|
PHA-543,613
PHA-543,613 is a drug that acts as a potent and selective agonist for the α7 subtype of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, with a high level of brain penetration and good oral bioavailability. It is under development as a possible treatment for cognitive deficits in schizophrenia. It reduces excitotoxicity and protects striatal dopaminergic neurons in rat models. It also potentiates cognitive enhancement from memantine, decreases dynorphin release and inhibits GSK-B3. See also * Nefiracetam Nefiracetam is a nootropic drug of the racetam family. Preliminary research suggests that it may possess certain antidementia properties in rats. Effects Nefiracetam's cytoprotective actions are mediated by enhancement of GABAergic, cholinergic, ... References {{Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor modulators Nicotinic agonists Stimulants Quinuclidines Carboxamides Furopyridines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
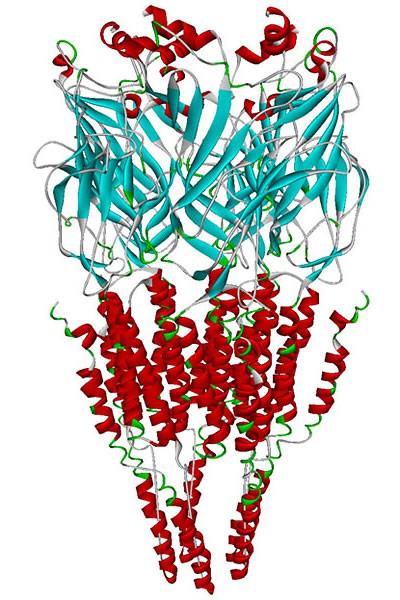
Alpha-7 Nicotinic Receptor
The alpha-7 nicotinic receptor, also known as the α7 receptor, is a type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor implicated in long-term memory, consisting entirely of α7 subunits.Pharmacology, (Rang, Dale, Ritter & Moore, , 5th ed., Churchill Livingstone 2003) p. 138. As with other nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, functional α7 receptors are pentameric .e., (α7)5 stoichiometry">stoichiometry.html" ;"title=".e., (α7)5 stoichiometry">.e., (α7)5 stoichiometry It is located in the brain, spleen, and lymphocytes of lymph nodes where activation yields Excitatory postsynaptic potential, post- and excitatory presynaptic potential, presynaptic excitation, mainly by increased Ca2+ permeability. Further, recent work has implicated this receptor as being important for generation of adult mammal neurons in the retina. Functional α7 receptors are present in the submucous plexus neurons of the guinea-pig ileum. Medical relevance Recent work has demonstrated a potential role in red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology From the Greek αγωνιστής (agōnistēs), contestant; champion; rival < αγων (agōn), contest, combat; exertion, struggle < αγω (agō), I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive Types of agonists can be activated by either endogenous agonists (such as |
Quinuclidines
Quinuclidine is an organic compound and a bicyclic amine and used as a catalyst and a chemical building block. It is a strong base with p''K''a of the conjugate acid of 11.0.{{cite journal , title=Azatriquinanes: Synthesis, Structure, and Reactivity , author1=Hext, N. M. , author2=Hansen, J. , author3=Blake, A. J. , author4=Hibbs, D. E. , author5=Hursthouse, M. B. , author6=Shishkin, O. V. , author7=Mascal, M. , journal=J. Org. Chem. , year=1998 , volume=63 , issue=17 , pages=6016–6020 , doi=10.1021/jo980788s , pmid=11672206 It can be prepared by reduction of quinuclidone. In alkane solvents quinuclidine is a Lewis base that forms adducts with a variety of Lewis acids. The compound is structurally related to DABCO, in which the other bridgehead is also nitrogen, and to tropane, which has a slightly different carbon frame. Quinuclidine is found as a structural component of some biomolecules including quinine Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimulants
Stimulants (also often referred to as psychostimulants or colloquially as uppers) is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and invigorating, or drugs that have Sympathomimetic drug, sympathomimetic effects. Stimulants are widely used throughout the world as prescription medicines as well as without a prescription (either legally or Prohibition (drugs), illicitly) as performance-enhancing substance, performance-enhancing or recreational drug use, recreational drugs. Among narcotics, stimulants produce a noticeable crash or ''Comedown (drugs), comedown'' at the end of their effects. The most frequently prescribed stimulants as of 2013 were lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse), methylphenidate (Ritalin), and amphetamine (Adderall). It was estimated in 2015 that the percentage of the world population that had used cocaine during a year was 0.4%. For the category "amphetamines and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotinic Agonists
A nicotinic agonist is a drug that mimics the action of acetylcholine (ACh) at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). The nAChR is named for its affinity for nicotine. Examples include nicotine (by definition), acetylcholine (the endogenous agonist of nAChRs), choline, epibatidine, lobeline, varenicline and cytisine. History Nicotine has been known for centuries for its intoxicating effect. It was first isolated in 1828 from the tobacco plant by German chemists Posselt and Reimann. The discovery of positive effects from nicotine on animal memory was discovered by in vivo researches in the mid 1980s. Those researches led to a new era in studies of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) and their stimulation but until then the focus had mainly been on nicotine addiction. The development of nAChR agonists began in the early 1990s after the discovery of nicotine's positive effects. Some research showed a possible therapy option in preclinical researches. ABT-418 was one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nefiracetam
Nefiracetam is a nootropic drug of the racetam family. Preliminary research suggests that it may possess certain antidementia properties in rats. Effects Nefiracetam's cytoprotective actions are mediated by enhancement of GABAergic, cholinergic, and monoaminergic neuronal systems. Preliminary studies suggest that it improves apathy and motivation in post-stroke patients. It may also exhibit antiamnesia effects for the Alzheimer's type and cerebrovascular type of dementia. In addition, research in animal models suggests antiamnesic effects against a number of memory impairing substances, including: ethanol, chlorodiazepoxide, scopolamine, bicuculline, picrotoxin, and cycloheximide. Pharmacology Unlike other racetams, nefiracetam shows high affinity for the GABAA receptor ( IC50) = 8.5 nM), where it is presumed to be an agonist. It was able to potently inhibit 80% of muscimol binding to the GABAA receptor, although it failed to displace the remaining 20% of specific muscimol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functioning properly. Signs and symptoms of a stroke may include an inability to move or feel on one side of the body, problems understanding or speaking, dizziness, or loss of vision to one side. Signs and symptoms often appear soon after the stroke has occurred. If symptoms last less than one or two hours, the stroke is a transient ischemic attack (TIA), also called a mini-stroke. A hemorrhagic stroke may also be associated with a severe headache. The symptoms of a stroke can be permanent. Long-term complications may include pneumonia and loss of bladder control. The main risk factor for stroke is high blood pressure. Other risk factors include high blood cholesterol, tobacco smoking, obesity, diabetes mellitus, a previous TIA, end-st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Research
''Brain Research'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal focusing on several aspects of neuroscience. It publishes research reports and " minireviews". The editor-in-chief is Matthew J. LaVoie (University of Florida). Until 2011, full reviews were published in ''Brain Research Reviews'', which is now integrated into the main section, albeit with independent volume numbering. In 2006, four other previously established semi-independent journal sections ('' Cognitive Brain Research, Developmental Brain Research, Molecular Brain Research,'' and '' Brain Research Protocols'') were merged with ''Brain Research''. The journal has nine main subsections: * ''Cellular and Molecular Systems'' * ''Nervous System Development, Regeneration and Aging'' * ''Neurophysiology, Neuropharmacology and other forms of Intercellular Communication'' * ''Structural Organization of the Brain'' * ''Sensory and Motor Systems'' * ''Regulatory Systems'' * ''Cognitive and Behavioral Neuroscience'' * ''Disease-Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychopharmacology
Psychopharmacology (from Greek grc, ψῡχή, psȳkhē, breath, life, soul, label=none; grc, φάρμακον, pharmakon, drug, label=none; and grc, -λογία, -logia, label=none) is the scientific study of the effects drugs have on mood, sensation, thinking, behavior, judgment and evaluation, and memory. It is distinguished from neuropsychopharmacology, which emphasizes the correlation between drug-induced changes in the functioning of cells in the nervous system and changes in consciousness and behavior. The field of psychopharmacology studies a wide range of substances with various types of psychoactive properties, focusing primarily on the chemical interactions with the brain. The term "psychopharmacology" was likely first coined by David Macht in 1920. Psychoactive drugs interact with particular target sites or receptors found in the nervous system to induce widespread changes in physiological or psychological functions. The specific interaction between drugs and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontiers In Pharmacology
Frontiers Media SA is a publisher of peer-reviewed, open access, scientific journals currently active in science, technology, and medicine. It was founded in 2007 by Kamila and Henry Markram, and has since expanded to other academic fields. Frontiers is based in Lausanne, Switzerland, with other offices in London, Madrid, Seattle and Brussels. In 2022, Frontiers employed more than 1,400 people, across 14 countries. All Frontiers journals are published under a Creative Commons Attribution License. As of 2022, Frontiers publishes over 185 academic journals, including 48 journals indexed within the Science Citation Index Expanded, and 4 journals indexed within the Social Sciences Citation Index, with a total of 51 journals ranked with an impact factor. Frontiers journals are included in the Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ). Frontiers is also a member of the Open Access Scholarly Publishers Association (OASPA), a participating publisher and supporter of the Initiative for O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memantine
Memantine is a medication used to slow the progression of moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include headache, constipation, sleepiness, and dizziness. Severe side effects may include blood clots, psychosis, and heart failure. It is believed to work by acting on NMDA receptors, working as pore blockers of these ion channels. Memantine was approved for medical use in the United States in 2003. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 152nd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 3million prescriptions. Medical use Alzheimer's disease and dementia Memantine is used to treat moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease, especially for people who are intolerant of or have a contraindication to AChE (acetylcholinesterase) inhibitors.NICE review of technology appraisal guidance 111 January 18, 201Alzheimer's disease - donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine and memantine (review): final ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontiers In Medicine
''Frontiers in Medicine'' is a peer-reviewed open access medical journal covering all aspects of medicine in 18 sections. It was established in 2014 and is published by Frontiers Media. The editor-in-chief is Michel Goldman (Institute for Interdisciplinary Innovation in healthcare). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in PubMed and Scopus. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 5.091. References External links * {{Official website, https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/medicine English-language journals General medical journals Open access journals Publications established in 2014 Frontiers Media academic journals Online-only journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |