Îą7-nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
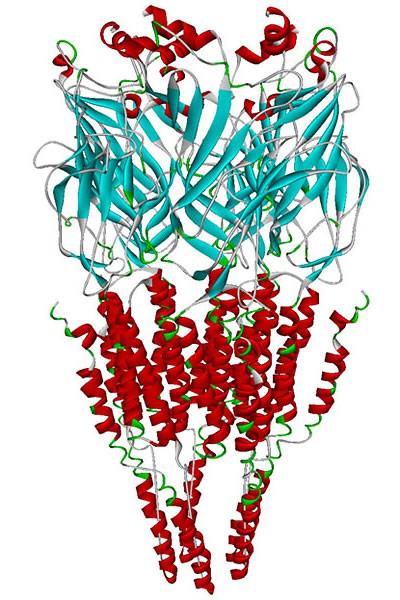 The alpha-7 nicotinic receptor, also known as the Îą7 receptor, is a type of
The alpha-7 nicotinic receptor, also known as the Îą7 receptor, is a type of
 The alpha-7 nicotinic receptor, also known as the Îą7 receptor, is a type of
The alpha-7 nicotinic receptor, also known as the Îą7 receptor, is a type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are receptor polypeptides that respond to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Nicotinic receptors also respond to drugs such as the agonist nicotine. They are found in the central and peripheral ne ...
implicated in long-term memory, consisting entirely of Îą7 subunits.Pharmacology, (Rang, Dale, Ritter & Moore, , 5th ed., Churchill Livingstone 2003) p. 138. As with other nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, functional Îą7 receptors are pentameric
A pentamer is an entity composed of five sub-units.
In chemistry, it applies to molecules made of five monomers.
In biochemistry, it applies to macromolecules, in particular to pentameric proteins, made of five proteic sub-units.
In microbiolog ...
.e.,_(Îą7)5_stoichiometry.html" ;"title="stoichiometry.html" ;"title=".e., (Îą7)5 stoichiometry">.e., (Îą7)5 stoichiometry">stoichiometry.html" ;"title=".e., (Îą7)5 stoichiometry">.e., (Îą7)5 stoichiometry
It is located in the brain, spleen, and lymphocytes of lymph nodes where activation yields Excitatory postsynaptic potential, post- and excitatory presynaptic potential, presynaptic excitation, mainly by increased Ca2+ permeability.
Further, recent work has implicated this receptor as being important for generation of adult mammal neurons in the retina. Functional Îą7 receptors are present in the submucous plexus
The submucosal plexus (Meissner's plexus, plexus of the submucosa, plexus submucosus) lies in the submucosa of the intestinal wall. The nerves of this plexus are derived from the myenteric plexus which itself is derived from the plexuses of paras ...
neurons of the guinea-pig ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine ma ...
.
Medical relevance
Recent work has demonstrated a potential role in reducing inflammatory neurotoxicity instroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functionin ...
, myocardial infarction, sepsis, and Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60â70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term me ...
.
An Îą7 nicotinic agonist appears to have positive effects on neurocognition in persons with schizophrenia.
Activation of Îą7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor on mast cells, is a mechanism by which nicotine enhances atherosclerosis.
Both Îą4Îē2
The alpha-4 beta-2 nicotinic receptor, also known as the Îą4Îē2 receptor, is a type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor implicated in learning, consisting of Îą4 and Îē2 subunits. It is located in the brain, where activation yields post- and pre ...
and Îą7 nicotinic receptors appear to be critical for memory, working memory, learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, value (personal and cultural), values, attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals, and some machine learning, machines ...
, and attention
Attention is the behavioral and cognitive process of selectively concentrating on a discrete aspect of information, whether considered subjective or objective, while ignoring other perceivable information. William James (1890) wrote that "Atte ...
.
Îą7-nicotinic receptors also appear to be involved in cancer progression. They have been shown to mediate cancer cell proliferation
Cell proliferation is the process by which ''a cell grows and divides to produce two daughter cells''. Cell proliferation leads to an exponential increase in cell number and is therefore a rapid mechanism of tissue growth. Cell proliferation re ...
and metastasis. Îą7 receptors are also involved in angiogenic and neurogenic activity, and have anti- apoptotic effects.
Ligands
Agonists
* (+)-''N''-(1-azabicyclo .2.2ct-3-yl)benzo 'b''uran- 2-carboxamide: potent and highly subtype-selective * Tilorone. * A-582941: partial agonist; activates ERK1/ 2 and CREBphosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, wh ...
; enhances cognitive performance
* AR-R17779
AR-R17779 is a drug that acts as a potent and selective full agonist for the Îą7 subtype of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It has nootropic effects in animal studies, but its effects do not substitute for those of nicotine
Nicotin ...
: full agonist, nootropic
* Amyloid beta
Amyloid beta (AÎē or Abeta) denotes peptides of 36â43 amino acids that are the main component of the amyloid plaques found in the brains of people with Alzheimer's disease. The peptides derive from the amyloid precursor protein (APP), which is ...
: neurotoxic marker of Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60â70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term me ...
* TC-1698: subtype-selective; neuroprotective effects via activation of the JAK2/PI-3K
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks), also called phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases, are a family of enzymes involved in cellular functions such as cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, motility, survival and intracellular trafficking, which i ...
cascade, neutralized by angiotensin II AT(2) receptor activation
* Bradanicline
Bradanicline (INN, code name TC-5619) is a drug which was being developed by Targacept that acts as a partial agonist at the Îą7 subtype of the neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It showed cognitive enhancing effects in animal studies, ...
- partial agonist, in development for treatment of schizophrenia
* Encenicline
Encenicline (INN, USAN, code names EVP-6124, MT-4666) is a selective partial agonist of the Îą7 nicotinic receptor. It was in phase III clinical trials for the treatment of cognitive impairment in schizophrenia, but failed to meet the study e ...
- partial agonist with nootropic properties, in development for treatment of schizophrenia and Alzheimer's disease
* GTS-21 - partial agonist, in development for treatment of schizophrenia and/or Alzheimer's disease
* PHA-543,613
PHA-543,613 is a drug that acts as a potent and selective agonist for the Îą7 subtype of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, with a high level of brain penetration and good oral bioavailability. It is under development as a possible treat ...
- selective and potent agonist with nootropic properties
* PNU-282,987
PNU-282,987 is a drug that acts as a potent and selective agonist for the Îą7 subtype of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. In animal studies, it shows nootropic effects, and derivatives may be useful in the treatment of schizophrenia, ...
- selective and potent agonist, but may cause long QT syndrome
Long QT syndrome (LQTS) is a condition affecting repolarization (relaxing) of the heart after a heartbeat, giving rise to an abnormally lengthy QT interval. It results in an increased risk of an irregular heartbeat which can result in fainting, d ...
* PHA-709829: potent and subtype-selective; robust in vivo efficacy in a rat auditory sensory gating model
** Analogues: improved hERG safety profile over PNU-282,987
*SSR-180,711
SSR180711 is a drug that acts as a potent and selective partial agonist for the Îą7 subtype of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. In animal studies, it shows nootropic effects and may be useful in the treatment of schizophrenia
Sc ...
: partial agonist
* Tropisetron: subtype-selective partial agonist; 5-HT3 receptor antagonist
* WAY-317,538
WAY-317538 (SEN-12333) is a drug that acts as a potent and selective full agonist for the Îą7 subtype of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It was not the most potent compound in the series, but was selected for further development on the ...
- selective potent full agonist with nootropic and neuroprotective properties
* Anabasine
* Acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic chemical that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Part ...
* Nicotine
Nicotine is a naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and ''Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As a pharmaceutical drug, it is used fo ...
* Epiboxidine
* Choline
* ICH-3: subtype-selective partial agonist
Positive Allosteric Modulators (PAMs)
At least two types of positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) can be distinguished. *PNU-120,596
PNU-120596 is a drug that acts as a potent and selective positive allosteric modulator for the Îą7 subtype of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are receptor polypeptides that respond to th ...
*NS-1738: marginal effects on Îą7 desensitization kinetics; modestly brain-penetrant
* AVL-3288: unlike the above PAMs, AVL-3288 does not affect Îą7 desensitization kinetics, and is readily brain penetrant. Improves cognitive behavior in animal models In clinical development for cognitive deficits in schizophrenia.
* A-867744
* Ivermectin
Other
* NefiracetamAntagonists
It is found that anandamide and ethanol cause an additive inhibition on the function of Îą7-receptor by interacting with distinct regions of the receptor. Although ethanol inhibition of the Îą7-receptor is likely to involve theN-terminal
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the ami ...
region of the receptor, the site of action for anandamide is located in the transmembrane and carboxyl-terminal
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is ...
domains of the receptors.
* Anandamide
* Îą-Bungarotoxin
* Îą- Conotoxin ArIB 11L,V16D potent and highly subtype-selective; slowly reversible
*Îē-Caryophyllene
Caryophyllene (), more formally (â)-Îē-caryophyllene, (BCP), is a natural bicyclic sesquiterpene that is a constituent of many essential oils, especially clove oil, the oil from the stems and flowers of ''Syzygium aromaticum'' (cloves), the esse ...
* Bupropion
Bupropion, sold under the brand names Wellbutrin and Zyban among others, is an atypical antidepressant primarily used to treat major depressive disorder and to support smoking cessation. It is also popular as an add-on medication in the case ...
(very weakly)
* Dehydronorketamine
Dehydronorketamine (DHNK), or 5,6-dehydronorketamine, is a minor metabolite of ketamine which is formed by dehydrogenation of its metabolite norketamine. Though originally considered to be inactive, DHNK has been found to act as a potent and sele ...
* Ethanol
* Hydroxybupropion (very weakly)
* Hydroxynorketamine
Hydroxynorketamine (HNK), or 6-hydroxynorketamine, is a minor metabolite of the anesthetic, dissociative, and antidepressant drug ketamine. It is formed by hydroxylation of the intermediate norketamine, another metabolite of ketamine. As of l ...
* Ketamine
* Kynurenic acid
* Memantine
* Lobeline
* Methyllycaconitine
Methyllycaconitine (MLA) is a diterpenoid alkaloid found in many species of ''Delphinium'' (larkspurs). In common with many other diterpenoid alkaloids, it is toxic to animals, although the acute toxicity varies with species. Early research was f ...
* Norketamine
* Quinolizidine (â)-1-epi-207I: Îą7 subtype preferring blocker
See also
* Îą3Îē2-Nicotinic receptor * Îą3Îē4-Nicotinic receptor * Îą4Îē2-Nicotinic receptor *RIC3
RIC-3 also known as resistance to inhibitors of cholinesterase 3 is a chaperone protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RIC3'' gene. The RIC3 gene was first discovered in ''Caenorhabditis elegans, C. elegans''. RIC-3 protein is conserved in mos ...
, a chaperone protein for Îą7 receptors
* Endocannabinoids
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Alpha-7 Nicotinic Receptor Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors Ion channels