|
Kōjin
Kōjin, also known as , is the Japanese ''kami'' (''god'') of fire, the hearth and the kitchen. He is sometimes called Kamado-gami ( 竃神), literally ''the god of the stove''. He represents violent forces that are turned toward the betterment of humankind. Mythology The name ''Sambō-Kōjin'' means ''three-way rough deity'', and he is considered a deity of uncertain temper.Ashkenazy, Michael. ''Handbook of Japanese Mythology''. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-Clio, 2003. 244 Fire, which he represents, is a destructive force, as shown in the myth of Kagu-tsuchi, the original fire deity, whose birth caused his mother's death. However, Kōjin embodies fire controlled and turned toward a good purpose. He is said to destroy all impurity. He is also responsible for watching over the household and reporting any misdeeds to the ''kami'' of the village or city. These reports are discussed, and the according rewards or punishments assigned, by an assembly of gods in Izumo province ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ofuda
In Shinto and Buddhism in Japan, an is a talisman made out of various materials such as paper, wood, cloth or metal. are commonly found in both Shinto shrines and Buddhist temples and are considered to be imbued with the power of the deities () or Buddhist figures revered therein. Such amulets are also called . Certain kinds of are intended for a specific purpose (such as protection against calamity or misfortune, safety within the home, or finding love) and may be kept on one's person or placed on other areas of the home (such as gates, doorways, kitchens, or ceilings). Paper may also be referred to as , while those made of wood may be called . , another kind of Japanese amulet, originated and may be considered as a smaller, portable version of . A specific type of is a talisman issued by a Shinto shrine on which is written the name of the shrine or its enshrined and stamped with the shrine's seal. Such , also called , or , are often placed on household Shinto altar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
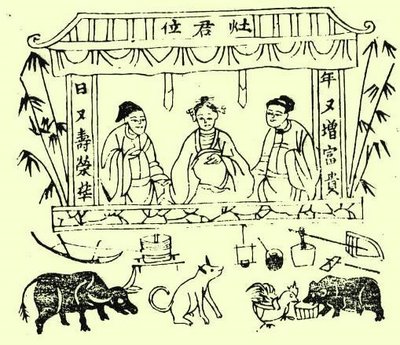
Kitchen God
The Kitchen deity – also known as the Stove God, named Zao Jun, Zao Shen, Zao kimjah, Cokimjah or Zhang Lang – is the most important of a plethora of Chinese domestic gods that protect the hearth and family. The Kitchen God is recognized in Chinese folk religion, Chinese mythology, and Taoism. Under different names, he is also celebrated in several other Asian religions. It is believed that on the twenty third day of the twelfth lunar month, just before Chinese New Year, the Kitchen deity returns to Heaven to report the activities of every household over the past year to Yu Huang Da Di (玉皇大帝), the Jade Emperor. The Jade Emperor, emperor of the heavens, either rewards or punishes a family based on Zao Jun's yearly report. Story Zhang Lang Though there are many stories on how Zao Jun became the Kitchen God, the most popular one dates back to around the 2nd Century BC. Zao Jun was originally a mortal man living on earth whose name was Zhang Lang. He eventually became ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ông Táo
Ông Táo (翁灶) also known as Táo Quân (灶君, Mandarin Táo), Táo Vương (灶王), Thần Bếp (神灶) or the Kitchen god is regarded in Vietnamese culture as the advocate of the Vietnamese family with the gods and the emissary between heaven to earth. Mythology A long time ago, there was a couple, Trọng Cao and his wife Thị Nhi who were married for many years but had no children. One day, they quarreled over some trivial matter, and the husband, in a fit of anger, beat and threw his wife out of their home. Although Thị Nhi still loved her husband, she had no choice but to go away. Thị Nhi went far away and met a very kind man called Phạm Lang. He married her and he loved Thị Nhi very much. Their life was happy and peaceful but Thị Nhi could not forget her first love. As for Trọng Cao, he had been filled with remorse from the day he sent his wife away. He waited, and waited hopelessly for his wife’s return. Eventually, he decided to set out from his home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zàojūn
The Kitchen deity – also known as the Stove God, named Zao Jun, Zao Shen, Zao kimjah, Cokimjah or Zhang Lang – is the most important of a plethora of Chinese domestic gods that protect the hearth and family. The Kitchen God is recognized in Chinese folk religion, Chinese mythology, and Taoism. Under different names, he is also celebrated in several other Asian religions. It is believed that on the twenty third day of the twelfth lunar month, just before Chinese New Year, the Kitchen deity returns to Heaven to report the activities of every household over the past year to Yu Huang Da Di (玉皇大帝), the Jade Emperor. The Jade Emperor, emperor of the heavens, either rewards or punishes a family based on Zao Jun's yearly report. Story Zhang Lang Though there are many stories on how Zao Jun became the Kitchen God, the most popular one dates back to around the 2nd Century BC. Zao Jun was originally a mortal man living on earth whose name was Zhang Lang. He eventually became ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire Gods
This is a list of deities in fire worship. African mythology Yoruba mythology * Ogun, fire god and patron of blacksmiths, iron, warfare, metal tools * Ọya, goddess of fire, wind, transforms into buffalo, fertility * Shango, god of thunder and fire, considered the storm-god * Aggayu, god of volcanoes, magma, sunlight, and heat Egyptian mythology * Ra, fire god of the sun, light, warmth, and growth * Sekhmet, protective lioness goddess of war, along with some elements of disease and curing of disease. Sometimes referenced in relation to the sun and its power, so possibly had to do with upkeep of the sun at times and fire * Wadjet, the protective serpent goddess who sends fire to burn her enemies Asian mythology Ainu mythology * Kamuy-huci, goddess of the fire Chinese mythology * Zhurong (Huoshen, God of Fire) * Huilu (Huoshen, Goddess of Fire) * Yandi (Huozhu, Accident of Fire) * Shennong (Huozhu, Accident of Fire) * Hua Guang Da Di * Ebo (Huozheng, Primary Fire) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Gods
This is a list of divinities native to Japanese beliefs and religious traditions. Many of these are from Shinto, while others were imported via Buddhism or Taoism and were "integrated" into Japanese mythology and folklore. Major kami * Amaterasu-Ōmikami (), she is the goddess of the sun as well as the purported ancestress of the Imperial Household of Japan. Her name means "Shines from Heaven" or "the great kami who shine Heaven". For many reasons, one among them being her ties to the Imperial family, she is often considered (though not officially) to be the "primary god" of Shinto. * Ame-no-Uzume ( or ) Commonly called Uzume, she is the goddess of dawn and revelry in Shinto. * Fūjin () Also known as , he is the Japanese god of the wind and one of the eldest Shinto gods, said to have been present at the creation of the world. He is often depicted as an oni with a bag slung over his back. * Hachiman () is the god of war and the divine protector of Japan and its people. Origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kagu-tsuchi
Kagutsuchi (カグツチ; Old Japanese: ''Kagututi''), also known as Hi-no-Kagutsuchi or Homusubi among other names, is the kami of fire in classical Japanese mythology. Mythology Kagutsuchi's birth burned his mother Izanami, causing her death. His father Izanagi, in his grief, beheaded Kagutsuchi with his sword, Ame no Ohabari (天之尾羽張), and cut his body into eight pieces, which became eight volcanoes. Kagutsuchi’s corpse created numerous deities, which typically includes Watatsumi, Kuraokami, Takemikazuchi, Futsunushi, Amatsumikaboshi, and Ōyamatsumi. Kagutsuchi's birth, in Japanese mythology, comes at the end of the creation of the world and marks the beginning of death.Ashkenazy, Michael. ''Handbook of Japanese Mythology''. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-Clio, 2003. 186 In the ''Engishiki'', a source which contains the myth, Izanami, in her death throes, bears the water god Mizuhanome, instructing her to pacify Kagu-tsuchi if he should become violent. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamuy-huci
Kamuy-huci (カムイフチ, ''Kamui Fuchi'') is the Ainu ''kamuy'' (''goddess'') of the hearth. Her full name is Apemerukoyan-mat Unamerukoyan-mat (''Rising Fire Sparks Woman/ Rising Cinder Sparks Woman''), and she is also known as Iresu Kamuy (''People Teacher''). She is among the most important ''kamuy'' of Ainu mythology, serving as keeper of the gateway between the world of humans and the world of ''kamuy''. Depiction Kamuy-huci is a woman who lives in the hearth. Her position is so important that she never leaves her home. Accordingly, the hearth fire must never be extinguished completely.Ashkenazy, Michael. ''Handbook of Japanese Mythology''. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-Clio, 2003. 191-192 Mythology There are a few myths of Kamuy-huci's origins. In the most common, she descends from the heavens, accompanied by Kanna Kamuy, the ''kamuy'' of thunder and lightning. In another version, she was born from the fire-producing drill and is the sister of Hasinaw-uk-kamuy, the go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jowangshin
Jowangshin (in Hangul, ''조왕신'', in hanja, 竈王神) is the goddess of fire and the hearth in Korean shamanism. As the goddess of the hearth, the rituals dedicated to her were generally kept alive by housewives. She is no longer the subject of worship, but still remains one of the most famous Korean deities. History It is regarded that Jowangshin was worshipped by the Korean people for millennia, since the Proto Three Kingdoms era. For example, in the ''Sanguo Zhi'', a history book of China, there are records of a kitchen god. "There are many different rituals that they (the people of the Samhan Confederacy, in modern South Korea) hold, but all worship a kitchen god in their western wings." Ritual Jowangshin was regarded to embody a bowl of water held on a clay altar above the hearth. The housewife awoke early every morning and poured fresh water from a nearby well into the bowl, then knelt before it, wishing for luck. The ritual of Jowangshin was especially well develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinto Kami
Shinto () is a religion from Japan. Classified as an East Asian religion by scholars of religion, its practitioners often regard it as Japan's indigenous religion and as a nature religion. Scholars sometimes call its practitioners ''Shintoists'', although adherents rarely use that term themselves. There is no central authority in control of Shinto, with much diversity of belief and practice evident among practitioners. A polytheistic and animistic religion, Shinto revolves around supernatural entities called the . The are believed to inhabit all things, including forces of nature and prominent landscape locations. The are worshiped at household shrines, family shrines, and ''jinja'' public shrines. The latter are staffed by priests, known as , who oversee offerings of food and drink to the specific enshrined at that location. This is done to cultivate harmony between humans and and to solicit the latter's blessing. Other common rituals include the dances, rites of pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist Gods
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; "taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and the ; and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
-_Sanbō_Kōjin.jpg)