafi and extended into Iran during the reign of Caliph Al-Nasir
Abu'l-Abbas Ahmad ibn al-Hassan al-Mustadi' ( ar, أبو العباس أحمد بن الحسن المستضيء) better known by his laqab Al-Nasir li-Din Allah ( ar, الناصر لدين الله; 6 August 1158 – 5 October 1225) or simply as A ...
. The Abbasids age of cultural revival and fruition ended in 1258 with the sack of Baghdad by the Mongols under Hulagu Khan and the execution of Al-Musta'sim. The Abbasid line of rulers, and Muslim culture in general, re-centred themselves in the Mamluk capital of Cairo in 1261. Though lacking in political power (with the brief exception of Caliph Al-Musta'in of Cairo), the dynasty continued to claim religious authority until a few years after the Ottoman conquest of Egypt in 1517, with the last Abbasid caliph being Al-Mutawakkil III.
History
Abbasid Revolution (750–751)
The Abbasid caliphs were Arabs descended from Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib, one of the youngest uncles of Muhammad and of the sameBanu Hashim
)
, type = Qurayshi Arab clan
, image =
, alt =
, caption =
, nisba = al-Hashimi
, location = Mecca, Hejaz Middle East, North Africa, Horn of Africa
, descended = Hashim ibn Abd Manaf
, parent_tribe = Qu ...
clan. The Abbasids claimed to be the true successors of Muhammad in replacing the Umayyad descendants of Banu Umayya by virtue of their closer bloodline to Muhammad.
The Abbasids also distinguished themselves from the Umayyads by attacking their moral character and administration in general. According to Ira Lapidus
Ira M. Lapidus is an Emeritus Professor of Middle Eastern and Islamic History at The University of California at Berkeley. He is the author of ''A History of Islamic Societies'', and ''Contemporary Islamic Movements in Historical Perspective'', ...
, "The Abbasid revolt was supported largely by Arabs, mainly the aggrieved settlers of Merv with the addition of the Yemeni faction and their Mawali". The Abbasids also appealed to non-Arab Muslims, known as '' mawali'', who remained outside the kinship-based society of the Arabs and were perceived as a lower class within the Umayyad empire. Muhammad ibn 'Ali, a great-grandson of Abbas, began to campaign in Persia for the return of power to the family of Muhammad, the Hashemites, during the reign of Umar II
Umar ibn Abd al-Aziz ( ar, عمر بن عبد العزيز, ʿUmar ibn ʿAbd al-ʿAzīz; 2 November 680 – ), commonly known as Umar II (), was the eighth Umayyad caliph. He made various significant contributions and reforms to the society, and ...
.
During the reign of Marwan II, this opposition culminated in the rebellion of , the fourth in descent from Abbas. Supported by the province of Khorasan
Khorasan may refer to:
* Greater Khorasan, a historical region which lies mostly in modern-day northern/northwestern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
* Khorasan Province, a pre-2004 province of Ira ...
(Eastern Persia), even though the governor opposed them, and the Shia Arabs, he achieved considerable success, but was captured in the year 747 and died, possibly assassinated, in prison.
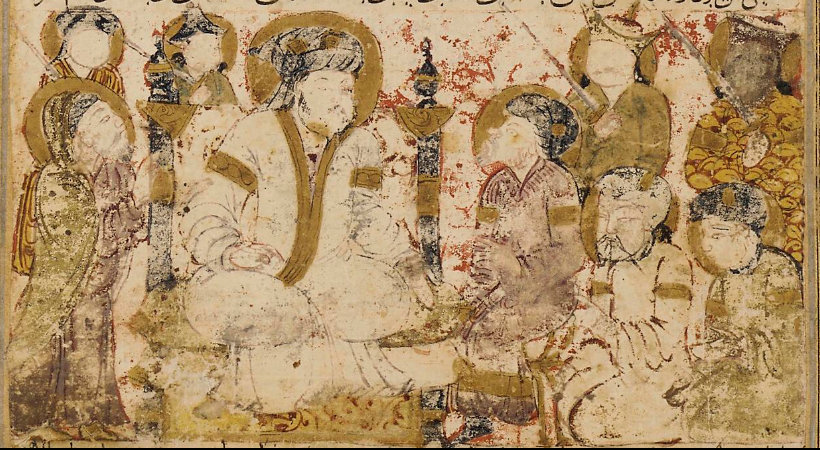
On 9 June 747 (15 Ramadan AH 129), Abu Muslim
, image = Abu Muslim chastises a man for telling tales, Folio from the Ethics of Nasir (Akhlaq-e Nasiri) by Nasir al-Din Tusi (fol. 248r).jpg
, caption = "Abu Muslim chastises a man for telling tales," Folio from the '' ...
, rising from Khorasan, successfully initiated an open revolt against Umayyad rule, which was carried out under the sign of the Black Standard. Close to 10,000 soldiers were under Abu Muslim's command when the hostilities officially began in Merv. General Qahtaba followed the fleeing governor Nasr ibn Sayyar
Naṣr ibn Sayyār al-Lāythi al-Kināni ( ar, نصر بن سيار الليثي الكناني; 663 – 9 December 748) was an Arab general and the last Umayyad governor of Khurasan in 738–748. Nasr played a distinguished role in the wars agai ...
west defeating the Umayyads at the Battle of Gorgan, the Battle of Nahāvand and finally in the Battle of Karbala, all in the year 748.
 The quarrel was taken up by Ibrahim's brother Abdallah, known by the name of Abu al-'Abbas as-Saffah, who defeated the Umayyads in 750 in the battle near the Great Zab and was subsequently proclaimed caliph. After this loss,
The quarrel was taken up by Ibrahim's brother Abdallah, known by the name of Abu al-'Abbas as-Saffah, who defeated the Umayyads in 750 in the battle near the Great Zab and was subsequently proclaimed caliph. After this loss, Marwan
Marwan, Merwan or Mervan ( ar, مروان ''marwān''), is an Arabic male given name derived from the word ''marū/ maruw'' (مرو) with the meaning of either minerals, "flint(-stone)", "quartz" or "a hard stone of nearly pure silica". However, ...
fled to Egypt, where he was subsequently killed. The remainder of his family, barring one male, were also eliminated.
Immediately after their victory, As-Saffah sent his forces to Central Asia, where his forces fought against Tang
Tang or TANG most often refers to:
* Tang dynasty
* Tang (drink mix)
Tang or TANG may also refer to:
Chinese states and dynasties
* Jin (Chinese state) (11th century – 376 BC), a state during the Spring and Autumn period, called Tang (唐) b ...
expansion during the Battle of Talas
The Battle of Talas or Battle of Artlakh (; ar, معركة نهر طلاس, translit=Maʿrakat nahr Ṭalās, Persian: Nabard-i Tarāz) was a military encounter and engagement between the Abbasid Caliphate along with its ally, the Tibetan Empir ...
. The noble Iranian family Barmakids
The Barmakids ( fa, برمکیان ''Barmakiyân''; ar, البرامكة ''al-Barāmikah''Harold Bailey, 1943. "Iranica" BSOAS 11: p. 2. India - Department of Archaeology, and V. S. Mirashi (ed.), ''Inscriptions of the Kalachuri-Chedi Era'' vol ...
, who were instrumental in building Baghdad, introduced the world's first recorded paper mill
A paper mill is a factory devoted to making paper from vegetable fibres such as wood pulp, old rags, and other ingredients. Prior to the invention and adoption of the Fourdrinier machine and other types of paper machine that use an endless belt, ...
in the city, thus beginning a new era of intellectual rebirth in the Abbasid domain. As-Saffah focused on putting down numerous rebellions in Syria and Mesopotamia. The Byzantines conducted raids during these early distractions.
Power (752–775)

 The first change made by the Abbasids under Al-Mansur was to move the empire's capital from
The first change made by the Abbasids under Al-Mansur was to move the empire's capital from Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
to a newly founded city. Established on the Tigris River in 762, Baghdad was closer to the Persian ''mawali'' support base of the Abbasids, and this move addressed their demand for less Arab dominance in the empire. A new position, that of the wazir
Wazir often refers to:
* Vizier or wazir, a high-ranking political advisor or minister
Wazir may also refer to:
Places
* Wazirabad, a City in Punjab, Pakistan
* Waziristan, a region in tribal belt of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan
* Wazir Akbar K ...
, was also established to delegate central authority, and even greater authority was delegated to local emirs. Al-Mansur centralised the judicial administration, and later, Harun al-Rashid established the institution of Chief Qadi to oversee it.
This resulted in a more ceremonial role for many Abbasid caliphs relative to their time under the Umayyads; the viziers began to exert greater influence, and the role of the old Arab aristocracy was slowly replaced by a Persian bureaucracy. During Al-Mansur's time, control of Al-Andalus was lost, and the Shia revolted and were defeated a year later at the Battle of Bakhamra.
The Abbasids had depended heavily on the support of Persians in their overthrow of the Umayyads. Abu al-'Abbas' successor Al-Mansur welcomed non-Arab Muslims to his court. While this helped integrate Arab and Persian cultures, it alienated many of their Arab supporters, particularly the Khorasanian Arabs who had supported them in their battles against the Umayyads. This fissure in support led to immediate problems. The Umayyads, while out of power, were not destroyed; the only surviving member of the Umayyad royal family ultimately made his way to Spain where he established himself as an independent Emir ( Abd ar-Rahman I, 756). In 929, Abd ar-Rahman III
ʿAbd al-Rahmān ibn Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd al-Raḥmān ibn al-Ḥakam al-Rabdī ibn Hishām ibn ʿAbd al-Raḥmān al-Dākhil () or ʿAbd al-Rahmān III (890 - 961), was the Umayyad Emir of Córdoba from 912 to 92 ...
assumed the title of Caliph, establishing Al Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the M ...
from Córdoba as a rival to Baghdad as the legitimate capital of the Islamic Empire.
The Umayyad empire was mostly Arab; however, the Abbasids progressively became made up of more and more converted Muslims in which the Arabs were only one of many ethnicities.
In 756, Al-Mansur sent over 4,000 Arab mercenaries to assist the Chinese Tang dynasty in the An Shi Rebellion against An Lushan. The Abbasids, or "Black Flags" as they were commonly called, were known in Tang dynasty chronicles as the ''hēiyī Dàshí'', "The Black-robed Tazi" () ("Tazi" being a borrowing from Persian '' Tāzī'', the word for "Arab"). Al-Rashid sent embassies to the Chinese Tang dynasty and established good relations with them. After the war, these embassies remained in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
with Caliph Harun al-Rashid establishing an alliance with China. Several embassies from the Abbasid Caliphs to the Chinese court have been recorded in the T'ang Annals, the most important of these being those of Abul Abbas al-Saffah, the first Abbasid caliph; his successor Abu Jafar; and Harun al-Rashid.
Abbasid Golden Age (775–861)
The Abbasid leadership had to work hard in the last half of the 8th century (750–800) under several competent caliphs and their viziers to usher in the administrative changes needed to keep order of the political challenges created by the far-flung nature of the empire, and the limited communication across it. It was also during this early period of the dynasty, in particular during the governance of Al-Mansur, Harun al-Rashid, andal-Ma'mun
Abu al-Abbas Abdallah ibn Harun al-Rashid ( ar, أبو العباس عبد الله بن هارون الرشيد, Abū al-ʿAbbās ʿAbd Allāh ibn Hārūn ar-Rashīd; 14 September 786 – 9 August 833), better known by his regnal name Al-Ma'mu ...
, that its reputation and power were created.
Al-Mahdi restarted the fighting with the Byzantines, and his sons continued the conflict until Empress Irene
Irene of Athens ( el, Εἰρήνη, ; 750/756 – 9 August 803), surname Sarantapechaina (), was Byzantine empress consort to Emperor Leo IV from 775 to 780, regent during the childhood of their son Constantine VI from 780 until 790, co-ruler ...
pushed for peace. After several years of peace, Nikephoros I
Nikephoros I or Nicephorus I ( gr, Νικηφόρος; 750 – 26 July 811) was Byzantine emperor from 802 to 811. Having served Empress Irene as '' genikos logothetēs'', he subsequently ousted her from power and took the throne himself. In r ...
broke the treaty, then fended off multiple incursions during the first decade of the 9th century. These attacks pushed into the Taurus Mountains, culminating with a victory at the Battle of Krasos and the massive invasion of 806, led by Rashid himself.
Rashid's navy also proved successful, taking Cyprus. Rashid decided to focus on the rebellion of Rafi ibn al-Layth in Khorasan
Khorasan may refer to:
* Greater Khorasan, a historical region which lies mostly in modern-day northern/northwestern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
* Khorasan Province, a pre-2004 province of Ira ...
and died while there. Military operations by the caliphate were minimal while the Byzantine Empire was fighting Abbasid rule in Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
and Anatolia, with focus shifting primarily to internal matters; Abbasid governors exerted greater autonomy and, using this increasing power, began to make their positions hereditary.
At the same time, the Abbasids faced challenges closer to home. Harun al-Rashid turned on and killed most of the Barmakids
The Barmakids ( fa, برمکیان ''Barmakiyân''; ar, البرامكة ''al-Barāmikah''Harold Bailey, 1943. "Iranica" BSOAS 11: p. 2. India - Department of Archaeology, and V. S. Mirashi (ed.), ''Inscriptions of the Kalachuri-Chedi Era'' vol ...
, a Persian family that had grown significantly in administrative power. During the same period, several factions began either to leave the empire for other lands or to take control of distant parts of the empire. Still, the reigns of al-Rashid and his sons were considered to be the apex of the Abbasids.
After Rashid's death, the empire was split by a civil war between the caliph al-Amin and his brother al-Ma'mun
Abu al-Abbas Abdallah ibn Harun al-Rashid ( ar, أبو العباس عبد الله بن هارون الرشيد, Abū al-ʿAbbās ʿAbd Allāh ibn Hārūn ar-Rashīd; 14 September 786 – 9 August 833), better known by his regnal name Al-Ma'mu ...
, who had the support of Khorasan. This war ended with a two-year siege of Baghdad and the eventual death of Al-Amin in 813. Al-Ma'mun
Abu al-Abbas Abdallah ibn Harun al-Rashid ( ar, أبو العباس عبد الله بن هارون الرشيد, Abū al-ʿAbbās ʿAbd Allāh ibn Hārūn ar-Rashīd; 14 September 786 – 9 August 833), better known by his regnal name Al-Ma'mu ...
ruled for 20 years of relative calm interspersed with a rebellion in Azerbaijan by the Khurramites, which was supported by the Byzantines. Al-Ma'mun was also responsible for the creation of an autonomous Khorasan, and the continued repulsing of Byzantine forays.
Al-Mu'tasim gained power in 833 and his rule marked the end of the strong caliphs. He strengthened his personal army with Turkish mercenaries and promptly restarted the war with the Byzantines. Though his attempt to seize Constantinople failed when his fleet was destroyed by a storm, his military excursions were generally successful, culminating with a resounding victory in the Sack of Amorium. The Byzantines responded by sacking Damietta in Egypt, and Al-Mutawakkil
Abū al-Faḍl Jaʿfar ibn Muḥammad al-Muʿtaṣim bi-ʾllāh ( ar, جعفر بن محمد المعتصم بالله; March 822 – 11 December 861), better known by his regnal name Al-Mutawakkil ʿalā Allāh (, "He who relies on God") was t ...
responded by sending his troops into Anatolia again, sacking and marauding until they were eventually annihilated in 863.
Fracture to autonomous dynasties (861–945)
Even by 820, theSamanid
The Samanid Empire ( fa, سامانیان, Sāmāniyān) also known as the Samanian Empire, Samanid dynasty, Samanid amirate, or simply as the Samanids) was a Persianate Sunni Muslim empire, of Iranian dehqan origin. The empire was centred in Kho ...
s had begun the process of exercising independent authority in Transoxiana and Greater Khorasan, and the succeeding
Saffarid dynasty of Iran. The Saffarids, from Khorasan, nearly seized Baghdad in 876, and the Tulunids took control of most of Syria. The trend of weakening of the central power and strengthening of the minor caliphates on the periphery continued.
An exception was the 10-year period of Al-Mu'tadid's rule ( r. 892–902). He brought parts of Egypt, Syria, and Khorasan back into Abbasid control. Especially after the " Anarchy at Samarra" (861–870), the Abbasid central government was weakened and centrifugal tendencies became more prominent in the Caliphate's provinces. By the early 10th century, the Abbasids almost lost control of Iraq to various amirs, and the caliph al-Radi
Abu'l-Abbas Ahmad (Muhammad) ibn Ja'far al-Muqtadir ( ar, أبو العباس أحمد (محمد) بن جعفر المقتدر, Abū al-ʿAbbās Aḥmad (Muḥammad) ibn al-Muqtadir; December 909 – 23 December 940), usually simply known by his r ...
was forced to acknowledge their power by creating the position of "Prince of Princes" ('' amir al-umara'').
Al-Mustakfi had a short reign from 944 to 946, and it was during this period that the Persian faction known as the Buyids from Daylam swept into power and assumed control over the bureaucracy in Baghdad. According to the history of Miskawayh
Ibn Miskawayh ( fa, مُسْکُـوْيَه Muskūyah, 932–1030), full name Abū ʿAlī Aḥmad ibn Muḥammad ibn Yaʿqūb ibn Miskawayh was a Persian chancery official of the Buyid era, and philosopher and historian from Parandak, Iran. As ...
, they began distributing iqtas ( fiefs in the form of tax farms) to their supporters. This period of localized secular control was to last nearly 100 years. The loss of Abbasid power to the Buyids would shift as the Seljuks would take over from the Persians.
At the end of the eighth century, the Abbasids found they could no longer keep together a polity, which had grown larger than that of Rome, from Baghdad. In 793 the Zaydi-Shia dynasty of Idrisids
The Idrisid dynasty or Idrisids ( ar, الأدارسة ') were an Arab Muslim dynasty from 788 to 974, ruling most of present-day Morocco and parts of present-day western Algeria. Named after the founder, Idris I, the Idrisids were an Alid and ...
set up a state from Fez in Morocco, while a family of governors under the Abbasids became increasingly independent until they founded the Aghlabid Emirate
The Aghlabids ( ar, الأغالبة) were an Arab dynasty of emirs from the Najdi tribe of Banu Tamim, who ruled Ifriqiya and parts of Southern Italy, Sicily, and possibly Sardinia, nominally on behalf of the Abbasid Caliph, for about a c ...
from the 830s. Al-Mu'tasim started the downward slide by utilizing non-Muslim mercenaries in his personal army. Also during this period, officers started assassinating superiors with whom they disagreed, in particular the caliphs.


 By the 870s, Egypt became autonomous under
By the 870s, Egypt became autonomous under Ahmad ibn Tulun
Ahmad ibn Tulun ( ar, أحمد بن طولون, translit=Aḥmad ibn Ṭūlūn; c. 20 September 835 – 10 May 884) was the founder of the Tulunid dynasty that ruled Egypt and Syria between 868 and 905. Originally a Turkic slave-soldier, in 868 ...
. In the East, governors decreased their ties to the center as well. The Saffarids of Herat and the Samanids of Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
began breaking away around this time, cultivating a much more Persianate culture
A Persianate society is a society that is based on or strongly influenced by the Persian language, culture, literature, art and/or identity.
The term "Persianate" is a neologism credited to Marshall Hodgson. In his 1974 book, ''The Venture of I ...
and statecraft. Only the central lands of Mesopotamia were under direct Abbasid control, with Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
and the Hijaz often managed by the Tulunids. Byzantium, for its part, had begun to push Arab Muslims
Arab Muslims ( ar, العرب المسلمون) are adherents of Islam who identify linguistically, culturally, and genealogically as Arabs. Arab Muslims greatly outnumber other ethnoreligious groups in the Middle East and North Africa. Arab Mu ...
farther east in Anatolia.
By the 920s, North Africa was lost to the Fatimid dynasty
The Fatimid dynasty () was an Isma'ili Shi'a dynasty of Arab descent that ruled an extensive empire, the Fatimid Caliphate, between 909 and 1171 CE. Claiming descent from Fatima and Ali, they also held the Isma'ili imamate, claiming to be the right ...
, a Shia sect tracing its roots to Muhammad's daughter Fatimah. The Fatimid dynasty took control of Idrisid and Aghlabid domains, advanced to Egypt in 969, and established their capital near Fustat in Cairo, which they built as a bastion of Shia learning and politics. By 1000 they had become the chief political and ideological challenge to Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagre ...
and the Abbasids, who by this time had fragmented into several governorships that, while recognizing caliphal authority from Baghdad, remained mostly autonomous. The Caliph himself was under 'protection' of the Buyid Emirs who possessed all of Iraq and Western Iran, and were quietly Shia in their sympathies.
 Outside Iraq, all the autonomous provinces slowly took on the characteristic of de facto states with hereditary rulers, armies, and revenues and operated under only nominal caliph suzerainty, which may not necessarily be reflected by any contribution to the treasury, such as the Soomro Emirs that had gained control of
Outside Iraq, all the autonomous provinces slowly took on the characteristic of de facto states with hereditary rulers, armies, and revenues and operated under only nominal caliph suzerainty, which may not necessarily be reflected by any contribution to the treasury, such as the Soomro Emirs that had gained control of Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
and ruled the entire province from their capital of Mansura
Mansoura (' , rural: ) is a city in Egypt, with a population of 960,423. It is the capital of the Dakahlia Governorate.
Etymology
''Mansoura'' in Arabic means "victorious". The city is named after the El Mansoura Battle against Louis IX of Fr ...
. Mahmud of Ghazni
Yamīn-ud-Dawla Abul-Qāṣim Maḥmūd ibn Sebüktegīn ( fa, ; 2 November 971 – 30 April 1030), usually known as Mahmud of Ghazni or Mahmud Ghaznavi ( fa, ), was the founder of the Turkic Ghaznavid dynasty, ruling from 998 to 1030. At th ...
took the title of sultan, as opposed to the "amir" that had been in more common usage, signifying the Ghaznavid Empire
The Ghaznavid dynasty ( fa, غزنویان ''Ġaznaviyān'') was a culturally Persianate society, Persianate, Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim dynasty of Turkic peoples, Turkic ''mamluk'' origin, ruling, at its greatest extent, large parts of Persia, ...
's independence from caliphal authority, despite Mahmud's ostentatious displays of Sunni orthodoxy and ritual submission to the caliph. In the 11th century, the loss of respect for the caliphs continued, as some Islamic rulers no longer mentioned the caliph's name in the Friday khutba, or struck it off their coinage.
The Isma'ili Fatimid dynasty of Cairo contested the Abbasids for the titular authority of the Islamic ummah. They commanded some support in the Shia sections of Baghdad (such as Karkh), although Baghdad was the city most closely connected to the caliphate, even in the Buyid and Seljuq eras. The challenge of the Fatimids only ended with their downfall in the 12th century.
Buyid and Seljuq control (945–1118)
 Despite the power of the Buyid amirs, the Abbasids retained a highly ritualized court in Baghdad, as described by the Buyid bureaucrat
Despite the power of the Buyid amirs, the Abbasids retained a highly ritualized court in Baghdad, as described by the Buyid bureaucrat Hilal al-Sabi'
Abūʾl-Ḥusayn Hilāl b. Muḥassin b. Ibrāhīm al-Ṣābīʾ (Arabic: ابو الحسين هلال بن محسن بن ابراهيم الصابئ) (born: 358 A.H./c. 969 A.D., died: 447-448 A.H./1056 A.D.) (aged 90 lunar) was a historian, bu ...
, and they retained a certain influence over Baghdad as well as religious life. As Buyid power waned with the rule of Baha' al-Daula
Abu Nasr Firuz Kharshadh ( ar, أبو نصر فيروز خوارشاذ; died December 22, 1012), better known by his ''laqab'' of Baha al-Dawla ( ar, بهاء الدوله, Bahaʾ al-Dawla, Splendour of the State) was the Buyid amir of Iraq (988– ...
, the caliphate was able to regain some measure of strength. The caliph al-Qadir, for example, led the ideological struggle against the Shia with writings such as the ''Baghdad Manifesto
The Baghdad Manifesto was a polemical tract issued in 1011 on behalf of the Abbasid caliph al-Qadir against the rival Isma'ili Fatimid Caliphate.
Background
The manifesto was the result of the steady expansion of the Fatimid Caliphate since its es ...
''. The caliphs kept order in Baghdad itself, attempting to prevent the outbreak of fitnas in the capital, often contending with the '' ayyarun''.
With the Buyid dynasty on the wane, a vacuum was created that was eventually filled by the dynasty of Oghuz Turks
The Oghuz or Ghuzz Turks (Middle Turkic languages, Middle Turkic: ٱغُز, ''Oγuz'', ota, اوغوز, Oġuz) were a western Turkic people that spoke the Oghuz languages, Oghuz branch of the Turkic languages, Turkic language family. In th ...
known as the Seljuqs
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
. By 1055, the Seljuqs had wrested control from the Buyids and Abbasids, and took any remaining temporal power. When the amir and former slave Basasiri
Abuʾl-Ḥārith Arslān al-Muẓaffar al-Basāsīrī (died 15 January 1059) was a Turkic peoples, Turkish slave-soldier (''mamlūk'') who rose to become a military commander of the Buwayhid dynasty in Iraq (region), Iraq. When the Buwayhids were ...
took up the Shia Fatimid banner in Baghdad in 1056–57, the caliph al-Qa'im was unable to defeat him without outside help. Toghril Beg
Abu Talib Muhammad Tughril ibn Mika'il ( fa, ابوطالب محمد تغریل بن میکائیل), better known as Tughril (; also spelled Toghril), was a Turkmen"The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
, the Seljuq sultan, restored Baghdad to Sunni rule and took Iraq for his dynasty.
Once again, the Abbasids were forced to deal with a military power that they could not match, though the Abbasid caliph remained the titular head of the Islamic community. The succeeding sultans Alp Arslan
Alp Arslan was the second Sultan of the Seljuk Empire and great-grandson of Seljuk, the eponymous founder of the dynasty. He greatly expanded the Seljuk territory and consolidated his power, defeating rivals to the south and northwest, and his v ...
and Malikshah
Jalāl al-Dawla Mu'izz al-Dunyā Wa'l-Din Abu'l-Fatḥ ibn Alp Arslān (8 August 1055 – 19 November 1092, full name: fa, ), better known by his regnal name of Malik-Shah I ( fa, ), was the third sultan of the Great Seljuk Empire from 1072 to ...
, as well as their vizier Nizam al-Mulk
Abu Ali Hasan ibn Ali Tusi (April 10, 1018 – October 14, 1092), better known by his honorific title of Nizam al-Mulk ( fa, , , Order of the Realm) was a Persian scholar, jurist, political philosopher and Vizier of the Seljuk Empire. Rising fro ...
, took up residence in Persia, but held power over the Abbasids in Baghdad. When the dynasty began to weaken in the 12th century, the Abbasids gained greater independence once again.
Revival of military strength (1118–1258)
siege of Baghdad (1157)
The siege of Baghdad in 1157 was the last Seljuq attempt to capture Baghdad from the Abbasids. Caliph al-Muqtafi successfully defended his capital against the coalition armies of Seljuq Sultan Muhammad of Hamadan and Qutb ad-Din of Mosul.
B ...
, thus securing Iraq for the Abbasids. The reign of al-Nasir
Abu'l-Abbas Ahmad ibn al-Hassan al-Mustadi' ( ar, أبو العباس أحمد بن الحسن المستضيء) better known by his laqab Al-Nasir li-Din Allah ( ar, الناصر لدين الله; 6 August 1158 – 5 October 1225) or simply as A ...
(d. 1225) brought the caliphate back into power throughout Iraq, based in large part on the Sufi
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, ...
futuwwa organizations that the caliph headed. Al-Mustansir built the Mustansiriya School
Mustansiriya Madrasah () was a medieval-era scholarly complex that provided a universal system of higher education. It was established in 1227 CE and was named after and built by the Abbasid Caliph Al-Mustansir (Baghdad), al-Mustansir in Baghdad ...
, in an attempt to eclipse the Seljuq-era Nizamiyya built by Nizam al Mulk
Abu Ali Hasan ibn Ali Tusi (April 10, 1018 – October 14, 1092), better known by his honorific title of Nizam al-Mulk ( fa, , , Order of the Realm) was a Persian scholar, jurist, political philosopher and Vizier of the Seljuk Empire. Rising fr ...
.
Mongol invasion (1206–1258)
 In 1206,
In 1206, Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
established a powerful dynasty among the Mongols of central Asia. During the 13th century, this Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
conquered most of the Eurasian land mass, including both China in the east and much of the old Islamic caliphate (as well as Kievan Rus') in the west. Hulagu Khan's destruction of Baghdad in 1258 is traditionally seen as the approximate end of the Golden Age. Mongols feared that a supernatural disaster would strike if the blood of Al-Musta'sim, a direct descendant of Muhammad's uncle Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib, and the last reigning Abbasid caliph in Baghdad, was spilled. The Shia of Persia stated that no such calamity had happened after the death of Husayn ibn Ali
Abū ʿAbd Allāh al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib ( ar, أبو عبد الله الحسين بن علي بن أبي طالب; 10 January 626 – 10 October 680) was a grandson of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a son of Ali ibn Abi ...
in the Battle of Karbala; nevertheless, as a precaution and in accordance with a Mongol taboo which forbade spilling royal blood, Hulagu had Al-Musta'sim wrapped in a carpet and trampled to death by horses on 20 February 1258. The Caliph's immediate family was also executed, with the lone exceptions of his youngest son who was sent to Mongolia, and a daughter who became a slave in the harem of Hulagu.
Abbasid Caliphate of Cairo (1261–1517)
In the 9th century, the Abbasids created an army loyal only to their caliphate, composed of non-Arab origin people, known asMamluks
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning "slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') i ...
. This force, created in the reign of al-Ma'mun
Abu al-Abbas Abdallah ibn Harun al-Rashid ( ar, أبو العباس عبد الله بن هارون الرشيد, Abū al-ʿAbbās ʿAbd Allāh ibn Hārūn ar-Rashīd; 14 September 786 – 9 August 833), better known by his regnal name Al-Ma'mu ...
(813–833) and his brother and successor al-Mu'tasim (833–842), prevented the further disintegration of the empire. The Mamluk army, though often viewed negatively, both helped and hurt the caliphate. Early on, it provided the government with a stable force to address domestic and foreign problems. However, creation of this foreign army and al-Mu'tasim's transfer of the capital from Baghdad to Samarra
Samarra ( ar, سَامَرَّاء, ') is a city in Iraq. It stands on the east bank of the Tigris in the Saladin Governorate, north of Baghdad. The city of Samarra was founded by Abbasid Caliph Al-Mutasim for his Turkish professional army ...
created a division between the caliphate and the peoples they claimed to rule. In addition, the power of the Mamluks steadily grew until al-Radi
Abu'l-Abbas Ahmad (Muhammad) ibn Ja'far al-Muqtadir ( ar, أبو العباس أحمد (محمد) بن جعفر المقتدر, Abū al-ʿAbbās Aḥmad (Muḥammad) ibn al-Muqtadir; December 909 – 23 December 940), usually simply known by his r ...
(934–941) was constrained to hand over most of the royal functions to Muhammad ibn Ra'iq.
Similarly to how a Mamluk Army was created by the Abbasids, a Mamluk Army was created by the Egypt-based Ayyubid dynasty
The Ayyubid dynasty ( ar, الأيوبيون '; ) was the founding dynasty of the medieval Sultan of Egypt, Sultanate of Egypt established by Saladin in 1171, following his abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimid Caliphate of Egypt. A Sunni ...
. These Mamluks decided to directly overthrow their masters and came to power in 1250 in what is known as the Mamluk Sultanate. In 1261, following the devastation of Baghdad by the Mongols, the Mamluk rulers of Egypt re-established the Abbasid caliphate in Cairo. The first Abbasid caliph of Cairo was Al-Mustansir. The Abbasid caliphs in Egypt continued to maintain the presence of authority, but it was confined to religious matters. The Abbasid caliphate of Cairo lasted until the time of Al-Mutawakkil III, who was taken away as a prisoner by Selim I to Constantinople where he had a ceremonial role. He died in 1543, following his return to Cairo.
Culture
Islamic Golden Age
 The Abbasid historical period lasting to the
The Abbasid historical period lasting to the Mongol conquest of Baghdad
The siege of Baghdad was a siege that took place in Baghdad in 1258, lasting for 13 days from January 29, 1258 until February 10, 1258. The siege, laid by Ilkhanate Mongol forces and allied troops, involved the investment, capture, and sack of ...
in 1258 CE is considered the Islamic Golden Age. The Islamic Golden Age was inaugurated by the middle of the 8th century by the ascension of the Abbasid Caliphate and the transfer of the capital from Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
to Baghdad. The Abbasids were influenced by the Qur'anic injunctions and hadith, such as "the ink of a scholar is more holy than the blood of a martyr", stressing the value of knowledge. During this period the Muslim world became an intellectual center for science, philosophy, medicine and education as the Abbasids championed the cause of knowledge and established the House of Wisdom
The House of Wisdom ( ar, بيت الحكمة, Bayt al-Ḥikmah), also known as the Grand Library of Baghdad, refers to either a major Abbasid public academy and intellectual center in Baghdad or to a large private library belonging to the Abba ...
in Baghdad, where both Muslim and non-Muslim scholars sought to translate and gather all the world's knowledge into Arabic. Many classic works of antiquity that would otherwise have been lost were translated into Arabic and Persian and later in turn translated into Turkish, Hebrew and Latin. During this period the Muslim world was a cauldron of cultures which collected, synthesized and significantly advanced the knowledge gained from the Roman, Chinese, Indian, Persian, Egyptian
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of ...
, North African, Ancient Greek and Medieval Greek civilizations. According to Huff, " virtually every field of endeavor—in astronomy, alchemy, mathematics, medicine, optics and so forth—the Caliphate's scientists were in the forefront of scientific advance."
Science
 The reigns of Harun al-Rashid (786–809) and his successors fostered an age of great intellectual achievement. In large part, this was the result of the schismatic forces that had undermined the Umayyad regime, which relied on the assertion of the superiority of Arab culture as part of its claim to legitimacy, and the Abbasids' welcoming of support from non-Arab Muslims. It is well established that the Abbasid caliphs modeled their administration on that of the Sassanids. Harun al-Rashid's son,
The reigns of Harun al-Rashid (786–809) and his successors fostered an age of great intellectual achievement. In large part, this was the result of the schismatic forces that had undermined the Umayyad regime, which relied on the assertion of the superiority of Arab culture as part of its claim to legitimacy, and the Abbasids' welcoming of support from non-Arab Muslims. It is well established that the Abbasid caliphs modeled their administration on that of the Sassanids. Harun al-Rashid's son, Al-Ma'mun
Abu al-Abbas Abdallah ibn Harun al-Rashid ( ar, أبو العباس عبد الله بن هارون الرشيد, Abū al-ʿAbbās ʿAbd Allāh ibn Hārūn ar-Rashīd; 14 September 786 – 9 August 833), better known by his regnal name Al-Ma'mu ...
(whose mother was Persian), is even quoted as saying:
 A number of medieval thinkers and scientists living under Islamic rule played a role in transmitting Islamic science to the Christian West. In addition, the period saw the recovery of much of the Alexandrian mathematical, geometric and astronomical knowledge, such as that of Euclid and Claudius Ptolemy. These recovered mathematical methods were later enhanced and developed by other Islamic scholars, notably by Persian scientists Al-Biruni and Abu Nasr Mansur.
Christians (particularly Nestorian Christians) contributed to the Arab Islamic Civilization during the Umayyads and the Abbasids by translating works of Greek philosophers to Syriac and afterwards to Arabic. Nestorians played a prominent role in the formation of Arab culture, with the
A number of medieval thinkers and scientists living under Islamic rule played a role in transmitting Islamic science to the Christian West. In addition, the period saw the recovery of much of the Alexandrian mathematical, geometric and astronomical knowledge, such as that of Euclid and Claudius Ptolemy. These recovered mathematical methods were later enhanced and developed by other Islamic scholars, notably by Persian scientists Al-Biruni and Abu Nasr Mansur.
Christians (particularly Nestorian Christians) contributed to the Arab Islamic Civilization during the Umayyads and the Abbasids by translating works of Greek philosophers to Syriac and afterwards to Arabic. Nestorians played a prominent role in the formation of Arab culture, with the Academy of Gondishapur
The Academy of Gondishapur ( fa, فرهنگستان گندیشاپور, Farhangestân-e Gondišâpur), also known as the Gondishapur University (دانشگاه گندیشاپور Dânešgâh-e Gondišapur), was one of the three Sasanian ...
being prominent in the late Sassanid, Umayyad and early Abbasid periods. Notably, eight generations of the Nestorian Bukhtishu
The Bukhtīshūʿ (or Boḵtīšūʿ) were a family of either Persian or Nestorian Christian physicians from the 7th, 8th, and 9th centuries, spanning six generations and 250 years. The Middle Persian-Syriac name which can be found as early as at ...
family served as private doctors to caliphs and sultans between the eighth and eleventh centuries.
Algebra was significantly developed by Persian scientist Muhammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī
Muḥammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī ( ar, محمد بن موسى الخوارزمي, Muḥammad ibn Musā al-Khwārazmi; ), or al-Khwarizmi, was a Persians, Persian polymath from Khwarazm, who produced vastly influential works in Mathematics ...
during this time in his landmark text, '' Kitab al-Jabr wa-l-Muqabala'', from which the term ''algebra'' is derived. He is thus considered to be the father of algebra by some, although the Greek mathematician Diophantus
Diophantus of Alexandria ( grc, Διόφαντος ὁ Ἀλεξανδρεύς; born probably sometime between AD 200 and 214; died around the age of 84, probably sometime between AD 284 and 298) was an Alexandrian mathematician, who was the aut ...
has also been given this title. The terms algorism and algorithm are derived from the name of al-Khwarizmi, who was also responsible for introducing the Arabic numerals
Arabic numerals are the ten numerical digits: , , , , , , , , and . They are the most commonly used symbols to write Decimal, decimal numbers. They are also used for writing numbers in other systems such as octal, and for writing identifiers ...
and Hindu–Arabic numeral system beyond the Indian subcontinent.
 Arab scientist Ibn al-Haytham (Alhazen) developed an early scientific method in his ''
Arab scientist Ibn al-Haytham (Alhazen) developed an early scientific method in his ''Book of Optics
The ''Book of Optics'' ( ar, كتاب المناظر, Kitāb al-Manāẓir; la, De Aspectibus or ''Perspectiva''; it, Deli Aspecti) is a seven-volume treatise on optics and other fields of study composed by the medieval Arab scholar Ibn al- ...
'' (1021). The most important development of the scientific method was the use of experiments to distinguish between competing scientific theories set within a generally empirical
Empirical evidence for a proposition is evidence, i.e. what supports or counters this proposition, that is constituted by or accessible to sense experience or experimental procedure. Empirical evidence is of central importance to the sciences and ...
orientation, which began among Muslim scientists. Ibn al-Haytham's empirical proof of the intromission theory of light (that is, that light rays entered the eyes rather than being emitted by them) was particularly important. Alhazen was significant in the history of scientific method
The history of scientific method considers changes in the methodology of scientific inquiry, as distinct from the history of science itself. The development of rules for scientific reasoning has not been straightforward; scientific method has been ...
, particularly in his approach to experimentation, and has been referred to as the "world's first true scientist".
Medicine in medieval Islam was an area of science that advanced particularly during the Abbasids' reign. During the 9th century, Baghdad contained over 800 doctors, and great discoveries in the understanding of anatomy and diseases were made. The clinical distinction between measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
and smallpox was described during this time. Famous Persian scientist Ibn Sina
Ibn Sina ( fa, ابن سینا; 980 – June 1037 CE), commonly known in the West as Avicenna (), was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant physicians, astronomers, philosophers, and writers of the Islamic G ...
(known to the West as Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( fa, ابن سینا; 980 – June 1037 CE), commonly known in the West as Avicenna (), was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant physicians, astronomers, philosophers, and writers of the Islamic G ...
) produced treatises and works that summarized the vast amount of knowledge that scientists had accumulated, and was very influential through his encyclopedias, '' The Canon of Medicine'' and ''The Book of Healing
''The Book of Healing'' (; ; also known as ) is a scientific and philosophical encyclopedia written by Abu Ali ibn Sīna (aka Avicenna) from medieval Persia, near Bukhara in Maverounnahr. He most likely began to compose the book in 1014, comp ...
''. The work of him and many others directly influenced the research of European scientists during the Renaissance.
Astronomy in medieval Islam
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies ...
was advanced by Al-Battani, who improved the precision of the measurement of the precession of the Earth's axis. The corrections made to the geocentric model
In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, often exemplified specifically by the Ptolemaic system) is a superseded description of the Universe with Earth at the center. Under most geocentric models, the Sun, Moon, stars, an ...
by al-Battani, Averroes, Nasir al-Din al-Tusi
Muhammad ibn Muhammad ibn al-Hasan al-Tūsī ( fa, محمد ابن محمد ابن حسن طوسی 18 February 1201 – 26 June 1274), better known as Nasir al-Din al-Tusi ( fa, نصیر الدین طوسی, links=no; or simply Tusi in the West ...
, Mo'ayyeduddin Urdi
Al-Urdi (full name: Moayad Al-Din Al-Urdi Al-Amiri Al-Dimashqi) () (d. 1266) was a medieval Syrian Arab astronomer and geometer.
Born circa 1200, presumably (from the nisba ''al‐ʿUrḍī'') in the village of ''ʿUrḍ'' in the Syrian desert b ...
and Ibn al-Shatir were later incorporated into the Copernican heliocentric model. The astrolabe
An astrolabe ( grc, ἀστρολάβος ; ar, ٱلأَسْطُرلاب ; persian, ستارهیاب ) is an ancient astronomical instrument that was a handheld model of the universe. Its various functions also make it an elaborate inclin ...
, though originally developed by the Greeks, was developed further by Islamic astronomers and engineers, and subsequently brought to medieval Europe.
Muslim alchemists influenced medieval European alchemists, particularly the writings attributed to Jābir ibn Hayyān (Geber).
Literature
The best known fiction from the Islamic world is ''One Thousand and One Nights
''One Thousand and One Nights'' ( ar, أَلْفُ لَيْلَةٍ وَلَيْلَةٌ, italic=yes, ) is a collection of Middle Eastern folk tales compiled in Arabic during the Islamic Golden Age. It is often known in English as the ''Arabian ...
'', a collection of fantastical folk tales, legends and parables compiled primarily during the Abbasid era. The collection is recorded as having originated from an Arabic translation of a Sassanian era Persian prototype, with likely origins in Indian literary traditions. Stories from Arabic, Persian, Mesopotamian, and Egyptian
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of ...
folklore and literature were later incorporated. The epic is believed to have taken shape in the 10th century and reached its final form by the 14th century; the number and type of tales have varied from one manuscript to another.. All Arabian fantasy tales were often called "Arabian Nights" when translated into English, regardless of whether they appeared in ''The Book of One Thousand and One Nights''. This epic has been influential in the West since it was translated in the 18th century, first by Antoine Galland
Antoine Galland (; 4 April 1646 – 17 February 1715) was a French orientalist and archaeologist, most famous as the first European translator of '' One Thousand and One Nights'', which he called ''Les mille et une nuits''. His version of the t ...
. Many imitations were written, especially in France. Various characters from this epic have themselves become cultural icons in Western culture, such as Aladdin
Aladdin ( ; ar, علاء الدين, ', , ATU 561, ‘Aladdin') is a Middle-Eastern folk tale. It is one of the best-known tales associated with ''The Book of One Thousand and One Nights'' (''The Arabian Nights''), despite not being part of ...
, Sinbad and Ali Baba.
A famous example of Islamic poetry on romance was '' Layla and Majnun'', an originally Arabic story which was further developed by Iranian, Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani may refer to:
* Something of, or related to Azerbaijan
* Azerbaijanis
* Azerbaijani language
See also
* Azerbaijan (disambiguation)
* Azeri (disambiguation)
* Azerbaijani cuisine
* Culture of Azerbaijan
The culture of Azerbaijan ...
and other poets in the Persian, Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani may refer to:
* Something of, or related to Azerbaijan
* Azerbaijanis
* Azerbaijani language
See also
* Azerbaijan (disambiguation)
* Azeri (disambiguation)
* Azerbaijani cuisine
* Culture of Azerbaijan
The culture of Azerbaijan ...
, and Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
languages. It is a tragic story of undying love much like the later ''Romeo and Juliet
''Romeo and Juliet'' is a Shakespearean tragedy, tragedy written by William Shakespeare early in his career about the romance between two Italian youths from feuding families. It was among Shakespeare's most popular plays during his lifetim ...
''.
Arabic poetry reached its greatest height in the Abbasid era, especially before the loss of central authority and the rise of the Persianate dynasties. Writers like Abu Tammam and Abu Nuwas were closely connected to the caliphal court in Baghdad during the early 9th century, while others such as al-Mutanabbi received their patronage from regional courts.
Under Harun al-Rashid, Baghdad was renowned for its bookstores, which proliferated after the making of paper was introduced. Chinese papermakers had been among those taken prisoner by the Arabs at the Battle of Talas
The Battle of Talas or Battle of Artlakh (; ar, معركة نهر طلاس, translit=Maʿrakat nahr Ṭalās, Persian: Nabard-i Tarāz) was a military encounter and engagement between the Abbasid Caliphate along with its ally, the Tibetan Empir ...
in 751. As prisoners of war, they were dispatched to Samarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
, where they helped set up the first Arab paper mill. In time, paper replaced parchment as the medium for writing, and the production of books greatly increased. These events had an academic and societal impact that could be broadly compared to the introduction of the printing press in the West. Paper aided in communication and record-keeping, it also brought a new sophistication and complexity to businesses, banking, and the civil service. In 794, Jafa al-Barmak built the first paper mill in Baghdad, and from there the technology circulated. Harun required that paper be employed in government dealings, since something recorded on paper could not easily be changed or removed, and eventually, an entire street in Baghdad's business district was dedicated to selling paper and books.
Philosophy
One of the common definitions for "Islamic philosophy" is "the style of philosophy produced within the framework of Islamic culture." Islamic philosophy, in this definition is neither necessarily concerned with religious issues, nor is exclusively produced by Muslims. Their works on Aristotle were a key step in the transmission of learning from ancient Greeks to the Islamic world and the West. They often corrected the philosopher, encouraging a lively debate in the spirit ofijtihad
''Ijtihad'' ( ; ar, اجتهاد ', ; lit. physical or mental ''effort'') is an Islamic legal term referring to independent reasoning by an expert in Islamic law, or the thorough exertion of a jurist's mental faculty in finding a solution to a le ...
. They also wrote influential original philosophical works, and their thinking was incorporated into Christian philosophy during the Middle Ages, notably by Thomas Aquinas.
Three speculative thinkers, al-Kindi, al-Farabi, and Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( fa, ابن سینا; 980 – June 1037 CE), commonly known in the West as Avicenna (), was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant physicians, astronomers, philosophers, and writers of the Islamic G ...
, combined Aristotelianism and Neoplatonism with other ideas introduced through Islam, and Avicennism
Avicennism is a school of Persian philosophy which was established by Avicenna. He developed his philosophy throughout the course of his life after being deeply moved and concerned by the ''Metaphysics (Aristotle), Metaphysics'' of Aristotle and s ...
was later established as a result. Other influential Abbasid philosophers include al-Jahiz, and Ibn al-Haytham (Alhacen).
Architecture

 As power shifted from the Umayyads to the Abbasids, the architectural styles changed also, from Greco-Roman tradition (which features elements of Hellenistic and Roman representative style) to Eastern tradition which retained their independent architectural traditions from Mesopotamia and Persia. The Abbasid architecture was particularly influenced by Sasanian architecture, which in turn featured elements present since ancient Mesopotamia. The Christian styles evolved into a style based more on the
As power shifted from the Umayyads to the Abbasids, the architectural styles changed also, from Greco-Roman tradition (which features elements of Hellenistic and Roman representative style) to Eastern tradition which retained their independent architectural traditions from Mesopotamia and Persia. The Abbasid architecture was particularly influenced by Sasanian architecture, which in turn featured elements present since ancient Mesopotamia. The Christian styles evolved into a style based more on the Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th cen ...
, utilizing mud bricks and baked bricks with carved stucco. Another major development was the creation or vast enlargement of cities as they were turned into the capital of the empire, beginning with the creation of Baghdad in 762, which was planned as a walled city with four gates, and a mosque and palace in the center. Al-Mansur, who was responsible for the creation of Baghdad, also planned the city of Raqqa, along the Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
. Finally, in 836, al-Mu'tasim moved the capital to a new site that he created along the Tigris, called Samarra. This city saw 60 years of work, with race-courses and game preserves to add to the atmosphere. Due to the dry remote nature of the environment, some of the palaces built in this era were isolated havens. Al-Ukhaidir Fortress is a fine example of this type of building, which has stables, living quarters, and a mosque, all surrounding inner courtyards. Other mosques of this era, such as the Great Mosque of Kairouan in Tunisia, while ultimately built during the Umayyad dynasty, were substantially renovated in the 9th century. These renovations, so extensive as to ostensibly be rebuilds, were in the furthest reaches of the Muslim world, in an area that the Aghlabids controlled; however, the styles utilized were mainly Abbasid. In Egypt, Ahmad Ibn Tulun commissioned the Ibn Tulun Mosque
The Mosque of Ibn Tulun ( ar, مسجد إبن طولون, Masjid Ibn Ṭūlūn) is located in Cairo, Egypt. It is one of the oldest mosques in Egypt as well as the whole of Africa surviving in its full original form, and is the largest mosque in ...
, completed in 879, that is based on the style of Samarra and is now one of the best-preserved Abbasid-style mosques from this period. Mesopotamia only has one surviving mausoleum
A mausoleum is an external free-standing building constructed as a monument enclosing the interment space or burial chamber of a deceased person or people. A mausoleum without the person's remains is called a cenotaph. A mausoleum may be consid ...
from this era, in Samarra. This octagonal dome is the final resting place of al-Muntasir. Other architectural innovations and styles were few, such as the four-centered arch, and a dome erected on squinch
In architecture, a squinch is a triangular corner that supports the base of a dome. Its visual purpose is to translate a rectangle into an octagon. See also: pendentive.
Construction
A squinch is typically formed by a masonry arch that spans ...
es. Unfortunately, much was lost due to the ephemeral nature of the stucco and luster tiles.
Foundation of Baghdad
The Caliph al-Mansur founded the epicenter of the empire, Baghdad, in 762 CE, as a means of disassociating his dynasty from that of the preceding Umayyads (centered at Damascus) and the rebellious cities of Kufa and Basrah. Mesopotamia was an ideal locale for a capital city due to its high agricultural output, access to the Euphrates and Tigris Rivers (allowing for trade and communication across the region), central locale between the corners of the vast empire (stretching from Egypt to Afghanistan) and access to the Silk Road and Indian Ocean trade routes, all key reasons as to why the region has hosted important capital cities such as Ur,Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
, Nineveh
Nineveh (; akk, ; Biblical Hebrew: '; ar, نَيْنَوَىٰ '; syr, ܢܝܼܢܘܹܐ, Nīnwē) was an ancient Assyrian city of Upper Mesopotamia, located in the modern-day city of Mosul in northern Iraq. It is located on the eastern ban ...
and Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon ( ; Middle Persian: 𐭲𐭩𐭮𐭯𐭥𐭭 ''tyspwn'' or ''tysfwn''; fa, تیسفون; grc-gre, Κτησιφῶν, ; syr, ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢThomas A. Carlson et al., “Ctesiphon — ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢ ” in The Syriac Gazetteer last modi ...
and was later desired by the British Empire as an outpost by which to maintain access to India. The city was organized in a circular fashion next to the Tigris River, with massive brick walls being constructed in successive rings around the core by a workforce of 100,000 with four huge gates (named Kufa, Basrah, Khorasan and Syria). The central enclosure of the city contained Mansur's palace of in area and the great mosque of Baghdad, encompassing . Travel across the Tigris and the network of waterways allowing the drainage of the Euphrates into the Tigris was facilitated by bridges and canals servicing the population.
Glass and crystal
The Near East has, since Roman times, been recognized as a center of quality glassware and crystal. 9th-century finds from Samarra show styles similar to Sassanian forms. The types of objects made were bottles, flasks, vases, and cups intended for domestic use, with decorations including molded flutes, honeycomb patterns, and inscriptions. Other styles seen that may not have come from the Sassanians were stamped items. These were typically round stamps, such as medallions or disks with animals, birds, or Kufic inscriptions. Colored lead glass, typically blue or green, has been found inNishapur
Nishapur or officially Romanized as Neyshabur ( fa, ;Or also "نیشاپور" which is closer to its original and historic meaning though it is less commonly used by modern native Persian speakers. In Persian poetry, the name of this city is wr ...
, along with prismatic perfume bottles. Finally, cut glass may have been the high point of Abbasid glass-working, decorated with floral and animal designs.
Painting
 Early Abbasid painting has not survived in great quantities, and is sometimes harder to differentiate; however, Samarra provides good examples, as it was built by the Abbasids and abandoned 56 years later. The walls of the principal rooms of the palace that have been excavated show wall paintings and lively carved stucco dadoes. The style is obviously adopted with little variation from Sassanian art, bearing not only similar styles, with harems, animals, and dancing people, all enclosed in scrollwork, but the garments are also Persian.
Early Abbasid painting has not survived in great quantities, and is sometimes harder to differentiate; however, Samarra provides good examples, as it was built by the Abbasids and abandoned 56 years later. The walls of the principal rooms of the palace that have been excavated show wall paintings and lively carved stucco dadoes. The style is obviously adopted with little variation from Sassanian art, bearing not only similar styles, with harems, animals, and dancing people, all enclosed in scrollwork, but the garments are also Persian. Nishapur
Nishapur or officially Romanized as Neyshabur ( fa, ;Or also "نیشاپور" which is closer to its original and historic meaning though it is less commonly used by modern native Persian speakers. In Persian poetry, the name of this city is wr ...
had its own school of painting. Excavations at Nishapur show both monochromatic and polychromatic artwork from the 8th and 9th centuries. One famous piece of art consists of hunting nobles with falcons and on horseback, in full regalia; the clothing identifies them as Tahirid, which was, again, a sub-dynasty of the Abbasids. Other styles are of vegetation, and fruit in nice colors on a four-foot high dedo.
Pottery
 Whereas painting and architecture were not areas of strength for the Abbasid dynasty, pottery was a different story. Islamic culture as a whole, and the Abbasids in particular, were at the forefront of new ideas and techniques. Some examples of their work were pieces engraved with decorations and then colored with yellow-brown, green, and purple glazes. Designs were diverse with geometric patterns, Kufic lettering, and arabesque scrollwork, along with rosettes, animals, birds, and humans. Abbasid pottery from the 8th and 9th centuries has been found throughout the region, as far as Cairo. These were generally made with a yellow clay and fired multiple times with separate glazes to produce metallic luster in shades of gold, brown, or red. By the 9th century, the potters had mastered their techniques and their decorative designs could be divided into two styles. The Persian style would show animals, birds, and humans, along with Kufic lettering in gold. Pieces excavated from
Whereas painting and architecture were not areas of strength for the Abbasid dynasty, pottery was a different story. Islamic culture as a whole, and the Abbasids in particular, were at the forefront of new ideas and techniques. Some examples of their work were pieces engraved with decorations and then colored with yellow-brown, green, and purple glazes. Designs were diverse with geometric patterns, Kufic lettering, and arabesque scrollwork, along with rosettes, animals, birds, and humans. Abbasid pottery from the 8th and 9th centuries has been found throughout the region, as far as Cairo. These were generally made with a yellow clay and fired multiple times with separate glazes to produce metallic luster in shades of gold, brown, or red. By the 9th century, the potters had mastered their techniques and their decorative designs could be divided into two styles. The Persian style would show animals, birds, and humans, along with Kufic lettering in gold. Pieces excavated from Samarra
Samarra ( ar, سَامَرَّاء, ') is a city in Iraq. It stands on the east bank of the Tigris in the Saladin Governorate, north of Baghdad. The city of Samarra was founded by Abbasid Caliph Al-Mutasim for his Turkish professional army ...
exceed in vibrancy and beauty any from later periods. These predominantly being made for the Caliphs use. Tiles were also made using this same technique to create both monochromatic and polychromatic lusterware tiles.
Textiles
Egypt being a center of the textile industry was part of Abbasid cultural advancement. Copts were employed in the textile industry and produced linens and silks.Tinnis
Tennis or Tinnīs ( arz, تنيس, cop, ⲑⲉⲛⲛⲉⲥⲓ) was a medieval city in Egypt which no longer exists. It was most prosperous from the 9th century to the 11th century until its abandonment. It was located at 31°12′N 32°14′E, o ...
was famous for its factories and had over 5,000 looms. Examples of textiles were ''kasab'', a fine linen for turbans, and ''badana'' for upper-class garments. The kiswah
Kiswa ( ar, كسوة الكعبة, ''kiswat al-ka'bah'') is the cloth that covers the Kaaba in Mecca, Saudi Arabia. It is draped annually on the 9th day of the month of Dhu al-Hijjah, the day pilgrims leave for the plains of Mount Arafat during ...
for the kaaba
The Kaaba (, ), also spelled Ka'bah or Kabah, sometimes referred to as al-Kaʿbah al-Musharrafah ( ar, ٱلْكَعْبَة ٱلْمُشَرَّفَة, lit=Honored Ka'bah, links=no, translit=al-Kaʿbah al-Musharrafah), is a building at the c ...
in Mecca was made in a town named Tuna near Tinnis. Fine silk was also made in Dabik and Damietta. Of particular interest are stamped and inscribed fabrics, which used not only inks but also liquid gold. Some of the finer pieces were colored in such a manner as to require six separate stamps to achieve the proper design and color. This technology spread to Europe eventually.
Technology
 In technology, the Abbasids adopted
In technology, the Abbasids adopted papermaking
Papermaking is the manufacture of paper and cardboard, which are used widely for printing, writing, and packaging, among many other purposes. Today almost all paper is made using industrial machinery, while handmade paper survives as a speciali ...
from China. The use of paper spread from China into the caliphate in the 8th century CE, arriving in al-Andalus (Islamic Spain) and then the rest of Europe in the 10th century. It was easier to manufacture than parchment, less likely to crack than papyrus, and could absorb ink, making it ideal for making records and copies of the Qur'an. "Islamic paper makers devised assembly-line methods of hand-copying manuscripts to turn out editions far larger than any available in Europe for centuries." It was from the Abbasids that the rest of the world learned to make paper from linen. The knowledge of gunpowder was also transmitted from China via the caliphate, where the formulas for pure potassium nitrate and an explosive
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An expl ...
gunpowder effect were first developed.
Advances were made in irrigation and farming, using new technology such as the windmill. Crops such as almond
The almond (''Prunus amygdalus'', syn. ''Prunus dulcis'') is a species of tree native to Iran and surrounding countries, including the Levant. The almond is also the name of the edible and widely cultivated seed of this tree. Within the genus ...
s and citrus fruit were brought to Europe through al-Andalus, and sugar cultivation was gradually adopted by the Europeans. Apart from the Nile, Tigris and Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
, navigable rivers were uncommon, so transport by sea was very important. Navigational sciences were highly developed, making use of a rudimentary sextant
A sextant is a doubly reflecting navigation instrument that measures the angular distance between two visible objects. The primary use of a sextant is to measure the angle between an astronomical object and the horizon for the purposes of celes ...
(known as a kamal). When combined with detailed maps of the period, sailors were able to sail across oceans rather than skirt along the coast. Abbasid sailors were also responsible for reintroducing large three masted merchant vessels to the Mediterranean. The name caravel may derive from an earlier Arab ship known as the ''qārib''. Arab merchants dominated trade in the Indian Ocean until the arrival of the Portuguese in the 16th century. Hormuz was an important center for this trade. There was also a dense network of trade routes in the Mediterranean, along which Muslim countries traded with each other and with European powers such as Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
or Genoa. The Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
crossing Central Asia passed through the Abbasid caliphate between China and Europe.
 Engineers in the Abbasid caliphate made a number of innovative industrial uses of hydropower, and early industrial uses of tidal power, wind power, and petroleum (notably by distillation into kerosene). The industrial uses of watermills in the Islamic world date back to the 7th century, while horizontal-
Engineers in the Abbasid caliphate made a number of innovative industrial uses of hydropower, and early industrial uses of tidal power, wind power, and petroleum (notably by distillation into kerosene). The industrial uses of watermills in the Islamic world date back to the 7th century, while horizontal-wheeled
A wheel is a circular component that is intended to rotate on an axle bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the six simple machines. Wheels, in conjunction with axles, allow heavy objects to be ...
and vertical-wheeled water mills were both in widespread use since at least the 9th century. By the time of the Crusades, every province throughout the Islamic world had mills in operation, from al-Andalus and North Africa to the Middle East and Central Asia. These mills performed a variety of agricultural and industrial tasks. Abbasid engineers also developed machines (such as pumps) incorporating crankshaft
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating shaft containing one or more crankpins, that are driven by the pistons via the connecting ...
s, employed gears in mills and water-raising machines, and used dams to provide additional power to watermills and water-raising machines. Such advances made it possible for many industrial tasks that were previously driven by manual labour in ancient times to be mechanized and driven by machinery instead in the medieval Islamic world. It has been argued that the industrial use of waterpower had spread from Islamic to Christian Spain, where fulling mills, paper mills, and forge mills were recorded for the first time in Catalonia.
A number of industries were generated during the Arab Agricultural Revolution, including early industries for textiles, sugar, rope-making, matting, silk, and paper. Latin translations of the 12th century passed on knowledge of chemistry and instrument making in particular. The agricultural and handicraft industries also experienced high levels of growth during this period.
Status of women
In contrast to the earlier era, women in Abbasid society were absent from all arenas of the community's central affairs. While their Muslim forbears led men into battle, started rebellions, and played an active role in community life, as demonstrated in the Hadith literature, Abbasid women were ideally kept in seclusion. Conquests had brought enormous wealth and large numbers of slaves to the Muslim elite. The majority of the slaves were women and children,Morony, Michael G. Iraq after the Muslim conquest. Gorgias Press LLC, 2005 many of whom had been dependents or harem-members of the defeated Sassanian upper classes.Abbott, Nabia. Two queens of Baghdad: mother and wife of Hārūn al Rashīd. University of Chicago Press, 1946. In the wake of the conquests an elite man could potentially own a thousand slaves, and ordinary soldiers could have ten people serving them.Concubines were expected to be treated well, treating them poorly would have been deviation from Islamic ethics however some from the ruling class engaged in acts of disbelief and deviancy behind closed doors with and without their harem's It was narrated from Ibn Abbas that Muhammad said: "There is no man whose two daughters reach the age of puberty and he treats them kindly for the time they are together, but they will gain him admittance to Paradise." "Whoever has three daughters and is patient towards them, and feeds them, gives them to drink, and clothes them from his wealth; they will be a shield for him from the Fire on the Day of Resurrection.'" Even so, slave courtesans ( qiyans and jawaris) and princesses produced prestigious and important poetry. Enough survives to give us access to women's historical experiences, and reveals some vivacious and powerful figures, such as the Sufi mystic Raabi'a al-Adwiyya (714–801 CE), the princess and poet'Ulayya bint al-Mahdi
Ulayya bint al-Mahdi ( ar, عُلَيّة بنت المهدي, ʿUlayya bint al-Mahdī, 777–825) was an Abbasid princess, noted for her legacy as a poet and musician.
Biography
‘Ulayya was one of the daughters of the third Abbasid Caliph al- ...
(777–825 CE), and the singing-girls Shāriyah
Shāriyah ( ar, شارِية, born c. 815 in al-Basra; died c. 870 C.E.) was an ‘Abbasid ''qayna'' (enslaved singing-girl), who enjoyed a prominent place in the court of Al-Wathiq (r. 842–847).
Biography
The main source for Shāriyah's life ...
(–870 CE), Fadl Ashsha'ira (d. 871 CE) and Arib al-Ma'muniyya
ʿArīb al-Ma’mūnīya ( ar, عريب المأمونية, b. 181/797–98, d. 277/890–91) was a ''qayna'' (slave trained in the arts of entertainment) of the early Abbasid period, who has been characterised as 'the most famous slave singer to ...
(797–890 CE).
Each wife in the Abbasid harem had an additional home or flat, with her own enslaved personals staff of eunuchs and maidservants. When a concubine gave birth to a son, she was elevated in rank to umm walad and also received apartments and (slave) servants as a gift.
Treatment of Jews and Christians
 The status and treatment of Jews, Christians, and non-Muslims in the Abbasid Caliphate was a complex and continually changing issue. Non-Muslims were called
The status and treatment of Jews, Christians, and non-Muslims in the Abbasid Caliphate was a complex and continually changing issue. Non-Muslims were called dhimmi
' ( ar, ذمي ', , collectively ''/'' "the people of the covenant") or () is a historical term for non-Muslims living in an Islamic state with legal protection. The word literally means "protected person", referring to the state's obligatio ...
s. Dhimmis did not have all of the privileges that Muslims had and commonly had to pay jizya
Jizya ( ar, جِزْيَة / ) is a per capita yearly taxation historically levied in the form of financial charge on dhimmis, that is, permanent Kafir, non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The jizya tax has been unde ...
, a tax for not being a Muslim. One of the common aspects of the treatment of the dhimmis is that their treatment depended on who the Caliph was at the time. Some Abbasid rulers, like Al-Mutawakkil
Abū al-Faḍl Jaʿfar ibn Muḥammad al-Muʿtaṣim bi-ʾllāh ( ar, جعفر بن محمد المعتصم بالله; March 822 – 11 December 861), better known by his regnal name Al-Mutawakkil ʿalā Allāh (, "He who relies on God") was t ...
(822–861 CE) imposed strict restrictions on what dhimmis could wear in public, often yellow garments that distinguished them from Muslims. Other restrictions al-Mutawakkil imposed included limiting the role of the dhimmis in government, seizing dhimmi housing and making it harder for dhimmis to become educated. Most other Abbasid caliphs were not as strict as al-Mutawakkil, though. During the reign of Al-Mansur (714–775 CE), it was common for Jews and Christians to influence the overall culture in the Caliphate, specifically in Baghdad. Jews and Christians did this by participating in scholarly work
It was common that laws that were imposed against dhimmis during one caliph's rule were either discarded or not practiced during future caliphs' reigns. Al-Mansur and al-Mutawakkil both instituted laws that forbade non-Muslims from participating in public office. Al-Mansur did not follow his own law very closely, bringing dhimmis back to the Caliphate's treasury due to the needed expertise of dhimmis in the area of finance. Al-Mutawakkil followed the law banning dhimmis from public office more seriously, although, soon after his reign, many of the laws concerning dhimmis participating in government were completely unobserved or at least less strictly observed. Even Al-Muqtadir
Abu’l-Faḍl Jaʿfar ibn Ahmad al-Muʿtaḍid ( ar, أبو الفضل جعفر بن أحمد المعتضد) (895 – 31 October 932 AD), better known by his regnal name Al-Muqtadir bi-llāh ( ar, المقتدر بالله, "Mighty in God"), wa ...
(), who held a similar stance as al-Mutawakkil on barring non-Muslims from public office, himself had multiple Christian secretaries, indicating that non-Muslims still had access to many of the most important figures within the Caliphate. Past having a casual association or just being a secretary to high-ranking Islamic officials, some of them achieved the second highest office after the caliph: the vizier.
Jews and Christians may have had a lower overall status compared to Muslims in the Abbasid Caliphate, but dhimmis were often allowed to hold respectable and even prestigious occupations in some cases, such as doctors and public officeholders. Jews and Christians were also allowed to be rich even if they were taxed for being a dhimmi. Dhimmis were capable of moving up and down the social ladder, though this largely depended on the particular caliph. An indication as to the social standing of Jews and Christians at the time was their ability to live next to Muslim people. While al-Mansur was ruling the Caliphate, for instance, it was not uncommon for dhimmis to live in the same neighborhoods as Muslims. One of the biggest reasons why dhimmis were allowed to hold prestigious jobs and positions in government is that they were generally important to the well-being of the state and were proficient to excellent with the work at hand. Some Muslims in the Caliphate took offense to the idea that there were dhimmis in public offices who were in a way ruling over them although it was an Islamic state, while other Muslims were at time jealous of some dhimmis for having a level of wealth or prestige greater than other Muslims, even if Muslims were still the majority of the ruling class. In general, Muslims, Jews, and Christians had close relations that could be considered positive at times, especially for Jews, in contrast to how Jews were being treated in Europe.
Many of the laws and restrictions that were imposed on dhimmis often resembled other laws that previous states had used to discriminate against a minority religion, specifically Jewish people. Romans in the fourth century banned Jewish people from holding public offices, banned Roman citizens from converting to Judaism, and often demoted Jews who were serving in the Roman military. In direct contrast, there was an event in which two viziers, Ibn al-Furat and Ali ibn Isa ibn al-Jarrah, argued about Ibn al-Furat's decision to make a Christian the head of the military. A previous vizier, Abu Muhammad al-Hasan al-Bazuri, had done so. These laws predated al-Mansur's laws against dhimmis and often had similar restrictions, although Roman emperors were often much more strict on enforcing these laws than many Abbasid caliphs.
Most of Baghdad's Jews were incorporated into the Arab community and considered Arabic their native language. Some Jews studied Hebrew in their schools and Jewish religious education flourished. The united Muslim empire allowed Jews to reconstruct links between their dispersed communities throughout the Middle East. The city's Talmudic institute helped spread the rabbinical tradition to Europe, and the Jewish community in Baghdad went on to establish ten rabbinical schools and twenty-three synagogues. Baghdad not only contained the tombs of Muslim saints and martyrs, but also the tomb of Yusha, whose corpse had been brought to Iraq during the first migration of the Jews out of the Levant.
Arabization
While the Abbasids originally gained power by exploiting the social inequalities against non-Arabs in the Umayyad Empire, during Abbasid rule the empire rapidly Arabized, particularly in the Fertile Crescent region (namely Mesopotamia and the Levant) as had begun under Umayyad rule. As knowledge was shared in the Arabic language throughout the empire, many people from different nationalities and religions began to speak Arabic in their everyday lives. Resources from other languages began to be translated into Arabic, and a unique Islamic identity began to form that fused previous cultures with Arab culture, creating a level of civilization and knowledge that was considered a marvel in Europe at the time.Holidays
There were large feasts on certain days, as the Muslims of the empire celebrated Christian holidays as well as their own. There were two main Islamic feasts: one marked by the end of Ramadan; the other, "the Feast of Sacrifice". The former was especially joyful because children would purchase decorations and sweetmeats; people prepared the best food and bought new clothes. At midmorning, the caliph, wearing Muhammad's thobe, would guide officials, accompanied by armed soldiers to theGreat Mosque
A congregational mosque or Friday mosque (, ''masjid jāmi‘'', or simply: , ''jāmi‘''; ), or sometimes great mosque or grand mosque (, ''jāmi‘ kabir''; ), is a mosque for hosting the Friday noon prayers known as ''jumu'ah''.*
*
*
*
*
*
*
...
, where he led prayers. After the prayer, all those in attendance would exchange the best wishes and hug their kin and companions. The festivities lasted for three days. During those limited number of nights, the palaces were lit up and boats on the Tigris hung lights. It was said that Baghdad “glittered ‘like a bride." During “the Feast of Sacrifice.”, sheep were butchered in public arenas and the caliph participated in a large-scale sacrifice in the palace courtyard. Afterward, the meat would be divided and given to the poor.
In addition to these two holidays, Shias celebrated the birthdays of Fatimah and Ali ibn Abi Talib
ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib ( ar, عَلِيّ بْن أَبِي طَالِب; 600 – 661 CE) was the last of four Rightly Guided Caliphs to rule Islam (r. 656 – 661) immediately after the death of Muhammad, and he was the first Shia Imam. ...
. Matrimonies and births in the royal family were observed by all in the empire. The announcement that one of the caliph's sons could recite the Koran smoothly was greeted by communal jubilation. When Harun developed this holy talent, the people lit torches and decorated the streets with wreaths of flowers, and his father, Al-Mahdi, freed 500 slaves.
Of all the holidays imported from other cultures and religions, the one most celebrated in Baghdad (a city with many Persians) was Nowruz, which celebrated the arrival of spring. In a ceremonial ablution introduced by Persian troops, residents sprinkled themselves with water and ate almond cakes. The palaces of the imperial family were lit up for six days and nights. The Abbasids also celebrated the Persian holiday of Mihraj, which marked the onset of winter (signified with pounding drums), and Sadar, when homes burned incense and the masses would congregate along the Tigris to witness princes and viziers pass by.
Military
In Baghdad there were many Abbasid military leaders who were or said they were of Arab descent. However, it is clear that most of the ranks were of Iranian origin, the vast majority being fromKhorasan
Khorasan may refer to:
* Greater Khorasan, a historical region which lies mostly in modern-day northern/northwestern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
* Khorasan Province, a pre-2004 province of Ira ...
and Transoxiana, not from western Iran or Azerbaijan. Most of the Khorasani soldiers who brought the Abbasids to power were Arabs.
 The standing army of the Muslims in Khorosan was overwhelmingly Arab. The unit organization of the Abbasids was designed with the goal of ethnic and racial equality among supporters. When Abu Muslim recruited officers along the Silk Road, he registered them based not on their tribal or ethno-national affiliations but on their current places of residence. The Cambridge History of Iran
The standing army of the Muslims in Khorosan was overwhelmingly Arab. The unit organization of the Abbasids was designed with the goal of ethnic and racial equality among supporters. When Abu Muslim recruited officers along the Silk Road, he registered them based not on their tribal or ethno-national affiliations but on their current places of residence. The Cambridge History of Iranp. 62
Ed. Richard N. Frye. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1975. Under the Abbasids, Iranian peoples became better represented in the army and bureaucracy as compared to before. The Abbasid army was centred on the Khurasan
Abna al-dawla
The ''abnāʾ al-dawla'' ( ar, أبناء الدولة, meaning "sons of the regime/dynasty"), often simply " the ''Abnāʾ''", is a term for the Khorasani Arabs who had participated in the Abbasid Revolution of 749–750 and their descendants, wh ...
infantry and the Khurasaniyya heavy cavalry, led by their own semi-autonomous commanders (qa'id) who recruited and deployed their own men with Abbasid resource grants. al-Mu‘tasim began the practice of recruiting Turkic slave soldiers from the Samanids into a private army, which allowed him to take over the reins of the Caliphate. He abolished the old ''jund'' system created by Umar and diverted the salaries of the original Arab military descendants to the Turkic slave soldiers. The Turkic soldiers transformed the style of warfare, as they were known as capable horse archers, trained from childhood to ride. This military was now drafted from the ethnic groups of the faraway borderlands, and were completely separate from the rest of society. Some could not speak Arabic properly. This led to the decline of the Caliphate starting with the Anarchy at Samarra.
Although the Abbasids never retained a substantial regular army, the caliph could recruit a considerable number of soldiers in a short time when needed from levies. There were also cohorts of regular troops who received steady pay and a special forces unit. At any moment, 125,000 Muslim soldiers could be assembled along the Byzantine frontier, Baghdad, Medina, Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
, Rayy, and other geostrategic locations in order to quell any unrest.
The cavalry was entirely covered in iron, with helmets. Similar to medieval knights, their only exposed spots were the end of their noses and small openings in front of their eyes. Their foot soldiers were issued spears, swords, and pikes, and (in line with Persian fashion) trained to stand so solidly that, one contemporary wrote "you would have thought them held fast by clamps of bronze."
The Abbasid army amassed an array of siege equipment, such as catapult
A catapult is a ballistic device used to launch a projectile a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants – particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden release of stored p ...
s, mangonels, battering rams, ladders, grappling irons, and hooks. All such weaponry was operated by military engineers. However, the primary siege weapon was the manjaniq, a type of siege weapon that was comparable to the trebuchet employed in Western medieval times. From the seventh century onward, it had largely replaced torsion artillery. By Harun al-Rashid's time, the Abbasid army employed fire grenade
A grenade is an explosive weapon typically thrown by hand (also called hand grenade), but can also refer to a shell (explosive projectile) shot from the muzzle of a rifle (as a rifle grenade) or a grenade launcher. A modern hand grenade genera ...
s. The Abbasids also utilized field hospitals and ambulances drawn by camels.
Civil administration
 As a result of such a vast Empire, the caliphate was decentralized and divided into 24 provinces.
In keeping with Persian tradition, Harun's vizier enjoyed close to unchecked powers. Under Harun, a special "bureau of confiscation" was created. This governmental wing made it possible for the vizier to seize the property and riches of any corrupt governor or civil servant. In addition, it allowed governors to confiscate the estates of lower-ranking officials. Finally, the caliph could impose the same penalty on a vizier who fell from grace. As one later caliph put it: "The vizier is our representative throughout the land and amongst our subjects. Therefore, he who obeys him obeys us; and he who obeys us obeys God, and God shall cause him who obeys Him to enter paradise."
Every regional metropolis had a post office and hundreds of roads were paved in order to link the imperial capital with other cities and towns. The empire employed a system of relays to deliver mail. The central post office in Baghdad even had a map with directions that noted the distances between each town. The roads were provided with roadside inns, hospices, and wells and could reach eastward through Persia and Central Asia, to as far as China. The post office not only enhanced civil services but also served as intelligence for the caliph. Mailmen were employed as spies who kept an eye on local affairs.
Early in the days of the caliphate, the Barmakids took the responsibility of shaping the
As a result of such a vast Empire, the caliphate was decentralized and divided into 24 provinces.
In keeping with Persian tradition, Harun's vizier enjoyed close to unchecked powers. Under Harun, a special "bureau of confiscation" was created. This governmental wing made it possible for the vizier to seize the property and riches of any corrupt governor or civil servant. In addition, it allowed governors to confiscate the estates of lower-ranking officials. Finally, the caliph could impose the same penalty on a vizier who fell from grace. As one later caliph put it: "The vizier is our representative throughout the land and amongst our subjects. Therefore, he who obeys him obeys us; and he who obeys us obeys God, and God shall cause him who obeys Him to enter paradise."
Every regional metropolis had a post office and hundreds of roads were paved in order to link the imperial capital with other cities and towns. The empire employed a system of relays to deliver mail. The central post office in Baghdad even had a map with directions that noted the distances between each town. The roads were provided with roadside inns, hospices, and wells and could reach eastward through Persia and Central Asia, to as far as China. The post office not only enhanced civil services but also served as intelligence for the caliph. Mailmen were employed as spies who kept an eye on local affairs.
Early in the days of the caliphate, the Barmakids took the responsibility of shaping the civil service
The civil service is a collective term for a sector of government composed mainly of career civil servants hired on professional merit rather than appointed or elected, whose institutional tenure typically survives transitions of political leaders ...
. The family had roots in a Buddhist monastery in northern Afghanistan. In the early 8th century, the family converted to Islam and began to take on a sizable part of the civil administration for the Abbasids.
Capital poured into the caliphate's treasury from a variety of taxes, including a real estate tax; a levy on cattle, gold and silver, and commercial wares; a special tax on non-Muslims; and customs dues.
Trade
UnderHarun
Harun, also transliterated as Haroon or Haroun ( ar, هارون, ) is a common male given name of Arabic origin, related to the Hebrew name of the Prophet Aaron. Both are most likely of Ancient Egyptian origin, from ''aha rw'', meaning "warrior li ...
, maritime trade through the Persian Gulf thrived, with Arab vessels trading as far south as Madagascar and as far east as China, Korea, and Japan. The growing economy of Baghdad and other cities inevitably led to the demand for luxury items and formed a class of entrepreneurs who organized long-range caravans for the trade and then the distribution of their goods. A whole section in the East Baghdad suq was dedicated to Chinese goods. Arabs traded with the Baltic region
The terms Baltic Sea Region, Baltic Rim countries (or simply the Baltic Rim), and the Baltic Sea countries/states refer to slightly different combinations of countries in the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea, mainly in Northern Europe. ...
and made it as far north as the British Isles. Tens of thousands of Arab coins have been discovered in parts of Russia and Sweden, which bear witness to the comprehensive trade networks set up by the Abbasids. King Offa of Mercia (in England) minted gold coins similar to those of the Abbasids in the eighth century.
Muslim merchants employed ports in Bandar Siraf
Bandar Siraf ( fa, بندر سیراف), also Romanized as Bandar-e Sīraf; also known as Sīraf, Ṭāherī, and Tāhiri; as well as Bandar-e Ṭāherī and Bandar-i Ṭāhirī ( fa, بندر طاهری, Bandar-e Ṭāherī), is a city in the Ce ...
, Basra, and Aden
Aden ( ar, عدن ' Yemeni: ) is a city, and since 2015, the temporary capital of Yemen, near the eastern approach to the Red Sea (the Gulf of Aden), some east of the strait Bab-el-Mandeb. Its population is approximately 800,000 people. ...
and some Red Sea ports to travel and trade with India and South East Asia. Land routes were also utilized through Central Asia. Arab businessmen were present in China as early as the eighth century. Arab merchants sailed the Caspian Sea to reach and trade with Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
and Samarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
.
Many caravans and goods never made it to their intended destinations. Some Chinese exports perished in fires, while other ships sank. It was said that anybody who made it to China and back unharmed was blessed by God. Common sea routes were also plagued by pirates who built and crewed vessels that were faster than most merchant ships. It is said that many of the adventures at sea in the Sinbad tales were based on historical fiction of mariners of the day.
The Arabs also established overland trade with Africa, largely for gold and slaves
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
. When trade with Europe ceased due to hostilities, Jews served as a link between the two hostile worlds.
Decline
Abbasids found themselves at odds with the Shia Muslims, most of whom had supported their war against the Umayyads since the Abbasids and the Shias claimed legitimacy by their familial connection to Muhammad. Once in power, the Abbasids disavowed any support for Shia beliefs in favor ofSunni
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagr ...
Islam. Shortly thereafter, Berber Kharijite
The Kharijites (, singular ), also called al-Shurat (), were an Islamic sect which emerged during the First Fitna (656–661). The first Kharijites were supporters of Ali who rebelled against his acceptance of arbitration talks to settle the c ...
s set up an independent state in North Africa in 801. Within 50 years, the Idrisids in the Maghreb and Aghlabids of Ifriqiya
Ifriqiya ( '), also known as al-Maghrib al-Adna ( ar, المغرب الأدنى), was a medieval historical region comprising today's Tunisia and eastern Algeria, and Tripolitania (today's western Libya). It included all of what had previously ...
and soon the Tulunids and Ikshidid
The Ikhshidid dynasty (, ) was a Turkic mamluk dynasty who ruled Egypt and the Levant from 935 to 969. Muhammad ibn Tughj al-Ikhshid, a Turkic mamluk soldier, was appointed governor by the Abbasid Caliph al-Radi. The dynasty carried the Arabic ti ...
s of Misr Misr or MISR may refer to:
* Misr, the romanized Arabic name for Egypt
* misr, singular of Arabic ''amsar'', which were early Arabic "garrison towns"
* Misr (domain name), a top-level Internet domain name
* Misr, a variant of the AKM assault rifle ...
were effectively independent in Africa. The Abbasid authority began to deteriorate during the reign of al-Radi
Abu'l-Abbas Ahmad (Muhammad) ibn Ja'far al-Muqtadir ( ar, أبو العباس أحمد (محمد) بن جعفر المقتدر, Abū al-ʿAbbās Aḥmad (Muḥammad) ibn al-Muqtadir; December 909 – 23 December 940), usually simply known by his r ...
when their Turkic Army generals, who already had de facto independence, stopped paying the caliphate. Even provinces close to Baghdad began to seek local dynastic rule. Also, the Abbasids found themselves to be often at conflict with the Umayyads in Spain. The Abbasid financial position weakened as well, with tax revenues from the Sawād
Sawad was the name used in early Islamic times (7th–12th centuries) for southern Iraq. It means "black land" or "arable land" and refers to the stark contrast between the alluvial plain of Mesopotamia and the Arabian Desert. Under the Umayyad ...
decreasing in the 9th and the 10th centuries.
Separatist dynasties and their successors
The following list represents the succession of Islamic dynasties that emerged from the fractured Abbasid empire by their general geographic location. Dynasties often overlap, where a vassal emir revolted from and later conquered his lord. Gaps appear during periods of contest where the dominating power was unclear. Except for theFatimid Caliphate
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Isma'ilism, Ismaili Shia Islam, Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the ea ...
in Egypt, recognizing a Shia succession through Ali, and the Andalusian Caliphates of the Umayyads and Almohads
The Almohad Caliphate (; ar, خِلَافَةُ ٱلْمُوَحِّدِينَ or or from ar, ٱلْمُوَحِّدُونَ, translit=al-Muwaḥḥidūn, lit=those who profess the unity of God) was a North African Berber Muslim empire fo ...
, every Muslim dynasty at least acknowledged the nominal suzerainty of the Abbasids as Caliph and Commander of the Faithful.
* (Maghrib al Aqsa or Extreme Maghreb) Morocco: Idrisids
The Idrisid dynasty or Idrisids ( ar, الأدارسة ') were an Arab Muslim dynasty from 788 to 974, ruling most of present-day Morocco and parts of present-day western Algeria. Named after the founder, Idris I, the Idrisids were an Alid and ...
(788–974) → Almoravids
The Almoravid dynasty ( ar, المرابطون, translit=Al-Murābiṭūn, lit=those from the ribats) was an imperial Berber Muslim dynasty centered in the territory of present-day Morocco. It established an empire in the 11th century that ...
(1040–1147) → Almohads (1120–1269) → Marinids (1472–1554) → Wattasids (1472–1554) → Saadis
The Saadi Sultanate (also rendered in English as Sa'di, Sa'did, Sa'dian, or Saadian; ar, السعديون, translit=as-saʿdiyyūn) was a state which ruled present-day Morocco and parts of West Africa in the 16th and 17th centuries. It was l ...
(1510–1659) → 'Alawi dynasty
The Alawi dynasty ( ar, سلالة العلويين الفيلاليين, translit=sulālat al-ʿalawiyyīn al-fīlāliyyīn) – also rendered in English as Alaouite, Alawid, or Alawite – is the current Moroccan royal family and reigning d ...
* Ifriqiya
Ifriqiya ( '), also known as al-Maghrib al-Adna ( ar, المغرب الأدنى), was a medieval historical region comprising today's Tunisia and eastern Algeria, and Tripolitania (today's western Libya). It included all of what had previously ...
(modern Tunisia, eastern Algeria and western Libya): Aghlabids
The Aghlabids ( ar, الأغالبة) were an Arab dynasty of emirs from the Najdi tribe of Banu Tamim, who ruled Ifriqiya and parts of Southern Italy, Sicily, and possibly Sardinia, nominally on behalf of the Abbasid Caliph, for about a cen ...
(800–909 CE) → Fatimids (temporaly in Kairouan) (909–973 CE) → Zirids (at their collapse) (973–1148) → Almohads
The Almohad Caliphate (; ar, خِلَافَةُ ٱلْمُوَحِّدِينَ or or from ar, ٱلْمُوَحِّدُونَ, translit=al-Muwaḥḥidūn, lit=those who profess the unity of God) was a North African Berber Muslim empire fo ...
(1148–1229) → Hafsids (1229–1574) → Husainid dynasty (1705–1957) → Kingdom of Tunisia
* Egypt and Palestine: Tulunids (868–905 CE) → Ikhshidids
The Ikhshidid dynasty (, ) was a Turkic mamluk dynasty who ruled Egypt and the Levant from 935 to 969. Muhammad ibn Tughj al-Ikhshid, a Turkic mamluk soldier, was appointed governor by the Abbasid Caliph al-Radi. The dynasty carried the Arabic ti ...
(935–969) → Fatimid Caliphate
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Isma'ilism, Ismaili Shia Islam, Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the ea ...
(909–1171) → Ayyubid dynasty
The Ayyubid dynasty ( ar, الأيوبيون '; ) was the founding dynasty of the medieval Sultan of Egypt, Sultanate of Egypt established by Saladin in 1171, following his abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimid Caliphate of Egypt. A Sunni ...
(1171–1250) → Mamluks
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning "slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') i ...
(1250–1517)
* Al-Jazira (modern East Syria and Western Iraq): Hamdanids (890–1004 CE) → Marwanids
Marwanids may refer to:
* Marwanids (Diyar Bakr), a Kurdish dynasty that ruled in Diyar Bakr in the 10th–11th centuries
* Marwanids, a branch of the Umayyad dynasty
Umayyad dynasty ( ar, بَنُو أُمَيَّةَ, Banū Umayya, Sons of Um ...
(990–1085) and Uqaylids (990–1096) → Seljuks (1034–1194) → Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
and the Ilkhanate (1231–1335)
* Southwest Iran: Buyids (934–1055) → Seljuks (1034–1194) → Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
→ Injuids (1335–1357) → Muzaffarids (1314–1393)
* Khorasan
Khorasan may refer to:
* Greater Khorasan, a historical region which lies mostly in modern-day northern/northwestern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
* Khorasan Province, a pre-2004 province of Ira ...
(modern Iran, Afghanistan and Turkmenistan): Tahirids
The Tahirid dynasty ( fa, طاهریان, Tâheriyân, ) was a culturally Arabized Sunni Muslim dynasty of Persian dehqan origin, that ruled as governors of Khorasan from 821 to 873 as well as serving as military and security commanders in Ab ...
(821–873) → Saffarids (873–903) → Samanids (903–995) → Ghaznavids
The Ghaznavid dynasty ( fa, غزنویان ''Ġaznaviyān'') was a culturally Persianate, Sunni Muslim dynasty of Turkic ''mamluk'' origin, ruling, at its greatest extent, large parts of Persia, Khorasan, much of Transoxiana and the northwest ...
(995–1038) → Seljuks (1038–1194) → Ghurids (1011–1215) → Khwarazmians (1077–1231) → Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
and the Ilkhanate (1231–1335)
* Transoxiana (modern Central Asia): Samanids (819–999) → Karakhanids (840–1212) → Khwarazmians (1077–1231) → Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
and the Chagatai Khanate (1225–1687)
*(Maghrib al Awsat or Central Maghreb) Algeria: Emirate of Tlemcen
The Ifranid Emirate of Tlemcen or Ifranid Kingdom of Tlemcen,
was a Kharijite state, founded by Berbers of the Banu Ifran in the eighth century, with its capital at Tlemcen in modern Algeria.
Background
After the Muslim conquest of the ...
→ Sulaymanids Dynasty → Rustamids → Zirid dynasty (apogee) → Ifranid dynasty → Abd al-Mu'min (Almohad founder from Nedroma) → Zayyanid dynasty and Marinid dynasty
The Marinid Sultanate was a Berber Muslim empire from the mid-13th to the 15th century which controlled present-day Morocco and, intermittently, other parts of North Africa (Algeria and Tunisia) and of the southern Iberian Peninsula (Spain) a ...
(from Zibans in Algeria) → Sultanate of Tuggurt
The Sultanate of Tuggurt was a state that extended over Tuggurt, the oases of the neighbouring region and the Oued Righ valley between the fifteenth century and 1881. It was governed by sultans of the Banu Djellab dynasty.
Background
The cit ...
→ Kingdom of Beni Abbas
The Kingdom of the Ait Abbas or Sultanate of the Beni Abbas ( ber, translit=tagelda n At Ɛebbas, ⵜⴰⴳⴻⵍⴷⴰ ⵏ ⴰⵜ ⵄⴻⴱⴱⴰⵙ; ar, سلطنة بني عباس ''salṭanat Beni Ɛabbas'') was a Kabyle, Berber state of Nor ...
→ Kingdom of Kuku → Emirate of Abdelkader
The Emirate of Mascara, Emirate of Abd al-Qadir, or the Resistance of Mascara, was founded by Abd al-Qadir al-Jazairi with the allegiance of the people of Algeria to resist the French conquest of Algeria with its first capital at Mascara then ...
*Indus Valley: Habbari dynasty (841–1025) and Emirate of Multan (855–1010) → Ghaznavid Empire
The Ghaznavid dynasty ( fa, غزنویان ''Ġaznaviyān'') was a culturally Persianate society, Persianate, Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim dynasty of Turkic peoples, Turkic ''mamluk'' origin, ruling, at its greatest extent, large parts of Persia, ...
(995–1038)
Dynasties claiming Abbasid descent
Centuries after the ''Abbasids'' fall, several dynasties have claimed descent from them, as "claiming kinship relation with Muhammad", that is, claiming an affiliation to the 'People of the House' or the status of a sayyid or sharif, has arguably been the most widespread way in Muslim societies of supporting one's moral or material objectives with genealogical credentials." Such claims of continuity with Muhammad or his Hashemite kin such as the Abbasids foster a sense of "political viability" for a candidate dynasty, with the intention of "serving an internal audience" (or in other words, gaining legitimacy in the view of the masses). TheWadai Empire
The Wadai Sultanate ( ar, سلطنة وداي ''Saltanat Waday'', french: royaume du Ouaddaï, Fur: ''Burgu'' or ''Birgu''; 1501–1912) was an African sultanate located to the east of Lake Chad in present-day Chad and the Central African Repub ...
which ruled parts of modern-day Sudan also claimed Abbasid descent, alongside the Khairpur and Bahawalpur states in Pakistan and the Khanate of Bastak.
A common trope among Abbasid claimant dynasties is that they are descended from Abbasid princes of Baghdad, "dispersed" by the Mongol invasion in 1258 CE. These surviving princes would leave Baghdad for a safe haven not controlled by the Mongols, assimilate to their new societies, and their descendants would grow to establish their own dynasties with their Abbasid 'credentials' centuries later. This is highlighted by the origin myth of the Bastak khanate which relates that in 656 AH/1258 CE, the year of the fall of Baghdad, and following the sack of the city, a few surviving members of the Abbasid dynastic family led by the eldest amongst them, Ismail II son of Hamza son of Ahmed son of Mohamed migrated to Southern Iran, in the village of Khonj and later to Bastak where their khanate was established in the 17th century CE.
Meanwhile, the Wadai Empire
The Wadai Sultanate ( ar, سلطنة وداي ''Saltanat Waday'', french: royaume du Ouaddaï, Fur: ''Burgu'' or ''Birgu''; 1501–1912) was an African sultanate located to the east of Lake Chad in present-day Chad and the Central African Repub ...
related a similar origin story, claiming descent from a man by the name of Salih ibn Abdullah ibn Abbas, whose father Abdullah was an Abbasid prince who fled Baghdad for Hijaz upon the Mongol invasion. He had a son named Salih who would grow to become an "able jurist" and a "very devout man". The Muslim ulama on pilgrimage in Mecca met him and, impressed by his knowledge, invited him to return with him to Sennar. Seeing the population's deviation from Islam, he "pushed further" until he found the Abu Sinun mountain in Wadai where he converted the local people to Islam and taught them its rules, after which they made him sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it ...
, thus laying the foundations of the Wadai Empire.
With regards to the Bastak khanate, Shaikh Mohamed Khan Bastaki was the first Abbasid ruler of Bastak to hold the title of "Khan" after the local people accepted him as a ruler ( Persian: خان, Arabic: الحاكم), meaning "ruler" or "king", a title which was reportedly bestowed upon him by Karim Khan Zand. The title then became that of all the subsequent Abbasid rulers of Bastak and Jahangiriyeh, and also collectively refers in plural form – i.e., "Khans" ( Persian: خوانين) – to the descendants of Shaikh Mohamed Khan Bastaki. The last Abbasid ruler of Bastak and Jahangiriyeh was Mohamed A’zam Khan Baniabbassian son of Mohamed Reza Khan "Satvat al-Mamalek" Baniabbasi. He authored the book ''Tarikh-e Jahangiriyeh va Baniabbassian-e Bastak'' (1960), in which is recounted the history of the region and the Abbasid family that ruled it. Mohamed A’zam Khan Baniabbassian died in 1967, regarded as the end of the Abbasid reign in Bastak.
See also
References
Notes
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* * . * . , - , - {{Authority control Arab dynasties Muslim dynasties Former countries in Asia Countries in medieval Africa States in medieval Anatolia Former countries in Europe Iraq under the Abbasid Caliphate History of Saudi Arabia History of Pakistan Medieval history of Iran States and territories established in the 750s States and territories disestablished in 1258 States and territories established in 1261 States and territories disestablished in 1517 750 establishments 1510s disestablishments in Asia 8th-century establishments in Africa 1258 disestablishments in Asia 13th-century disestablishments in Africa Historical transcontinental empires Caliphates Former empires