|
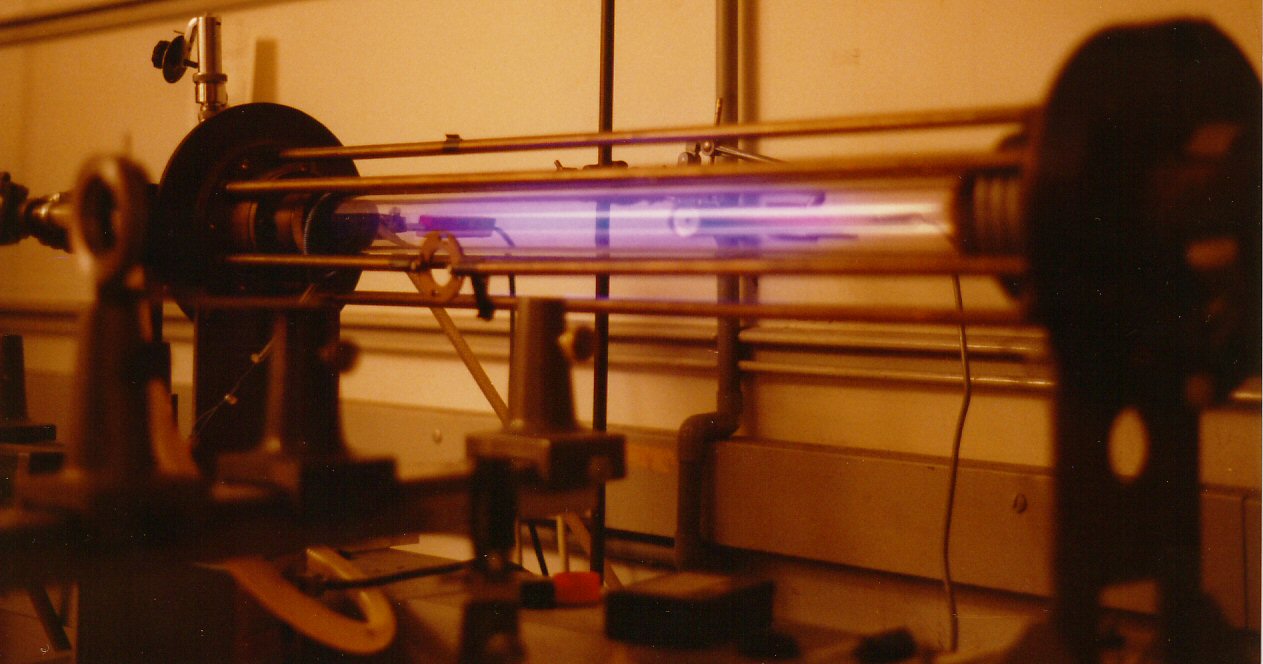
Z-pinch H-gamma
In fusion power research, the Z-pinch (zeta pinch) is a type of plasma confinement system that uses an electric current in the plasma to generate a magnetic field that compresses it (see pinch). These systems were originally referred to simply as pinch or Bennett pinch (after Willard Harrison Bennett), but the introduction of the θ-pinch (theta pinch) concept led to the need for clearer, more precise terminology. The name refers to the direction of the current in the devices, the Z-axis on a normal three-dimensional graph. Any machine that causes a pinch effect due to current running in that direction is correctly referred to as a Z-pinch system, and this encompasses a wide variety of devices used for an equally wide variety of purposes. Early uses focused on fusion research in donut-shaped tubes with the Z-axis running down the inside the tube, while modern devices are generally cylindrical and used to generate high-intensity x-ray sources for the study of nuclear weapons an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Z-pinch H-gamma
In fusion power research, the Z-pinch (zeta pinch) is a type of plasma confinement system that uses an electric current in the plasma to generate a magnetic field that compresses it (see pinch). These systems were originally referred to simply as pinch or Bennett pinch (after Willard Harrison Bennett), but the introduction of the θ-pinch (theta pinch) concept led to the need for clearer, more precise terminology. The name refers to the direction of the current in the devices, the Z-axis on a normal three-dimensional graph. Any machine that causes a pinch effect due to current running in that direction is correctly referred to as a Z-pinch system, and this encompasses a wide variety of devices used for an equally wide variety of purposes. Early uses focused on fusion research in donut-shaped tubes with the Z-axis running down the inside the tube, while modern devices are generally cylindrical and used to generate high-intensity x-ray sources for the study of nuclear weapons an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marx Generator
A Marx generator is an electrical circuit first described by Erwin Otto Marx in 1924. Its purpose is to generate a high-voltage pulse from a low-voltage DC supply. Marx generators are used in high-energy physics experiments, as well as to simulate the effects of lightning on power-line gear and aviation equipment. A bank of 36 Marx generators is used by Sandia National Laboratories to generate X-rays in their Z Machine. Principle of operation The circuit generates a high-voltage pulse by charging a number of capacitors in parallel, then suddenly connecting them in series. See the circuit above. At first, ''n'' capacitors (''C'') are charged in parallel to a voltage ''VC'' by a DC power supply through the resistors (''R''C). The spark gaps used as switches have the voltage ''VC'' across them, but the gaps have a breakdown voltage greater than ''VC'', so they all behave as open circuits while the capacitors charge. The last gap isolates the output of the generator from the load; wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokamak
A tokamak (; russian: токамáк; otk, 𐱃𐰸𐰢𐰴, Toḳamaḳ) is a device which uses a powerful magnetic field to confine plasma in the shape of a torus. The tokamak is one of several types of magnetic confinement devices being developed to produce controlled thermonuclear fusion power. , it was the leading candidate for a practical fusion reactor. Tokamaks were initially conceptualized in the 1950s by Soviet physicists Igor Tamm and Andrei Sakharov, inspired by a letter by Oleg Lavrentiev. The first working tokamak was attributed to the work of Natan Yavlinsky on the T-1 in 1958. It had been demonstrated that a stable plasma equilibrium requires magnetic field lines that wind around the torus in a helix. Devices like the z-pinch and stellarator had attempted this, but demonstrated serious instabilities. It was the development of the concept now known as the safety factor (labelled ''q'' in mathematical notation) that guided tokamak development; by arranging the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust
Thrust is a reaction force described quantitatively by Newton's third law. When a system expels or accelerates mass in one direction, the accelerated mass will cause a force of equal magnitude but opposite direction to be applied to that system. The force applied on a surface in a direction perpendicular or normal to the surface is also called thrust. Force, and thus thrust, is measured using the International System of Units (SI) in newtons (symbol: N), and represents the amount needed to accelerate 1 kilogram of mass at the rate of 1 meter per second per second. In mechanical engineering, force orthogonal to the main load (such as in parallel helical gears) is referred to as static thrust. Examples A fixed-wing aircraft propulsion system generates forward thrust when air is pushed in the direction opposite to flight. This can be done by different means such as the spinning blades of a propeller, the propelling jet of a jet engine, or by ejecting hot gases from a rocket ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Impulse
Specific impulse (usually abbreviated ) is a measure of how efficiently a reaction mass engine (a rocket using propellant or a jet engine using fuel) creates thrust. For engines whose reaction mass is only the fuel they carry, specific impulse is exactly proportional to the effective exhaust gas velocity. A propulsion system with a higher specific impulse uses the mass of the propellant more efficiently. In the case of a rocket, this means less propellant needed for a given delta-v, so that the vehicle attached to the engine can more efficiently gain altitude and velocity. In an atmospheric context, specific impulse can include the contribution to impulse provided by the mass of external air that is accelerated by the engine in some way, such as by an internal turbofan or heating by fuel combustion participation then thrust expansion or by external propeller. Jet engines breathe external air for both combustion and by-pass, and therefore have a much higher specific impulse than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sceptre (fusion Reactor)
Sceptre was an early fusion power device based on the Z-pinch concept of plasma confinement, built in the UK starting in 1957. They were the ultimate versions of a series of devices tracing their history to the original pinch machines, built at Imperial College London by Cousins and Ware in 1947. When the UK's fusion work was classified in 1950, Ware's team was moved to the Associated Electrical Industries (AEI) labs at Aldermaston. The team worked on the problems associated with using metal tubes with high voltages, in support of the efforts at Harwell. When Harwell's ZETA machine apparently produced fusion, AEI quickly built a smaller machine, Sceptre, to test their results. Sceptre also produced neutrons, apparently confirming the ZETA experiment. It was later found that the neutrons were spurious, and UK work on Z-pinch ended in the early 1960s. History Background Fusion research in the UK started on a shoestring budget at Imperial College in 1946. When George Paget Thomso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , which has a neutral (not positive or negative) charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the nuclei of atoms. Since protons and neutrons behave similarly within the nucleus, and each has a mass of approximately one atomic mass unit, they are both referred to as nucleons. Their properties and interactions are described by nuclear physics. Protons and neutrons are not elementary particles; each is composed of three quarks. The chemical properties of an atom are mostly determined by the configuration of electrons that orbit the atom's heavy nucleus. The electron configuration is determined by the charge of the nucleus, which is determined by the number of protons, or atomic number. The number of neutrons is the neutron number. Neutrons do not affect the electron configuration, but the sum of atomic and neutron numbers is the mass of the nucleus. Atoms of a chemical element t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
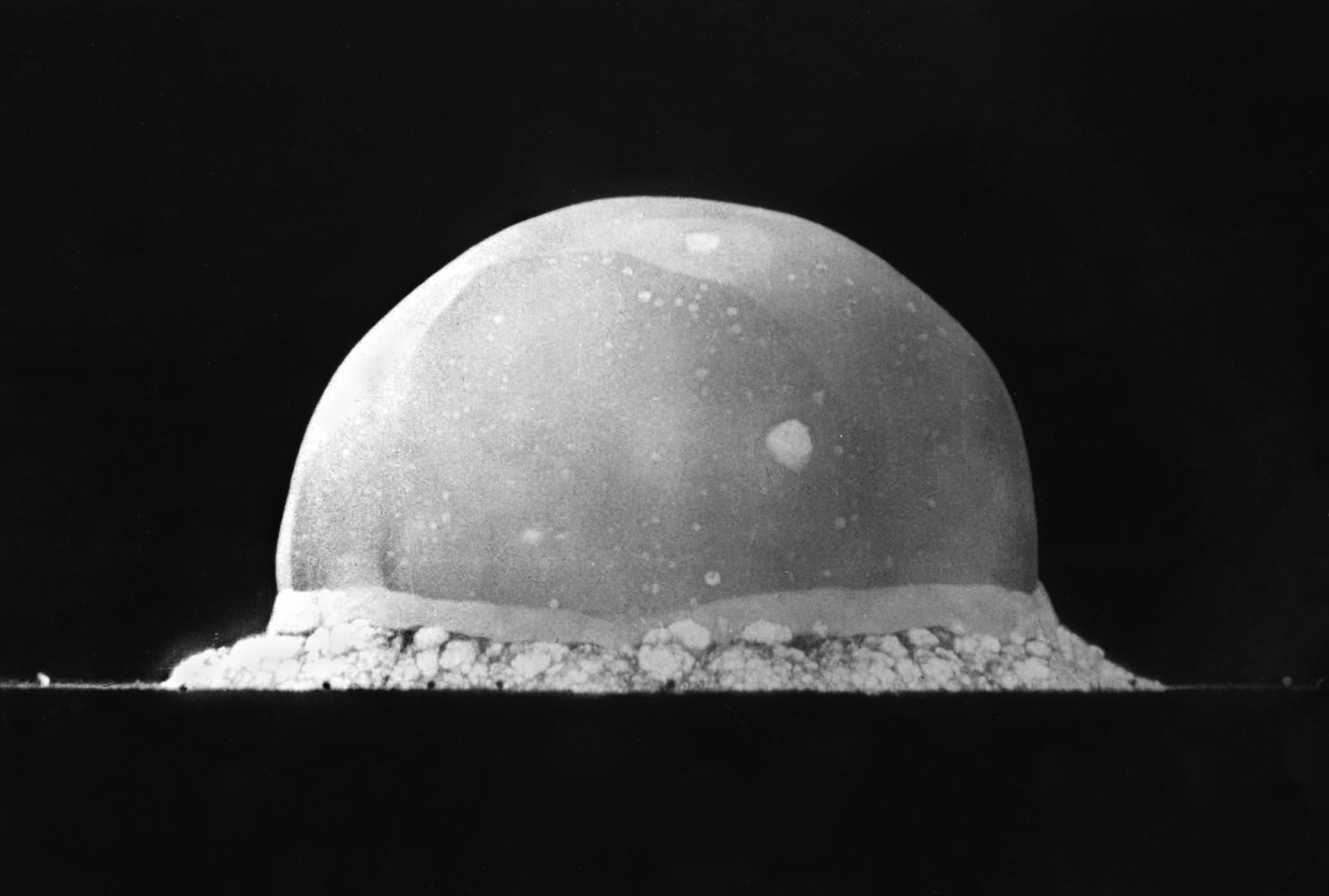
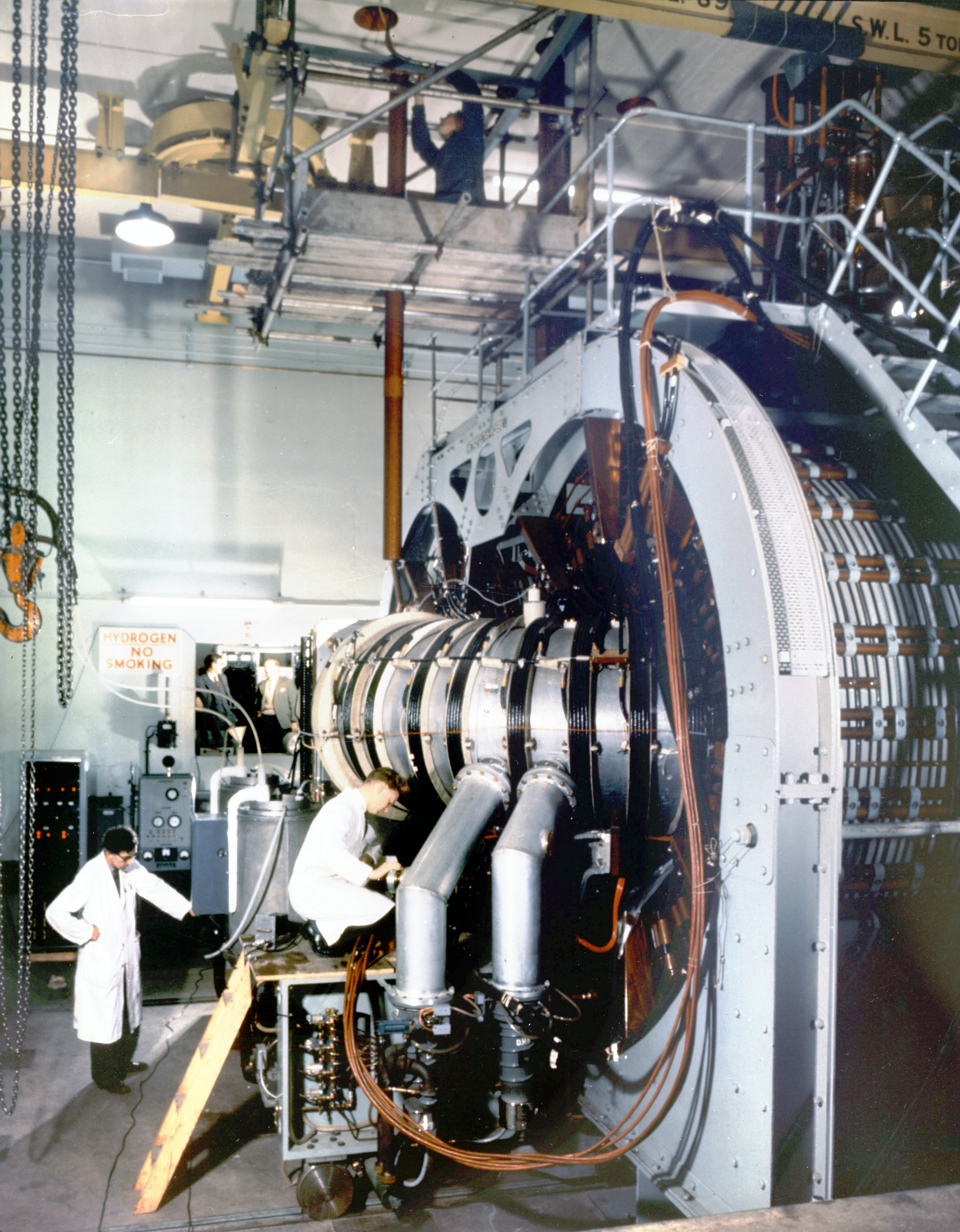
ZETA (fusion Reactor)
ZETA, short for Zero Energy Thermonuclear Assembly, was a major experiment in the early history of fusion power research. Based on the Z-pinch, pinch Plasma (physics), plasma confinement technique, and built at the Atomic Energy Research Establishment in the United Kingdom, ZETA was larger and more powerful than any fusion machine in the world at that time. Its goal was to produce large numbers of fusion reactions, although it was not large enough to produce net energy. ZETA went into operation in August 1957 and by the end of the month it was giving off bursts of about a million neutrons per pulse. Measurements suggested the fuel was reaching between 1 and 5 million kelvins, a temperature that would produce nuclear fusion reactions, explaining the quantities of neutrons being seen. Early results were leaked to the press in September 1957, and the following January an extensive review was released. Front-page articles in newspapers around the world announced it as a breakthro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kink Instability
A kink instability (also kink oscillation or kink mode), is a current-driven plasma instability characterized by transverse displacements of a plasma column's cross-section from its center of mass without any change in the characteristics of the plasma. It typically develops in a thin plasma column carrying a strong axial current which exceeds the Kruskal–Shafranov limit and is sometimes known as the Kruskal–Shafranov (kink) instability. The kink instability was first widely explored in fusion power machines with Z-pinch configurations in the 1950s. It is one of the common magnetohydrodynamic instability modes which can develop in a pinch plasma and is sometimes referred to as the m=1 mode. (The other is the m=0 mode known as the sausage instability.) If a "kink" begins to develop in a column the magnetic force In physics (specifically in electromagnetism) the Lorentz force (or electromagnetic force) is the combination of electric and magnetic force on a point charge due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LANL
Los Alamos National Laboratory (often shortened as Los Alamos and LANL) is one of the sixteen research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy (DOE), located a short distance northwest of Santa Fe, New Mexico, in the American southwest. Best known for its central role in helping develop the first atomic bomb, LANL is one of the world's largest and most advanced scientific institutions. Los Alamos was established in 1943 as Project Y, a top-secret site for designing nuclear weapons under the Manhattan Project during World War II.The site was variously called Los Alamos Laboratory and Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory. Chosen for its remote yet relatively accessible location, it served as the main hub for conducting and coordinating nuclear research, bringing together some of the world's most famous scientists, among them numerous Nobel Prize winners. The town of Los Alamos, directly north of the lab, grew extensively through this period. Aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perhapsatron
The Perhapsatron was an early fusion power device based on the pinch concept in the 1950s. Conceived by James (Jim) Tuck while working at Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL), he whimsically named the device on the chance that it might be able to create fusion reactions. The first example was built in the winter of 1952/53, and it quickly demonstrated a series of instabilities in the plasma that plagued the pinch concept. A series of modifications followed which attempted to correct these problems, leading to the ultimate "S-4" model. None of these proved fruitful. History Early fusion efforts Scientists at Los Alamos National Laboratory had a long history of studying nuclear fusion, and by 1946 they had calculated that a steady-state plasma would have to be heated to 100 million degrees Celsius (180 million degrees Fahrenheit) to "ignite" and release net energy. This was of vital interest in the nuclear bomb establishment, where the use of a small atomic bomb "trigger" was us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |