|
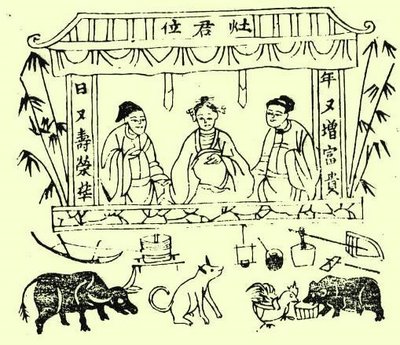
Jowangsin
Jowangshin (in Hangul, ''조왕신'', in hanja, 竈王神) is the goddess of fire and the hearth in Korean shamanism. As the goddess of the hearth, the rituals dedicated to her were generally kept alive by housewives. She is no longer the subject of worship, but still remains one of the most famous Korean deities. History It is regarded that Jowangshin was worshipped by the Korean people for millennia, since the Proto Three Kingdoms era. For example, in the ''Sanguo Zhi'', a history book of China, there are records of a kitchen god. "There are many different rituals that they (the people of the Samhan Confederacy, in modern South Korea) hold, but all worship a kitchen god in their western wings." Ritual Jowangshin was regarded to embody a bowl of water held on a clay altar above the hearth. The housewife awoke early every morning and poured fresh water from a nearby well into the bowl, then knelt before it, wishing for luck. The ritual of Jowangshin was especially well develope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munjeon Bonpuli
The ''Munjeon Bonpuri'' ( ko, 문전본풀이), meaning 'Annals of the Door', 'Book of the Door', 'Narration of the Door' or 'Explanation of the Door', is a myth of Jeju Island regarding Gasin, or deities that are believed to reside within the house. It is one of the better-known myths of the Korean Peninsula. Plot In the village of Namseon in the kingdom of Junyeon lived Namseonbi and his wife, Yeosan Buin. Yeosan Buin was a very capable wife who raised the money for the family. However, her husband Namseonbi wasted all of the money whenever Yeosan Buin gathered enough. The family of Yeosan Buin had nine members: Namseonbi, Yeosan Buin, and their seven sons. The name of the seventh was Nokdisaengin. Because of the family's poverty, all of the family starved and lacked clothing. Yeosan Buin was worried by their pitiful condition, and bought fine cotton clothes and hats and fifty silver coins by selling her treasures she had brought from her family. She suggested that with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chasa Bonpuli
The ''Chasa Bonpuri'', known in other versions as the ''Chesa Bonpuri'' (1933 version) or the ''Cheseo Bonpuri'' (2006 and 2008 versions), is a Korean myth of Jeju Island. It is a myth that tells how Gangnim, the death god, came to be. As one of the best-known myths in the Korean peninsula, the ''Chasa Bonpuri'' is a characteristic Heroic epic, hero epic. Etymology The term ''Chasa Bonpuri'' (차사 본풀이) means "Solving the origins of the death god"; modern academic circles synonymize "Bonpuli" with "myth". ''Chasa'' is the Standard Korean pronunciation of the Chinese language, Chinese word ''Chaishi'' (差使), meaning "messenger". In the Jeju language however, ''chaishi'' is pronounced ''Chesɒ'' or ''Cheshi'', leading to the different names per each version. Collections The Chasa Bonpuli has been directly collected from shamans nine times; below is a chart of these collections. Major plot Like all oral myths, there are multiple versions of the Chasa Bonpuli. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gasin Faith
In Korean shamanism, Gasin (, literally ''House's God'') are a branch of deities believed to protect the various objects and rooms of the house, such as jangdok or the kitchen. The Gasin faith is the faith based on worshipping these deities. The worshipping of the Gasin form a central and integral part of the traditional Korean folk religion. Joryeong faith The faith of Joryeong is the deification of one's ancestors. The earliest mentions of the faith is in the ''Samguk Sagi'', a Medieval Korean history book, which mentions the 'golden chest' of Kim Alji, the first member of the Gyeongju Kim clan. This bears resemblance to modern ancestor worship. In the modern Honam region in southwest Korea, Koreans keep a large pot in the house, filled with rice. This is called the ''Jeseok Ogari'', and holds rice. The Jeseok Ogari is accompanied with ''Mom Ogari'', which are smaller potteries. The name of the ancestor or rice is put in the Mom Ogari. In the Yeongnam region, Jeseok Ogari a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gashin Cult
In Korean shamanism, Gasin (, literally ''House's God'') are a branch of deities believed to protect the various objects and rooms of the house, such as jangdok or the kitchen. The Gasin faith is the faith based on worshipping these deities. The worshipping of the Gasin form a central and integral part of the traditional Korean folk religion. Joryeong faith The faith of Joryeong is the deification of one's ancestors. The earliest mentions of the faith is in the ''Samguk Sagi'', a Medieval Korean history book, which mentions the 'golden chest' of Kim Alji, the first member of the Gyeongju Kim clan. This bears resemblance to modern ancestor worship. In the modern Honam region in southwest Korea, Koreans keep a large pot in the house, filled with rice. This is called the ''Jeseok Ogari'', and holds rice. The Jeseok Ogari is accompanied with ''Mom Ogari'', which are smaller potteries. The name of the ancestor or rice is put in the Mom Ogari. In the Yeongnam region, Jeseok Ogari a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ông Táo
Ông Táo (翁灶) also known as Táo Quân (灶君, Mandarin Táo), Táo Vương (灶王), Thần Bếp (神灶) or the Kitchen god is regarded in Vietnamese culture as the advocate of the Vietnamese family with the gods and the emissary between heaven to earth. Mythology A long time ago, there was a couple, Trọng Cao and his wife Thị Nhi who were married for many years but had no children. One day, they quarreled over some trivial matter, and the husband, in a fit of anger, beat and threw his wife out of their home. Although Thị Nhi still loved her husband, she had no choice but to go away. Thị Nhi went far away and met a very kind man called Phạm Lang. He married her and he loved Thị Nhi very much. Their life was happy and peaceful but Thị Nhi could not forget her first love. As for Trọng Cao, he had been filled with remorse from the day he sent his wife away. He waited, and waited hopelessly for his wife’s return. Eventually, he decided to set out from his home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zàojūn
The Kitchen deity – also known as the Stove God, named Zao Jun, Zao Shen, Zao kimjah, Cokimjah or Zhang Lang – is the most important of a plethora of Chinese domestic gods that protect the hearth and family. The Kitchen God is recognized in Chinese folk religion, Chinese mythology, and Taoism. Under different names, he is also celebrated in several other Asian religions. It is believed that on the twenty third day of the twelfth lunar month, just before Chinese New Year, the Kitchen deity returns to Heaven to report the activities of every household over the past year to Yu Huang Da Di (玉皇大帝), the Jade Emperor. The Jade Emperor, emperor of the heavens, either rewards or punishes a family based on Zao Jun's yearly report. Story Zhang Lang Though there are many stories on how Zao Jun became the Kitchen God, the most popular one dates back to around the 2nd Century BC. Zao Jun was originally a mortal man living on earth whose name was Zhang Lang. He eventually became m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitchen God
The Kitchen deity – also known as the Stove God, named Zao Jun, Zao Shen, Zao kimjah, Cokimjah or Zhang Lang – is the most important of a plethora of Chinese domestic gods that protect the hearth and family. The Kitchen God is recognized in Chinese folk religion, Chinese mythology, and Taoism. Under different names, he is also celebrated in several other Asian religions. It is believed that on the twenty third day of the twelfth lunar month, just before Chinese New Year, the Kitchen deity returns to Heaven to report the activities of every household over the past year to Yu Huang Da Di (玉皇大帝), the Jade Emperor. The Jade Emperor, emperor of the heavens, either rewards or punishes a family based on Zao Jun's yearly report. Story Zhang Lang Though there are many stories on how Zao Jun became the Kitchen God, the most popular one dates back to around the 2nd Century BC. Zao Jun was originally a mortal man living on earth whose name was Zhang Lang. He eventually became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hangul
The Korean alphabet, known as Hangul, . Hangul may also be written as following South Korea's standard Romanization. ( ) in South Korea and Chosŏn'gŭl in North Korea, is the modern official writing system for the Korean language. The letters for the five basic consonants reflect the shape of the speech organs used to pronounce them, and they are systematically modified to indicate phonetic features; similarly, the vowel letters are systematically modified for related sounds, making Hangul a featural writing system. It has been described as a syllabic alphabet as it combines the features of alphabetic and syllabic writing systems, although it is not necessarily an abugida. Hangul was created in 1443 CE by King Sejong the Great in an attempt to increase literacy by serving as a complement (or alternative) to the logographic Sino-Korean ''Hanja'', which had been used by Koreans as its primary script to write the Korean language since as early as the Gojoseon period (spanni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makgeolli
''Makgeolli'' ( ko, 막걸리, raw rice wine ), sometimes anglicized to makkoli (, ), is a Korean alcoholic beverage. The milky, off-white, and lightly sparkling rice wine has a slight viscosity that tastes slightly sweet, tangy, bitter, and astringent. Chalky sediment gives it a cloudy appearance. As a low proof drink of six to nine percent alcohol by volume, it is often considered a "communal beverage" rather than hard liquor. In Korea, ''makgeolli'' is often unpasteurized, and the wine continues to mature in the bottle. Because of the short shelf life of unpasteurized "draft" ''makgeolli'', many exported ''makgeolli'' undergo pasteurization, which deprives the beverage of complex enzymes and flavor compounds. Recently, various fruits such as strawberries and bananas are added to makgeolli to drink in new forms. Names The name ''makgeolli'' () is a compound, consisting of ''mak'' (; "roughly, recklessly, carelessly") and a deverbal noun derived from the verb stem ''georeu-'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire Goddesses
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material (the fuel) in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction products. At a certain point in the combustion reaction, called the ignition point, flames are produced. The ''flame'' is the visible portion of the fire. Flames consist primarily of carbon dioxide, water vapor, oxygen and nitrogen. If hot enough, the gases may become ionized to produce plasma. Depending on the substances alight, and any impurities outside, the color of the flame and the fire's intensity will be different. Fire in its most common form can result in conflagration, which has the potential to cause physical damage through burning. Fire is an important process that affects ecological systems around the globe. The positive effects of fire include stimulating growth and maintaining various ecological systems. Its negative effects include hazard to life and property, atmospheric pollution, and water contamination. If fire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teojushin
Teojushin (Hangul: 터주신, Hanja: 터主神) is the patron of the ground on which the house is built in the Gashin cult of Korea. She is also known as Jishin, or 'earth goddess'. In Honam, there is no entity that resembles Teojushin. However, there is a deity called Cheollyungshin, the patron of Jangdok, or sauce containers. Compared with the worship of other Gashin, such as Jowangshin or Seongjushin, Teojushin is less known; still, she remains an important deity in Korean mythology. Worship Teojushin was believed to embody a pot holding rice, peas, or red beans. The pot was then buried or just placed on the corners of the backyard or the jangdokdae, an open area holding jangdok. The pot was covered with a cone-shaped umbrella woven of rice stalks. The grains within the pot was replaced every year, and the family made tteok, or rice cakes, out of them. The rice cakes were never shared; this is because the tteoks represented luck, and because of the belief that Teojushin was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vesta (mythology)
Vesta () is the virgin goddess of the hearth, home, and family in Roman religion. She was rarely depicted in human form, and was more often represented by the fire of her temple in the Forum Romanum. Entry to her temple was permitted only to her priestesses, the Vestal Virgins, who guarded particular sacred objects within, prepared flour and sacred salt (''mola salsa'') for official sacrifices, and tended Vesta's sacred fire at the temple hearth. Their virginity was thought essential to Rome's survival; if found guilty of inchastity, they were punished by burial alive. As Vesta was considered a guardian of the Roman people, her festival, the '' Vestalia'' (7–15 June), was regarded as one of the most important Roman holidays. During the ''Vestalia'' privileged matrons walked barefoot through the city to the temple, where they presented food-offerings. Such was Vesta's importance to Roman religion that following the rise of Christianity, hers was one of the last non-Christian cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |