|
Methemoglobin
Methemoglobin (British: methaemoglobin) (pronounced "met-hemoglobin") is a hemoglobin ''in the form of metalloprotein'', in which the iron in the heme group is in the Fe3+ (ferric) state, not the Fe2+ (ferrous) of normal hemoglobin. Sometimes, it is also referred to as ferrihemoglobin. Methemoglobin cannot bind oxygen, which means it cannot carry oxygen to tissues. It is bluish chocolate-brown in color. In human blood a trace amount of methemoglobin is normally produced spontaneously, but when present in excess the blood becomes abnormally dark bluish brown. The NADH-dependent enzyme methemoglobin reductase ( a type of diaphorase) is responsible for converting methemoglobin back to hemoglobin. Normally one to two percent of a person's hemoglobin is methemoglobin; a higher percentage than this can be genetic or caused by exposure to various chemicals and depending on the level can cause health problems known as methemoglobinemia. A higher level of methemoglobin will tend to cause a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methemoglobinemia
Methemoglobinemia, or methaemoglobinaemia, is a condition of elevated methemoglobin in the blood. Symptoms may include headache, dizziness, shortness of breath, nausea, poor muscle coordination, and blue-colored skin (cyanosis). Complications may include seizures and heart arrhythmias. Methemoglobinemia can be due to certain medications, chemicals, or food or it can be inherited from a person's parents. Substances involved may include benzocaine, nitrates, or dapsone. The underlying mechanism involves some of the iron in hemoglobin being converted from the ferrous e2+to the ferric e3+form. The diagnosis is often suspected based on symptoms and a low blood oxygen that does not improve with oxygen therapy. Diagnosis is confirmed by a blood gas. Treatment is generally with oxygen therapy and methylene blue. Other treatments may include vitamin C, exchange transfusion, and hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Outcomes are generally good with treatment. Methemoglobinemia is relatively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methemoglobin Crystal Structure
Methemoglobin (British: methaemoglobin) (pronounced "met-hemoglobin") is a hemoglobin ''in the form of metalloprotein'', in which the iron in the heme group is in the Fe3+ ( ferric) state, not the Fe2+ ( ferrous) of normal hemoglobin. Sometimes, it is also referred to as ferrihemoglobin. Methemoglobin cannot bind oxygen, which means it cannot carry oxygen to tissues. It is bluish chocolate-brown in color. In human blood a trace amount of methemoglobin is normally produced spontaneously, but when present in excess the blood becomes abnormally dark bluish brown. The NADH-dependent enzyme methemoglobin reductase ( a type of diaphorase) is responsible for converting methemoglobin back to hemoglobin. Normally one to two percent of a person's hemoglobin is methemoglobin; a higher percentage than this can be genetic or caused by exposure to various chemicals and depending on the level can cause health problems known as methemoglobinemia. A higher level of methemoglobin will tend to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoglobin M Disease
Hemoglobin M disease is a rare form of hemoglobinopathy, characterized by the presence of hemoglobin M (HbM) and elevated methemoglobin (metHb) level in blood. HbM is an altered form of hemoglobin (Hb) due to point mutation occurring in globin-encoding genes, mostly involving tyrosine substitution for proximal (F8) or distal (E7) histidine residues. HbM variants are inherited as autosomal dominant disorders and have altered oxygen affinity. The pathophysiology of hemoglobin M disease involves heme iron autoxidation promoted by heme pocket structural alteration. There exists at least 13 HbM variants, such as Boston, Osaka, Saskatoon, etc., named according to their geographical locations of discovery. Different HbM variants may give different signs and symptoms. Major signs include cyanosis and dark brown blood. Patients may be asymptomatic or experience dizziness, headache, mild dyspnea, etc. Diagnosis is usually suspected based on cyanosis. Biochemical testing, hemoglobin electrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dapsone
Dapsone, also known as 4,4'-sulfonyldianiline (SDA) or diaminodiphenyl sulfone (DDS), is an antibiotic commonly used in combination with rifampicin and clofazimine for the treatment of leprosy. It is a second-line medication for the treatment and prevention of pneumocystis pneumonia and for the prevention of toxoplasmosis in those who have poor immune function. Additionally, it has been used for acne, dermatitis herpetiformis, and various other skin conditions. Dapsone is available both topically and by mouth. Severe side effects may include a decrease in blood cells, red blood cell breakdown especially in those with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G-6-PD), or hypersensitivity. Common side effects include nausea and loss of appetite. Other side effects include liver inflammation, methemoglobinemia, and a number of types of skin rashes. While the safety of use during pregnancy is not entirely clear some physicians recommend that it be continued in those with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzocaine
Benzocaine, sold under the brand name Orajel amongst others, is an ester local anesthetic commonly used as a topical pain reliever or in cough drops. It is the active ingredient in many over-the-counter anesthetic ointments such as products for oral ulcers. It is also combined with antipyrine to form A/B otic drops to relieve ear pain and remove earwax. In the US, products containing benzocaine for oral application are contraindicated in children younger than two years old. In the European Union, the contraindication applies to children under 12 years of age. It was first synthesised in 1890 in Germany and approved for medical use in 1902. Medical uses Benzocaine is indicated to treat a variety of pain-related conditions. It may be used for: * Local anesthesia of oral and pharyngeal mucous membranes (sore throat, cold sores, mouth ulcers, toothache, sore gums, denture irritation)AHFS Drug Information 2007. McEvoy GK, ed. Benzocaine. Bethesda, MD: American Society o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
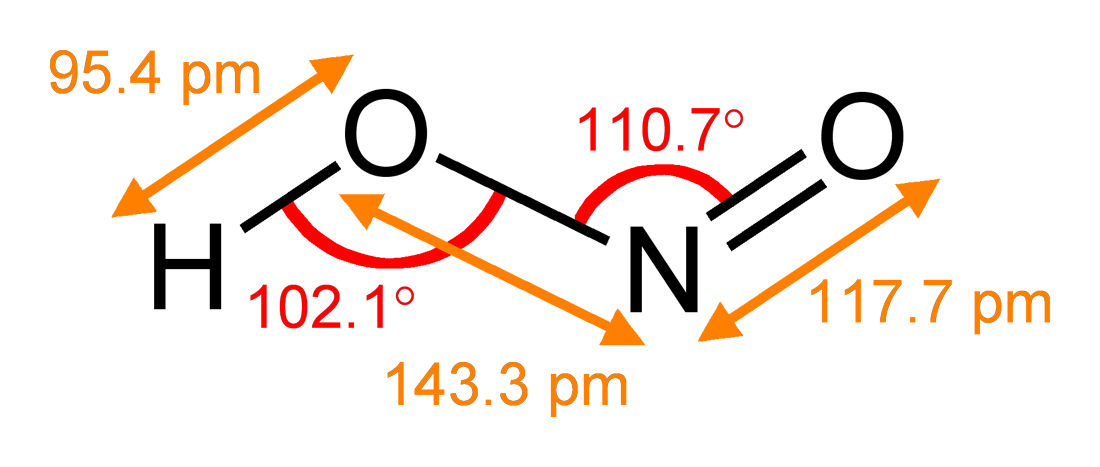
Nitrates
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are soluble in water. An example of an insoluble nitrate is bismuth oxynitrate. Structure The ion is the conjugate base of nitric acid, consisting of one central nitrogen atom surrounded by three identically bonded oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement. The nitrate ion carries a formal charge of −1. This charge results from a combination formal charge in which each of the three oxygens carries a − charge, whereas the nitrogen carries a +1 charge, all these adding up to formal charge of the polyatomic nitrate ion. This arrangement is commonly used as an example of resonance. Like the isoelectronic carbonate ion, the nitrate ion can be represented by resonance structures: Dietary nitrate A rich source of inorganic nitrate in the human diets come from leafy gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methemoglobin Reductase
Cytochrome-''b''5 reductase is a NADH-dependent enzyme that converts ferricytochrome from a Fe3+ form to a Fe2+ form. It contains FAD and catalyzes the reaction: In its b5-reducing capacity, this enzyme is involved in desaturation and elongation of fatty acids, cholesterol biosynthesis, and drug metabolism. This enzyme can also reduce methemoglobin to normal hemoglobin Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocyte ..., gaining it the inaccurate synonym methemoglobin reductase. Isoforms expressed in erythrocytes (CYB5R1, CYB5R3) perform this function ''in vivo''. Ferricyanide is another substrate ''in vitro''. The following four human genes encode cytochrome-''b''5 reductases: * CYB5R1 * CYB5R2 * CYB5R3 * CYB5R4 * CYB5RL See also * Cytochrome b5 * Diaphorase * Methem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome B5 Reductase
Cytochrome-''b''5 reductase is a NADH-dependent enzyme Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ... that converts ferricytochrome from a Fe3+ form to a Fe2+ form. It contains FAD and catalyzes the reaction: In its b5-reducing capacity, this enzyme is involved in desaturation and elongation of fatty acids, cholesterol biosynthesis, and drug metabolism. This enzyme can also reduce methemoglobin to normal hemoglobin, gaining it the inaccurate synonym methemoglobin reductase. Isoforms expressed in erythrocytes (CYB5R1, CYB5R3) perform this function ''in vivo''. Ferricyanide is another substrate ''in vitro''. The following four human genes encode cytochrome-''b''5 reductases: * CYB5R1 * CYB5R2 * CYB5R3 * CYB5R4 * CYB5RL See also * Cytochrome b5 * Diaphorase * Meth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
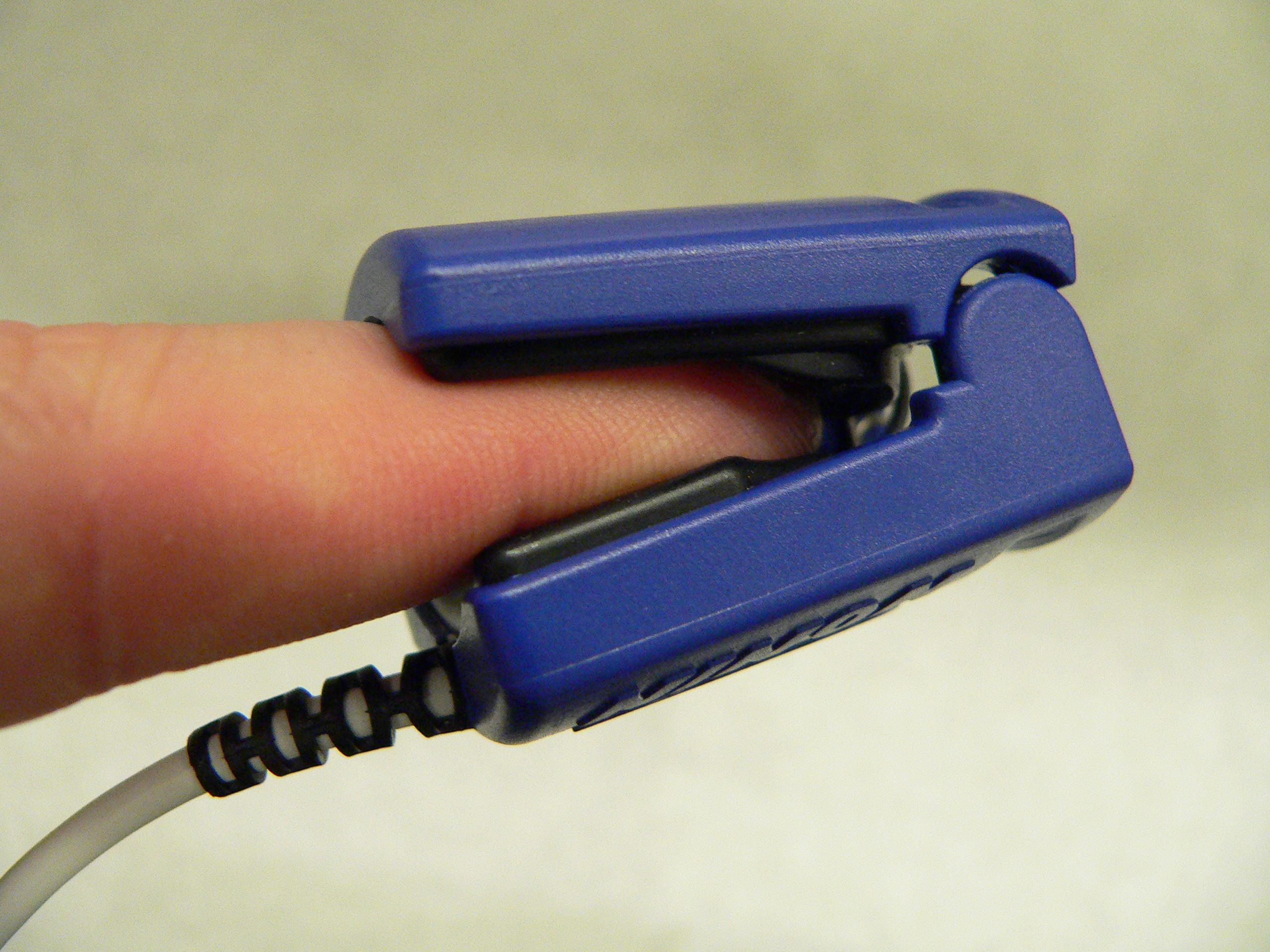
Pulse Oximeter
Pulse oximetry is a noninvasive method for monitoring a person's oxygen saturation. Peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) readings are typically within 2% accuracy (within 4% accuracy in 95% of cases) of the more accurate (and invasive) reading of arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) from arterial blood gas analysis. But the two are correlated well enough that the safe, convenient, noninvasive, inexpensive pulse oximetry method is valuable for measuring oxygen saturation in clinical use. The most common approach is ''transmissive pulse oximetry''. In this approach, a sensor device is placed on a thin part of the patient's body, usually a fingertip or earlobe, or an infant's foot. Fingertips and earlobes have higher blood flow rates than other tissues, which facilitates heat transfer. The device passes two wavelengths of light through the body part to a photodetector. It measures the changing absorbance at each of the wavelengths, allowing it to determine the absorbances due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocytes) of almost all vertebrates (the exception being the fish family Channichthyidae) as well as the tissues of some invertebrates. Hemoglobin in blood carries oxygen from the respiratory organs (''e.g.'' lungs or gills) to the rest of the body (''i.e.'' tissues). There it releases the oxygen to permit aerobic respiration to provide energy to power functions of an organism in the process called metabolism. A healthy individual human has 12to 20grams of hemoglobin in every 100mL of blood. In mammals, the chromoprotein makes up about 96% of the red blood cells' dry content (by weight), and around 35% of the total content (including water). Hemoglobin has an oxygen-binding capacity of 1.34mL O2 per gram, which increases the total blood oxygen ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyl Nitrite
Amyl nitrite is a chemical compound with the formula C5H11ONO. A variety of isomers are known, but they all feature an amyl group attached to the nitrite functional group. The alkyl group is unreactive and the chemical and biological properties are mainly due to the nitrite group. Like other alkyl nitrites, amyl nitrite is bioactive in mammals, being a vasodilator, which is the basis of its use as a prescription medicine. As an inhalant, it also has a psychoactive effect, which has led to its recreational use, with its smell being described as that of old socks or dirty feet. It is also referred to as ''banapple gas''. It was first documented in 1844 and came into medical use in 1867. Uses * Amyl nitrite is employed medically to treat heart diseases as well as angina. * Amyl nitrite is sometimes used as an antidote for cyanide poisoning. It can act as an oxidant, to induce the formation of methemoglobin. Methemoglobin in turn can sequester cyanide as cyanomethemoglobin. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrites
The nitrite ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite also refers to organic compounds having the –ONO group, which are esters of nitrous acid. Production Sodium nitrite is made industrially by passing a mixture of nitrogen oxides into aqueous sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate solution: : The product is purified by recrystallization. Alkali metal nitrites are thermally stable up to and beyond their melting point (441 °C for KNO2). Ammonium nitrite can be made from dinitrogen trioxide, N2O3, which is formally the anhydride of nitrous acid: :2 NH3 + H2O + N2O3 → 2 NH4NO2 Structure The nitrite ion has a symmetrical structure (C2v symmetry), with both N–O bonds having equal length and a bond angle of about 115°. In valence bond theory, it is described as a resonance hybrid with e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

2.jpg)