|
Phosphinidene
Phosphinidenes (IUPAC: phosphanylidenes, formerly phosphinediyls) are low-valent phosphorus compounds analogous to carbenes and nitrenes, having the general structure RP. The "free" form of these compounds is conventionally described as having a singly-coordinated phosphorus atom containing only 6 electrons in its valence level. Most phosphinidenes are highly reactive and short-lived, thereby complicating empirical studies on their chemical properties. In the last few decades, several strategies have been employed to stabilize phosphinidenes (e.g. π-donation, steric protection, transition metal complexation), and researchers have developed a number of reagents and systems that can generate and transfer phosphinidenes as reactive intermediates in the synthesis of various organophosphorus compounds. Electronic Structure Like carbenes, phosphinidenes can exist in either a singlet state or triplet state, with the triplet state typically being more stable. The stability of these state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphinidene Singlet Triplet
Phosphinidenes (IUPAC: phosphanylidenes, formerly phosphinediyls) are low-valent phosphorus compounds analogous to carbenes and nitrenes, having the general structure RP. The "free" form of these compounds is conventionally described as having a singly-coordinated phosphorus atom containing only 6 electrons in its valence level. Most phosphinidenes are highly reactive and short-lived, thereby complicating empirical studies on their chemical properties. In the last few decades, several strategies have been employed to stabilize phosphinidenes (e.g. π-donation, Steric effects, steric protection, transition metal complexation), and researchers have developed a number of reagents and systems that can generate and transfer phosphinidenes as reactive intermediates in the synthesis of various organophosphorus compounds. Electronic Structure Like carbenes, phosphinidenes can exist in either a singlet state or triplet state, with the triplet state typically being more stable. The stability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphinidene
Phosphinidenes (IUPAC: phosphanylidenes, formerly phosphinediyls) are low-valent phosphorus compounds analogous to carbenes and nitrenes, having the general structure RP. The "free" form of these compounds is conventionally described as having a singly-coordinated phosphorus atom containing only 6 electrons in its valence level. Most phosphinidenes are highly reactive and short-lived, thereby complicating empirical studies on their chemical properties. In the last few decades, several strategies have been employed to stabilize phosphinidenes (e.g. π-donation, steric protection, transition metal complexation), and researchers have developed a number of reagents and systems that can generate and transfer phosphinidenes as reactive intermediates in the synthesis of various organophosphorus compounds. Electronic Structure Like carbenes, phosphinidenes can exist in either a singlet state or triplet state, with the triplet state typically being more stable. The stability of these state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy Bertrand (chemist)
Guy Bertrand, born on July 17, 1952 at Limoges is a chemistry professor at the University of California, San Diego. Bertrand obtained his B.Sc. from the University of Montpellier in 1975 and his Ph.D. from the Paul Sabatier University, Toulouse, in 1979. He was a postdoctoral researcher at Sanofi Research, France, in 1981. Guy Bertrand's faculty homepageat UC San Diego. Accessed on 2013-1-22. The research interests of Bertrand and his co-workers lie mainly in the chemistry of with main group elements from group 13 to 16, at the border between organic, organometallic and inorganic chemistry; especially their use in stabilizing carbenes, nitrenes, phosphinidenes, radicals and biradicals, 1,3-dipoles, anti-aromatic heterocycles, and more. He has directed the synthesis of some original persistent carbenes, including bis(diisopropylamino)cyclopropenylidene, the first example of a carbene with all-carbon environment that is stable at room-temperature.V. Lavallo, Y. Canac, B. Donna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HOMO And LUMO
In chemistry, HOMO and LUMO are types of molecular orbitals. The acronyms stand for ''highest occupied molecular orbital'' and ''lowest unoccupied molecular orbital'', respectively. HOMO and LUMO are sometimes collectively called the ''frontier orbitals'', such as in the frontier molecular orbital theory. Gap The energy difference between the HOMO and LUMO is ''the HOMO–LUMO gap''. Its size can be used to predict the strength and stability of transition metal complexes, as well as the colors they produce in solution.Griffith, J. S. and L. E. Orgel"Ligand Field Theory" ''Q. Rev. Chem. Soc.'' 1957, 11, 381–383. As a rule of thumb, the larger a compound's HOMO-LUMO gap, the more stable the compound. Semiconductors The HOMO level is to organic semiconductors roughly what the maximum valence band is to inorganic semiconductors and quantum dots. The same analogy can be made between the LUMO level and the conduction band minimum.Bredas, J,-L"Mind the gap!" ''Mater. Horiz.'' 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isolated as a metal in 1783. Its important ores include scheelite and wolframite, the latter lending the element its alternate name. The free element is remarkable for its robustness, especially the fact that it has the highest melting point of all known elements barring carbon (which sublimes at normal pressure), melting at . It also has the highest boiling point, at . Its density is , comparable with that of uranium and gold, and much higher (about 1.7 times) than that of lead. Polycrystalline tungsten is an intrinsically brittle and hard material (under standard conditions, when uncombined), making it difficult to work. However, pure single-crystalline tungsten is more ductile and can be cut with a hard-steel hacksaw. Tungsten occurs in many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42 which is located in period 5 and group 6. The name is from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'', which is based on Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals have been known throughout history, but the element was discovered (in the sense of differentiating it as a new entity from the mineral salts of other metals) in 1778 by Carl Wilhelm Scheele. The metal was first isolated in 1781 by Peter Jacob Hjelm. Molybdenum does not occur naturally as a free metal on Earth; it is found only in various oxidation states in minerals. The free element, a silvery metal with a grey cast, has the sixth-highest melting point of any element. It readily forms hard, stable carbides in alloys, and for this reason most of the world production of the element (about 80%) is used in steel alloys, including high-strength alloys and superalloys. Most molybdenum compounds have low solubili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent to ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acidic "ligands". Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in almost all circumstances, although gaseous "naked" metal ions can be generated in a high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection requires critical consideration in many practical areas, including bioinorganic and medicinal chemistry, homogeneous catalysis, and environmental chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Metal Carbene Complexes
Transition or transitional may refer to: Mathematics, science, and technology Biology * Transition (genetics), a point mutation that changes a purine nucleotide to another purine (A ↔ G) or a pyrimidine nucleotide to another pyrimidine (C ↔ T) * Transitional fossil, any fossilized remains of a lifeform that exhibits the characteristics of two distinct taxonomic groups * A phase during childbirth contractions during which the cervix completes its dilation Gender and sex * Gender transitioning, the process of changing one's gender presentation to accord with one's internal sense of one's gender – the idea of what it means to be a man or woman * Sex reassignment therapy, the physical aspect of a gender transition Physics * Phase transition, a transformation of the state of matter; for example, the change between a solid and a liquid, between liquid and gas or between gas and plasma * Quantum phase transition, a phase transformation between different quantum phases * Quantum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
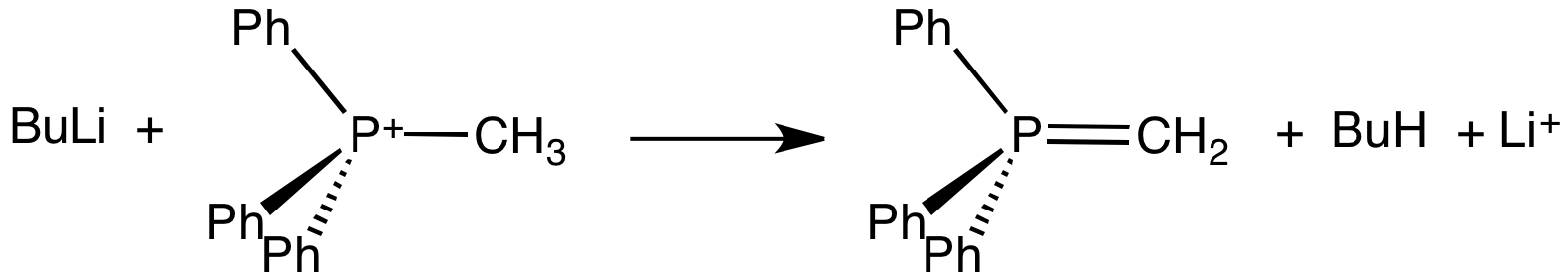
Wittig Reaction
The Wittig reaction or Wittig olefination is a chemical reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a triphenyl phosphonium ylide called a Wittig reagent. Wittig reactions are most commonly used to convert aldehydes and ketones to alkenes. Most often, the Wittig reaction is used to introduce a methylene group using methylenetriphenylphosphorane (Ph3P=CH2). Using this reagent, even a sterically hindered ketone such as camphor can be converted to its methylene derivative. Stereochemistry For the reaction with aldehydes, the double bond geometry is readily predicted based on the nature of the ylide. With unstabilised ylides (R3 = alkyl) this results in (''Z'')-alkene product with moderate to high selectivity. With stabilized ylides (R3 = ester or ketone), the (''E'')-alkene is formed with high selectivity. The (''E'')/(''Z'') selectivity is often poor with semistabilized ylides (R3 = aryl). To obtain the (''E'')-alkene for unstabilized ylides, the Schlosser modification of the W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ylide
An ylide or ylid () is a neutral dipolar molecule containing a formally negatively charged atom (usually a carbanion) directly attached to a heteroatom with a formal positive charge (usually nitrogen, phosphorus or sulfur), and in which both atoms have full octets of electrons. The result can be viewed as a structure in which two adjacent atoms are connected by both a covalent and an ionic bond; normally written X+–Y−. Ylides are thus 1,2-dipolar compounds, and a subclass of zwitterions. They appear in organic chemistry as reagents or reactive intermediates. The class name "ylide" for the compound should not be confused with the suffix "-ylide". Resonance structures Many ylides may be depicted by a multiple bond form in a resonance structure, known as the ylene form, while the actual structure lies in between both forms: : The actual bonding picture of these types of ylides is strictly zwitterionic (the structure on the right) with the strong Coulombic attraction between the " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zwitterion
In chemistry, a zwitterion ( ; ), also called an inner salt or dipolar ion, is a molecule that contains an equal number of positively- and negatively-charged functional groups. : With amino acids, for example, in solution a chemical equilibrium will be established between the "parent" molecule and the zwitterion. Betaines are zwitterions that cannot isomerize to an all-neutral form, such as when the positive charge is located on a quaternary ammonium group. Similarly, a molecule containing a phosphonium group and a carboxylate group cannot isomerize. Amino acids The equilibrium is established in two stages. In the first stage, a proton is transferred from the carboxyl group to a water molecule: :H2N(R)CO2H + H2O H2N(R)CO2- + H3O+ In the second stage, a proton is transferred from the hydronium ion to the amine group: :H2N(R)CO2- + H3O+ H3N+ (R)CO2- + H2O Overall, the reaction is an isomerization reaction :H2N(R)CO2H H3N+ (R)CO2- The ratio of the concentrations of the two spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





4-3D-balls.png)