|
Heatspreader
A heat spreader transfers energy as heat from a hotter source to a colder heat sink or heat exchanger. There are two thermodynamic types, passive and active. The most common sort of passive heat spreader is a plate or block of material having high thermal conductivity, such as copper, aluminum, or diamond. An active heat spreader speeds up heat transfer with expenditure of energy as work supplied by an external source. A heat pipe uses fluids inside a sealed case. The fluids circulate either passively, by spontaneous convection, triggered when a threshold temperature difference occurs; or actively, because of an impeller driven by an external source of work. Without sealed circulation, energy can be carried by transfer of fluid matter, for example externally supplied colder air, driven by an external source of work, from a hotter body to another external body, though this is not exactly heat transfer as defined in physics. Exemplifying increase of entropy according to the second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
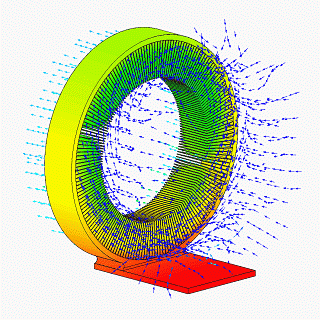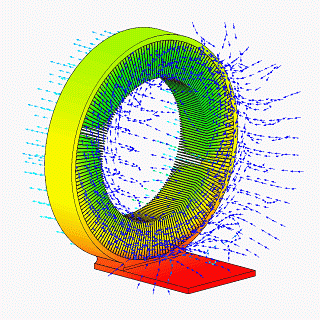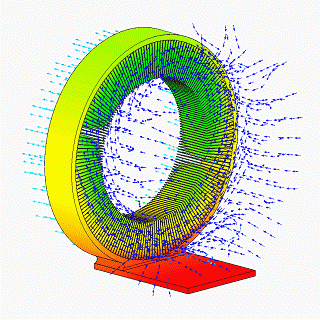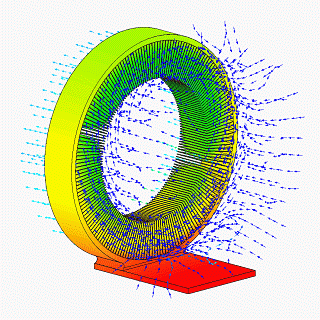
CFD Vapor Chamber Heat Sink Design V1
__NOTOC__ CFD may refer to: Science and computing * Computational fluid dynamics, a branch of fluid mechanics using computational methods to predict the behavior of fluid flows * Counterfactual definiteness, the ability, in quantum mechanics, to consider results of unperformed measurements * CFEngine daemon, the process that runs CFEngine * Common fill device, an electronic module used to load cryptographic keys into electronic encryption machines * Constant fraction discriminator, a signal processing component * Complement factor D, an enzyme encoded by the ''CFD'' gene Business * Contract for difference, a type of financial derivative, where two parties exchange the difference between opening and closing value of an underlying asset * Control Flow Diagram, is a diagram to describe the control flow of a business process, process or program * Cumulative Flow Diagram, an area graph that depicts the quantity of work in a given state Firefighting organizations * Calgary Fire De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concentrated Photovoltaics
Concentrator photovoltaics (CPV) (also known as concentration photovoltaics) is a photovoltaic technology that generates electricity from sunlight. Unlike conventional photovoltaic systems, it uses lenses or curved mirrors to focus sunlight onto small, highly efficient, multi-junction (MJ) solar cells. In addition, CPV systems often use solar trackers and sometimes a cooling system to further increase their efficiency. Systems using high-concentration photovoltaics (HCPV) possess the highest efficiency of all existing PV technologies, achieving near 40% for production modules and 30% for systems. They enable a smaller photovoltaic array that has the potential to reduce land use, waste heat and material, and balance of system costs. The rate of annual CPV installations peaked in 2012 and has fallen to near zero since 2018 with the faster price drop in crystalline silicon photovoltaics. In 2016, cumulative CPV installations reached 350 megawatts (MW), less than 0.2% of the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athlon 64 X2
The Athlon 64 X2 is the first native dual-core desktop central processing unit (CPU) designed by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). It was designed from scratch as native dual-core by using an already multi-CPU enabled Athlon 64, joining it with another functional core on one die, and connecting both via a shared dual-channel memory controller/north bridge and additional control logic. The initial versions are based on the E stepping model of the Athlon 64 and, depending on the model, have either 512 or 1024 KB of L2 cache per core. The Athlon 64 X2 can decode instructions for Streaming SIMD Extensions 3 (SSE3), except those few specific to Intel's architecture. The first Athlon 64 X2 CPUs were released in May 2005, in the same month as Intel's first dual-core processor, the Pentium D. In June 2007, AMD released low-voltage variants of their low-end 65 nm Athlon 64 X2, named "Athlon X2". The Athlon X2 processors feature reduced thermal design power (TDP) of 45 Watt (W). The name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has a great affinity towards oxygen, and forms a protective layer of oxide on the surface when exposed to air. Aluminium visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, non-magnetic and ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al; this isotope is very common, making aluminium the twelfth most common element in the Universe. The radioactivity of 26Al is used in radiodating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ is small and highly charged; as such, it is polarizing, and bonds aluminium forms tend towards covalency. The strong affinity towards ox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Module
In computing, a memory module or RAM (random-access memory) stick is a printed circuit board on which memory integrated circuits are mounted. Memory modules permit easy installation and replacement in electronic systems, especially computers such as personal computers, workstations, and servers. The first memory modules were proprietary designs that were specific to a model of computer from a specific manufacturer. Later, memory modules were standardized by organizations such as JEDEC and could be used in any system designed to use them. Types of memory module include: * TransFlash Memory Module * SIMM, a single in-line memory module * DIMM, dual in-line memory module ** Rambus memory modules are a subset of DIMMs, but are normally referred to as RIMMs ** SO-DIMM, small outline DIMM, a smaller version of the DIMM, used in laptops Distinguishing characteristics of computer memory modules include voltage, capacity, speed (i.e., bit rate), and form factor. For economic reasons, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beryllium
Beryllium is a chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with other elements to form minerals. Notable gemstones high in beryllium include beryl ( aquamarine, emerald) and chrysoberyl. It is a relatively rare element in the universe, usually occurring as a product of the spallation of larger atomic nuclei that have collided with cosmic rays. Within the cores of stars, beryllium is depleted as it is fused into heavier elements. Beryllium constitutes about 0.0004 percent by mass of Earth's crust. The world's annual beryllium production of 220 tons is usually manufactured by extraction from the mineral beryl, a difficult process because beryllium bonds strongly to oxygen. In structural applications, the combination of high flexural rigidity, thermal stability, thermal conductivity and low density (1.85 times that of water) ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beryllium Oxide
Beryllium oxide (BeO), also known as beryllia, is an inorganic compound with the formula BeO. This colourless solid is a notable electrical insulator with a higher thermal conductivity than any other non-metal except diamond, and exceeds that of most metals. As an amorphous solid, beryllium oxide is white. Its high melting point leads to its use as a refractory material. It occurs in nature as the mineral bromellite. Historically and in materials science, beryllium oxide was called glucina or glucinium oxide, owing to its sweet taste. Preparation and chemical properties Beryllium oxide can be prepared by calcining (roasting) beryllium carbonate, dehydrating beryllium hydroxide, or igniting metallic beryllium: :BeCO3 → BeO + CO2 :Be(OH)2 → BeO + H2O :2 Be + O2 → 2 BeO Igniting beryllium in air gives a mixture of BeO and the nitride Be3N2. Unlike the oxides formed by the other Group 2 elements (alkaline earth metals), beryllium oxide is amphoteric rather than basic. Berylliu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-Material
E-Material, also called E Material, is a metal matrix composite consisting of beryllium matrix with beryllium oxide particles. It has high thermal conductivity (210-230 W/m K), and its thermal expansion can be adjusted to match other materials, e.g. silicon and gallium arsenide chips and various ceramics. It is chiefly used in microelectronics as substrate for power semiconductor devices and high density multi-chip modules, where it aids with removal of waste heat. E-materials have low weight and high strength, making them especially suitable for aerospace technology. Their high elastic modulus is favorable for absorbing vibrations and lowering material fatigue of attached modules and wire bonds. Several variants exist: * E-20, containing 80 vol.% of beryllium and 20 vol.% (25.8-32.25 w.%) beryllium oxide. Its thermal conductivity is 210 W/(m·K). Its thermal expansion coefficient is 8.7. Its density at 25 °C is 2.045 g/cm3. * E-40, containing 60 vol.% of beryllium and 40 vol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dymalloy
Dymalloy is a metal matrix composite consisting of 20% copper and 80% silver alloy matrix with type I diamond. It has very high thermal conductivity of 420 W/(m·K), and its thermal expansion can be adjusted to match other materials, e.g. silicon and gallium arsenide chips. It is chiefly used in microelectronics as substrate for high power and high density multi-chip modules, where it aids with removal of waste heat. Dymalloy was developed as part of CRADA between Sun Microsystems and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. It was first researched for use in space-based electronics for the Brilliant Pebbles project. Dymalloy is prepared from diamond powder of about 25 micrometers size. The grains are coated by physical vapor deposition with 10 nanometers thick layer of alloy of tungsten with 26% rhenium, forming a tungsten carbide layer that assists bonding, then coated with 100 nanometers of copper to avoid carbide oxidation, then compacted in a mold and infiltrated with molt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder and crystal since 1893 for use as an abrasive. Grains of silicon carbide can be bonded together by sintering to form very hard ceramics that are widely used in applications requiring high endurance, such as car brakes, car clutches and ceramic plates in bulletproof vests. Large single crystals of silicon carbide can be grown by the Lely method and they can be cut into gems known as synthetic moissanite. Electronic applications of silicon carbide such as light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and Cat's whisker detector, detectors in early radios were first demonstrated around 1907. SiC is used in semiconductor electronics devices that operate at high temperatures or high voltages, or both. Natural occurrence Naturally occurring moissanite is found in only minut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AlSiC
AlSiC, pronounced "alsick", is a metal matrix composite consisting of aluminium matrix with silicon carbide particles. It has high thermal conductivity (180–200 W/m K), and its thermal expansion can be adjusted to match other materials, e.g. silicon and gallium arsenide chips and various ceramics. It is chiefly used in microelectronics as substrate for power semiconductor devices and high density multi-chip modules, where it aids with removal of waste heat. Several variants exist: *AlSiC-9, containing 37 vol.% of A 356.2 aluminium alloy and 63 vol.% silicon carbide. Its thermal conductivity is 190–200 W/m K. Its thermal expansion roughly matches gallium arsenide, silicon, indium phosphide, alumina, aluminium nitride, silicon nitride, and Direct Bonded Copper aluminium nitride. It is also compatible with some low temperature co-fired ceramics, e.g. Ferro A6M and A6S, Heraeus CT 2000, and Kyocera GL560. Its density at 25 °C is 3.01 g/cm3. *AlSiC-10, containing 45 vol.% o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper–tungsten
Copper–tungsten (tungsten–copper, CuW, or WCu) is a mixture of copper and tungsten. As copper and tungsten are not mutually soluble, the material is composed of distinct particles of one metal dispersed in a matrix of the other one. The microstructure is therefore rather a metal matrix composite instead of a true alloy. The material combines the properties of both metals, resulting in a material that is heat-resistant, ablation-resistant, highly thermally and electrically conductive, and easy to machine. Parts are made from the CuW composite by pressing the tungsten particles into the desired shape, sintering the compacted part, then infiltrating with molten copper. Sheets, rods, and bars of the composite mixture are available as well. Commonly used copper tungsten mixtures contains 10–50 wt.% of copper, the remaining portion being mostly tungsten. The typical properties is dependent on its composition. The mixture with less wt.% of copper has higher density, higher hardn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |