|
Iron(tetraphenylporphyrinato) Chloride
Iron(tetraporphyriinato) chloride is the coordination complex with the formula Fe(TPP)Cl where TPP is the dianion 2-. The compound forms blue microcrystals that dissolve in chlorinated solvent to give brown solutions. In terms of structure, the complex is five-coordinate with idealized C4v point group symmetry. It is one of more common transition metal porphyrin complexes. Synthesis and reactions Fe(TPP)Cl is prepared by the reaction of tetraphenylporphyrin (H2TPP) and ferrous chloride in the presence of air: :H2TPP + FeCl2 + 1/4 O2 → Fe(TPP)Cl + HCl + 1/2 H2O The chloride can be replaced with other halides and pseudohalides. Base gives the "mu-oxo dimer": :2 Fe(TPP)Cl + 2 NaOH → e(TPP)sub>2O + 2 NaCl + H2O Most relevant to catalysis, the complex is easily reduced to give ferrous derivatives (L = pyridine, imidazole): :Fe(TPP)Cl + e- + 2 L → Fe(TPP)L2 + Cl− The complex is widely studied as a catalyst Catalysis () is the process o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Complex
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the Periodic Table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom are common. These compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Metal Porphyrin Complexes
220px, A picket-fence porphyrin complex of Fe, with axial coordination sites occupied by methylimidazole (green) and dioxygen (R = amide groups). Transition metal porphyrin complexes are a family of coordination complexes of the conjugate base of porphyrins. Iron porphyrin complexes occur widely in Nature, which has stimulated extensive studies on related synthetic complexes. The metal-porphyrin interaction is a strong one such that metalloporphyrins are thermally robust. They are catalysts and exhibit rich optical properties, although these complexes remain mainly of academic interest. Formation Metal porphyrin complexes are almost always prepared by direct reaction of a metal halide with the free porphyrin, abbreviated here as H2P: :MClx + H2P → M(P)Cl2−x + 2HCl Two pyrrole protons are lost. The porphyrin dianion is an L2X2 ligand. These syntheses require somewhat forcing conditions, consistent with the tight fit of the metal in the N42- "pocket." In nature, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
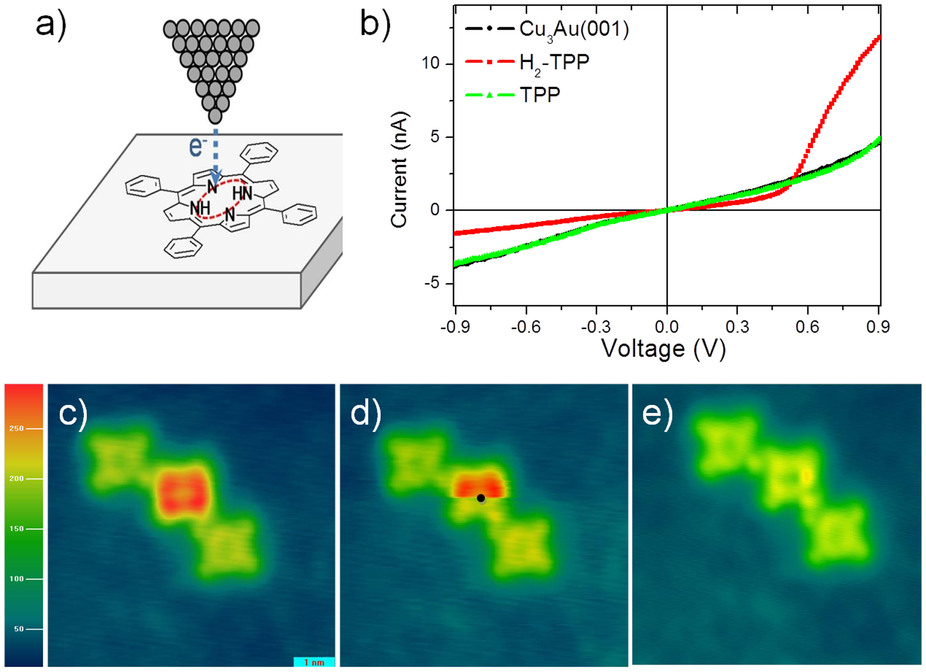
Tetraphenylporphyrin
Tetraphenylporphyrin, abbreviated TPP or H2TPP, is a synthetic heterocyclic compound that resembles naturally occurring porphyrins. Porphyrins are dyes and cofactors found in hemoglobin and cytochromes and are related to chlorophyll and vitamin B12. The study of naturally occurring porphyrins is complicated by their low symmetry and the presence of polar substituents. Tetraphenylporphyrin is hydrophobic, symmetrically substituted, and easily synthesized. The compound is a dark purple solid that dissolves in nonpolar organic solvents such as chloroform and benzene. Synthesis and structure Tetraphenylporphyrin was first synthesized in 1935 by Rothemund, who caused benzaldehyde and pyrrole to react in a sealed bomb at 150 °C for 24 h. Adler and Longo modified the Rothemund method by allowing benzaldehyde and pyrrole to react for 30 min in refluxing propionic acid (141 °C) open to the air: :8 C4H4NH + 8 C6H5CHO + 3 O2 → 2 (C6H5C)4(C4H2N)2(C4H2NH)2 + 14 H2O D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyridine
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group replaced by a nitrogen atom. It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a distinctive, unpleasant fish-like smell. Pyridine is colorless, but older or impure samples can appear yellow, due to the formation of extended, unsaturated polymeric chains, which show significant electrical conductivity. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. Historically, pyridine was produced from coal tar. As of 2016, it is synthesized on the scale of about 20,000 tons per year worldwide. Properties Physical properties The molecular electric dipole moment is 2.2 debyes. Pyridine is diamagnetic and has a diamagnetic susceptibility of −48.7 × 10−6 cm3·mol−1. The standard enthalpy of formation is 100.2 kJ·mol−1 in the liquid phase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imidazole
Imidazole (ImH) is an organic compound with the formula C3N2H4. It is a white or colourless solid that is soluble in water, producing a mildly alkaline solution. In chemistry, it is an aromatic heterocycle, classified as a diazole Diazole refers to either one of a pair of isomeric chemical compounds with molecular formula C3H4N2, having a five-membered ring consisting of three carbon atoms and two nitrogen atoms. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usually gaseous or liquid) as the reactant, or heterogeneous, whose components are not in the same phase. Enzymes and other biocatalysts are often considered as a third category. Catalysis is ubiquitous in chemical industry of all kinds. Estimates are that 90% of all commercially produced chemical products involve catalysts at some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelating Agents
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are called chelants, chelators, chelating agents, or sequestering agents. They are usually organic compounds, but this is not a necessity, as in the case of zinc and its use as a maintenance therapy to prevent the absorption of copper in people with Wilson's disease. Chelation is useful in applications such as providing nutritional supplements, in chelation therapy to remove toxic metals from the body, as contrast agents in MRI scanning, in manufacturing using homogeneous catalysts, in chemical water treatment to assist in the removal of metals, and in fertilizers. Chelate effect The chelate effect is the greater affinity of chelating ligands for a metal ion than that of similar nonchelating (monodentate) ligands for the same metal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapyrroles
Tetrapyrroles are a class of chemical compounds that contain four pyrrole or pyrrole-like rings. The pyrrole/pyrrole derivatives are linked by ( =- or -- units), in either a linear or a cyclic fashion. Pyrroles are a five-atom ring with four carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom. Tetrapyrroles are common cofactors in biochemistry and their biosynthesis and degradation feature prominently in the chemistry of life. Some tetrapyrroles form the active core of compounds with crucial biochemical roles in living systems, such as hemoglobin and chlorophyll. In these two molecules, in particular, the pyrrole macrocycle ring frames a metal atom, that forms a coordination compound with the pyrroles and plays a central role in the biochemical function of those molecules. Structure Linear tetrapyrroles (called bilanes) include: *Heme breakdown products (e.g., bilirubin, biliverdin) * Phycobilins (found in cyanobacteria) *Luciferins as found in dinoflagellates and euphausiid shrimps (krill) F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrocycles
Macrocycles are often described as molecules and ions containing a ring of twelve or more atoms. Classical examples include the crown ethers, calixarenes, porphyrins, and cyclodextrins. Macrocycles describe a large, mature area of chemistry. Synthesis The formation of macrocycles by ring-closure is called macrocylization. Pioneering work was reported for studies on terpenoid macrocycles. The central challenge to macrocyclization is that ring-closing reactions do not favor the formation of large rings. Instead, small rings or polymers tend to form. This kinetic problem can be addressed by using high-dilution reactions, whereby intramolecular processes are favored relative to polymerizations. Some macrocyclizations are favored using template reactions. Templates are ions, molecules, surfaces etc. that bind and pre-organize compounds, guiding them toward formation of a particular ring size. The crown ethers are often generated in the presence of an alkali metal cation, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |