|
Tinnis
Tennis or Tinnīs ( arz, تنيس, cop, ⲑⲉⲛⲛⲉⲥⲓ) was a medieval city in Egypt which no longer exists. It was most prosperous from the 9th century to the 11th century until its abandonment. It was located at 31°12′N 32°14′E, on an island in Lake Manzala, southwest of Port Said. Etymology The city's name was taken from Lake Tinnis, Lake Manzala's name at the time. History Prosperity Tennis was an important port, exporting agricultural products of Egypt, particularly textiles, of which itself is famed for producing throughout the Middle East, due to its geographical location served by the main eastern tributary of the Nile in medieval times, according to Muhammad al-Idrisi. By using the tributary, ships could enter the calmer waters of Lake Tinnis before entering the Mediterranean proper to avoid rough waves, which was a huge problem for ships at that era should they directly enter the sea, owing to the conditions at the mouth. The lake allowed for boats to wai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Said Governorate
Port Said Governorate is one of the Canal Zone governorates of Egypt. It is located in the northeastern part of the country, on the Mediterranean Sea at the northern gate of the Suez Canal, making it the second most important harbor in Egypt. Its capital is the city of Port Said, and it is the home of the Suez Canal Authority historical administrative building and the Lighthouse of Port Said. Port Said Governorate is wholly urban, with 98.2% of the area populated. Most of the districts of the Governorate lie on the African side of the Suez Canal, although Port Fuad lies on the Asian side. Geography In 2015 a huge natural gas reserve was discovered off the coast of Port Said and was described as "the largest ever found in the Mediterranean Sea". Egypt now has one of the largest areas of natural gas and Italian company, ENI has been contracted to work on the natural gas liquefaction for Egypt. It was welcome news as Egypt has long suffered an energy crisis. The New Suez Can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 UN member states, 2 UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a special political status (2 states, both in free association with New Zealand). Compiling a list such as this can be a complicated and controversial process, as there is no definition that is binding on all the members of the community of nations concerni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equivalent to a stretch of land bordering the Mediterranean in South-western Asia,Gasiorowski, Mark (2016). ''The Government and Politics of the Middle East and North Africa''. }, ), meaning "the eastern place, where the Sun rises". In the 13th and 14th centuries, the term ''levante'' was used for Italian maritime commerce in the Eastern Mediterranean, including Greece, Anatolia, Syria-Palestine, and Egypt, that is, the lands east of Venice. Eventually the term was restricted to the Muslim countries of Syria-Palestine and Egypt. In 1581, England set up the Levant Company to monopolize commerce with the Ottoman Empire. The name ''Levant States'' was used to refer to the French mandate over Syria and Lebanon after World War I. This is probab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
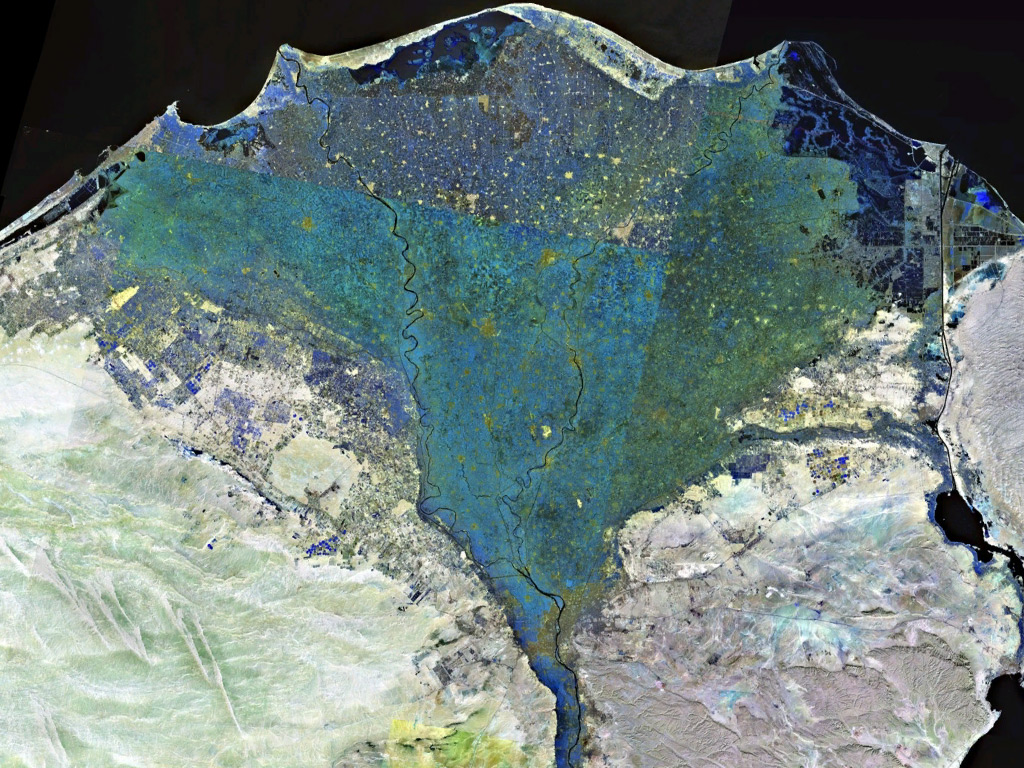
Nile Delta
The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east, it covers of Mediterranean coastline and is a rich agricultural region. From north to south the delta is approximately in length. The Delta begins slightly down-river from Cairo. Geography From north to south, the delta is approximately in length. From west to east, it covers some of coastline. The delta is sometimes divided into sections, with the Nile dividing into two main distributaries, the Damietta and the Rosetta, flowing into the Mediterranean at port cities with the same name. In the past, the delta had several distributaries, but these have been lost due to flood control, silting and changing relief. One such defunct distributary is Wadi Tumilat. The Suez Canal is east of the delta and enters the coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Egypt
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the adv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Damietta (1218–19)
Battle of Damietta, Sack of Damietta or Siege of Damietta may refer to: *Sack of Damietta (853), a part of the Arab–Byzantine wars * Siege of Damietta (1169), a part of the Crusader invasions of Egypt *Siege of Damietta (1218–1219), a part of the Fifth Crusade *Siege of Damietta (1249), a part of the Seventh Crusade *Battle of Damietta (1732) Battle of Damietta, Sack of Damietta or Siege of Damietta may refer to: *Sack of Damietta (853), a part of the Arab–Byzantine wars * Siege of Damietta (1169), a part of the Crusader invasions of Egypt *Siege of Damietta (1218–1219) The siege ..., a naval battle by the Maltese over the Turks * Siege of Damietta (1799), a French victory over the Turks * Battle of Damietta (1973) or Battle of Baltim, a part of the Yom Kippur War {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, سهلاحهدین, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt and Syria. An important figure of the Third Crusade, he spearheaded the Muslim military effort against the Crusader states in the Levant. At the height of his power, Ayyubid territorial control spanned Egypt, Syria, Upper Mesopotamia, the Hejaz, Yemen, the Maghreb, and Nubia. Alongside his uncle Shirkuh, a military general of the Zengid dynasty, Saladin was sent to Egypt under the Fatimid Caliphate in 1164, on the orders of Nur ad-Din. With their original purpose being to help restore Shawar as the to the teenage Fatimid caliph al-Adid, a power struggle ensued between Shirkuh and Shawar after the latter was reinstated. Saladin, meanwhile, climbed the ranks of the Fatimid government by virtue of his military successes against Crusader assault ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Ma'mun
Abu al-Abbas Abdallah ibn Harun al-Rashid ( ar, أبو العباس عبد الله بن هارون الرشيد, Abū al-ʿAbbās ʿAbd Allāh ibn Hārūn ar-Rashīd; 14 September 786 – 9 August 833), better known by his regnal name Al-Ma'mun ( ar, المأمون, al-Maʾmūn), was the seventh Abbasid caliph, who reigned from 813 until his death in 833. He succeeded his half-brother al-Amin after a civil war, during which the cohesion of the Abbasid Caliphate was weakened by rebellions and the rise of local strongmen; much of his domestic reign was consumed in pacification campaigns. Well educated and with a considerable interest in scholarship, al-Ma'mun promoted the Translation Movement, the flowering of learning and the sciences in Baghdad, and the publishing of al-Khwarizmi's book now known as "Algebra". He is also known for supporting the doctrine of Mu'tazilism and for imprisoning Imam Ahmad ibn Hanbal, the rise of religious persecution ('' mihna''), and for the resum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Zulaq
Abu Muhammad ibn al-Hasan ibn Ibrahim ibn Zulaq al-Laythi (c. 919–996), commonly known as Ibn Zulaq (or Ibn Zawlaq), was an Egyptian historian, whose work focuses on the local history of Egypt during the Ikhshidid dynasty and the early years of the Fatimid Caliphate there. Ibn Zulaq was born in 918/9 in Egypt and died there in 996/7. Most of his work does not survive directly, but was extensively used and quoted by later historians such as Ibn Sa'id al-Maghribi (13th century), al-Maqrizi (15th century), and Ibn Hajar al-Asqalani (16th century). His works included a history of the governors and judges of Egypt, which continued the similar work of the 9th-century polymath al-Kindi; a history of the al-Madhara'i family of viziers; and books on the founder of the Ikhshidid dynasty, Muhammad ibn Tughj al-Ikhshid and the Ikhshidid strongman Abu'l-Misk Kafur. His biography of al-Ikhshid in particular is stated to have been written at the request of his son Abu'l-Hasan Ali ibn al-Ikhshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosetta
Rosetta or Rashid (; ar, رشيد ' ; french: Rosette ; cop, ϯⲣⲁϣⲓⲧ ''ti-Rashit'', Ancient Greek: Βολβιτίνη ''Bolbitinē'') is a port city of the Nile Delta, east of Alexandria, in Egypt's Beheira governorate. The Rosetta Stone was discovered there in 1799. Founded around the 9th century on site of the ancient town Bolbitine, Rosetta boomed with the decline of Alexandria following the Ottoman conquest of Egypt in 1517, only to wane in importance after Alexandria's revival. During the 19th century, it was a popular British tourist destination, known for its Ottoman mansions, citrus groves and relative cleanliness. Etymology The name of the town most likely comes from an Arabic name '' Rašīd'' (meaning "guide") and was transcribed and corrupted in numerous ways – the name ''Rexi'' was used by the Crusaders in Middle Ages and ''Rosetta'' or ''Rosette'' ("little rose" in Italian and French respectively) was used by the French at the time of Napoleon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_-_front_-_TIMEA.jpg)

.png)
.jpg)

