|
Yanun
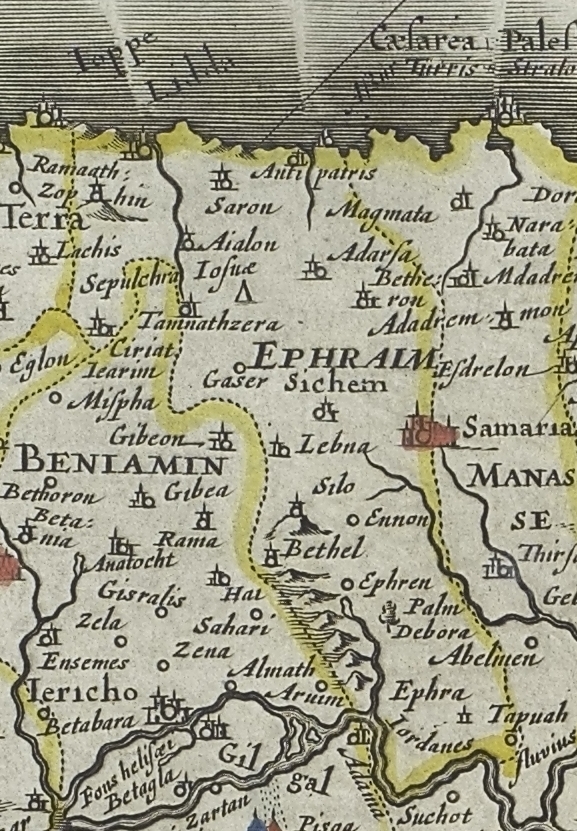
Yanun ( ar, يانون, translit=Yânûn) is a Palestinian territories, Palestinian village in the Nablus Governorate of the State of Palestine, in the northern West Bank, located southeast of Nablus, and 3 miles north of Aqraba, Nablus, Aqraba. It lies within West Bank#Administration, Area C, under total Israeli control, of the West Bank. It is divided into two sites, upper and lower Yanun. Upper or northern Yanin is considered illegal by the Israeli authorities, and development is prohibited there. Victor Guérin argued that both Eusebius and Jerome had confused the Yanoḥah of the tribe of Ephraim with the quite distinct, homophonous village belonging to the tribe of Naphtali (p. 7) Modern researchers, following Guerin, have suggested that the Biblical Yanoḥah refers to Khirbet Yanun, as pottery sherds from Ancient Near East#Iron Age, lron Age I has been found there, and not at Yanun.Finkelstein and Lederman, 1997, p. 828 Several caves dot the area, which the local school ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqraba, Nablus
Aqraba ( ar, عقربا) is a Palestinian town in the Nablus Governorate of the State of Palestine, located eighteen kilometers southeast of Nablus in the northern West Bank. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS), Aqraba had a population of approximately 8,180 inhabitants in 2007.2007 PCBS Census . . p.110. Aqraba is an ancient settlement, and the earliest traces of its history date from the . During |
Janohah
Janoah or Janohah ( ''Yānōwaḥ'') is the name of one or more places mentioned in the Bible. Etymology Janohah means "he rests" in Hebrew. Places in the Bible The Book of Joshua (), places a Janohah on the northern border of the Tribe of Ephraim: "the border went about eastward unto Taanathshiloh, and passed by it on the east to Janohah; And it went down from Janohah to Ataroth". The site of Janohah is thought by some to be at Yanun or nearby Khirbet Yanun, but this is disputed. A Janohah is also mentioned in the Second Book of Kings (): "came Tiglath-Pileser I king of Assyria, and took Ijon, and Abel-beth-maachah, and Janoah, and Kedesh, and Hazor, and Gilead, and Galilee, all the land of Naphtali According to the Book of Genesis, Naphtali (; ) was the last of the two sons of Jacob and Bilhah (Jacob's sixth son). He was the founder of the Israelite Tribe of Naphtali. Some biblical commentators have suggested that the name ''Naphtali'' ma ..., and carried them captive to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beit Furik
Beit Furik ( ar, بيت فوريك) is a Palestinian town located nine kilometers southeast of Nablus, in the Nablus Governorate of the State of Palestine, in the northern West Bank. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics, the town had a population of 10,339 inhabitants in 2007. increasing in the 1931 census, where Beit Furik (together with the smaller location Kh. Beita) had a population of 867 Muslims, in a total of 262 houses.Mills, 1932, p60/ref> In the 1945 statistics Beit Furik (including Kh. Kafr Beita) had a population of 1,240, all Muslims,Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics, 1945, p18/ref> with 36,663 dunams of land, according to an official land and population survey. Of this, 2,645 dunams were plantations and irrigable land, 12,453 used for cereals, while 53 dunams were built-up land. Jordanian era In the wake of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, and after the 1949 Armistice Agreements, Beit Furik came under Jordanian rule. In 1961 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nablus Governorate
The Nablus Governorate ( ar, محافظة نابلس ') is an administrative district of State of Palestine, Palestine located in the Central Highlands of the West Bank, 53 km north of Jerusalem. It covers the area around the city of Nablus which serves as the ''muhfaza'' (seat) of the governorate. The governor of the district is Mahmoud Aloul. During the first six months of the First Intifada 85 people were killed in Nablus Governorate by the Israeli army. This was the highest total of all the West Bank Governorates.B'Tselem information sheet July 1989. p. 4pdf/ref> Municipalities Cities *Nablus Towns The following localities have populations over 4,000 and Municipality (Palestinian Authority), municipal councils of 11-15 members. *Aqraba, Nablus, Aqraba *Asira ash-Shamaliya *Beita, Nablus, Beita *Huwara *Jammain *Qabalan *Sebastia, Nablus, Sebastia *Beit Furik Village councils The following localities have populations above 1,000 and Village Council (Palestinian Autho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Script
The Arabic script is the writing system used for Arabic and several other languages of Asia and Africa. It is the second-most widely used writing system in the world by number of countries using it or a script directly derived from it, and the third-most by number of users (after the Latin and Chinese scripts). The script was first used to write texts in Arabic, most notably the Quran, the holy book of Islam. With the religion's spread, it came to be used as the primary script for many language families, leading to the addition of new letters and other symbols. Such languages still using it are: Persian (Farsi/Dari), Malay ( Jawi), Uyghur, Kurdish, Punjabi (Shahmukhi), Sindhi, Balti, Balochi, Pashto, Lurish, Urdu, Kashmiri, Rohingya, Somali and Mandinka, Mooré among others. Until the 16th century, it was also used for some Spanish texts, and—prior to the language reform in 1928—it was the writing system of Turkish. The script is written from right to left in a cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Robinson (scholar)
Edward Robinson (April 10, 1794 – January 27, 1863) was an American biblical scholar known for his magnum opus, ''Biblical Researches in Palestine'', the first major work in Biblical Geography and Biblical Archaeology, which earned him the epithets "Father of Biblical Geography" and "Founder of Modern Palestinology." He studied in the United States and Germany, a center of biblical scholarship and exploration of the Bible as history. He translated scriptural works from classical languages, as well as German translations. His ''Greek and English Lexicon of the New Testament'' (1836; last revision, 1850) became a standard authority in the United States, and was reprinted several times in Great Britain. Biography Robinson was born in Southington, Connecticut, and raised on a farm. His father was a minister in the Congregational Church of the town for four decades. The younger Robinson taught at schools in East Haven and Farmington in 1810–11 to earn money for college. He atte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος ; 260/265 – 30 May 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilus (from the grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος τοῦ Παμφίλου), was a Greek historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christian polemicist. In about AD 314 he became the bishop of Caesarea Maritima in the Roman province of Syria Palaestina. Together with Pamphilus, he was a scholar of the biblical canon and is regarded as one of the most learned Christians during late antiquity. He wrote ''Demonstrations of the Gospel'', '' Preparations for the Gospel'' and ''On Discrepancies between the Gospels'', studies of the biblical text. As "Father of Church History" (not to be confused with the title of Church Father), he produced the ''Ecclesiastical History'', ''On the Life of Pamphilus'', the ''Chronicle'' and ''On the Martyrs''. He also produced a biographical work on Constantine the Great, the first Christian Roman emperor, who was ''augustus'' between AD 306 and A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerome
Jerome (; la, Eusebius Sophronius Hieronymus; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος Σωφρόνιος Ἱερώνυμος; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was a Christian presbyter, priest, Confessor of the Faith, confessor, theologian, and historian; he is commonly known as Saint Jerome. Jerome was born at Stridon, a village near Emona on the border of Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia and Pannonia. He is best known for his translation of the Bible into Latin (the translation that became known as the Vulgate) and his commentaries on the whole Bible. Jerome attempted to create a translation of the Old Testament based on a Hebrew version, rather than the Septuagint, as Vetus Latina, Latin Bible translations used to be performed before him. His list of writings is extensive, and beside his biblical works, he wrote polemical and historical essays, always from a theologian's perspective. Jerome was known for his teachings on Christian moral life, especially to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Fathers
The Church Fathers, Early Church Fathers, Christian Fathers, or Fathers of the Church were ancient and influential Christian theologians and writers who established the intellectual and doctrinal foundations of Christianity. The historical period in which they worked became known as the Patristic Era and spans approximately from the late 1st to mid-8th centuries, flourishing in particular during the 4th and 5th centuries, when Christianity was in the process of establishing itself as the state church of the Roman Empire. In traditional dogmatic theology, authors considered Church Fathers are treated as authoritative, and a somewhat restrictive definition is used. The academic field of patristics, the study of the Church Fathers, has extended the scope of the term, and there is no definitive list. Some, such as Origen and Tertullian, made major contributions to the development of later Christian theology, but certain elements of their teaching were later condemned. Great Fathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naphtali
According to the Book of Genesis, Naphtali (; ) was the last of the two sons of Jacob and Bilhah (Jacob's sixth son). He was the founder of the Israelite Tribe of Naphtali. Some biblical commentators have suggested that the name ''Naphtali'' may refer to the struggle between Rachel and Leah for the favours of Jacob. Bilhah was the handmaid of Rachel, who was infertile at the time, and had persuaded Jacob to have a child with Bilhah as a proxy for having one with herself. Biblical references According to the Targum Pseudo-Jonathan, Naphtali was a swift runner, though this appears to have been inferred from the Blessing of Jacob, which equates Naphtali to a hind. However, Biblical scholars believe this to actually be a description of the tribe of Naphtali. Naphtali is listed in Deuteronomy 34.2 when God takes Moses up to the mountain of Nebo and shows him the extent of the land which he had promised to Abraham, Isaac and Jacob. See article on Tribe of Simeon for a map of the twe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crusader States
The Crusader States, also known as Outremer, were four Catholic realms in the Middle East that lasted from 1098 to 1291. These feudal polities were created by the Latin Catholic leaders of the First Crusade through conquest and political intrigue. The four states were the County of Edessa (10981150), the Principality of Antioch (10981287), the County of Tripoli (11021289), and the Kingdom of Jerusalem (10991291). The Kingdom of Jerusalem covered what is now Israel and Palestine, the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, and adjacent areas. The other northern states covered what are now Syria, south-eastern Turkey, and Lebanon. The description "Crusader states" can be misleading, as from 1130 very few of the Frankish population were crusaders. The term Outremer, used by medieval and modern writers as a synonym, is derived from the French for ''overseas''. In 1098, the armed pilgrimage to Jerusalem passed through Syria. The crusader Baldwin of Boulogne replaced the Greek Orthodox ruler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribe Of Ephraim
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Ephraim ( he, אֶפְרַיִם, ''ʾEp̄rayīm,'' in pausa: אֶפְרָיִם, ''ʾEp̄rāyīm'') was one of the tribes of Israel. The Tribe of Manasseh together with Ephraim formed the ''House of Joseph''. It is one of the ten lost tribes. The etymology of the name is disputed.For the etymology, see Ephraim as portrayed in biblical narrative According to the Bible, the Tribe of Ephraim is descended from a man named Ephraim, who is recorded as the son of Joseph, the son of Jacob, and Asenath, the daughter of Potiphera. The descendants of Joseph formed two of the tribes of Israel, whereas the other sons of Jacob were the founders of one tribe each. The Bible records that the Tribe of Ephraim entered the land of Canaan during its conquest by Joshua, a descendant of Ephraim himself. However, many archeologists have abandoned the idea that Joshua carried out a conquest of Canaan similar to that described in the Book of Joshua, seein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |