|
Ylide
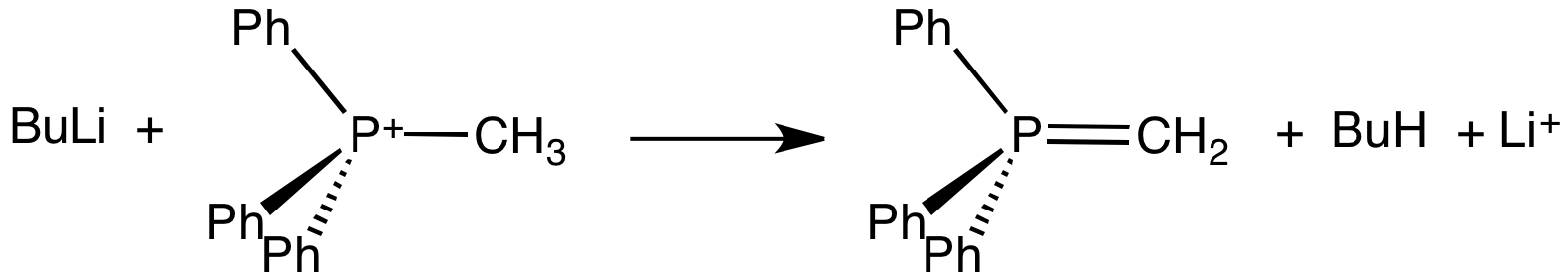
An ylide () or ylid () is a neutral dipolar molecule containing a formally negatively charged atom (usually a carbanion) directly attached to a heteroatom with a formal positive charge (usually nitrogen, phosphorus or sulfur), and in which both atoms have full octets of electrons. The result can be viewed as a structure in which two adjacent atoms are connected by both a covalent and an ionic bond; normally written X+–Y−. Ylides are thus 1,2- dipolar compounds, and a subclass of zwitterions. They appear in organic chemistry as reagents or reactive intermediates. The class name "ylide" for the compound should not be confused with the suffix "-ylide". Resonance structures Many ylides may be depicted by a multiply bonded form in a resonance structure, known as the ylene form, while the actual structure lies in between both forms: : The actual bonding picture of these types of ylides is strictly zwitterionic (the structure on the right) with the strong Coulombic attractio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipolar Compound
In organic chemistry, a dipolar compound or simply dipole is an electrically neutral molecule carrying a positive and a negative charge in at least one canonical description. In most dipolar compounds the charges are Delocalized electron, delocalized. Unlike Salt (chemistry), salts, dipolar compounds have charges on separate atoms, not on positive and negative ions that make up the compound. Dipolar compounds exhibit a Dipole#Molecular dipoles, dipole moment. Dipolar compounds can be represented by a Resonance (chemistry), resonance structure. Contributing structures containing charged atoms are denoted as zwitterions. {{cite journal, last1=MacHiguchi, first1=Takahisa, last2=Okamoto, first2=Junko, last3=Takachi, first3=Junpei, last4=Hasegawa, first4=Toshio, last5=Yamabe, first5=Shinichi, last6=Minato, first6=Tsutomu, title=Exclusive Formation of α-Methyleneoxetanes in Ketene−Alkene Cycloadditions. Evidence for Intervention of Both an α-Methyleneoxetane and the Subsequent 1,4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wittig Reaction
The Wittig reaction or Wittig olefination is a chemical reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a triphenyl phosphonium ylide called a Wittig reagent. Wittig reactions are most commonly used to convert aldehydes and ketones to alkenes. Most often, the Wittig reaction is used to introduce a methylene group using methylenetriphenylphosphorane (Ph3P=CH2). Using this reagent, even a sterically hindered ketone such as camphor can be converted to its methylene derivative. Reaction mechanism Mechanistic studies have focused on unstabilized ylides, because the intermediates can be followed by NMR spectroscopy. The existence and interconversion of the betaine (3a and 3b) is subject of ongoing research. For lithium-free Wittig reactions, studies support a concerted formation of the oxaphosphetane without intervention of a betaine. In particular, phosphonium ylides 1 react with carbonyl compounds 2 via a +2cycloaddition that is sometimes described as having π2s+π2a">sub>π2s+π2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Charge
Electric charge (symbol ''q'', sometimes ''Q'') is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be ''positive'' or ''negative''. Like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract each other. An object with no net charge is referred to as neutral particle, electrically neutral. Early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still accurate for problems that do not require consideration of quantum mechanics, quantum effects. In an isolated system, the total charge stays the same - the amount of positive charge minus the amount of negative charge does not change over time. Electric charge is carried by subatomic particles. In ordinary matter, negative charge is carried by electrons, and positive charge is carried by the protons in the atomic nucleus, nuclei of atoms. If there are more electrons than protons in a piece of matter, it will have a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butyllithium
Butyllithium may refer to one of 5 isomeric organolithium reagents of which 3 are commonly used in chemical synthesis: * ''n''-Butyllithium, abbreviated BuLi or nBuLi * ''sec''-Butyllithium, abbreviated ''sec''-BuLi or sBuLi, has 2 stereoisomers, but is commonly used as racemate * ''tert''-Butyllithium, abbreviated ''tert''-BuLi or tBuLi * Isobutyllithium {{Chemistry index ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphonium
In chemistry, the term phosphonium (more obscurely: phosphinium) describes polyatomic cations with the chemical formula (where R is a hydrogen or an alkyl, aryl, organyl or halogen group). These cations have tetrahedral structures. The salts are generally colorless or take the color of the anions. Types of phosphonium cations Protonated phosphines The parent phosphonium is as found in the iodide salt, phosphonium iodide. Salts of the parent are rarely encountered, but this ion is an intermediate in the preparation of the industrially useful tetrakis(hydroxymethyl)phosphonium chloride: :PH3 + HCl + 4 CH2O → Many organophosphonium salts are produced by protonation of primary, secondary, and tertiary phosphines: :PR3 + H+ → The basicity of phosphines follows the usual trends, with R = alkyl being more basic than R = aryl. Tetraorganophosphonium cations The most common phosphonium compounds have four organic substituents attached to phosphorus. The quaternary p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternization
In organic chemistry, the Menshutkin reaction converts a tertiary amine into a quaternary ammonium salt by reaction with an alkyl halide. Similar reactions occur when tertiary phosphines are treated with alkyl halides. The reaction is the method of choice for the preparation of quaternary ammonium salts. Some phase transfer catalysts (PTC) can be prepared according to the Menshutkin reaction, for instance the synthesis of triethyl benzyl ammonium chloride (TEBA) from triethylamine and benzyl chloride: Scope Reactions are typically conducted in polar solvents such as alcohols. Alkyl iodides are superior alkylating agents relative to the bromides, which in turn are superior to chlorides. As is typical for an SN2 process, benzylic, allylic, and α-carbonylated alkyl halides are excellent reactants. Even though alkyl chlorides are poor alkylating agents (''gem''-dichlorides especially so), amines should not be handled in chlorinated solvents such as dichloromethane and dich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SN2 Reaction
The bimolecular nucleophilic substitution (SN2) is a type of reaction mechanism that is common in organic chemistry. In the SN2 reaction, a strong nucleophile forms a new bond to an sp3-hybridised carbon atom via a backside attack, all while the leaving group detaches from the reaction center in a concerted (i.e. simultaneous) fashion. The name SN2 refers to the Hughes-Ingold symbol of the mechanism: "SN" indicates that the reaction is a nucleophilic substitution, and "2" that it proceeds via a bimolecular mechanism, which means both the reacting species are involved in the rate-determining step. What distinguishes SN2 from the other major type of nucleophilic substitution, the SN1 reaction, is that the displacement of the leaving group, which is the rate-determining step, is separate from the nucleophilic attack in SN1. The SN2 reaction can be considered as an organic-chemistry analogue of the associative substitution from the field of inorganic chemistry. Reaction mech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyl Halide
The haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are alkanes containing one or more halogen substituents of hydrogen atom. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes that contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to P Ph3 or Ph3P. It is versatile compound that is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis and as a ligand for transition metal complexes, including ones that serve as catalysts in organometallic chemistry. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether. Preparation and structure Triphenylphosphine can be prepared in the laboratory by treatment of phosphorus trichloride with phenylmagnesium bromide or phenyllithium. The industrial synthesis involves the reaction between phosphorus trichloride, chlorobenzene, and sodium: :PCl3 + 3 PhCl + 6 Na → PPh3 + 6 NaCl Triphenylphosphine crystallizes in triclinic and monoclinic modification. In both cases, the molecule adopts a pyramidal structure with propeller-like arrangement of the thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |