|
PNU-282,987
PNU-282,987 is a drug that acts as a potent and selective agonist for the α7 subtype of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. In animal studies, it shows nootropic effects, and derivatives may be useful in the treatment of schizophrenia, although PNU-282,987 is not suitable for use in humans because of excessive inhibition of the hERG antitarget In pharmacology, an antitarget (or off-target) is a receptor, enzyme, or other biological target that, when affected by a drug, causes undesirable side-effects. During drug design and development, it is important for pharmaceutical companies to ens .... PNU-282987 has been shown to initiate signaling that leads to adult neurogeneis in mammals. References Nicotinic agonists Stimulants Nootropics Quinuclidines Benzamides Chloroarenes {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
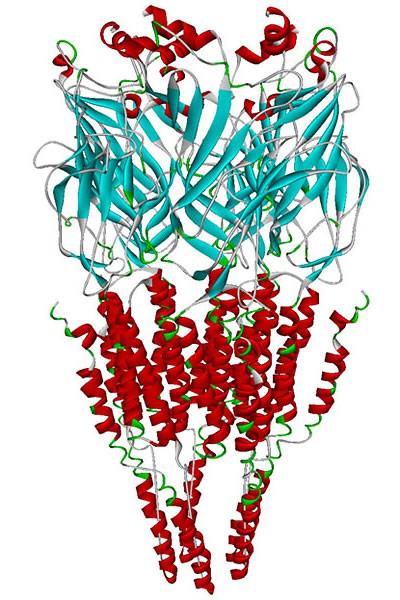
Alpha-7 Nicotinic Receptor
The alpha-7 nicotinic receptor, also known as the α7 receptor, is a type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor implicated in long-term memory, consisting entirely of α7 subunits.Pharmacology, (Rang, Dale, Ritter & Moore, , 5th ed., Churchill Livingstone 2003) p. 138. As with other nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, functional α7 receptors are pentameric .e., (α7)5 stoichiometry">stoichiometry.html" ;"title=".e., (α7)5 stoichiometry">.e., (α7)5 stoichiometry It is located in the brain, spleen, and lymphocytes of lymph nodes where activation yields Excitatory postsynaptic potential, post- and excitatory presynaptic potential, presynaptic excitation, mainly by increased Ca2+ permeability. Further, recent work has implicated this receptor as being important for generation of adult mammal neurons in the retina. Functional α7 receptors are present in the submucous plexus neurons of the guinea-pig ileum. Medical relevance Recent work has demonstrated a potential role in redu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology From the Greek αγωνιστής (agōnistēs), contestant; champion; rival < αγων (agōn), contest, combat; exertion, struggle < αγω (agō), I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive Types of agonists can be activated by either endogenous agonists (such as |
Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are receptor polypeptides that respond to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Nicotinic receptors also respond to drugs such as the agonist nicotine. They are found in the central and peripheral nervous system, muscle, and many other tissues of many organisms. At the neuromuscular junction they are the primary receptor in muscle for motor nerve-muscle communication that controls muscle contraction. In the peripheral nervous system: (1) they transmit outgoing signals from the presynaptic to the postsynaptic cells within the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, and (2) they are the receptors found on skeletal muscle that receive acetylcholine released to signal for muscular contraction. In the immune system, nAChRs regulate inflammatory processes and signal through distinct intracellular pathways. In insects, the cholinergic system is limited to the central nervous system. The nicotinic receptors are considered cholinergi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Medicinal Chemistry
A journal, from the Old French ''journal'' (meaning "daily"), may refer to: *Bullet journal, a method of personal organization *Diary, a record of what happened over the course of a day or other period *Daybook, also known as a general journal, a daily record of financial transactions *Logbook, a record of events important to the operation of a vehicle, facility, or otherwise *Record (other) *Transaction log, a chronological record of data processing *Travel journal In publishing, ''journal'' can refer to various periodicals or serials: *Academic journal, an academic or scholarly periodical **Scientific journal, an academic journal focusing on science **Medical journal, an academic journal focusing on medicine **Law review, a professional journal focusing on legal interpretation *Magazine, non-academic or scholarly periodicals in general **Trade magazine, a magazine of interest to those of a particular profession or trade **Literary magazine, a magazine devoted to literat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nootropic
Nootropics ( , or ) (colloquial: smart drugs and cognitive enhancers, similar to adaptogens) are a wide range of natural or synthetic supplements or drugs and other substances that are claimed to improve cognitive function or to promote relaxation, particularly boosting mood, executive functions, attention, memory, creativity, or motivation in healthy individuals. The use of cognition-enhancing supplements by healthy individuals in the absence of a medical indication spans numerous controversial issues, including the ethics and fairness of their use, concerns over adverse effects, and the diversion of prescription drugs for non-medical uses. Nonetheless, the international sales of cognitive- or mood-enhancing supplements have continued to grow over time and in 2012 reached 0.69 billion. With sales supported by global health trends, the market is expected to reach US$33.85 billion by the year 2030, at a CAGR of 14.8%. While most nootropics are not regulated, there are ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social withdrawal, decreased emotional expression, and apathy. Symptoms typically develop gradually, begin during young adulthood, and in many cases never become resolved. There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. To be diagnosed with schizophrenia, symptoms and functional impairment need to be present for six months (DSM-5) or one month (ICD-11). Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders, especially substance use disorders, depressive disorders, anxiety disorders, and obsessive–compulsive disorder. About 0.3% to 0.7% of people are diagnosed with schizophrenia during their lifetime. In 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HERG
hERG (the human '' Ether-à-go-go''-Related Gene) is a gene () that codes for a protein known as Kv11.1, the alpha subunit of a potassium ion channel. This ion channel (sometimes simply denoted as 'hERG') is best known for its contribution to the electrical activity of the heart: the hERG channel mediates the repolarizing ''I''Kr current in the cardiac action potential, which helps coordinate the heart's beating. When this channel's ability to conduct electrical current across the cell membrane is inhibited or compromised, either by application of drugs or by rare mutations in some families, it can result in a potentially fatal disorder called long QT syndrome. Conversely, genetic mutations that increase the current through these channels can lead to the related inherited heart rhythm disorder Short QT syndrome. A number of clinically successful drugs in the market have had the tendency to inhibit hERG, lengthening the QT and potentially leading to a fatal irregularity of the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antitarget
In pharmacology, an antitarget (or off-target) is a receptor, enzyme, or other biological target that, when affected by a drug, causes undesirable side-effects. During drug design and development, it is important for pharmaceutical companies to ensure that new drugs do not show significant activity at any of a range of antitargets, most of which are discovered largely by chance. Among the best-known and most significant antitargets are the hERG channel and the 5-HT2B receptor, both of which cause long-term problems with heart function that can prove fatal (long QT syndrome and cardiac fibrosis, respectively), in a small but unpredictable proportion of users. Both of these targets were discovered as a result of high levels of distinctive side-effects during the marketing of certain medicines, and, while some older drugs with significant hERG activity are still used with caution, most drugs that have been found to be strong 5-HT2B agonists were withdrawn from the market, and any new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotinic Agonists
A nicotinic agonist is a drug that mimics the action of acetylcholine (ACh) at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). The nAChR is named for its affinity for nicotine. Examples include nicotine (by definition), acetylcholine (the endogenous agonist of nAChRs), choline, epibatidine, lobeline, varenicline and cytisine. History Nicotine has been known for centuries for its intoxicating effect. It was first isolated in 1828 from the tobacco plant by German chemists Posselt and Reimann. The discovery of positive effects from nicotine on animal memory was discovered by in vivo researches in the mid 1980s. Those researches led to a new era in studies of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) and their stimulation but until then the focus had mainly been on nicotine addiction. The development of nAChR agonists began in the early 1990s after the discovery of nicotine's positive effects. Some research showed a possible therapy option in preclinical researches. ABT-418 was one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimulants
Stimulants (also often referred to as psychostimulants or colloquially as uppers) is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and invigorating, or drugs that have Sympathomimetic drug, sympathomimetic effects. Stimulants are widely used throughout the world as prescription medicines as well as without a prescription (either legally or Prohibition (drugs), illicitly) as performance-enhancing substance, performance-enhancing or recreational drug use, recreational drugs. Among narcotics, stimulants produce a noticeable crash or ''Comedown (drugs), comedown'' at the end of their effects. The most frequently prescribed stimulants as of 2013 were lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse), methylphenidate (Ritalin), and amphetamine (Adderall). It was estimated in 2015 that the percentage of the world population that had used cocaine during a year was 0.4%. For the category "amphetamines and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nootropics
Nootropics ( , or ) (colloquial: smart drugs and cognitive enhancers, similar to adaptogens) are a wide range of natural or synthetic supplements or drugs and other substances that are claimed to improve cognitive function or to promote relaxation, particularly boosting mood, executive functions, attention, memory, creativity, or motivation in healthy individuals. The use of cognition-enhancing supplements by healthy individuals in the absence of a medical indication spans numerous controversial issues, including the ethics and fairness of their use, concerns over adverse effects, and the diversion of prescription drugs for non-medical uses. Nonetheless, the international sales of cognitive- or mood-enhancing supplements have continued to grow over time and in 2012 reached 0.69 billion. With sales supported by global health trends, the market is expected to reach US$33.85 billion by the year 2030, at a CAGR of 14.8%. While most nootropics are not regulated, there are othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinuclidines
Quinuclidine is an organic compound and a bicyclic amine and used as a catalyst and a chemical building block. It is a strong base with p''K''a of the conjugate acid of 11.0.{{cite journal , title=Azatriquinanes: Synthesis, Structure, and Reactivity , author1=Hext, N. M. , author2=Hansen, J. , author3=Blake, A. J. , author4=Hibbs, D. E. , author5=Hursthouse, M. B. , author6=Shishkin, O. V. , author7=Mascal, M. , journal=J. Org. Chem. , year=1998 , volume=63 , issue=17 , pages=6016–6020 , doi=10.1021/jo980788s , pmid=11672206 It can be prepared by reduction of quinuclidone. In alkane solvents quinuclidine is a Lewis base that forms adducts with a variety of Lewis acids. The compound is structurally related to DABCO, in which the other bridgehead is also nitrogen, and to tropane, which has a slightly different carbon frame. Quinuclidine is found as a structural component of some biomolecules including quinine Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |