Myoglobin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Myoglobin (symbol Mb or MB) is an
/ref> Despite being one of the most studied proteins in biology, its physiological function is not yet conclusively established: mice genetically engineered to lack myoglobin can be viable and fertile, but show many cellular and physiological adaptations to overcome the loss. Through observing these changes in myoglobin-depleted mice, it is hypothesised that myoglobin function relates to increased oxygen transport to muscle, and to oxygen storage; as well, it serves as a scavenger of
File:MbO2MO.png, Molecular orbital description of Fe-O2 interaction in myoglobin.
File:1a6m Oxy-Myoglobin.jpg, This is an image of an oxygenated myoglobin molecule. The image shows the structural change when oxygen is bound to the iron atom of the heme prosthetic group. The oxygen atoms are colored in green, the iron atom is colored in red, and the heme group is colored in blue.
Proteopedia article about this finding
The Myoglobin Protein
''The New York Times'', February 21, 2006 article regarding meat industry use of carbon monoxide to keep meat looking red.
''The New York Times'', March 1, 2006 article on the use of carbon monoxide to make meat appear fresh. * {{Authority control Hemoproteins Human proteins
iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
- and oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
-binding protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
found in the cardiac and skeletal
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ...
muscle tissue
Muscle tissue (or muscular tissue) is soft tissue that makes up the different types of muscles in most animals, and give the ability of muscles to contract. Muscle tissue is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. Mu ...
of vertebrates in general and in almost all mammals. Myoglobin is distantly related to hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocyte ...
. Compared to hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocyte ...
, myoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen and does not have cooperative binding
Molecular binding is an interaction between molecules that results in a stable physical association between those molecules. Cooperative binding occurs in binding systems containing more than one type, or species, of molecule and in which one of th ...
with oxygen like hemoglobin does. In humans, myoglobin is only found in the bloodstream after muscle injury. (Google books link is the 2008 edition)
High concentrations of myoglobin in muscle cells allow organisms to hold their breath for a longer period of time. Diving mammals such as whales and seals have muscles with particularly high abundance of myoglobin. Myoglobin is found in Type I muscle, Type II A, and Type II B; although many texts consider myoglobin not to be found in smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit mus ...
, this has proved erroneous: there is also myoglobin in smooth muscle cells.
Myoglobin was the first protein to have its three-dimensional structure revealed by X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
. This achievement was reported in 1958 by John Kendrew
Sir John Cowdery Kendrew, (24 March 1917 – 23 August 1997) was an English biochemist, crystallographer, and science administrator. Kendrew shared the 1962 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Max Perutz, for their work at the Cavendish Labo ...
and associates. For this discovery, Kendrew shared the 1962 Nobel Prize in chemistry
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "M ...
with Max Perutz
Max Ferdinand Perutz (19 May 1914 – 6 February 2002) was an Austrian-born British molecular biologist, who shared the 1962 Nobel Prize for Chemistry with John Kendrew, for their studies of the structures of haemoglobin and myoglobin. He went ...
.The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1962/ref> Despite being one of the most studied proteins in biology, its physiological function is not yet conclusively established: mice genetically engineered to lack myoglobin can be viable and fertile, but show many cellular and physiological adaptations to overcome the loss. Through observing these changes in myoglobin-depleted mice, it is hypothesised that myoglobin function relates to increased oxygen transport to muscle, and to oxygen storage; as well, it serves as a scavenger of
reactive oxygen species
In chemistry, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (). Examples of ROS include peroxides, superoxide, hydroxyl radical, singlet oxygen, and alpha-oxygen.
The reduction of molecular oxygen () p ...
.
In humans, myoglobin is encoded by the ''MB'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
.
Myoglobin can take the forms oxymyoglobin (MbO2), carboxymyoglobin (MbCO), and metmyoglobin Metmyoglobin is the oxidized form of the oxygen-carrying hemeprotein myoglobin.
Metmyoglobin is the cause of the characteristic brown colouration of meat that occurs as it ages.
In living muscle, the concentration of metmyoglobin is vanishingly sm ...
(met-Mb), analogously to hemoglobin taking the forms oxyhemoglobin (HbO2), carboxyhemoglobin
Carboxyhemoglobin (carboxyhaemoglobin BrE) (symbol COHb or HbCO) is a stable complex of carbon monoxide and hemoglobin (Hb) that forms in red blood cells upon contact with carbon monoxide. Carboxyhemoglobin is often mistaken for the compound form ...
(HbCO), and methemoglobin
Methemoglobin (British: methaemoglobin) (pronounced "met-hemoglobin") is a hemoglobin ''in the form of metalloprotein'', in which the iron in the heme group is in the Fe3+ (ferric) state, not the Fe2+ (ferrous) of normal hemoglobin. Sometimes, it i ...
(met-Hb).
Differences from hemoglobin
Like hemoglobin, myoglobin is a cytoplasmic protein that binds oxygen on aheme
Heme, or haem (pronounced / hi:m/ ), is a precursor to hemoglobin, which is necessary to bind oxygen in the bloodstream. Heme is biosynthesized in both the bone marrow and the liver.
In biochemical terms, heme is a coordination complex "consisti ...
group. It harbors only one globulin group, whereas hemoglobin has four. Although its heme group is identical to those in Hb, Mb has a higher affinity for oxygen than does hemoglobin. This difference is related to its different role: whereas hemoglobin transports oxygen, myoglobin's function is to store oxygen.
Role in cuisine
Myoglobin contains hemes,pigment
A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compo ...
s responsible for the colour of red meat
In gastronomy, red meat is commonly red when raw and a dark color after it is cooked, in contrast to white meat, which is pale in color before and after cooking. In culinary terms, only flesh from mammals or fowl (not fish) is classified as ...
. The colour that meat takes is partly determined by the degree of oxidation of the myoglobin. In fresh meat the iron atom is in the ferrous (+2) oxidation state bound to an oxygen molecule (O2). Meat cooked well done
Doneness is a gauge of how thoroughly cooked a cut of meat is based on its color, juiciness, and internal temperature. The gradations are most often used in reference to beef (especially steaks and roasts) but are also applicable to other type ...
is brown because the iron atom is now in the ferric (+3) oxidation state, having lost an electron. If meat has been exposed to nitrites
The nitrite ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite also re ...
, it will remain pink because the iron atom is bound to NO, nitric oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its che ...
(true of, e.g., corned beef
Corned beef, or salt beef in some of the Commonwealth of Nations, is Salt-cured meat, salt-cured brisket of beef. The term comes from the treatment of the meat with large-grained rock salt, also called "corns" of salt. Sometimes, sugar and sp ...
or cured ham
Ham is pork from a leg cut of pork, cut that has been food preservation, preserved by wet or dry Curing (food preservation), curing, with or without smoking (cooking), smoking."Bacon: Bacon and Ham Curing" in ''Chambers's Encyclopædia''. Lo ...
s). Grilled meats can also take on a reddish pink "smoke ring" that comes from the heme center binding to carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simple ...
. Raw meat packed in a carbon monoxide atmosphere also shows this same pink "smoke ring" due to the same principles. Notably, the surface of this raw meat also displays the pink color, which is usually associated in consumers' minds with fresh meat. This artificially induced pink color can persist, reportedly up to one year. Hormel and Cargill (meat processing companies in the US) are both reported to use this meat-packing process, and meat treated this way has been in the consumer market since 2003.
Role in disease
Myoglobin is released from damaged muscle tissue (rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis (also called rhabdo) is a condition in which damaged skeletal muscle breaks down rapidly. Symptoms may include muscle pains, weakness, vomiting, and confusion. There may be tea-colored urine or an irregular heartbeat. Some of th ...
), which has very high concentrations of myoglobin. The released myoglobin is filtered by the kidneys
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood ...
but is toxic to the renal tubular epithelium and so may cause acute kidney injury
Acute kidney injury (AKI), previously called acute renal failure (ARF), is a sudden decrease in kidney function that develops within 7 days, as shown by an increase in serum creatinine or a decrease in urine output, or both.
Causes of AKI are cla ...
. It is not the myoglobin itself that is toxic (it is a protoxin
Toxication, toxification or toxicity exaltation is the conversion of a chemical compound into a more toxic form in living organisms or in substrates such as soil or water. The conversion can be caused by enzymatic metabolism in the organisms, as we ...
) but the ferrihemate portion that is dissociated from myoglobin in acidic environments (e.g., acidic urine, lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane prot ...
s).
Myoglobin is a sensitive marker for muscle injury, making it a potential marker for heart attack
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may tr ...
in patients with chest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with n ...
. However, elevated myoglobin has low specificity for acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and thus CK-MB
The CPK-MB test (creatine phosphokinase-MB), also known as CK-MB test, is a cardiac marker used to assist diagnoses of an acute myocardial infarction, myocardial ischemia, or myocarditis. It measures the blood level of CK-MB (creatine kinase myoca ...
, cardiac troponin, ECG
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart's electrical activity. It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of the electrical activity of the hear ...
, and clinical signs should be taken into account to make the diagnosis.
Structure and bonding
Myoglobin belongs to theglobin
The globins are a superfamily of heme-containing globular proteins, involved in binding and/or transporting oxygen. These proteins all incorporate the globin fold, a series of eight alpha helical segments. Two prominent members include myo ...
superfamily of proteins, and as with other globins, consists of eight alpha helices
The alpha helix (α-helix) is a common motif in the secondary structure of proteins and is a right hand-helix conformation in which every backbone N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid located four residues ear ...
connected by loops. Myoglobin contains 153 amino acids.
Myoglobin contains a porphyrin
Porphyrins ( ) are a group of heterocyclic macrocycle organic compounds, composed of four modified pyrrole subunits interconnected at their α carbon atoms via methine bridges (=CH−). The parent of porphyrin is porphine, a rare chemical com ...
ring with an iron at its center. A ''proximal'' histidine
Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated –NH3+ form under biological conditions), a carboxylic acid group (which is in the de ...
group (His-93) is attached directly to iron, and a ''distal'' histidine group (His-64) hovers near the opposite face. The distal imidazole is not bonded to the iron but is available to interact with the substrate O2. This interaction encourages the binding of O2, but not carbon monoxide (CO), which still binds about 240× more strongly than O2.
The binding of O2 causes substantial structural change at the Fe center, which shrinks in radius and moves into the center of N4 pocket. O2-binding induces "spin-pairing": the five-coordinate ferrous deoxy form is high spin Spin states when describing transition metal coordination complexes refers to the potential spin configurations of the central metal's d electrons. For several oxidation states, metals can adopt high-spin and low-spin configurations. The ambiguity o ...
and the six coordinate oxy form is low spin and diamagnetic
Diamagnetic materials are repelled by a magnetic field; an applied magnetic field creates an induced magnetic field in them in the opposite direction, causing a repulsive force. In contrast, paramagnetic and ferromagnetic materials are attracted ...
.
Synthetic analogues
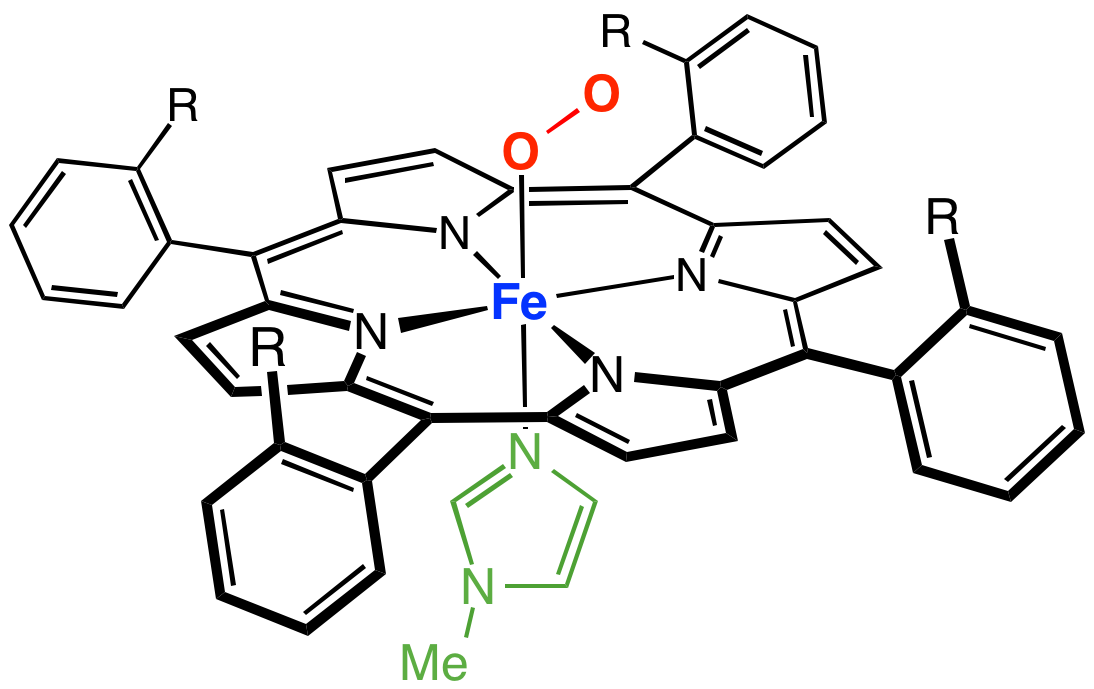
Many models of myoglobin have been synthesized as part of a broad interest intransition metal dioxygen complex
Transition or transitional may refer to:
Mathematics, science, and technology Biology
* Transition (genetics), a point mutation that changes a purine nucleotide to another purine (A ↔ G) or a pyrimidine nucleotide to another pyrimidine (C ↔ ...
es. A well known example is the ''picket fence porphyrin'', which consists of a ferrous complex of a sterically bulky derivative of tetraphenylporphyrin
Tetraphenylporphyrin, abbreviated TPP or H2TPP, is a synthetic heterocyclic compound that resembles naturally occurring porphyrins. Porphyrins are dyes and cofactors found in hemoglobin and cytochromes and are related to chlorophyll and vitamin ...
. In the presence of an imidazole
Imidazole (ImH) is an organic compound with the formula C3N2H4. It is a white or colourless solid that is soluble in water, producing a mildly alkaline solution. In chemistry, it is an aromatic heterocycle, classified as a diazole Diazole refers ...
ligand, this ferrous complex reversibly binds O2. The O2 substrate adopts a bent geometry, occupying the sixth position of the iron center. A key property of this model is the slow formation of the μ-oxo dimer, which is an inactive diferric state. In nature, such deactivation pathways are suppressed by protein matrix that prevents close approach of the Fe-porphyrin assemblies.
:
See also
*Cytoglobin
Cytoglobin is the protein product of CYGB, a human and mammalian gene.
Cytoglobin is a globin molecule ubiquitously expressed in all tissues and most notably utilized in marine mammals. It was discovered in 2001 and named cytoglobin in 2002. It i ...
* Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocyte ...
* Hemoprotein
A hemeprotein (or haemprotein; also hemoprotein or haemoprotein), or heme protein, is a protein that contains a heme prosthetic group. They are a very large class of metalloproteins. The heme group confers functionality, which can include oxygen ...
* Neuroglobin
Neuroglobin is a member of the vertebrate globin family involved in cellular oxygen homeostasis and reactive oxygen/nitrogen scavenging. It is an intracellular hemoprotein expressed in the central and peripheral nervous system, cerebrospinal fluid ...
* Phytoglobin
Phytoglobins are globular plant (algae and land plant) proteins classified into the globin superfamily, which contain a heme, ''i''.''e''. protoporphyrin IX-Fe, prosthetic group. The earliest known phytoglobins are leghemoglobins, discovered in 1 ...
* Myoglobinuria
Myoglobinuria is the presence of myoglobin in the urine, which usually results from rhabdomyolysis or muscle injury. Myoglobin is present in muscle cells as a reserve of oxygen.
Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms of myoglobinuria are usual ...
- The presence of myoglobin in the urine
* Ischemia-reperfusion injury of the appendicular musculoskeletal system Ischemia-reperfusion (IR) tissue injury is the resultant pathology from a combination of factors, including tissue hypoxia, followed by tissue damage associated with re-oxygenation. IR injury contributes to disease and mortality in a variety of pa ...
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * . Also seProteopedia article about this finding
External links
* human geneticsThe Myoglobin Protein
''The New York Times'', February 21, 2006 article regarding meat industry use of carbon monoxide to keep meat looking red.
''The New York Times'', March 1, 2006 article on the use of carbon monoxide to make meat appear fresh. * {{Authority control Hemoproteins Human proteins