|
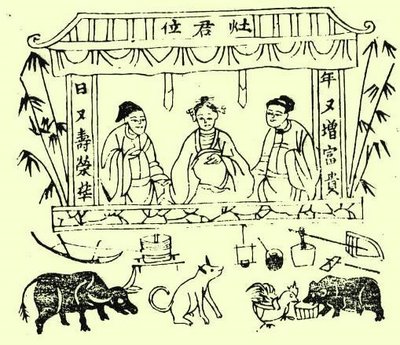
Zàojūn
Kitchen gods are mythical beings that represent abstract concepts such as luck or just propel the minor changes of everyday life. Little things that cannot be explained, such as losing small objects like socks in the laundry, are often attributed to these creatures because the explanation eludes the believer. See also *Di Penates *Hestia *Household deity * Jowangsin is a Korean kitchen god. * Kōjin is a Japanese kitchen god. *List of deities * Ông Táo Ông Táo (翁灶) also known as Táo Quân (灶君, Mandarin Táo), Táo Vương (灶王), Thần Bếp (神灶), Vua Bếp (𢂜灶) or the Kitchen god is regarded in Vietnamese culture as the advocate of the Vietnamese family with the gods and ... is a Vietnamese kitchen god. * Zàojūn is a Chinese kitchen god. References European mythology {{europe-myth-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kōjin
Kōjin, also known as , is the Japanese ''kami'' (''god'') of fire, the hearth and the kitchen. He is sometimes called Kamado-gami ( 竃神), literally ''the god of the stove''. He represents violent forces that are turned toward the betterment of humankind. Mythology The name ''Sambō-Kōjin'' means ''three-way rough deity'', and he is considered a deity of uncertain temper.Ashkenazy, Michael. ''Handbook of Japanese Mythology''. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-Clio, 2003. 244 Fire, which he represents, is a destructive force, as shown in the myth of Kagu-tsuchi, the original fire deity, whose birth caused his mother's death. However, Kōjin embodies fire controlled and turned toward a good purpose. He is said to destroy all impurity. He is also responsible for watching over the household and reporting any misdeeds to the ''kami'' of the village or city. These reports are discussed, and the according rewards or punishments assigned, by an assembly of gods in Izumo province in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jowangsin
Jowangshin (in Hangul, ''조왕신'', in hanja, 竈王神) is the goddess of fire and the hearth in Korean shamanism. As the goddess of the hearth, the rituals dedicated to her were generally kept alive by housewives. She is no longer the subject of worship, but still remains one of the most famous Korean deities. History It is regarded that Jowangshin was worshipped by the Korean people for millennia, since the Proto Three Kingdoms era. For example, in the ''Sanguo Zhi'', a history book of China, there are records of a kitchen god. "There are many different rituals that they (the people of the Samhan, Samhan Confederacy, in modern South Korea) hold, but all worship a kitchen god in their western wings." Ritual Jowangshin was regarded to embody a bowl of water held on a clay altar above the hearth. The housewife awoke early every morning and poured fresh water from a nearby well into the bowl, then knelt before it, wishing for luck. The ritual of Jowangshin was especially well d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ông Táo
Ông Táo (翁灶) also known as Táo Quân (灶君, Mandarin Táo), Táo Vương (灶王), Thần Bếp (神灶), Vua Bếp (𢂜灶) or the Kitchen god is regarded in Vietnamese culture as the advocate of the Vietnamese family with the gods and the emissary between heaven to earth. Mythology A long time ago, there was a couple, Trọng Cao and his wife Thị Nhi who were married for many years but had no children. One day, they quarreled over some trivial matter, and the husband, in a fit of anger, beat and threw his wife out of their home. Although Thị Nhi still loved her husband, she had no choice but to go away. Thị Nhi went far away and met a very kind man called Phạm Lang. He married her and he loved Thị Nhi very much. Their life was happy and peaceful but Thị Nhi could not forget her first love. As for Trọng Cao, he had been filled with remorse from the day he sent his wife away. He waited, and waited hopelessly for his wife’s return. Eventually, he decided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zàojūn
Kitchen gods are mythical beings that represent abstract concepts such as luck or just propel the minor changes of everyday life. Little things that cannot be explained, such as losing small objects like socks in the laundry, are often attributed to these creatures because the explanation eludes the believer. See also *Di Penates *Hestia *Household deity * Jowangsin is a Korean kitchen god. * Kōjin is a Japanese kitchen god. *List of deities * Ông Táo Ông Táo (翁灶) also known as Táo Quân (灶君, Mandarin Táo), Táo Vương (灶王), Thần Bếp (神灶), Vua Bếp (𢂜灶) or the Kitchen god is regarded in Vietnamese culture as the advocate of the Vietnamese family with the gods and ... is a Vietnamese kitchen god. * Zàojūn is a Chinese kitchen god. References European mythology {{europe-myth-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mythology
Myth is a genre of folklore consisting primarily of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society. For scholars, this is very different from the vernacular usage of the term "myth" that refers to a belief that is not true. Instead, the veracity of a myth is not a defining criterion. Myths are often endorsed by religious (when they are closely linked to religion or spirituality) and secular authorities. Many societies group their myths, legends, and history together, considering myths and legends to be factual accounts of their remote past. In particular, creation myths take place in a primordial age when the world had not achieved its later form. Origin myths explain how a society's customs, institutions, and taboos were established and sanctified. National myths are narratives about a nation's past that symbolize the nation's values. There is a complex relationship between recital of myths and the enactment of rituals. Etymology The word "myth" comes from Ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luck
Luck is the phenomenon and belief that defines the experience of improbable events, especially improbably positive or negative ones. The Naturalism (philosophy), naturalistic interpretation is that positive and negative events may happen at any time, both due to random and non-random natural and artificial processes, and that even improbable events can happen by random chance. In this view, the epithet "lucky" or "unlucky" is a descriptive label that refers to an event's positivity, negativity, or improbability. Supernatural interpretations of luck consider it to be an attribute of a person or object, or the result of a favorable or unfavorable view of a deity upon a person. These interpretations often ''prescribe'' how luckiness or unluckiness can be obtained, such as by carrying a lucky charm or offering sacrifices or prayers to a deity. Saying someone is "born lucky" may hold different meanings, depending on the interpretation: it could simply mean that they have been bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Di Penates
In ancient Roman religion, the Di Penates () or Penates ( ) were among the ''dii familiares'', or household deities, invoked most often in domestic rituals. When the family had a meal, they threw a bit into the fire on the hearth for the Penates. They were thus associated with Vesta, the Lares, and the Genius of the ''pater familias'' in the "little universe" of the ''domus''. Like other domestic deities, the Penates had a public counterpart. Function An etymological interpretation of the Penates would make them in origin tutelary deities of the storeroom, Latin ''penus'', the innermost part of the house, where they guarded the household's food, wine, oil, and other supplies. As they were originally associated with the source of food, they eventually became a symbol of the continuing life of the family. Cicero explained that they "dwell inside, from which they are also called ''penetrales'' by the poets". The 2nd-century AD grammarian Festus defined ''penus'', however, as "the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hestia
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Hestia (; ) is the virgin goddess of the hearth and the home. In myth, she is the firstborn child of the Titans Cronus and Rhea, and one of the Twelve Olympians. In Greek mythology, newborn Hestia, along with four of her five siblings, was devoured by her father Cronus, who feared being overthrown by one of his offspring. Zeus, the youngest child, escaped with his mother's help, and made his father disgorge all his siblings. Cronus was supplanted by this new generation of deities; and Hestia thus became one of the Olympian gods, the new rulers of the cosmos, alongside her brothers and sisters. In spite of her status, she has little prominence in Greek mythology. Like Athena and Artemis, Hestia elected never to marry and remained an eternal virgin goddess instead, forever tending to the hearth of Olympus. As the goddess of sacrificial fire, Hestia received the first offering at every domestic sacrifice. In the public domain, the hearth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Household Deity
A household deity is a deity or spirit that protects the home, looking after the entire household or certain key members. It has been a common belief in paganism as well as in folklore across many parts of the world. Household deities fit into two types; firstly, a specific deity typically a goddess often referred to as a hearth goddess or domestic goddess who is associated with the home and hearth, such as the ancient Greek Hestia. The second type of household deity is not one singular deity but a type or species of animistic, which usually has lesser powers than major deities. This type was common in the religions of antiquity, such as the lares of ancient Roman religion, the gashin of Korean shamanism, and cofgodas of Anglo-Saxon paganism. These survived Christianisation as fairy-like creatures existing in folklore, such as the Anglo-Scottish brownie and Slavic domovoy. Household deities were usually worshipped not in temples but in the home, where they would be repres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Deities
A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but lists are frequently written down on paper, or maintained electronically. Lists are "most frequently a tool", and "one does not ''read'' but only ''uses'' a list: one looks up the relevant information in it, but usually does not need to deal with it as a whole". Lucie Doležalová,The Potential and Limitations of Studying Lists, in Lucie Doležalová, ed., ''The Charm of a List: From the Sumerians to Computerised Data Processing'' (2009). Purpose It has been observed that, with a few exceptions, "the scholarship on lists remains fragmented". David Wallechinsky, a co-author of '' The Book of Lists'', described the attraction of lists as being "because we live in an era of overstimulation, especially in terms of information, and lists help ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |