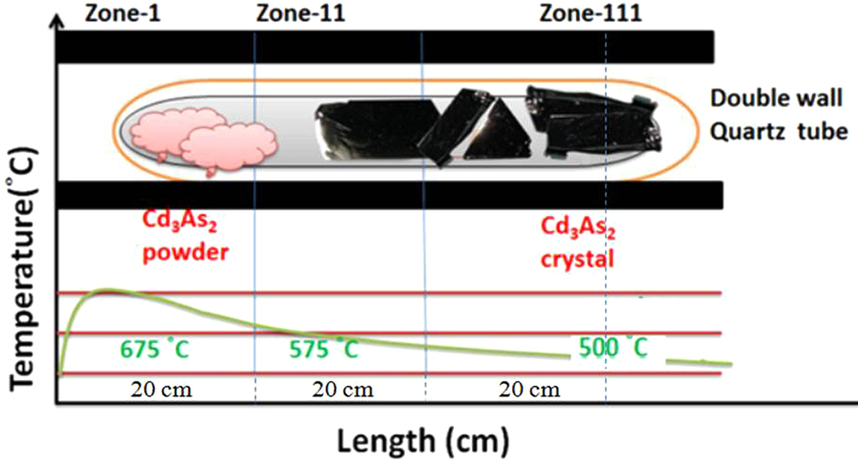
|
Zinc Cadmium Phosphide Arsenide
Zinc cadmium phosphide arsenide ( Zn- Cd- P- As) is a quaternary system of group II (IUPAC group 12) and group V (IUPAC group 15) elements. Many of the inorganic compounds in the system are II-V semiconductor materials. The quaternary system of II3V2 compounds, (Zn1−xCdx)3(P1−yAsy)2, has been shown to allow solid solution continuously over the whole compositional range. This material system and its subsets have applications in electronics, optoelectronics, including photovoltaics, and thermoelectrics. List of all binary compounds This system of elements contains numerous binary compounds and their solid solutions. Stable at atmospheric pressure The binary compounds thermodynamically stable at atmospheric pressure are listed in the following table: Metastable or unstable at atmospheric pressure Compounds metastable or unstable at atmospheric pressure are the following: Quaternary compounds The compounds of the form II3V2 have similar crystalline structures and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic table. In some respects, zinc is chemically similar to magnesium: both elements exhibit only one normal oxidation state (+2), and the Zn2+ and Mg2+ ions are of similar size.The elements are from different metal groups. See periodic table. Zinc is the 24th most abundant element in Earth's crust and has five stable isotopes. The most common zinc ore is sphalerite (zinc blende), a zinc sulfide mineral. The largest workable lodes are in Australia, Asia, and the United States. Zinc is refined by froth flotation of the ore, roasting, and final extraction using electricity ( electrowinning). Zinc is an essential trace element for humans, animals, plants and for microorganisms and is necessary for prenatal and postnatal development. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Phosphide
Zinc phosphide ( Zn3 P2) is an inorganic chemical compound. It is a grey solid, although commercial samples are often dark or even black. It is used as a rodenticide. Zn3P2 is a II-V semiconductor with a direct band gap of 1.5 eV and may have applications in photovoltaic cells. A second compound exists in the zinc-phosphorus system, zinc diphosphide (ZnP2). Synthesis and reactions Zinc phosphide can be prepared by the reaction of zinc with phosphorus; however, for critical applications, additional processing to remove arsenic compounds may be needed. :6 Zn + P4 → 2 Zn3P2 Another method of preparation include reacting tri-n-octylphosphine with dimethylzinc. Zinc phosphide reacts with water to produce phosphine (PH3) and zinc hydroxide (Zn(OH)2): :Zn3P2 + 6 H2O → 2 PH3 + 3 Zn(OH)2 Structure Zn3P2 has a room-temperature tetragonal form that converts to a cubic form at around 845 °C.Evgeniĭ I︠U︡rʹevich Tonkov, 1992, High Pressure Phase Transformati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band Gap
In solid-state physics, a band gap, also called an energy gap, is an energy range in a solid where no electronic states can exist. In graphs of the electronic band structure of solids, the band gap generally refers to the energy difference (in electron volts) between the top of the valence band and the bottom of the conduction band in insulators and semiconductors. It is the energy required to promote a valence electron bound to an atom to become a conduction electron, which is free to move within the crystal lattice and serve as a charge carrier to conduct electric current. It is closely related to the HOMO/LUMO gap in chemistry. If the valence band is completely full and the conduction band is completely empty, then electrons cannot move within the solid because there are no available states. If the electrons are not free to move within the crystal lattice, then there is no generated current due to no net charge carrier mobility. However, if some electrons transfer from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nernst Effect
In physics and chemistry, the Nernst effect (also termed first Nernst–Ettingshausen effect, after Walther Nernst and Albert von Ettingshausen) is a thermoelectric (or thermomagnetic) phenomenon observed when a sample allowing electrical conduction is subjected to a magnetic field and a temperature gradient normal (perpendicular) to each other. An electric field will be induced normal to both. This effect is quantified by the Nernst coefficient , ''N'', , which is defined to be ::, N, =\frac where E_Y is the y-component of the electric field that results from the magnetic field's z-component B_Z and the temperature gradient dT/dx. The reverse process is known as the Ettingshausen effect and also as the second Nernst–Ettingshausen effect. Physical picture Mobile energy carriers (for example conduction-band electrons in a semiconductor) will move along temperature gradients due to statistics and the relationship between temperature and kinetic energy. If there is a magne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semimetal
A semimetal is a material with a very small overlap between the bottom of the conduction band and the top of the valence band. According to electronic band theory, solids can be classified as insulators, semiconductors, semimetals, or metals. In insulators and semiconductors the filled valence band is separated from an empty conduction band by a band gap. For insulators, the magnitude of the band gap is larger (e.g., > 4 eV) than that of a semiconductor (e.g., < 4 eV). Because of the slight overlap between the conduction and valence bands, semimetals have no band gap and a negligible at the Fermi level. A metal, by contrast, has an appreciable density of states at the Fermi level because the conduction band is partially filled. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topological Order
In physics, topological order is a kind of order in the zero-temperature phase of matter (also known as quantum matter). Macroscopically, topological order is defined and described by robust ground state degeneracy and quantized non-Abelian geometric phases of degenerate ground states. Microscopically, topological orders correspond to patterns of long-range quantum entanglement. States with different topological orders (or different patterns of long range entanglements) cannot change into each other without a phase transition. Various topologically ordered states have interesting properties, such as (1) topological degeneracy and fractional statistics or non-abelian statistics that can be used to realize a topological quantum computer; (2) perfect conducting edge states that may have important device applications; (3) emergent gauge field and Fermi statistics that suggest a quantum information origin of elementary particles; See also (4) topological entanglement entropy that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthorhombic Crystal System
In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Orthorhombic lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, resulting in a rectangular prism with a rectangular base (''a'' by ''b'') and height (''c''), such that ''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' are distinct. All three bases intersect at 90° angles, so the three lattice vectors remain mutually orthogonal. Bravais lattices There are four orthorhombic Bravais lattices: primitive orthorhombic, base-centered orthorhombic, body-centered orthorhombic, and face-centered orthorhombic. For the base-centered orthorhombic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of a right rhombic prism;See , row oC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β = 90° it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be described with primitive rhombic axes. Note that the length a of the primiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetragonal Crystal System
In crystallography, the tetragonal crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Tetragonal crystal lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along one of its lattice vectors, so that the cube becomes a rectangular prism with a square base (''a'' by ''a'') and height (''c'', which is different from ''a''). Bravais lattices There are two tetragonal Bravais lattices: the primitive tetragonal and the body-centered tetragonal. The base-centered tetragonal lattice is equivalent to the primitive tetragonal lattice with a smaller unit cell, while the face-centered tetragonal lattice is equivalent to the body-centered tetragonal lattice with a smaller unit cell. Crystal classes The point groups that fall under this crystal system are listed below, followed by their representations in international notation, Schoenflies notation, orbifold notation, Coxeter notation and mineral examples.Hurlbut, Cornelius S.; Klein, Cornelis, 1985, ''Manual of Mineralogy'', 20th ed., pp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexagonal Crystal Family
In crystallography, the hexagonal crystal family is one of the six crystal families, which includes two crystal systems (hexagonal and trigonal) and two lattice systems (hexagonal and rhombohedral). While commonly confused, the trigonal crystal system and the rhombohedral lattice system are not equivalent (see section crystal systems below). In particular, there are crystals that have trigonal symmetry but belong to the hexagonal lattice (such as α-quartz). The hexagonal crystal family consists of the 12 point groups such that at least one of their space groups has the hexagonal lattice as underlying lattice, and is the union of the hexagonal crystal system and the trigonal crystal system. There are 52 space groups associated with it, which are exactly those whose Bravais lattice is either hexagonal or rhombohedral. __TOC__ Lattice systems The hexagonal crystal family consists of two lattice systems: hexagonal and rhombohedral. Each lattice system consists of one Bravais la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadmium Arsenide
Cadmium arsenide ( Cd3 As2) is an inorganic semimetal in the II-V family. It exhibits the Nernst effect. Properties Thermal Cd3As2 dissociates between 220 and 280 °C according to the reaction :2 Cd3As2(s) → 6 Cd(g) + As4(g) An energy barrier was found for the nonstoichiometric vaporization of arsenic due to the irregularity of the partial pressures with temperature. The range of the energy gap is from 0.5 to 0.6 eV. Cd3As2 melts at 716 °C and changes phase at 615 °C/ Phase transition Pure cadmium arsenide undergoes several phase transitions at high temperatures, making phases labeled α (stable), α’, α” (metastable), and β. At 593° the polymorphic transition α → β occurs. :α-Cd3As2 ↔ α’-Cd3As2 occurs at ~500 K. :α’-Cd3As2 ↔ α’’-Cd3As2 occurs at ~742 K and is a regular first order phase transition with marked hysteresis loop. :α”-Cd3As2 ↔ β-Cd3As2 occurs at 868 K. Single crystal x-ray diffraction was used to dete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadmium Diphosphide
Cadmium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12 element, group 12, zinc and mercury (element), mercury. Like zinc, it demonstrates oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds, and like mercury, it has a lower melting point than the transition metals in group 3 element, groups 3 through group 11 element, 11. Cadmium and its Congener (chemistry), congeners in group 12 are often not considered transition metals, in that they do not have partly filled ''d'' or ''f'' electron shells in the elemental or common oxidation states. The average concentration of cadmium in Earth's crust is between 0.1 and 0.5 parts per million (ppm). It was discovered in 1817 simultaneously by Friedrich Stromeyer, Stromeyer and Karl Samuel Leberecht Hermann, Hermann, both in Germany, as an impurity in zinc carbonate. Cadmium occurs as a minor component in most zinc ores a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadmium Phosphide
Cadmium phosphide ( Cd3 P2) is an inorganic chemical compound. It is a grey or white bluish solid semiconductor material with a bandgap of 0.5 eV. It has applications as a pesticide, material for laser diodes and for high-power-high-frequency electronics. Synthesis and reactions Cadmium phosphide can be prepared by the reaction of cadmium with phosphorus: :6 Cd + P4 → 2 Cd3P2 Structure Cd3P2 has a room-temperature tetragonal form. The crystalline structure of cadmium phosphide is very similar to that of zinc phosphide (Zn3P2), cadmium arsenide (Cd3As2) and zinc arsenide (Zn3As2). These compounds of the Zn-Cd-P-As quaternary system exhibit full continuous solid-solution. Applications Safety Like other metal phosphides, it is acutely toxic when swallowed due to the formation of phosphine gas when it reacts with gastric acid. It is also carcinogen and dangerous for the skin, eyes and other organs in a large part due to cadmium poisoning. References {{Phospho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |