|
Zhujiajiao Canal 4
Zhujiajiao (; Shanghainese: ''Chukakoq'') is an ancient town located in the Qingpu District of Shanghai. The population of Zhujiajiao is 60,000. Zhujiajiao is a water town on the outskirts of Shanghai, and was established about 1,700 years ago. Archaeological findings dating back 5,000 years have also been found. 36 stone bridges and numerous rivers line Zhujiajiao, and many ancient buildings still line the riverbanks today. Historic sights The village prospered through clothing and rice businesses. Today, old historical buildings such as rice shops, banks, spice stores and even a Qing dynasty post office can still be found. Zhujiajiao has many sights of historic interest, such as Fangsheng Bridge, Kezhi Garden and the Yuanjin Buddhist Temple. However, recent overdevelopment threatens the village's authenticity - most notably the current (since 2012) conversion of its people's square into shops and the large-scale shopping and entertainment complexes being constructed in an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Town (China)
When referring to political divisions of China, town is the standard English translation of the Chinese (traditional: ; ). The Constitution of the People's Republic of China classifies towns as third-level administrative units, along with for example townships (). A township is typically smaller in population and more remote than a town. Similarly to a higher-level administrative units, the borders of a town would typically include an urban core (a small town with the population on the order of 10,000 people), as well as rural area with some villages (, or ). Map representation A typical provincial map would merely show a town as a circle centered at its urban area and labeled with its name, while a more detailed one (e.g., a map of a single county-level division) would also show the borders dividing the county A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposes Chambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and Borders of China, borders fourteen countries by land, the List of countries and territories by land borders, most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces of China, provinces, five autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions, four direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities, and two special administrative regions of China, Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the List of cities in China by population, most populous cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct-controlled Municipality
A direct-controlled municipality is the highest level classification for cities used by unitary states, with status equal to that of the provinces in the respective countries. A direct-controlled municipality is similar to, but not the same as, a federal district, a common designation in various countries for a municipality that is not part of any state, and which usually hosts some governmental functions. Usually direct-controlled municipality are under central government control with limited power. Many countries have adopted this system with some different variations. Geographically and culturally, many of the municipalities are enclaves in the middle of provinces. Some occur in strategic positions in between provinces. References See also * Independent city * Federal city * Metropolitan Capitalism (Capital City) * Federal district * Federal territory A federal territory is an administrative division under the direct and usually exclusive jurisdiction of a federati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flowing through it. With a population of 24.89 million as of 2021, Shanghai is the most populous urban area in China with 39,300,000 inhabitants living in the Shanghai metropolitan area, the second most populous city proper in the world (after Chongqing) and the only city in East Asia with a GDP greater than its corresponding capital. Shanghai ranks second among the administrative divisions of Mainland China in human development index (after Beijing). As of 2018, the Greater Shanghai metropolitan area was estimated to produce a gross metropolitan product ( nominal) of nearly 9.1 trillion RMB ($1.33 trillion), exceeding that of Mexico with GDP of $1.22 trillion, the 15th largest in the world. Shanghai is one of the world's major centers fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
District (China)
The term ''district'', in the context of China, is used to refer to several unrelated political divisions in both ancient and modern China. In the modern context, district (), formally city-governed district, city-controlled district, or municipal district (), are subdivisions of a municipality or a prefecture-level city. The rank of a district derives from the rank of its city. Districts of a municipality are prefecture-level; districts of a sub-provincial city are sub-prefecture-level; and districts of a prefecture-level city are county-level. The term was also formerly used to refer to obsolete county-controlled districts (also known as district public office). However, if the word ''district'' is encountered in the context of ancient Chinese history, then it is a translation for '' xian'', another type of administrative division in China. Before the 1980s, cities in China were administrative divisions containing mostly urban, built-up areas, with very little farmla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qingpu District, Shanghai
Qingpu District, is a suburban district of Shanghai Municipality. Lake Dianshan is located in Qingpu. The population of Qingpu was counted at 1,081,000 people in the 2010 Census. It has an area of . Qingpu District is the westernmost district of Shanghai Municipality; it is adjacent to Jiangsu and Zhejiang Provinces. Around the lake are a number of tourist scenic areas, all complete in tourist facilities. Among the tourist areas is the waterside town Zhujiajiao, a major tourist destination in the Shanghai region. There are currently 21 domestic travel services, three international travel business departments, 14 star-rated hotels, and 3 AAAA-grade tourist spots in Qingpu District. Transport * Line 17 (Shanghai Metro) * China National Highway 318 Tourism Qingpu's tourist attractions include the Zhujiajiao Ancient Town, Oriental Land, Jinze Ancient Town, Lake Dianshan, and the Qushui Garden. Economy The China offices of Oishi are located here. Culture Baihe, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Standard Time
The time in China follows a single standard UTC offset, time offset of UTC+08:00 (eight hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time), even though the country spans almost five geographical time zones. The official national standard time is called ''Beijing Time'' (BJT, ) domestically and ''China Standard Time'' (CST) internationally. Daylight saving time has not been observed since 1991. China Standard Time (UTC+8) is consistent across Mainland China, Hong Kong Time, Hong Kong, Macau Standard Time, Macau, Time in Taiwan, Taiwan, Philippine Standard Time, Philippines, Singapore Standard Time, Singapore, Time in Brunei, Brunei, Time in Mongolia, Mongolia, etc. History In the 1870s, the Shanghai Xujiahui Observatory was constructed by a French Catholic missionary. In 1880s officials in Shanghai French Concession started to provide a time announcement service using the Shanghai Mean Solar Time provided by the aforementioned observatory for ships into and out of Shanghai. By the end o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanghainese
The Shanghainese language, also known as the Shanghai dialect, or Hu language, is a variety of Wu Chinese spoken in the central districts of the City of Shanghai and its surrounding areas. It is classified as part of the Sino-Tibetan language family. Shanghainese, like the rest of the Wu language group, is mutually unintelligible with other varieties of Chinese, such as Mandarin. Shanghainese belongs a separate group of the Taihu Wu subgroup. With nearly 14 million speakers, Shanghainese is also the largest single form of Wu Chinese. Since the late 19th century it has served as the lingua franca of the entire Yangtze River Delta region, but in recent decades its status has declined relative to Mandarin, which most Shanghainese speakers can also speak. Like other Wu varieties, Shanghainese is rich in vowels and consonants, with around twenty unique vowel qualities, twelve of which are phonemic. Similarly, Shanghainese also has voiced obstruent initials, which is rare outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Town (China)
Water towns, also called Canal towns (), are certain ancient and historic towns in China known for their bridges, rivers, and canals. Such towns exist in many regions in China, although those in Jiangsu and Zhejiang provinces are often the most renowned. Canal towns are generally concentrated in the Jiangnan area which includes the Jiangsu province, Zhejiang province and Shanghai area. They are located towards the south of the Yangtze River. These river-based settlements are widely advertised as tourism destinations because of their historical and cultural representations of China. The idyllic small-town setting, which demonstrates the harmonious relationship between nature and its residents, is also another attractive factor. The distribution of residential buildings in these water towns can be categorised into three types: against the water, by the water, and across the water. They are usually characterised by some of the traditional architectural features, including eaves g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhujiajiao Stone Bridge
Zhujiajiao (; Shanghainese: ''Chukakoq'') is an ancient town located in the Qingpu District of Shanghai. The population of Zhujiajiao is 60,000. Zhujiajiao is a water town on the outskirts of Shanghai, and was established about 1,700 years ago. Archaeological findings dating back 5,000 years have also been found. 36 stone bridges and numerous rivers line Zhujiajiao, and many ancient buildings still line the riverbanks today. Historic sights The village prospered through clothing and rice businesses. Today, old historical buildings such as rice shops, banks, spice stores and even a Qing dynasty post office can still be found. Zhujiajiao has many sights of historic interest, such as Fangsheng Bridge, Kezhi Garden and the Yuanjin Buddhist Temple. However, recent overdevelopment threatens the village's authenticity - most notably the current (since 2012) conversion of its people's square into shops and the large-scale shopping and entertainment complexes being constructed in an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Life Bridge
The Free Life Bridge () is a historic stone arch bridge over the Cao Port in Zhujiajiao, Qingpu District, Shanghai. History The bridge was originally built in 1571 with funds collected by monk Xingchao () from Cimen Temple (). In the Ming and Qing dynasties (1368–1911), local monks would hold a ceremony on the bridge, releasing live fish into the port. It had been on the list of "The Ten Views of Zhujiajiao". It was rebuilt in 1812, in the ruling of Jiaqing Emperor (1796–1820) of the Qing dynasty (1644–1911). On November 17, 1987, it has been designated as a municipal level cultural heritage by the Shanghai Municipal Government. Architecture long and wide, it is the largest stone bridge in Shanghai. It is of five-arch type. The bridge has a gentle slope as it adopts ultra-thin piers and arches with modest size changes, spanning naturally across the river, which looks majestic but not bulky. The stone carvings on the bridge are exquisite. Film Culture and Manga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
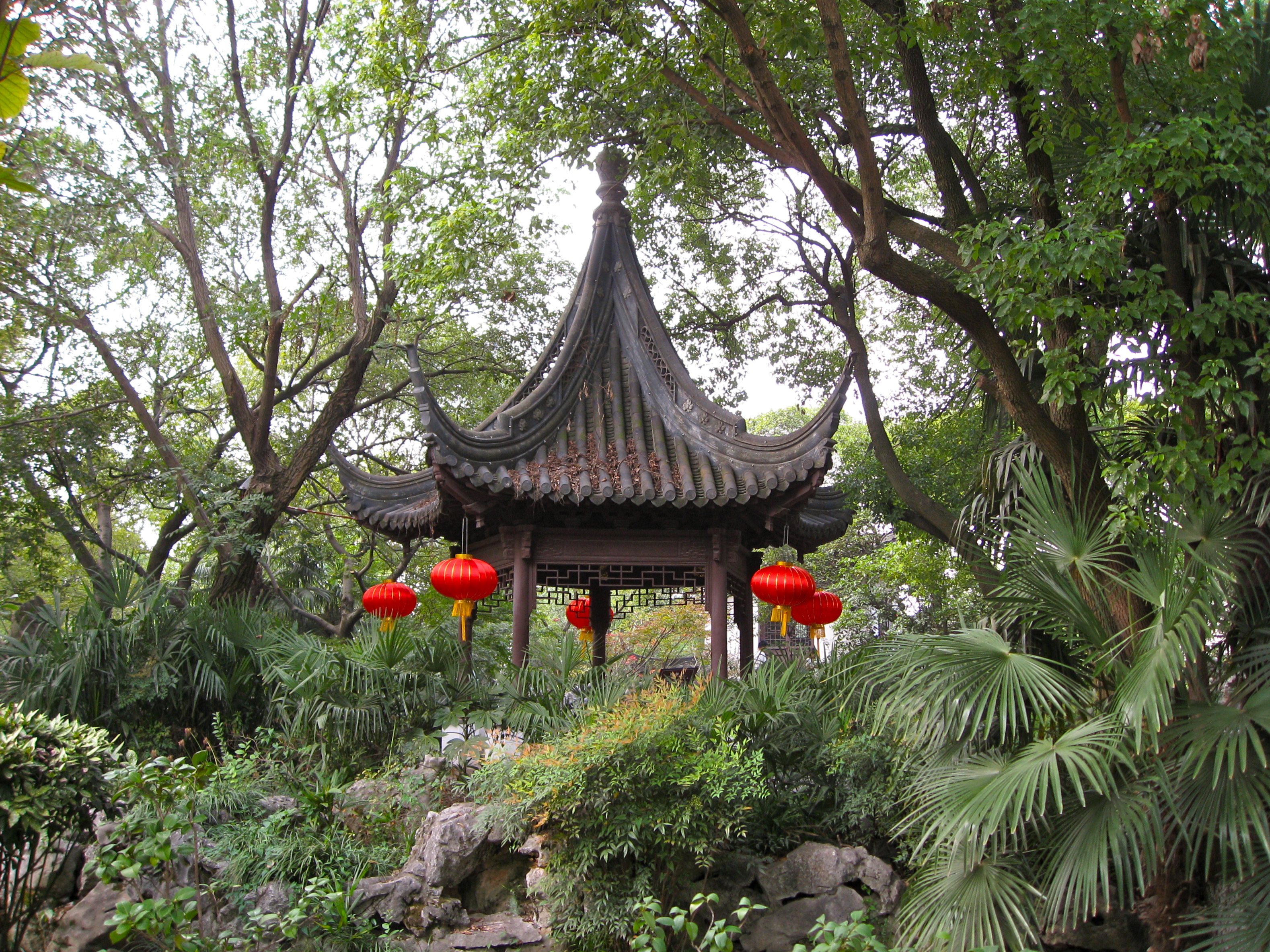
Upside Down Lion Pavilion In Kezhi Garden
Upside can refer to: * ''The Upside'', a 2017 American film * ''Upside'' (magazine) was a San Francisco-based business and technology magazine * Upside Records, a record label * ''Upside'' (film), a 2010 American film * "Upside", a 2008 song by James from the album '' Hey Ma'' See also * Downside (other) Downside may refer to: * Downside, North Somerset, a sub-district of Backwell, Somerset, England * Downside, Somerset, a hamlet near Chilcompton in England ** Downside Abbey, a monastery in Somerset, England ** Downside School, a public school ... * Upside Down (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |