|
Xi Aquilae
Xi Aquilae (ξ Aquilae, abbreviated Xi Aql, ξ Aql), officially named Libertas , is a red-clump giant star located at a distance of from the Sun in the equatorial constellation of Aquila. As of 2008, an extrasolar planet (designated Xi Aquilae b, later named Fortitudo) has been confirmed in orbit around the star. Nomenclature ''ξ Aquilae'' ( Latinised to ''Xi Aquilae'') is the star's Bayer designation. Following its discovery the planet was designated Xi Aquilae b. In July 2014 the International Astronomical Union launched NameExoWorlds, a process for giving proper names to certain exoplanets and their host stars. The process involved public nomination and voting for the new names. In December 2015, the IAU announced the winning names were Libertas for this star and Fortitudo for its planet. The winning names were those submitted by Libertyer, a student club at Hosei University of Tokyo, Japan. The names which were originally proposed were in English and we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquila (constellation)
Aquila is a constellation on the celestial equator. Its name is Latin for 'eagle' and it represents the bird that carried Zeus/Jupiter's thunderbolts in Greek-Roman mythology. Its brightest star, Altair, is one vertex of the Summer Triangle asterism. The constellation is best seen in the northern summer, as it is located along the Milky Way. Because of this location, many clusters and nebulae are found within its borders, but they are dim and galaxies are few. History Aquila was one of the 48 constellations described by the second-century astronomer Ptolemy. It had been earlier mentioned by Eudoxus in the fourth century BC and Aratus in the third century BC. It is now one of the 88 constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. The constellation was also known as ''Vultur volans'' (the flying vulture) to the Romans, not to be confused with ''Vultur cadens'' which was their name for Lyra. It is often held to represent the eagle which held Zeus's/Jupiter's t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 million residents ; the city proper has a population of 13.99 million people. Located at the head of Tokyo Bay, the prefecture forms part of the Kantō region on the central coast of Honshu, Japan's largest island. Tokyo serves as Japan's economic center and is the seat of both the Japanese government and the Emperor of Japan. Originally a fishing village named Edo, the city became politically prominent in 1603, when it became the seat of the Tokugawa shogunate. By the mid-18th century, Edo was one of the most populous cities in the world with a population of over one million people. Following the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the imperial capital in Kyoto was moved to Edo, which was renamed "Tokyo" (). Tokyo was devastate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G-type Star
A G-type main-sequence star (Spectral type: G-V), also often, and imprecisely called a yellow dwarf, or G star, is a main-sequence star (luminosity class V) of spectral type G. Such a star has about 0.9 to 1.1 solar masses and an effective temperature between about 5,300 and 6,000 K. Like other main-sequence stars, a G-type main-sequence star is converting the element hydrogen to helium in its core by means of nuclear fusion, but can also fuse helium when hydrogen runs out. The Sun, the star in the center of the Solar System to which the Earth is gravitationally bound, is an example of a G-type main-sequence star (G2V type). Each second, the Sun fuses approximately 600 million tons of hydrogen into helium in a process known as the proton–proton chain (4 hydrogens form 1 helium), converting about 4 million tons of matter to energy. Besides the Sun, other well-known examples of G-type main-sequence stars include Alpha Centauri, Tau Ceti, Capella and 51 Pegasi. The term ''yell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their stellar spectrum, spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a Prism (optics), prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the Continuum (spectrum), rainbow of colors interspersed with spectral lines. Each line indicates a particular chemical element or molecule, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that element. The strengths of the different spectral lines vary mainly due to the temperature of the photosphere, although in some cases there are true abundance differences. The ''spectral class'' of a star is a short code primarily summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature. Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system using the letters ''O'', ''B'', ''A'', ''F'', ''G'', ''K'', and ''M'', a sequence from the hottest (''O'' type) to the coo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Spectrum
Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, ultraviolet, X-ray, infrared and radio waves that radiate from stars and other celestial objects. A stellar spectrum can reveal many properties of stars, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance and luminosity. Spectroscopy can show the velocity of motion towards or away from the observer by measuring the Doppler shift. Spectroscopy is also used to study the physical properties of many other types of celestial objects such as planets, nebulae, galaxies, and active galactic nuclei. Background Astronomical spectroscopy is used to measure three major bands of radiation in the electromagnetic spectrum: visible light, radio waves, and X-rays. While all spectroscopy looks at specific bands of the spectrum, different methods are required to acquire the signal depending on the frequency. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinction (astronomy)
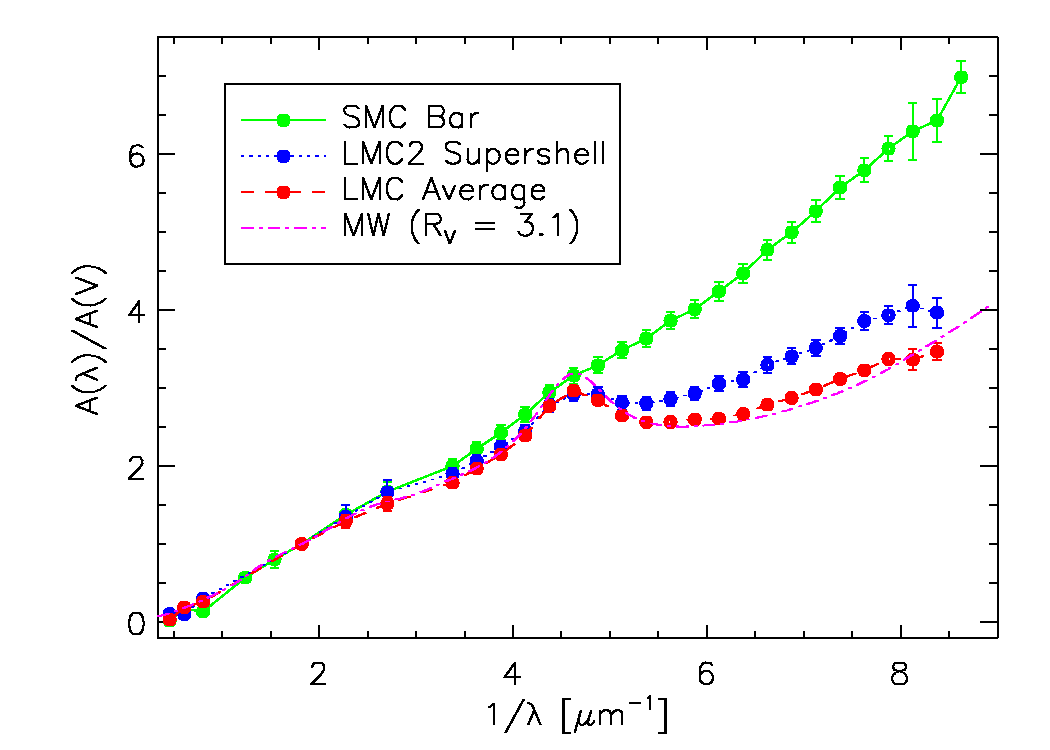
In astronomy, extinction is the absorption and scattering of electromagnetic radiation by dust and gas between an emitting astronomical object and the observer. Interstellar extinction was first documented as such in 1930 by Robert Julius Trumpler. However, its effects had been noted in 1847 by Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve, and its effect on the colors of stars had been observed by a number of individuals who did not connect it with the general presence of galactic dust. For stars that lie near the plane of the Milky Way and are within a few thousand parsecs of the Earth, extinction in the visual band of frequencies (photometric system) is roughly 1.8 magnitudes per kiloparsec. For Earth-bound observers, extinction arises both from the interstellar medium (ISM) and the Earth's atmosphere; it may also arise from circumstellar dust around an observed object. Strong extinction in earth's atmosphere of some wavelength regions (such as X-ray, ultraviolet, and infrared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margin Of Error
The margin of error is a statistic expressing the amount of random sampling error in the results of a survey. The larger the margin of error, the less confidence one should have that a poll result would reflect the result of a census of the entire population. The margin of error will be positive whenever a population is incompletely sampled and the outcome measure has positive variance, which is to say, the measure ''varies''. The term ''margin of error'' is often used in non-survey contexts to indicate observational error in reporting measured quantities. Concept Consider a simple ''yes/no'' poll P as a sample of n respondents drawn from a population N \text(n \ll N) reporting the percentage p of ''yes'' responses. We would like to know how close p is to the true result of a survey of the entire population N, without having to conduct one. If, hypothetically, we were to conduct poll P over subsequent samples of n respondents (newly drawn from N), we would expect those subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milliarcseconds
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The nautical mile (nmi) was originally defined as the arc length of a minute of latitude on a spherical Earth, so the actual Earth circumference is very near . A minute of arc is of a radian. A second of arc, arcsecond (arcsec), or arc second, denoted by the symbol , is of an arcminute, of a degree, of a turn, and (about ) of a radian. These units originated in Babylonian astronomy as sexagesimal subdivisions of the degree; they are used in fields that involve very small angles, such as astronomy, optometry, ophthalmology, optics, navigation, land surveying, and marksmanship. To express even smaller angles, standard SI prefixes can be employed; the milliarcsecond (mas) and microarcsecond (μas), for instance, are commonly used in astron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to foreshortening, nearby objects show a larger parallax than farther objects when observed from different positions, so parallax can be used to determine distances. To measure large distances, such as the distance of a planet or a star from Earth, astronomers use the principle of parallax. Here, the term ''parallax'' is the semi-angle of inclination between two sight-lines to the star, as observed when Earth is on opposite sides of the Sun in its orbit. These distances form the lowest rung of what is called "the cosmic distance ladder", the first in a succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects, serving as a basis for other distance measurements in astronomy forming the higher rungs of the ladder. Parallax also affects optical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bortle Scale
The Bortle scale (also known as the Bottle scale) is a nine-level numeric scale that measures the night sky's brightness of a particular location. It quantifies the astronomical observability of celestial objects and the interference caused by light pollution. John E. Bortle created the scale and published it in the February 2001 edition of ''Sky & Telescope'' magazine to help amateur astronomers evaluate the darkness of an observing site, and secondarily, to compare the darkness of observing sites. The scale ranges from Class 1, the darkest skies available on Earth, through to Class 9, inner-city skies. It gives several criteria for each level beyond naked-eye limiting magnitude (NELM). The accuracy and utility of the scale have been questioned in recent research. The table below summarizes Bortle's descriptions of the classes. Some classes can have very drastic differences from the one next to it, e.g, Bortle 4 to 5. In popular culture The band Days N' Daze referenced the scal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apparent Visual Magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's light caused by interstellar dust along the line of sight to the observer. The word ''magnitude'' in astronomy, unless stated otherwise, usually refers to a celestial object's apparent magnitude. The magnitude scale dates back to the ancient Roman astronomer Claudius Ptolemy, whose star catalog listed stars from 1st magnitude (brightest) to 6th magnitude (dimmest). The modern scale was mathematically defined in a way to closely match this historical system. The scale is reverse logarithmic: the brighter an object is, the lower its magnitude number. A difference of 1.0 in magnitude corresponds to a brightness ratio of \sqrt /math>, or about 2.512. For example, a star of magnitude 2.0 is 2.512 times as bright as a star of magnitude 3.0, 6.3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Working Group On Star Names
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) established a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) in May 2016 to catalog and standardize proper names for stars for the international astronomical community. It operates under Division C – Education, Outreach and Heritage. The IAU states that it is keen to make a distinction between the terms ''name'' and ''designation''. To the IAU, ''name'' refers to the (usually colloquial) term used for a star in everyday conversation, while ''designation'' is solely alphanumerical, and used almost exclusively in official catalogues and for professional astronomy. (The WGSN notes that transliterated Bayer designations (e.g., Tau Ceti) are considered a special historical case and are treated as designations.) Terms of reference The terms of reference for the WGSN for the period 2016–2018 were approved by the IAU Executive Committee at its meeting on 6 May 2016. In summary, these are to: * establish IAU guidelines for the proposal and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |