|
Tetraphenylporphyrin
Tetraphenylporphyrin, abbreviated TPP or H2TPP, is a synthetic heterocyclic compound that resembles naturally occurring porphyrins. Porphyrins are dyes and cofactors found in hemoglobin and cytochromes and are related to chlorophyll and vitamin B12. The study of naturally occurring porphyrins is complicated by their low symmetry and the presence of polar substituents. Tetraphenylporphyrin is hydrophobic, symmetrically substituted, and easily synthesized. The compound is a dark purple solid that dissolves in nonpolar organic solvents such as chloroform and benzene. Synthesis and structure Tetraphenylporphyrin was first synthesized in 1935 by Rothemund, who caused benzaldehyde and pyrrole to react in a sealed bomb at 150 °C for 24 h. Adler and Longo modified the Rothemund method by allowing benzaldehyde and pyrrole to react for 30 min in refluxing propionic acid (141 °C) open to the air: :8 C4H4NH + 8 C6H5CHO + 3 O2 → 2 (C6H5C)4(C4H2N)2(C4H2NH)2 + 14 H2O D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyrin
Porphyrins ( ) are a group of heterocyclic macrocycle organic compounds, composed of four modified pyrrole subunits interconnected at their α carbon atoms via methine bridges (=CH−). The parent of porphyrin is porphine, a rare chemical compound of exclusively theoretical interest. Substituted porphines are called porphyrins. With a total of 26 π-electrons, of which 18 π-electrons form a planar, continuous cycle, the porphyrin ring structure is often described as aromatic. One result of the large conjugated system is that porphyrins typically absorb strongly in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum, i.e. they are deeply colored. The name "porphyrin" derives from the Greek word πορφύρα (''porphyra''), meaning ''purple''. Complexes of porphyrins Concomitant with the displacement of two N-''H'' protons, porphyrins bind metal ions in the N4 "pocket". The metal ion usually has a charge of 2+ or 3+. A schematic equation for these syntheses is shown: :H2porp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyrinogen
In biochemistry a porphyrinogen is a member of a class of naturally occurring compounds with a tetrapyrrole core, a macrocycle Macrocycles are often described as molecules and ions containing a ring of twelve or more atoms. Classical examples include the crown ethers, calixarenes, porphyrins, and cyclodextrins. Macrocycles describe a large, mature area of chemistry. ... of four pyrrole rings connected by four methylene bridges. - IUPAC Gold Book They can be viewed as derived from the parent compound hexahydroporphine by the substitution of various functional groups for hydrogen atoms in the outermost (20-carbon) ring. Porphyrinogens are intermediates in the biosynthesis of porphyrins, Cofactor (biochemistry), cofactors with a porphine core which are found in many enzymes and proteins including myoglobin, hemoglobin, cytochromes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myoglobin
Myoglobin (symbol Mb or MB) is an iron- and oxygen-binding protein found in the cardiac and skeletal muscle tissue of vertebrates in general and in almost all mammals. Myoglobin is distantly related to hemoglobin. Compared to hemoglobin, myoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen and does not have cooperative binding with oxygen like hemoglobin does. In humans, myoglobin is only found in the bloodstream after muscle injury. (Google books link is the 2008 edition) High concentrations of myoglobin in muscle cells allow organisms to hold their breath for a longer period of time. Diving mammals such as whales and seals have muscles with particularly high abundance of myoglobin. Myoglobin is found in Type I muscle, Type II A, and Type II B; although many texts consider myoglobin not to be found in smooth muscle, this has proved erroneous: there is also myoglobin in smooth muscle cells. Myoglobin was the first protein to have its three-dimensional structure revealed by X-ray crystal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
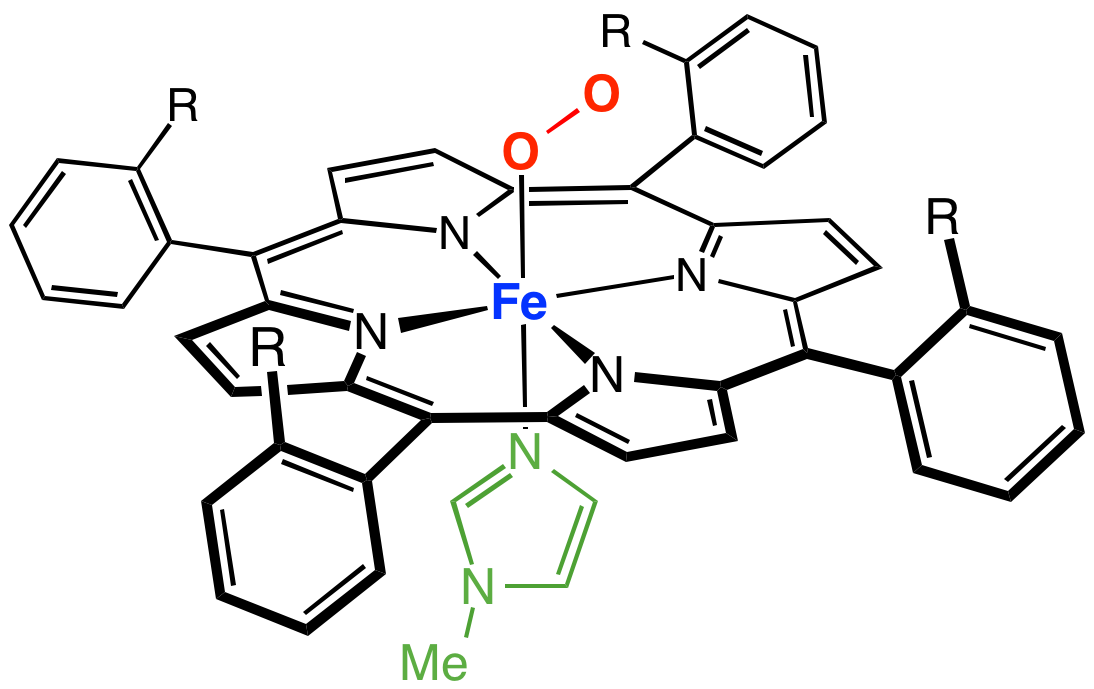
Daniel Mansuy
Daniel Mansuy is a French researcher and chemist born in 1945 in Châteauroux (Indre), a member of the French Academy of Sciences. Biography Daniel Mansuy graduated from the École nationale supérieure de chimie de Paris (now Chimie Paris Tech) in 1967 and obtained a doctorate in science from the Université Pierre-et-Marie-Curie in 1970 under the supervision of Marc Julia. He then joined the CNRS as a research manager and then director of research in 1992. He was co-founder in 1984 and director (1984-1996 and 1999-2005) of the Laboratory of Pharmaceutical and Toxicological Chemistry and Biochemistry at Paris Descartes University. He is currently Director of Research Emeritus Outstanding Class. Scientific work Daniel Mansuy is particularly interested in phenomena at the interface between chemistry and biology, and in particular in the chemistry and pharmacochemistry of cytochromes P450. His work has led to the discovery of a new class of carbene and nitrene iron complex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-molecule Electronics
Molecular scale electronics, also called single-molecule electronics, is a branch of nanotechnology that uses single molecules, or nanoscale collections of single molecules, as electronic components. Because single molecules constitute the smallest stable structures imaginable, this miniaturization is the ultimate goal for shrinking electrical circuits. The field is often termed simply as "molecular electronics", but this term is also used to refer to the distantly related field of conductive polymers and organic electronics, which uses the properties of molecules to affect the bulk properties of a material. A nomenclature distinction has been suggested so that ''molecular materials for electronics'' refers to this latter field of bulk applications, while ''molecular scale electronics'' refers to the nanoscale single-molecule applications treated here. Fundamental concepts Conventional electronics have traditionally been made from bulk materials. Ever since their invention in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron(tetraphenylporphyrinato) Chloride
Iron(tetraporphyriinato) chloride is the coordination complex with the formula Fe(TPP)Cl where TPP is the dianion 2-. The compound forms blue microcrystals that dissolve in chlorinated solvent to give brown solutions. In terms of structure, the complex is five-coordinate with idealized C4v point group symmetry. It is one of more common transition metal porphyrin complexes. Synthesis and reactions Fe(TPP)Cl is prepared by the reaction of tetraphenylporphyrin (H2TPP) and ferrous chloride in the presence of air: :H2TPP + FeCl2 + 1/4 O2 → Fe(TPP)Cl + HCl + 1/2 H2O The chloride can be replaced with other halides and pseudohalides. Base gives the "mu-oxo dimer": :2 Fe(TPP)Cl + 2 NaOH → e(TPP)sub>2O + 2 NaCl + H2O Most relevant to catalysis, the complex is easily reduced to give ferrous derivatives (L = pyridine, imidazole): :Fe(TPP)Cl + e- + 2 L → Fe(TPP)L2 + Cl− The complex is widely studied as a catalyst Catalysis () is the process o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octaethylporphyrin
Octaethylporphyrin (H2OEP) is an organic compound that is a relative of naturally occurring heme pigments. The compound is used in the preparation of models for the prosthetic group in heme proteins. It is a dark purple solid that is soluble in organic solvents. As its conjugate base OEP2-, it forms a range of transition metal porphyrin complexes. When treated with ferric chloride in hot acetic acid solution, it gives the square pyramidal complex Fe(OEP)Cl. It also forms the square planar complexes Ni(OEP) and Cu(OEP). Contrast with other porphyrins Unlike complexes of the naturally occurring porphyrins, OEP complexes have four-fold symmetry, which simplifies spectroscopic analysis. In contrast to tetraphenylporphyrin and related analogues, H2OEP features unprotected meso positions. In this way, it is a more accurate model for naturally occurring porphyrins. Synthesis H2OEP is prepared by condensation of 3,4-diethylpyrrole with formaldehyde Formaldehyde ( , ) (systema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapyrroles
Tetrapyrroles are a class of chemical compounds that contain four pyrrole or pyrrole-like rings. The pyrrole/pyrrole derivatives are linked by ( =- or -- units), in either a linear or a cyclic fashion. Pyrroles are a five-atom ring with four carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom. Tetrapyrroles are common cofactors in biochemistry and their biosynthesis and degradation feature prominently in the chemistry of life. Some tetrapyrroles form the active core of compounds with crucial biochemical roles in living systems, such as hemoglobin and chlorophyll. In these two molecules, in particular, the pyrrole macrocycle ring frames a metal atom, that forms a coordination compound with the pyrroles and plays a central role in the biochemical function of those molecules. Structure Linear tetrapyrroles (called bilanes) include: *Heme breakdown products (e.g., bilirubin, biliverdin) * Phycobilins (found in cyanobacteria) *Luciferins as found in dinoflagellates and euphausiid shrimps (krill) F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelating Agents
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are called chelants, chelators, chelating agents, or sequestering agents. They are usually organic compounds, but this is not a necessity, as in the case of zinc and its use as a maintenance therapy to prevent the absorption of copper in people with Wilson's disease. Chelation is useful in applications such as providing nutritional supplements, in chelation therapy to remove toxic metals from the body, as contrast agents in MRI scanning, in manufacturing using homogeneous catalysts, in chemical water treatment to assist in the removal of metals, and in fertilizers. Chelate effect The chelate effect is the greater affinity of chelating ligands for a metal ion than that of similar nonchelating (monodentate) ligands for the same metal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singlet Oxygen
Singlet oxygen, systematically named dioxygen(singlet) and dioxidene, is a gaseous inorganic chemical with the formula O=O (also written as or ), which is in a quantum state where all electrons are spin paired. It is kinetically unstable at ambient temperature, but the rate of decay is slow. The lowest excited state of the diatomic oxygen molecule is a singlet state. It is a gas with physical properties differing only subtly from those of the more prevalent triplet ground state of O2. In terms of its chemical reactivity, however, singlet oxygen is far more reactive toward organic compounds. It is responsible for the photodegradation of many materials but can be put to constructive use in preparative organic chemistry and photodynamic therapy. Trace amounts of singlet oxygen are found in the upper atmosphere and also in polluted urban atmospheres where it contributes to the formation of lung-damaging nitrogen dioxide. It often appears and coexists confounded in environments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosensitizer
Photosensitizers produce a physicochemical change in a neighboring molecule by either donating an electron to the substrate or by abstracting a hydrogen atom from the substrate. At the end of this process, the photosensitizer eventually returns to its ground state, where it remains chemically intact until the photosensitizer absorbs more light. This means that the photosensitizer remains unchanged before and after the energetic exchange, much like heterogeneous photocatalysis. One branch of chemistry which frequently utilizes photosensitizers is polymer chemistry, using photosensitizers in reactions such as photopolymerization, photocrosslinking, and photodegradation. Photosensitizers are also used to generate prolonged excited electronic states in organic molecules with uses in photocatalysis, photon upconversion and photodynamic therapy. Generally, photosensitizers absorb electromagnetic radiation consisting of infrared radiation, visible light radiation, and ultraviolet radiati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
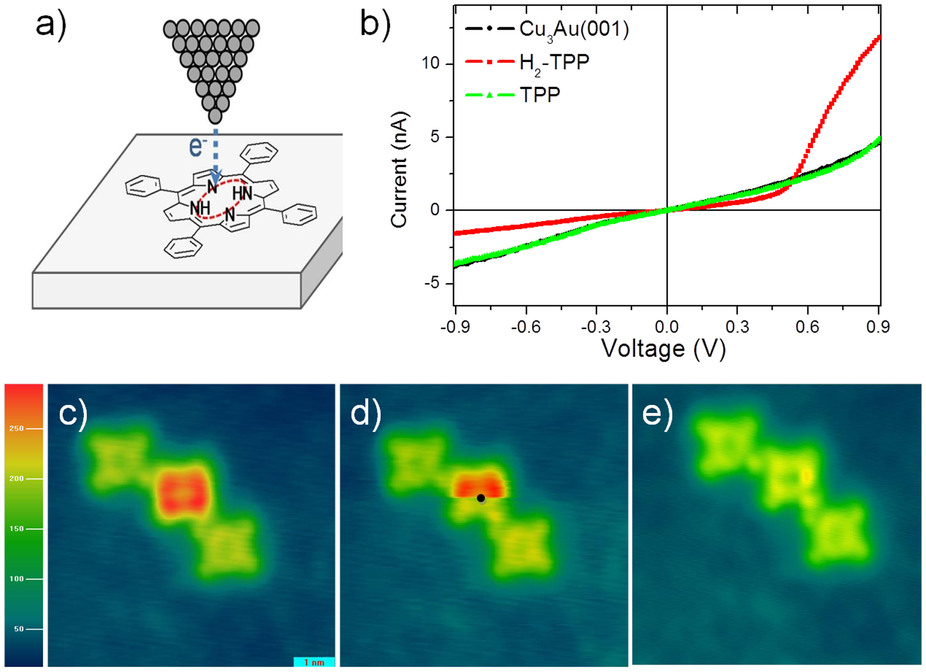
Dehydrogenation Of H2TPP By STM
In chemistry, dehydrogenation is a chemical reaction that involves the removal of hydrogen, usually from an organic molecule. It is the reverse of hydrogenation. Dehydrogenation is important, both as a useful reaction and a serious problem. At its simplest, it is useful way of converting alkanes, which are relatively inert and thus low-valued, to olefins, which are reactive and thus more valuable. Alkenes are precursors to aldehydes (), alcohols (), polymers, and aromatics. As a problematic reaction, the fouling and inactivation of many catalysts arises via coking, which is the dehydrogenative polymerization of organic substrates. Enzymes that catalyze dehydrogenation are called dehydrogenases. Heterogeneous catalytic routes Styrene Dehydrogenation processes are used extensively to produce aromatics in the petrochemical industry. Such processes are highly endothermic and require temperatures of 500 °C and above. Dehydrogenation also converts saturated fats to unsat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
