|
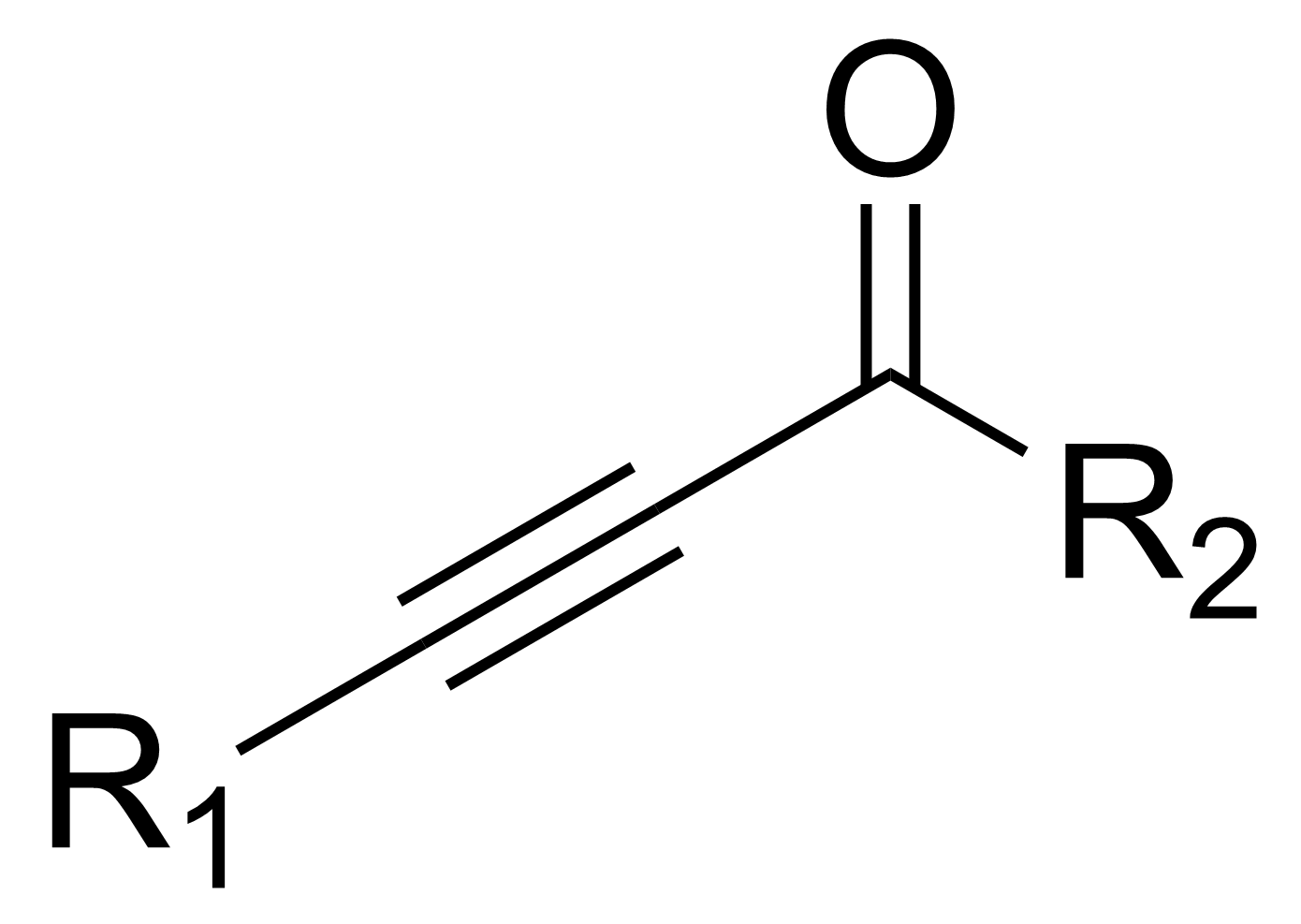
Ynone
In organic chemistry, an ynone is an organic compound containing a ketone () functional group and a triple bond. Many ynones are α,β-ynones, where the carbonyl and alkyne groups are conjugated. Capillin is a naturally occurring example. Some ynones are not conjugated. Synthesis of α,β-ynones One method for synthesizing ynones is the acyl substitution reaction of an alkynyldimethylaluminum with an acyl chloride. An alkynyldimethylaluminum compound is the reaction product of trimethylaluminum and a terminal alkyne. An alternative is the direct coupling of an acyl chloride with a terminal alkyne, using a copper-based nanocatalyst: Other methods utilize an oxidative cleavage of an aldehyde, followed by reaction with a hypervalent alkynyl iodide, using a gold catalyst. An alternative but longer synthetic method involves the reaction of an alkynyllithium compound with an aldehyde. The reaction produces a secondary alcohol that then can be oxidized via the Swern oxidation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketones
In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone (where R and R' is methyl), with the formula . Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids (e.g., testosterone), and the solvent acetone. Nomenclature and etymology The word ''ketone'' is derived from ''Aketon'', an old German word for ''acetone''. According to the rules of IUPAC nomenclature, ketone names are derived by changing the suffix ''-ane'' of the parent alkane to ''-anone''. Typically, the position of the carbonyl group is denoted by a number, but traditional nonsystematic names are still generally used for the most important ketones, for example acetone and benzophenone. These nonsystematic names are considered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Chemistry (journal)
''Green Chemistry'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering every aspect of sustainable chemistry and its implementation in chemical engineering. It is published by the Royal Society of Chemistry and was established in 1999 by James Clark (University of York). Articles published in this journal are intended to be conceptually accessible to a wide audience. The editors-in-chief is Philip Jessop (Queen's University). Article types * Research papers (which contain original scientific work that has not been published previously) * Communications (original scientific work that is of an urgent nature and that has not been published previously) * Green Chemistry news (an easy-to-read magazine style section) Abstracting, indexing, and impact factor According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 10.182. It is indexed in the following bibliographic databases: *Scopus * Web of Science See also *List of chemistry journals This is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Groups
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis. A functional group is a group of atoms in a molecule with distinctive chemical properties, regardless of the other atoms in the molecule. The atoms in a functional group are linked to each other and to the rest of the molecule by covalent bonds. For repeating units of polymers, functional groups attach to their nonpolar core of carbon atoms and thus add chemical character to carbon chains. Funct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diketone
In organic chemistry, a dicarbonyl is a molecule containing two carbonyl () groups. Although this term could refer to any organic compound containing two carbonyl groups, it is used more specifically to describe molecules in which both carbonyls are in close enough proximity that their reactivity is changed, such as 1,2-, 1,3-, and 1,4-dicarbonyls. Their properties often differ from those of monocarbonyls, and so they are usually considered functional groups of their own. These compounds can have symmetrical or unsymmetrical substituents on each carbonyl, and may also be functionally symmetrical (dialdehydes, diketones, diesters, ''etc.'') or unsymmetrical (keto-esters, keto-acids, ''etc.''). 1,2-Dicarbonyls 1,2-Dialdehyde The only 1,2-dialdehyde is glyoxal, . Like many alkyldialdehydes, glyoxal is encountered almost exclusively as its hydrate and oligomers thereof. These derivatives often behave equivalently to the aldehydes since hydration is reversible. Glyoxal condenses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Furan
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemical compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans. Furan is a colorless, flammable, highly volatile liquid with a boiling point close to room temperature. It is soluble in common organic solvents, including alcohol, ether, and acetone, and is slightly soluble in water. Its odor is "strong, ethereal; chloroform-like". It is toxic and may be carcinogenic in humans. Furan is used as a starting point for other speciality chemicals. History The name "furan" comes from the Latin ''furfur'', which means bran. (Furfural is produced from bran.) The first furan derivative to be described was 2-furoic acid, by Carl Wilhelm Scheele in 1780. Another important derivative, furfural, was reported by Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner in 1831 and characterised nine years later by John Stenhouse. Furan itself was first prepared by Heinrich Limp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycloaddition
In organic chemistry, a cycloaddition is a chemical reaction in which "two or more unsaturated molecules (or parts of the same molecule) combine with the formation of a cyclic adduct in which there is a net reduction of the bond multiplicity". The resulting reaction is a cyclization reaction. Many but not all cycloadditions are concerted and thus pericyclic. Nonconcerted cycloadditions are not pericyclic. As a class of addition reaction, cycloadditions permit carbon–carbon bond formation without the use of a nucleophile or electrophile. Cycloadditions can be described using two systems of notation. An older but still common notation is based on the size of linear arrangements of atoms in the reactants. It uses parentheses: where the variables are the numbers of linear atoms in each reactant. The product is a cycle of size . In this system, the standard Diels-Alder reaction is a (4 + 2)-cycloaddition, the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition is a (3 + 2)-cycloa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Syntheses
''Organic Syntheses'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1921. It publishes detailed and checked procedures for the synthesis of organic compounds. A unique feature of the review process is that all of the data and experiments reported in an article must be successfully repeated in the laboratory of a member of the editorial board as a check for reproducibility prior to publication. The journal is published by Organic Syntheses, Inc., a non-profit corporation. An annual print version is published by John Wiley & Sons on behalf of Organic Syntheses, Inc. History Prior to World War I, work on synthetic organic chemistry in the United States had been quite limited, and most of the reagents used in laboratories had to be imported from Europe. When export stoppages and trade embargoes cut off this source, Clarence Derick, a professor of chemistry at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, began an effort to synthesize these needed chemicals in industrial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swern Oxidation
The Swern oxidation, named after Daniel Swern, is a chemical reaction whereby a primary or secondary alcohol is oxidized to an aldehyde or ketone using oxalyl chloride, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and an organic base, such as triethylamine. It is one of the many oxidation reactions commonly referred to as 'activated DMSO' oxidations. The reaction is known for its mild character and wide tolerance of functional groups. The by-products are dimethyl sulfide ((CH3)2S), carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2) and—when triethylamine is used as base— triethylammonium chloride (Et3NHCl). Of the volatile by-products, dimethyl sulfide has a strong, pervasive odour and carbon monoxide is acutely toxic, so the reaction and the work-up needs to be performed in a fume hood. Dimethyl sulfide is a volatile liquid (B.P. 37 °C) with an unpleasant odour at even low concentrations. Mechanism The first step of the Swern oxidation is the low-temperature reaction of DMSO, 1a, formally as re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are common and play important roles in the technology and biological spheres. Structure and bonding Aldehydes feature a carbon center that is connected by a double bond to oxygen and a single bond to hydrogen and single bond to a third substituent, which is carbon or, in the case of formaldehyde, hydrogen. The central carbon is often described as being sp2-Orbital hybridisation, hybridized. The aldehyde group is somewhat polar molecule, polar. The C=O bond length is about 120-122 picometers. Physical properties and characterization Aldehydes have properties that are diverse and that depend on the remainder of the molecule. Smaller aldehydes are more soluble in water, formaldehyde and acetaldehyde completely so. The volatile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ynon Synthesis 2
Yinon ( he, יִנּוֹן, lit. "it shall flourish") is a moshav in southern Israel. Located near Kiryat Malakhi, it falls under the jurisdiction of Be'er Tuvia Regional Council. In it had a population of . History The moshav was founded 1952 by Jewish exodus from Yemen. Its name was taken from a passage in the Bible, Psalm 72:17: God's name "shall flourish as long as the sun". Yinon was founded on the lands of the depopulated Palestinian village of Al-Masmiyya al-Kabira Al-Masmiyya al-Kabira ( ar, المسمية الكبيرة) was a Palestinian people, Palestinian village in the Gaza Subdistrict, Mandatory Palestine, Gaza Subdistrict, located northeast of Gaza City, Gaza. With a land area of 20,687 dunams, the .... References {{Be'er Tuvia Regional Council Moshavim Populated places established in 1952 Populated places in Southern District (Israel) 1952 establishments in Israel Yemeni-Jewish culture in Israel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |