digit
Digit may refer to:
Mathematics and science
* Numerical digit, as used in mathematics or computer science
** Hindu-Arabic numerals, the most common modern representation of numerical digits
* Digit (anatomy), the most distal part of a limb, such ...
. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures.
In mathematics
Four is the smallest composite number, its proper divisors being and . Four is the sum and product of two with itself: + = = x , the only number such that + = = x , which also makes four the smallest squared prime number . In Knuth's up-arrow notation, , and so forth, for any number of up arrows. By consequence, four is the only square one more than a prime number, specifically three. The sum of the first four prime numbers two + three +five
5 is a number, numeral, and glyph.
5, five or number 5 may also refer to:
* AD 5, the fifth year of the AD era
* 5 BC, the fifth year before the AD era
Literature
* ''5'' (visual novel), a 2008 visual novel by Ram
* ''5'' (comics), an awa ...
+ seven
7 is a number, numeral, and glyph.
7 or seven may also refer to:
* AD 7, the seventh year of the AD era
* 7 BC, the seventh year before the AD era
* The month of
July
Music Artists
* Seven (Swiss singer) (born 1978), a Swiss recording artist ...
is the only sum of four consecutive prime numbers that yields an odd
Odd means unpaired, occasional, strange or unusual, or a person who is viewed as eccentric.
Odd may also refer to:
Acronym
* ODD (Text Encoding Initiative) ("One Document Does it all"), an abstracted literate-programming format for describing X ...
prime number, seventeen
Seventeen or 17 may refer to:
*17 (number), the natural number following 16 and preceding 18
* one of the years 17 BC, AD 17, 1917, 2017
Literature
Magazines
* ''Seventeen'' (American magazine), an American magazine
* ''Seventeen'' (Japanese m ...
, which is the fourth super-prime
Super-prime numbers, also known as higher-order primes or prime-indexed primes (PIPs), are the subsequence of prime numbers that occupy prime-numbered positions within the sequence of all prime numbers.
The subsequence begins
:3, 5, 11, 17, 31, ...
. Four lies between the first proper pair of twin primes
A twin prime is a prime number that is either 2 less or 2 more than another prime number—for example, either member of the twin prime pair (41, 43). In other words, a twin prime is a prime that has a prime gap of two. Sometimes the term ''twin pr ...
, three and five
5 is a number, numeral, and glyph.
5, five or number 5 may also refer to:
* AD 5, the fifth year of the AD era
* 5 BC, the fifth year before the AD era
Literature
* ''5'' (visual novel), a 2008 visual novel by Ram
* ''5'' (comics), an awa ...
, which are the first two Fermat primes, like seventeen
Seventeen or 17 may refer to:
*17 (number), the natural number following 16 and preceding 18
* one of the years 17 BC, AD 17, 1917, 2017
Literature
Magazines
* ''Seventeen'' (American magazine), an American magazine
* ''Seventeen'' (Japanese m ...
, which is the third. On the other hand, the square of four 42, equivalently the fourth power of two 24, is sixteen; the only number that has = as a form of factorization. Holistically, there are four elementary arithmetic operations
Operation or Operations may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* ''Operation'' (game), a battery-operated board game that challenges dexterity
* Operation (music), a term used in musical set theory
* ''Operations'' (magazine), Multi-Man ...
in mathematics: addition
Addition (usually signified by the Plus and minus signs#Plus sign, plus symbol ) is one of the four basic Operation (mathematics), operations of arithmetic, the other three being subtraction, multiplication and Division (mathematics), division. ...
(+), subtraction
Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. Subtraction is signified by the minus sign, . For example, in the adjacent picture, there are peaches—meaning 5 peaches with 2 taken ...
(−), multiplication
Multiplication (often denoted by the cross symbol , by the mid-line dot operator , by juxtaposition, or, on computers, by an asterisk ) is one of the four elementary mathematical operations of arithmetic, with the other ones being additi ...
(×), and division (÷); and four basic number systems, the real numbers , rational numbers , integers , and natural numbers .
Each natural number divisible by 4 is a difference of squares of two natural numbers, i.e. = − . A number is a multiple of 4 if its last two digits are a multiple of 4. For example, 1092 is a multiple of 4 because .
Lagrange's four-square theorem states that every positive integer can be written as the sum of at most four square numbers. Three are not always sufficient; for instance cannot be written as the sum of three squares.
There are four all-Harshad number
In mathematics, a harshad number (or Niven number) in a given number base is an integer that is divisible by the sum of its digits when written in that base.
Harshad numbers in base are also known as -harshad (or -Niven) numbers.
Harshad number ...
s: 1, 2, ''4'', and 6. 12, which is divisible by four thrice over, is a Harshad number in all bases except octal.
A four-sided plane figure is a quadrilateral or quadrangle, sometimes also called a ''tetragon''. It can be further classified as a rectangle
In Euclidean plane geometry, a rectangle is a quadrilateral with four right angles. It can also be defined as: an equiangular quadrilateral, since equiangular means that all of its angles are equal (360°/4 = 90°); or a parallelogram containi ...
or ''oblong'', kite, rhombus, and square.
Four is the highest degree general polynomial equation for which there is a solution in radicals
A solution in radicals or algebraic solution is a closed-form expression, and more specifically a closed-form algebraic expression, that is the solution of a polynomial equation, and relies only on addition, subtraction, multiplication, divi ...
.
The four-color theorem states that a planar graph
In graph theory, a planar graph is a graph that can be embedded in the plane, i.e., it can be drawn on the plane in such a way that its edges intersect only at their endpoints. In other words, it can be drawn in such a way that no edges cross ...
(or, equivalently, a flat map of two-dimensional regions such as countries) can be colored using four colors, so that adjacent vertices (or regions) are always different colors. Three colors are not, in general, sufficient to guarantee this. The largest planar complete graph has four vertices.
A solid figure with four faces as well as four vertices is a tetrahedron, which is the smallest possible number of faces and vertices a polyhedron can have. The regular tetrahedron, also called a 3-simplex
In geometry, a simplex (plural: simplexes or simplices) is a generalization of the notion of a triangle or tetrahedron to arbitrary dimensions. The simplex is so-named because it represents the simplest possible polytope in any given dimension. ...
, is the simplest Platonic solid. It has four regular triangles as faces that are themselves at dual positions with the vertices of another tetrahedron. Tetrahedra can be inscribed inside all other four Platonic solids, and tessellate space alongside the regular octahedron in the alternated cubic honeycomb.
Four-dimensional space
A four-dimensional space (4D) is a mathematical extension of the concept of three-dimensional or 3D space. Three-dimensional space is the simplest possible abstraction of the observation that one only needs three numbers, called ''dimensions'', ...
is the highest-dimensional space featuring more than three regular convex figures:
*Two-dimensional: infinitely many regular polygons.
*Three-dimensional: five regular polyhedra; the five Platonic solids which are the tetrahedron, cube
In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. Viewed from a corner it is a hexagon and its net is usually depicted as a cross.
The cube is the only r ...
, octahedron, dodecahedron, and icosahedron
In geometry, an icosahedron ( or ) is a polyhedron with 20 faces. The name comes and . The plural can be either "icosahedra" () or "icosahedrons".
There are infinitely many non- similar shapes of icosahedra, some of them being more symmetrica ...
.
*Four-dimensional: six regular polychora; the 5-cell
In geometry, the 5-cell is the convex 4-polytope with Schläfli symbol . It is a 5-vertex four-dimensional object bounded by five tetrahedral cells. It is also known as a C5, pentachoron, pentatope, pentahedroid, or tetrahedral pyramid. It i ...
, 8-cell or tesseract, 16-cell
In geometry, the 16-cell is the regular convex 4-polytope (four-dimensional analogue of a Platonic solid) with Schläfli symbol . It is one of the six regular convex 4-polytopes first described by the Swiss mathematician Ludwig Schläfli in the mi ...
, 24-cell
In geometry, the 24-cell is the convex regular 4-polytope (four-dimensional analogue of a Platonic solid) with Schläfli symbol . It is also called C24, or the icositetrachoron, octaplex (short for "octahedral complex"), icosatetrahedroid, oct ...
, 120-cell
In geometry, the 120-cell is the convex regular 4-polytope (four-dimensional analogue of a Platonic solid) with Schläfli symbol . It is also called a C120, dodecaplex (short for "dodecahedral complex"), hyperdodecahedron, polydodecahedron, heca ...
, and 600-cell. The 24-cell
In geometry, the 24-cell is the convex regular 4-polytope (four-dimensional analogue of a Platonic solid) with Schläfli symbol . It is also called C24, or the icositetrachoron, octaplex (short for "octahedral complex"), icosatetrahedroid, oct ...
, made of regular octahedra, has no analogue in any other dimension; it is self-dual
In mathematics, a duality translates concepts, theorems or mathematical structures into other concepts, theorems or structures, in a Injective function, one-to-one fashion, often (but not always) by means of an Involution (mathematics), involutio ...
, with its 24-cell honeycomb
In Four-dimensional space, four-dimensional Euclidean geometry, the 24-cell honeycomb, or icositetrachoric honeycomb is a regular polytope, regular space-filling tessellation (or honeycomb (geometry), honeycomb) of 4-dimensional Euclidean space by ...
dual to the 16-cell honeycomb
In Four-dimensional space, four-dimensional Euclidean geometry, the 16-cell honeycomb is one of the three regular space-filling tessellations (or honeycomb (geometry), honeycombs), represented by Schläfli symbol , and constructed by a 4-dimensiona ...
.
*Five-dimensional and every higher dimension: three regular convex - polytopes, all within the infinite family of regular -simplex
In geometry, a simplex (plural: simplexes or simplices) is a generalization of the notion of a triangle or tetrahedron to arbitrary dimensions. The simplex is so-named because it represents the simplest possible polytope in any given dimension. ...
es, -hypercube
In geometry, a hypercube is an ''n''-dimensional analogue of a square () and a cube (). It is a closed, compact, convex figure whose 1- skeleton consists of groups of opposite parallel line segments aligned in each of the space's dimensions, ...
s, and - orthoplexes.
The fourth dimension is also the highest dimension where regular self-intersecting figures exist:
*Two-dimensional: infinitaly many regular star polygon
In geometry, a star polygon is a type of non-convex polygon. Regular star polygons have been studied in depth; while star polygons in general appear not to have been formally defined, certain notable ones can arise through truncation operations ...
s.
*Three-dimensional: ''four'' regular star polyhedra
In geometry, a star polyhedron is a polyhedron which has some repetitive quality of nonconvexity giving it a star-like visual quality.
There are two general kinds of star polyhedron:
*Polyhedra which self-intersect in a repetitive way.
*Concave p ...
, the regular Kepler-Poinsot star polyhedra.
*Four-dimensional: ten regular star polychora, the Schläfli–Hess star polychora. They contain cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
of Kepler-Poinsot polyhedra alongside regular tetrahedra, icosahedra
In geometry, an icosahedron ( or ) is a polyhedron with 20 faces. The name comes and . The plural can be either "icosahedra" () or "icosahedrons".
There are infinitely many non- similar shapes of icosahedra, some of them being more symmetrica ...
and dodecahedra.
*Five-dimensional and every higher dimension: zero regular star-polytopes; uniform star polytopes in dimensions > are the most symmetric, which mainly originate from stellation
In geometry, stellation is the process of extending a polygon in two dimensions, polyhedron in three dimensions, or, in general, a polytope in ''n'' dimensions to form a new figure. Starting with an original figure, the process extends specific el ...
s of regular -polytopes.
Altogether, sixteen (or 16 = 42) regular convex and star polychora are generated from symmetries of ''four'' (4) Coxeter Weyl groups and point groups in the fourth dimension: the simplex, hypercube, icositetrachoric, and hexacosichoric groups; with the demihypercube group generating two alternative constructions.
There are also sixty-four (or 64 = 43) four-dimensional Bravais lattices, ''and'' sixty-four uniform polychora
In geometry, a uniform 4-polytope (or uniform polychoron) is a 4-dimensional polytope which is vertex-transitive and whose cells are uniform polyhedra, and faces are regular polygons.
There are 47 non-prismatic convex uniform 4-polytopes. There ...
in the fourth dimension based on the same , , and Coxeter groups
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after Harold Scott MacDonald Coxeter, H. S. M. Coxeter, is an group (mathematics), abstract group that admits a group presentation, formal description in terms of Reflection (mathematics), reflections (or Kal ...
, and extending to prismatic groups of uniform polyhedra, including one special non-Wythoffian form, the grand antiprism. There are also two infinite families of duoprisms and antiprismatic prisms in the fourth dimension.
Four-dimensional differential manifolds have some unique properties. There is only one differential structure on except when = , in which case there are uncountably many.
The smallest non- cyclic group has four elements; it is the Klein four-group. ''A'' alternating groups are not simple for values ≤ .
Further extensions of the real numbers under Hurwitz's theorem states that there are four normed division algebras: the real numbers , the complex numbers , the quaternion
In mathematics, the quaternion number system extends the complex numbers. Quaternions were first described by the Irish mathematician William Rowan Hamilton in 1843 and applied to mechanics in three-dimensional space. Hamilton defined a quatern ...
s , and the octonions . Under Cayley–Dickson constructions, the sedenions constitute a further fourth extension over . The real numbers are ordered, commutative and associative
In mathematics, the associative property is a property of some binary operations, which means that rearranging the parentheses in an expression will not change the result. In propositional logic, associativity is a valid rule of replacement f ...
algebras, as well as alternative algebras with power-associativity In mathematics, specifically in abstract algebra, power associativity is a property of a binary operation that is a weak form of associativity.
Definition
An algebra over a field, algebra (or more generally a magma (algebra), magma) is said to be ...
. The complex numbers share all four multiplicative algebraic properties of the reals , without being ordered. The quaternions loose a further commutative algebraic property, while holding associative, alternative, and power-associative properties. The octonions are alternative and power-associative, while the sedenions are only power-associative. The sedenions and all further ''extensions'' of these four normed division algebras are solely power-associative with non-trivial zero divisors, which makes them non-division algebras. has a vector space of dimension 1, while , , and work in algebraic number field
In mathematics, an algebraic number field (or simply number field) is an extension field K of the field of rational numbers such that the field extension K / \mathbb has finite degree (and hence is an algebraic field extension).
Thus K is a f ...
s of dimensions 2, 4, 8, and 16, respectively.
List of basic calculations
Evolution of the Hindu-Arabic digit

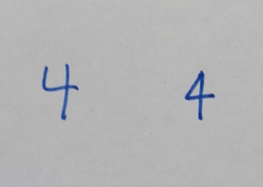
Brahmic numerals
The Brahmi numerals are a numeral system attested from the 3rd century BCE (somewhat later in the case of most of the tens). They are a non positional decimal system. They are the direct graphic ancestors of the modern Hindu–Arabic numeral s ...
represented 1, 2, and 3 with as many lines. 4 was simplified by joining its four lines into a cross that looks like the modern plus sign. The Shunga would add a horizontal line on top of the digit, and the Kshatrapa and Pallava evolved the digit to a point where the speed of writing was a secondary concern. The Arabs' 4 still had the early concept of the cross, but for the sake of efficiency, was made in one stroke by connecting the "western" end to the "northern" end; the "eastern" end was finished off with a curve. The Europeans dropped the finishing curve and gradually made the digit less cursive, ending up with a digit very close to the original Brahmin cross.
While the shape of the character for the digit 4 has an ascender in most modern typefaces, in typefaces with text figures the glyph usually has a descender, as, for example, in Canadian Aboriginal syllabics
Canadian syllabic writing, or simply syllabics, is a family of writing systems used in a number of Indigenous Canadian languages of the Algonquian, Inuit, and (formerly) Athabaskan language families. These languages had no formal writing s ...
letter ᔦ. The magnetic ink character recognition "CMC-7" font also uses this variety of "4".
In religion
Buddhism
*Four Noble Truths
In Buddhism, the Four Noble Truths (Sanskrit: ; pi, cattāri ariyasaccāni; "The four Arya satyas") are "the truths of the Noble Ones", the truths or realities for the "spiritually worthy ones". Four Noble Truths: BUDDHIST PHILOSOPHY Encycl ...
– Samudaya
In Buddhism, the Four Noble Truths (Sanskrit: ; pi, cattāri ariyasaccāni; "The four Arya satyas") are "the truths of the Noble Ones", the truths or realities for the "spiritually worthy ones".[aFour Noble Truths: BUDDHIST PHILOSOPHY Encycl ...
, Nirodha
In Buddhism, nirodha, "cessation," "extinction," or "suppression," refers to the cessation or renouncing of craving and desire. It is the third of the Four Noble Truths,_stating_that_suffering_(dukkha.html" ;"title="Four Noble Truths: BUDDHIST P ...
, Noble Eightfold Path">Magga
The Buddhist path (''marga'') to liberation, also referred to as awakening, is described in a wide variety of ways. The classical one is the Noble Eightfold Path, which is only one of several summaries presented in the Sutta Pitaka. A number of o ... *The symbolic meanings of the number four are linked to those of the cross and the square. "Almost from prehistoric times, the number four was employed to signify what was solid, what could be touched and felt. Its relationship to the cross (four points) made it an outstanding symbol of wholeness and universality, a symbol which drew all to itself". Where lines of latitude and longitude intersect, they divide the earth into four proportions. Throughout the world kings and chieftains have been called "lord of the four suns" or "lord of the four quarters of the earth", which is understood to refer to the extent of their powers both territorially and in terms of total control of their subjects' doings.
*The
*The symbolic meanings of the number four are linked to those of the cross and the square. "Almost from prehistoric times, the number four was employed to signify what was solid, what could be touched and felt. Its relationship to the cross (four points) made it an outstanding symbol of wholeness and universality, a symbol which drew all to itself". Where lines of latitude and longitude intersect, they divide the earth into four proportions. Throughout the world kings and chieftains have been called "lord of the four suns" or "lord of the four quarters of the earth", which is understood to refer to the extent of their powers both territorially and in terms of total control of their subjects' doings.
*The