|
Algorism
Algorism is the technique of performing basic arithmetic by writing numbers in place value form and applying a set of memorized rules and facts to the digits. One who practices algorism is known as an algorist. This positional notation system has largely superseded earlier calculation systems that used a different set of symbols for each numerical magnitude, such as Roman numerals, and in some cases required a device such as an abacus. Etymology The word ''algorism'' comes from the name Al-Khwārizmī (c. 780–850), a Persian mathematician, astronomer, geographer and scholar in the House of Wisdom in Baghdad, whose name means "the native of Khwarezm", which is now in modern-day Uzbekistan. He wrote a treatise in Arabic language in the 9th century, which was translated into Latin in the 12th century under the title ''Algoritmi de numero Indorum''. This title means "Algoritmi on the numbers of the Indians", where "Algoritmi" was the translator's Latinization of Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandre De Villedieu
Alexander of Villedieu was a French people, French writer, teacher and poet, who wrote text books on Latin grammar and arithmetic, everything in verse. He was born around 1175 in Villedieu-les-Poêles in Normandy, studied in Paris, and later taught at Dol-de-Bretagne, Dol in Brittany. His greatest fame stems from his versified Latin grammar book, the ''Doctrinale Puerorum''. He died in 1240, or perhaps in 1250. He was a Franciscan and a Master of the University of Paris. His ''Doctrinale puerorum'', a Latin mnemonics, versified grammar, soon became a classic. It was composed around 1200, and was all written in ''leonine verse, leonine hexameters''. Even after several centuries, with the advent of printing, it appeared in countless editions in Italy, Germany and France. It was based on the older works of Aelius Donatus, Donatus and Priscian. Alexander also wrote a short tract on arithmetic called ''Carmen de Algorismo''—''the Poem about Arithmetic'', which also achieved a wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
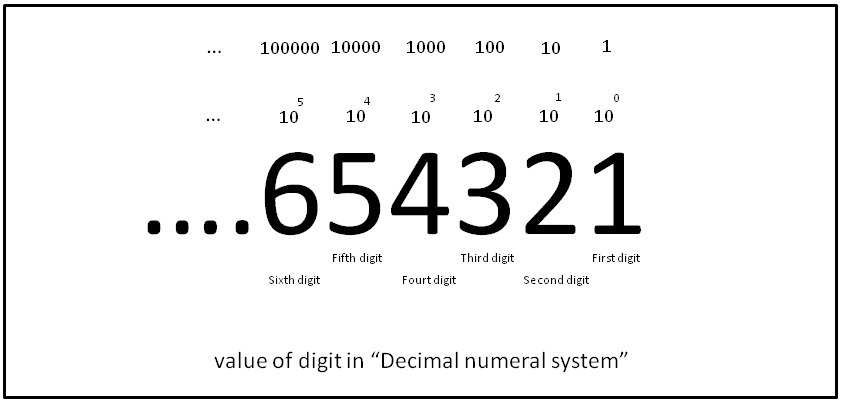
Base 10
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers (''decimal fractions'') of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. The way of denoting numbers in the decimal system is often referred to as ''decimal notation''. A decimal numeral (also often just ''decimal'' or, less correctly, ''decimal number''), refers generally to the notation of a number in the decimal numeral system. Decimals may sometimes be identified by a decimal separator (usually "." or "," as in or ). ''Decimal'' may also refer specifically to the digits after the decimal separator, such as in " is the approximation of to ''two decimals''". Zero-digits after a decimal separator serve the purpose of signifying the precision of a value. The numbers that may be represented in the decimal system are the decimal fractions. That is, fractions of the form , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Khwārizmī
Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi , or simply al-Khwarizmi, was a mathematician active during the Islamic Golden Age, who produced Arabic-language works in mathematics, astronomy, and geography. Around 820, he worked at the House of Wisdom in Baghdad, the contemporary capital city of the Abbasid Caliphate. One of the most prominent scholars of the period, his works were widely influential on later authors, both in the Islamic world and Europe. His popularizing treatise on algebra, compiled between 813 and 833 as ''Al-Jabr'' (''The Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing''),Oaks, J. (2009), "Polynomials and Equations in Arabic Algebra", ''Archive for History of Exact Sciences'', 63(2), 169–203. presented the first systematic solution of linear and quadratic equations. One of his achievements in algebra was his demonstration of how to solve quadratic equations by completing the square, for which he provided geometric justifications. Because al-Khwarizmi was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can use Conditional (computer programming), conditionals to divert the code execution through various routes (referred to as automated decision-making) and deduce valid inferences (referred to as automated reasoning). In contrast, a Heuristic (computer science), heuristic is an approach to solving problems without well-defined correct or optimal results.David A. Grossman, Ophir Frieder, ''Information Retrieval: Algorithms and Heuristics'', 2nd edition, 2004, For example, although social media recommender systems are commonly called "algorithms", they actually rely on heuristics as there is no truly "correct" recommendation. As an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu–Arabic Numeral System
The Hindu–Arabic numeral system (also known as the Indo-Arabic numeral system, Hindu numeral system, and Arabic numeral system) is a positional notation, positional Decimal, base-ten numeral system for representing integers; its extension to non-integers is the decimal, decimal numeral system, which is presently the most common numeral system. The system was invented between the 1st and 4th centuries by Indian mathematics, Indian mathematicians. By the 9th century, the system was adopted by Arabic mathematics, Arabic mathematicians who extended it to include fraction (mathematics), fractions. It became more widely known through the writings in Arabic of the Persian mathematician Al-Khwārizmī (''On the Calculation with Hindu Numerals'', ) and Arab mathematician Al-Kindi (''On the Use of the Hindu Numerals'', ). The system had spread to medieval Europe by the High Middle Ages, notably following Fibonacci's 13th century ''Liber Abaci''; until the evolution of the printing pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decimal Point
FIle:Decimal separators.svg, alt=Four types of separating decimals: a) 1,234.56. b) 1.234,56. c) 1'234,56. d) ١٬٢٣٤٫٥٦., Both a comma and a full stop (or period) are generally accepted decimal separators for international use. The apostrophe and Arabic decimal separator are also used in certain contexts. A decimal separator is a symbol that separates the integer part from the fractional part of a number written in decimal form. Different countries officially designate different symbols for use as the separator. The choice of symbol can also affect the choice of symbol for the #Digit grouping, thousands separator used in digit grouping. Any such symbol can be called a decimal mark, decimal marker, or decimal sign. Symbol-specific names are also used; decimal point and decimal comma refer to a dot (either Baseline dot, baseline or Middle dot, middle) and comma respectively, when it is used as a decimal separator; these are the usual terms used in English, with the aforem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positional Notation
Positional notation, also known as place-value notation, positional numeral system, or simply place value, usually denotes the extension to any radix, base of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system (or decimal, decimal system). More generally, a positional system is a numeral system in which the contribution of a digit to the value of a number is the value of the digit multiplied by a factor determined by the position of the digit. In early numeral systems, such as Roman numerals, a digit has only one value: I means one, X means ten and C a hundred (however, the values may be modified when combined). In modern positional systems, such as the decimal, decimal system, the position of the digit means that its value must be multiplied by some value: in 555, the three identical symbols represent five hundreds, five tens, and five units, respectively, due to their different positions in the digit string. The Babylonian Numerals, Babylonian numeral system, base 60, was the first positional sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algorithmic Art
Algorithmic art or algorithm art is art, mostly visual art, in which the design is generated by an algorithm. Algorithmic artists are sometimes called algorists. Algorithmic art is created in the form of digital paintings and sculptures, interactive installations and music compositions. Algorithmic art is not a new concept. Islamic art is a good example of the tradition of following a set of rules to create patterns. The even older practice of weaving includes elements of algorithmic art. As computers developed so did the art created with them. Algorithmic art encourages experimentation allowing artists to push their creativity in the digital age. Algorithmic art allows creators to devise intricate patterns and designs that would be nearly impossible to achieve by hand. Creators have a say on what the input criteria is, but not on the outcome. Overview Algorithmic art, also known as computer-generated art, is a subset of generative art (generated by an autonomous syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arithmetic
Arithmetic is an elementary branch of mathematics that deals with numerical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. In a wider sense, it also includes exponentiation, extraction of roots, and taking logarithms. Arithmetic systems can be distinguished based on the type of numbers they operate on. Integer arithmetic is about calculations with positive and negative integers. Rational number arithmetic involves operations on fractions of integers. Real number arithmetic is about calculations with real numbers, which include both rational and irrational numbers. Another distinction is based on the numeral system employed to perform calculations. Decimal arithmetic is the most common. It uses the basic numerals from 0 to 9 and their combinations to express numbers. Binary arithmetic, by contrast, is used by most computers and represents numbers as combinations of the basic numerals 0 and 1. Computer arithmetic deals with the specificities of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics In Medieval Islam
Mathematics during the Golden Age of Islam, especially during the 9th and 10th centuries, was built upon syntheses of Greek mathematics (Euclid, Archimedes, Apollonius) and Indian mathematics (Aryabhata, Brahmagupta). Important developments of the period include extension of the place-value system to include decimal fractions, the systematised study of algebra and advances in geometry and trigonometry. The medieval Islamic world underwent significant developments in mathematics. Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwārizmī played a key role in this transformation, introducing algebra as a distinct field in the 9th century. Al-Khwārizmī's approach, departing from earlier arithmetical traditions, laid the groundwork for the arithmetization of algebra, influencing mathematical thought for an extended period. Successors like Al-Karaji expanded on his work, contributing to advancements in various mathematical domains. The practicality and broad applicability of these mathematical metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integer
An integer is the number zero (0), a positive natural number (1, 2, 3, ...), or the negation of a positive natural number (−1, −2, −3, ...). The negations or additive inverses of the positive natural numbers are referred to as negative integers. The set (mathematics), set of all integers is often denoted by the boldface or blackboard bold The set of natural numbers \mathbb is a subset of \mathbb, which in turn is a subset of the set of all rational numbers \mathbb, itself a subset of the real numbers \mathbb. Like the set of natural numbers, the set of integers \mathbb is Countable set, countably infinite. An integer may be regarded as a real number that can be written without a fraction, fractional component. For example, 21, 4, 0, and −2048 are integers, while 9.75, , 5/4, and Square root of 2, are not. The integers form the smallest Group (mathematics), group and the smallest ring (mathematics), ring containing the natural numbers. In algebraic number theory, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |