|
AR-R17779
AR-R17779 is a drug that acts as a potent and selective full agonist for the α7 subtype of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It has nootropic effects in animal studies, but its effects do not substitute for those of nicotine Nicotine is a natural product, naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and ''Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreational drug use, recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As .... It has also been studied as a potential novel treatment for arthritis. References Nicotinic agonists Stimulants Nootropics 2-Oxazolidinones Spiro compounds {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
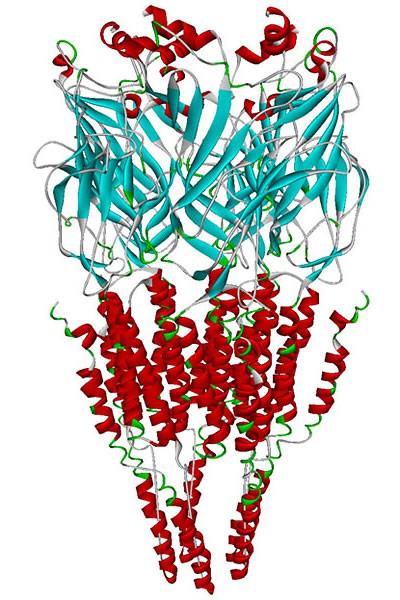
Alpha-7 Nicotinic Receptor
The alpha-7 nicotinic receptor, also known as the α7 receptor, is a type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor implicated in long-term memory, consisting entirely of α7 subunits.Pharmacology, (Rang, Dale, Ritter & Moore, , 5th ed., Churchill Livingstone 2003) p. 138. As with other nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, functional α7 receptors are pentameric .e., (α7)5 stoichiometry">stoichiometry.html" ;"title=".e., (α7)5 stoichiometry">.e., (α7)5 stoichiometry It is located in the brain, spleen, and lymphocytes of lymph nodes where activation yields Excitatory postsynaptic potential, post- and excitatory presynaptic potential, presynaptic excitation, mainly by increased Ca2+ permeability. Further, recent work has implicated this receptor as being important for generation of adult mammal neurons in the retina. Functional α7 receptors are present in the submucous plexus neurons of the guinea-pig ileum. Medical relevance Recent work has demonstrated a potential role in red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology From the Greek αγωνιστής (agōnistēs), contestant; champion; rival < αγων (agōn), contest, combat; exertion, struggle < αγω (agō), I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive Types of agonists can be activated by either endogenous agonists (such as |
Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are receptor polypeptides that respond to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Nicotinic receptors also respond to drugs such as the agonist nicotine. They are found in the central and peripheral nervous system, muscle, and many other tissues of many organisms. At the neuromuscular junction they are the primary receptor in muscle for motor nerve-muscle communication that controls muscle contraction. In the peripheral nervous system: (1) they transmit outgoing signals from the presynaptic to the postsynaptic cells within the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, and (2) they are the receptors found on skeletal muscle that receive acetylcholine released to signal for muscular contraction. In the immune system, nAChRs regulate inflammatory processes and signal through distinct intracellular pathways. In insects, the cholinergic system is limited to the central nervous system. The nicotinic receptors are considered cholinergi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Medicinal Chemistry
A journal, from the Old French ''journal'' (meaning "daily"), may refer to: *Bullet journal, a method of personal organization *Diary, a record of what happened over the course of a day or other period *Daybook, also known as a general journal, a daily record of financial transactions *Logbook, a record of events important to the operation of a vehicle, facility, or otherwise *Record (other) *Transaction log, a chronological record of data processing *Travel journal In publishing, ''journal'' can refer to various periodicals or serials: *Academic journal, an academic or scholarly periodical **Scientific journal, an academic journal focusing on science **Medical journal, an academic journal focusing on medicine **Law review, a professional journal focusing on legal interpretation *Magazine, non-academic or scholarly periodicals in general **Trade magazine, a magazine of interest to those of a particular profession or trade **Literary magazine, a magazine devoted to literat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nootropic
Nootropics ( , or ) (colloquial: smart drugs and cognitive enhancers, similar to adaptogens) are a wide range of natural or synthetic supplements or drugs and other substances that are claimed to improve cognitive function or to promote relaxation, particularly boosting mood, executive functions, attention, memory, creativity, or motivation in healthy individuals. The use of cognition-enhancing supplements by healthy individuals in the absence of a medical indication spans numerous controversial issues, including the ethics and fairness of their use, concerns over adverse effects, and the diversion of prescription drugs for non-medical uses. Nonetheless, the international sales of cognitive- or mood-enhancing supplements have continued to grow over time and in 2012 reached 0.69 billion. With sales supported by global health trends, the market is expected to reach US$33.85 billion by the year 2030, at a CAGR of 14.8%. While most nootropics are not regulated, there are ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotine
Nicotine is a naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and ''Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As a pharmaceutical drug, it is used for smoking cessation to relieve withdrawal symptoms. Nicotine acts as a receptor agonist at most nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs), except at two nicotinic receptor subunits (nAChRα9 and nAChRα10) where it acts as a receptor antagonist. Nicotine constitutes approximately 0.6–3.0% of the dry weight of tobacco. Nicotine is also present at ppb-concentrations in edible plants in the family Solanaceae, including potatoes, tomatoes, and eggplants, though sources disagree on whether this has any biological significance to human consumers. It functions as an antiherbivore toxin; consequently, nicotine was widely used as an insecticide in the past, and neonicotinoids (structurally similar to nicotine), such as imidacloprid, are s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthritis
Arthritis is a term often used to mean any disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In some types of arthritis, other organs are also affected. Onset can be gradual or sudden. There are over 100 types of arthritis. The most common forms are osteoarthritis (degenerative joint disease) and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis usually occurs with age and affects the fingers, knees, and hips. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that often affects the hands and feet. Other types include gout, lupus, fibromyalgia, and septic arthritis. They are all types of rheumatic disease. Treatment may include resting the joint and alternating between applying ice and heat. Weight loss and exercise may also be useful. Recommended medications may depend on the form of arthritis. These may include pain medications such as ibuprofen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotinic Agonists
A nicotinic agonist is a drug that mimics the action of acetylcholine (ACh) at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). The nAChR is named for its affinity for nicotine. Examples include nicotine (by definition), acetylcholine (the endogenous agonist of nAChRs), choline, epibatidine, lobeline, varenicline and cytisine. History Nicotine has been known for centuries for its intoxicating effect. It was first isolated in 1828 from the tobacco plant by German chemists Posselt and Reimann. The discovery of positive effects from nicotine on animal memory was discovered by in vivo researches in the mid 1980s. Those researches led to a new era in studies of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) and their stimulation but until then the focus had mainly been on nicotine addiction. The development of nAChR agonists began in the early 1990s after the discovery of nicotine's positive effects. Some research showed a possible therapy option in preclinical researches. ABT-418 was one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimulants
Stimulants (also often referred to as psychostimulants or colloquially as uppers) is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and invigorating, or drugs that have Sympathomimetic drug, sympathomimetic effects. Stimulants are widely used throughout the world as prescription medicines as well as without a prescription (either legally or Prohibition (drugs), illicitly) as performance-enhancing substance, performance-enhancing or recreational drug use, recreational drugs. Among narcotics, stimulants produce a noticeable crash or ''Comedown (drugs), comedown'' at the end of their effects. The most frequently prescribed stimulants as of 2013 were lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse), methylphenidate (Ritalin), and amphetamine (Adderall). It was estimated in 2015 that the percentage of the world population that had used cocaine during a year was 0.4%. For the category "amphetamines and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nootropics
Nootropics ( , or ) (colloquial: smart drugs and cognitive enhancers, similar to adaptogens) are a wide range of natural or synthetic supplements or drugs and other substances that are claimed to improve cognitive function or to promote relaxation, particularly boosting mood, executive functions, attention, memory, creativity, or motivation in healthy individuals. The use of cognition-enhancing supplements by healthy individuals in the absence of a medical indication spans numerous controversial issues, including the ethics and fairness of their use, concerns over adverse effects, and the diversion of prescription drugs for non-medical uses. Nonetheless, the international sales of cognitive- or mood-enhancing supplements have continued to grow over time and in 2012 reached 0.69 billion. With sales supported by global health trends, the market is expected to reach US$33.85 billion by the year 2030, at a CAGR of 14.8%. While most nootropics are not regulated, there are othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |