|
Encenicline
Encenicline (INN, USAN, code names EVP-6124, MT-4666) is a selective partial agonist of the α7 nicotinic receptor. It was in phase III clinical trials for the treatment of cognitive impairment in schizophrenia, but failed to meet the study endpoints in 2016. FORUM Pharmaceuticals, who currently is subjecting the drug to the FDA approval process, had all studies suspended until further notice in fall of 2015 due to rare, but serious gastrointestinal problems occurring in patients participating in the drug trial, potentially being a consequence of taking the drug. The trials were scheduled to be run until January 2017, but as of December 2016, they appear to still be on hold. There is speculation by FORUM Pharmaceuticals that this may be due to either the increased daily dose given in the phase III trial compared to earlier trials that showed promise. In previous trials, the highest dose given was 2 mg/day, with the most positive of effects having been realized in patients ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
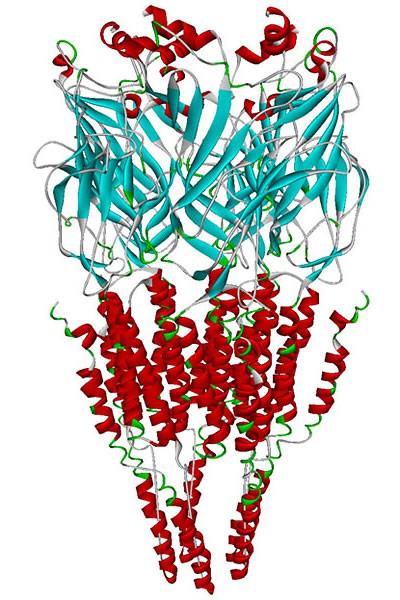
Alpha-7 Nicotinic Receptor
The alpha-7 nicotinic receptor, also known as the α7 receptor, is a type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor implicated in long-term memory, consisting entirely of α7 subunits.Pharmacology, (Rang, Dale, Ritter & Moore, , 5th ed., Churchill Livingstone 2003) p. 138. As with other nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, functional α7 receptors are pentameric .e., (α7)5 stoichiometry">stoichiometry.html" ;"title=".e., (α7)5 stoichiometry">.e., (α7)5 stoichiometry It is located in the brain, spleen, and lymphocytes of lymph nodes where activation yields Excitatory postsynaptic potential, post- and excitatory presynaptic potential, presynaptic excitation, mainly by increased Ca2+ permeability. Further, recent work has implicated this receptor as being important for generation of adult mammal neurons in the retina. Functional α7 receptors are present in the submucous plexus neurons of the guinea-pig ileum. Medical relevance Recent work has demonstrated a potential role in red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PNU-282,987
PNU-282,987 is a drug that acts as a potent and selective agonist for the α7 subtype of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. In animal studies, it shows nootropic effects, and derivatives may be useful in the treatment of schizophrenia, although PNU-282,987 is not suitable for use in humans because of excessive inhibition of the hERG antitarget In pharmacology, an antitarget (or off-target) is a receptor, enzyme, or other biological target that, when affected by a drug, causes undesirable side-effects. During drug design and development, it is important for pharmaceutical companies to ens .... PNU-282987 has been shown to initiate signaling that leads to adult neurogeneis in mammals. References Nicotinic agonists Stimulants Nootropics Quinuclidines Benzamides Chloroarenes {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotinic Agonists
A nicotinic agonist is a drug that mimics the action of acetylcholine (ACh) at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). The nAChR is named for its affinity for nicotine. Examples include nicotine (by definition), acetylcholine (the endogenous agonist of nAChRs), choline, epibatidine, lobeline, varenicline and cytisine. History Nicotine has been known for centuries for its intoxicating effect. It was first isolated in 1828 from the tobacco plant by German chemists Posselt and Reimann. The discovery of positive effects from nicotine on animal memory was discovered by in vivo researches in the mid 1980s. Those researches led to a new era in studies of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) and their stimulation but until then the focus had mainly been on nicotine addiction. The development of nAChR agonists began in the early 1990s after the discovery of nicotine's positive effects. Some research showed a possible therapy option in preclinical researches. ABT-418 was one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Drugs
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a particular factor is manipulated. Experiments vary greatly in goal and scale but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results. There also exist natural experimental studies. A child may carry out basic experiments to understand how things fall to the ground, while teams of scientists may take years of systematic investigation to advance their understanding of a phenomenon. Experiments and other types of hands-on activities are very important to student learning in the science classroom. Experiments can raise test scores and help a student become more engaged and interested in the material they are learning, especially when used over time. Experiments can vary from personal and informal natural comparisons (e. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroarenes
In organic chemistry, an aryl halide (also known as haloarene) is an aromatic compound in which one or more hydrogen atoms, directly bonded to an aromatic ring are replaced by a halide. The haloarene are different from haloalkanes because they exhibit many differences in methods of preparation and properties. The most important members are the aryl chlorides, but the class of compounds is so broad that there are many derivatives and applications. Preparation The two main preparatory routes to aryl halides are direct halogenation and via diazonium salts. Direct halogenation In the Friedel-Crafts halogenation, Lewis acids serve as catalysts. Many metal chlorides are used, examples include iron(III) chloride or aluminium chloride. The most important aryl halide, chlorobenzene is produced by this route. Monochlorination of benzene is always accompanied by formation of the dichlorobenzene derivatives. Arenes with electron donating groups react with halogens even in the absence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WAY-317,538
WAY-317538 (SEN-12333) is a drug that acts as a potent and selective full agonist for the α7 subtype of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It was not the most potent compound in the series, but was selected for further development on the basis of its high selectivity over related receptors, ease of synthesis, and good ''in vivo'' properties including high oral bioavailability and good brain penetration. It has nootropic and neuroprotective effects in animal studies, and is being investigated as a potential treatment for neurodegenerative and neurocognitive conditions including Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social wit .... References Nicotinic agonists Stimulants Nootropics 3-Pyridyl compounds 4-Morpholinyl compunds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TC-1698
TC-1698 is a drug developed by Targacept which acts as a partial agonist for the α7 subtype of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It has neuroprotective effects in animal studies, and has been used as a lead compound to find further potent derivatives. See also * Anabasine Anabasine is a pyridine and piperidine alkaloid found in the Tree Tobacco (''Nicotiana glauca'') plant, a close relative of the common tobacco plant (''Nicotiana tabacum''). It is a structural isomer of, and chemically similar to, nicotine. Its ... References Nicotinic agonists Stimulants 3-Pyridyl compounds {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SSR-180,711
SSR180711 is a drug that acts as a potent and selective partial agonist for the α7 subtype of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. In animal studies, it shows nootropic effects and may be useful in the treatment of schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social wit .... References Nicotinic agonists Stimulants Nootropics Organobromides Carbamates Nitrogen heterocycles {{pharma-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PHA-543,613
PHA-543,613 is a drug that acts as a potent and selective agonist for the α7 subtype of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, with a high level of brain penetration and good oral bioavailability. It is under development as a possible treatment for cognitive deficits in schizophrenia. It reduces excitotoxicity and protects striatal dopaminergic neurons in rat models. It also potentiates cognitive enhancement from memantine, decreases dynorphin release and inhibits GSK-B3. See also * Nefiracetam Nefiracetam is a nootropic drug of the racetam family. Preliminary research suggests that it may possess certain antidementia properties in rats. Effects Nefiracetam's cytoprotective actions are mediated by enhancement of GABAergic, cholinergic, ... References {{Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor modulators Nicotinic agonists Stimulants Quinuclidines Carboxamides Furopyridines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |