|
Tympan
A tympan is any drum-like object. Astrolabes In an astrolabe, a tympan is a metal plate on which the coordinates of the celestial sphere (azimuth and altitude) are engraved in a stereographic projection. A tympan is specific to a particular latitude, so most astrolabes come with a set of interchangeable tympans suitable for use at different latitudes, usually those of particular cities of importance (Cairo, Mecca, Medina, Jerusalem...). Printing In hand-operated letterpress printing, the bruzer tympan is the taut cloth or paper mounted in a frame which is placed over the sheet of paper immediately prior to lowering the platen A platen (or platten) is a platform with a variety of roles in printing or manufacturing. It can be a flat metal (or earlier, wooden) plate pressed against a medium (such as paper) to cause an impression in letterpress printing. Platen may al ... to make the impression. The Bruzer's Tympan is a sheet of oiled manilla paper which was securely fastened ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrolabe
An astrolabe (; ; ) is an astronomy, astronomical list of astronomical instruments, instrument dating to ancient times. It serves as a star chart and Model#Physical model, physical model of the visible celestial sphere, half-dome of the sky. Its various functions also make it an elaborate inclinometer and an analog computer, analog calculation device capable of working out several kinds of problems in astronomy. In its simplest form it is a metal disc with a pattern of wires, cutouts, and perforations that allows a user to calculate astronomical positions precisely. It is able to measure the horizontal coordinate system, altitude above the horizon of a celestial body, day or night; it can be used to identify stars or planets, to determine local latitude given local time (and vice versa), to survey, or to triangulation, triangulate. It was used in classical antiquity, the Islamic Golden Age, the European Middle Ages and the Age of Discovery for all these purposes. The astrolabe, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated with having electrons available at the Fermi level, as against nonmetallic materials which do not. Metals are typically ductile (can be drawn into a wire) and malleable (can be shaped via hammering or pressing). A metal may be a chemical element such as iron; an alloy such as stainless steel; or a molecular compound such as polythiazyl, polymeric sulfur nitride. The general science of metals is called metallurgy, a subtopic of materials science; aspects of the electronic and thermal properties are also within the scope of condensed matter physics and solid-state chemistry, it is a multidisciplinary topic. In colloquial use materials such as steel alloys are referred to as metals, while others such as polymers, wood or ceramics are nonmetallic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate (metal)
Structural steel is steel used for making construction materials in a variety of shapes. Many structural steel shapes take the form of an elongated beam having a profile of a specific cross section. Structural steel shapes, sizes, chemical composition, mechanical properties such as strengths, storage practices, etc., are regulated by standards in most industrialized countries. Structural steel shapes, such as I-beams, have high second moments of area, so can support a high load without excessive sagging. Structural shapes The shapes available are described in published standards worldwide, and specialist, proprietary cross sections are also available. *I-beam (serif capital 'I'-shaped cross-section – in Britain these include Universal Beams (UB) and Universal Columns (UC); in Europe it includes the IPE, HE, HL, HD and other sections; in the US it includes Wide Flange (WF or W-Shape) and H sections) *Z-Shape (half a flange in opposite directions) *HSS-Shape (Hollow str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordinates
In geometry, a coordinate system is a system that uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely determine and standardize the Position (geometry), position of the Point (geometry), points or other geometric elements on a manifold such as Euclidean space. The coordinates are not interchangeable; they are commonly distinguished by their position in an ordered tuple, or by a label, such as in "the ''x''-coordinate". The coordinates are taken to be real numbers in elementary mathematics, but may be complex numbers or elements of a more abstract system such as a commutative ring. The use of a coordinate system allows problems in geometry to be translated into problems about numbers and ''vice versa''; this is the basis of analytic geometry. Common coordinate systems Number line The simplest example of a coordinate system is the identification of points on a line (geometry), line with real numbers using the ''number line''. In this system, an arbitrary point ''O'' (the ''ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celestial Sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, which may be centered on Earth or the observer. If centered on the observer, half of the sphere would resemble a hemispherical screen over the observing location. The celestial sphere is a conceptual tool used in spherical astronomy to specify the position of an object in the sky without consideration of its linear distance from the observer. The celestial equator divides the celestial sphere into northern and southern hemispheres. Description Because astronomical objects are at such remote distances, casual observation of the sky offers no information on their actual distances. All celestial objects seem equally far away, as if fixed onto the inside of a sphere with a large but unknown radius, which appears to rotate westwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azimuth
An azimuth (; from ) is the horizontal angle from a cardinal direction, most commonly north, in a local or observer-centric spherical coordinate system. Mathematically, the relative position vector from an observer ( origin) to a point of interest is projected perpendicularly onto a reference plane (the horizontal plane); the angle between the projected vector and a reference vector on the reference plane is called the azimuth. When used as a celestial coordinate, the azimuth is the horizontal direction of a star or other astronomical object in the sky. The star is the point of interest, the reference plane is the local area (e.g. a circular area with a 5 km radius at sea level) around an observer on Earth's surface, and the reference vector points to true north. The azimuth is the angle between the north vector and the star's vector on the horizontal plane. Azimuth is usually measured in degrees (°), in the positive range 0° to 360° or in the signed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altitude
Altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum (geodesy), datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context (e.g., aviation, geometry, geographical survey, sport, or atmospheric pressure). Although the term ''altitude'' is commonly used to mean the height above sea level of a location, in geography the term elevation is often preferred for this usage. In aviation, altitude is typically measured relative to mean sea level or above ground level to ensure safe navigation and flight operations. In geometry and geographical surveys, altitude helps create accurate topographic maps and understand the terrain's elevation. For high-altitude trekking and sports, knowing and adapting to altitude is vital for performance and safety. Higher altitudes mean reduced oxygen levels, which can lead to altitude sickness if proper acclimatization measures are not taken. Vertical distance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
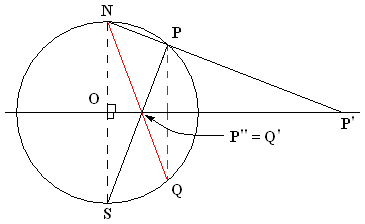
Stereographic Projection
In mathematics, a stereographic projection is a perspective transform, perspective projection of the sphere, through a specific point (geometry), point on the sphere (the ''pole'' or ''center of projection''), onto a plane (geometry), plane (the ''projection plane'') perpendicular to the diameter through the point. It is a smooth function, smooth, bijection, bijective function (mathematics), function from the entire sphere except the center of projection to the entire plane. It maps circle of a sphere, circles on the sphere to generalised circle, circles or lines on the plane, and is conformal map, conformal, meaning that it preserves angles at which curves meet and thus Local property, locally approximately preserves similarity (geometry), shapes. It is neither isometry, isometric (distance preserving) nor Equiareal map, equiareal (area preserving). The stereographic projection gives a way to representation (mathematics), represent a sphere by a plane. The metric tensor, metric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pole, with 0° at the Equator. Parallel (latitude), Lines of constant latitude, or ''parallels'', run east-west as circles parallel to the equator. Latitude and longitude are used together as a coordinate pair to specify a location on the surface of the Earth. On its own, the term "latitude" normally refers to the ''geodetic latitude'' as defined below. Briefly, the geodetic latitude of a point is the angle formed between the vector perpendicular (or ''Normal (geometry), normal'') to the ellipsoidal surface from the point, and the equatorial plane, plane of the equator. Background Two levels of abstraction are employed in the definitions of latitude and longitude. In the first step the physical surface i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, List of largest cities in the Arab world, the Arab world, and List of largest metropolitan areas of the Middle East, the Middle East. The Greater Cairo metropolitan area is List of largest cities, one of the largest in the world by population with over 22.1 million people. The area that would become Cairo was part of ancient Egypt, as the Giza pyramid complex and the ancient cities of Memphis, Egypt, Memphis and Heliopolis (ancient Egypt), Heliopolis are near-by. Located near the Nile Delta, the predecessor settlement was Fustat following the Muslim conquest of Egypt in 641 next to an existing ancient Roman empire, Roman fortress, Babylon Fortress, Babylon. Subsequently, Cairo was founded by the Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimid dynasty in 969. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above sea level. Its metropolitan population in 2022 was 2.4million, making it the List of cities in Saudi Arabia by population, third-most populated city in Saudi Arabia after Riyadh and Jeddah. Around 44.5% of the population are Saudis, Saudi citizens and around 55.5% are Muslim world, Muslim foreigners from other countries. Pilgrims more than triple the population number every year during the Pilgrimage#Islam, pilgrimage, observed in the twelfth Islamic calendar, Hijri month of . With over 10.8 million international visitors in 2023, Mecca was one of the ten List of cities by international visitors, most visited cities in the world. Mecca is generally considered "the fountainhead and cradle of Islam". Mecca is revered in Islam as the birthp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medina
Medina, officially al-Madinah al-Munawwarah (, ), also known as Taybah () and known in pre-Islamic times as Yathrib (), is the capital of Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province in the Hejaz region of western Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, Saudi Arabia. It is one of the oldest and most important places in Islamic history. The Holiest sites in Islam, second holiest city in Islam, the population as of 2022 is 1,411,599, making it the List of cities and towns in Saudi Arabia, fourth-most populous city in the country. Around 58.5% of the population are Saudi citizens and 41.5% are foreigners. Located at the core of the Medina Province in the western reaches of the country, the city is distributed over , of which constitutes the city's urban area, while the rest is occupied by the Hijaz Mountains, Hejaz Mountains, empty valleys, Agriculture in Saudi Arabia, agricultural spaces and older dormant volcanoes. Medina is generally considered to be the "cradle of Islamic culture and ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |