|
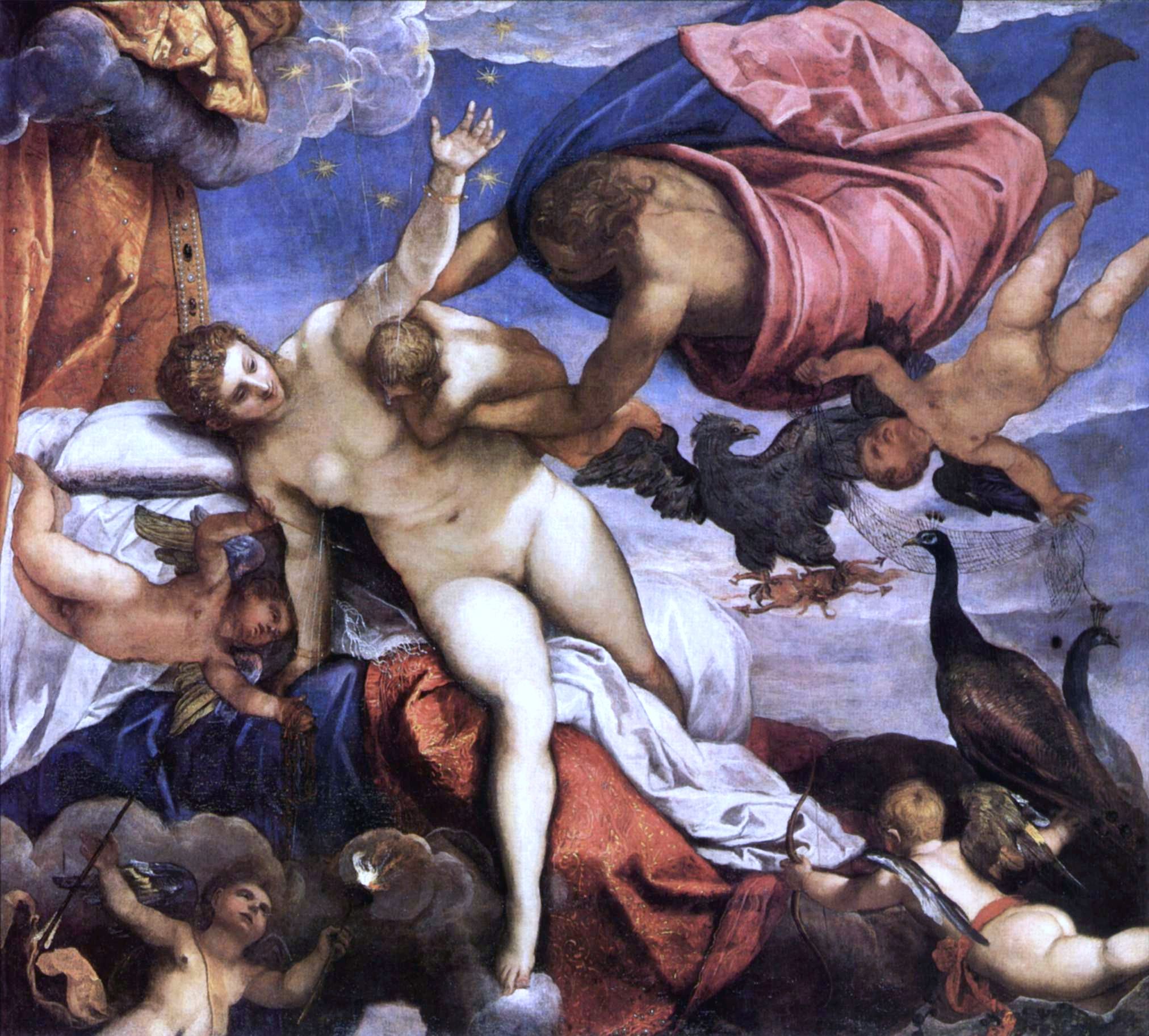
Aquila (constellation)
Aquila is a constellation on the celestial equator. Its name is Latin for 'eagle' and it represents the bird that carried Zeus/Jupiter's thunderbolts in Greek-Roman mythology. Its brightest star, Altair, is one vertex of the Summer Triangle asterism. The constellation is best seen in the northern summer, as it is located along the Milky Way. Because of this location, many clusters and nebulae are found within its borders, but they are dim and galaxies are few. History Aquila was one of the 48 constellations described by the second-century astronomer Ptolemy. It had been earlier mentioned by Eudoxus in the fourth century BC and Aratus in the third century BC. It is now one of the 88 constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. The constellation was also known as ''Vultur volans'' (the flying vulture) to the Romans, not to be confused with ''Vultur cadens'' which was their name for Lyra. It is often held to represent the eagle which held Zeus's/Jupiter's t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
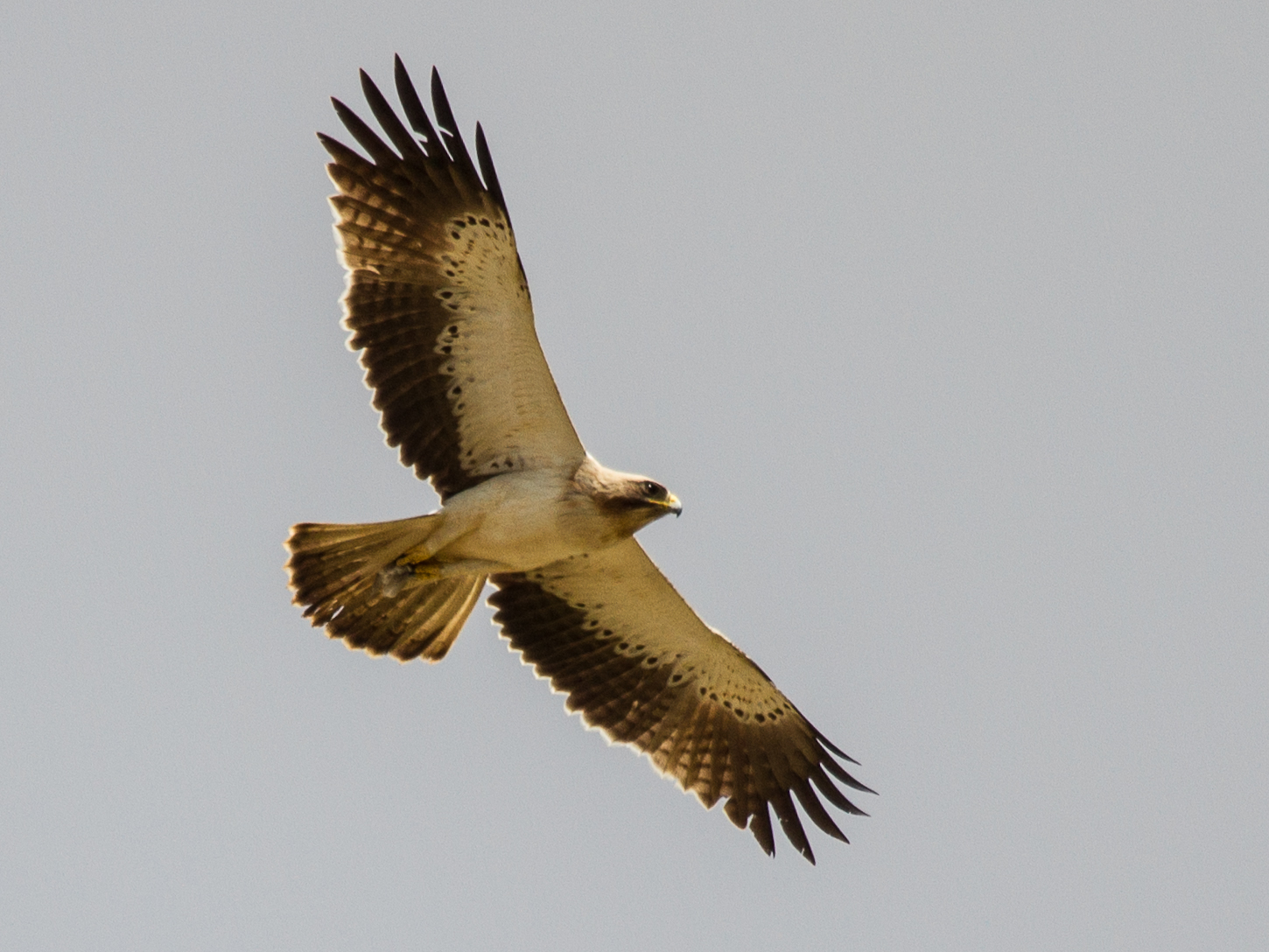
Eagle
Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 68 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, just 14 species can be found—2 in North America, 9 in Central and South America, and 3 in Australia. Eagles are not a natural group but denote essentially any kind of bird of prey large enough to hunt sizeable (about 50 cm long or more overall) vertebrates. Description Eagles are large, powerfully-built birds of prey, with heavy heads and beaks. Even the smallest eagles, such as the booted eagle (''Aquila pennata''), which is comparable in size to a common buzzard (''Buteo buteo'') or red-tailed hawk (''B. jamaicensis''), have relatively longer and more evenly broad wings, and more direct, faster flight – despite the reduced size of aerodynamic feathers. Most eagles are larger than any other raptors apart from some vultures. The smalles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
75th Parallel South
The 75th parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 75 degrees south of the Earth's equatorial plane in the Antarctic. It passes through the Southern Ocean and Antarctica. Around the world Starting at the Prime Meridian and heading eastwards, the parallel 75° south passes through: : See also *74th parallel south *76th parallel south The 76th parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 76 degrees south of the Earth's equatorial plane in the Antarctic. The parallel passes through the Southern Ocean and Antarctica. Around the world Starting at the Prime Meridian and head ... {{geographical coordinates, state=collapsed s75 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
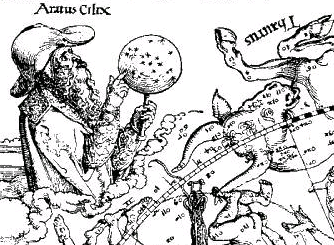
Aratus
Aratus (; grc-gre, Ἄρατος ὁ Σολεύς; c. 315 BC/310 BC240) was a Greek didactic poet. His major extant work is his hexameter poem ''Phenomena'' ( grc-gre, Φαινόμενα, ''Phainómena'', "Appearances"; la, Phaenomena), the first half of which is a verse setting of a lost work of the same name by Eudoxus of Cnidus. It describes the constellations and other celestial phenomena. The second half is called the ''Diosemeia'' (Διοσημεῖα "Forecasts"), and is chiefly about weather lore. Although Aratus was somewhat ignorant of Greek astronomy, his poem was very popular in the Greek and Roman world, as is proven by the large number of commentaries and Latin translations, some of which survive. Life There are several accounts of Aratus's life by anonymous Greek writers, and the Suda and Eudocia also mention him. From these it appears that he was a native of Soli in Cilicia, (although one authority says Tarsus). He is known to have studied with Menecrates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eudoxus Of Cnidus
Eudoxus of Cnidus (; grc, Εὔδοξος ὁ Κνίδιος, ''Eúdoxos ho Knídios''; ) was an ancient Greek astronomer, mathematician, scholar, and student of Archytas and Plato. All of his original works are lost, though some fragments are preserved in Hipparchus' commentary on Aratus's poem on astronomy. ''Sphaerics'' by Theodosius of Bithynia may be based on a work by Eudoxus. Life Eudoxus was born and died in Cnidus (also spelled Knidos), which was a city on the southwest coast of Asia Minor. The years of Eudoxus' birth and death are not fully known but the range may have been , or . His name Eudoxus means "honored" or "of good repute" (, from ''eu'' "good" and ''doxa'' "opinion, belief, fame"). It is analogous to the Latin name Benedictus. Eudoxus's father, Aeschines of Cnidus, loved to watch stars at night. Eudoxus first traveled to Tarentum to study with Archytas, from whom he learned mathematics. While in Italy, Eudoxus visited Sicily, where he studied medicine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance to later Byzantine, Islamic, and Western European science. The first is the astronomical treatise now known as the '' Almagest'', although it was originally entitled the ''Mathēmatikē Syntaxis'' or ''Mathematical Treatise'', and later known as ''The Greatest Treatise''. The second is the ''Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ''Apotelesmatika'' (lit. "On the Effects") but more commonly known as the '' Tetrábiblos'', from the Koine Greek meaning "Four Books", or by its Latin equivalent ''Quadrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetary Nebula
A planetary nebula (PN, plural PNe) is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives. The term "planetary nebula" is a misnomer because they are unrelated to planets. The term originates from the planet-like round shape of these nebulae observed by astronomers through early telescopes. The first usage may have occurred during the 1780s with the English astronomer William Herschel who described these nebulae as resembling planets; however, as early as January 1779, the French astronomer Antoine Darquier de Pellepoix described in his observations of the Ring Nebula, "very dim but perfectly outlined; it is as large as Jupiter and resembles a fading planet". Though the modern interpretation is different, the old term is still used. All planetary nebulae form at the end of the life of a star of intermediate mass, about 1-8 solar masses. It is expected that the Sun will form a planetary nebula a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The term ''Milky Way'' is a translation of the Latin ', from the Greek ('), meaning "milky circle". From Earth, the Milky Way appears as a band because its disk-shaped structure is viewed from within. Galileo Galilei first resolved the band of light into individual stars with his telescope in 1610. Until the early 1920s, most astronomers thought that the Milky Way contained all the stars in the Universe. Following the 1920 Great Debate between the astronomers Harlow Shapley and Heber Curtis, observations by Edwin Hubble showed that the Milky Way is just one of many galaxies. The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with an estimated D25 isophotal diameter of , but only about 1,000 light years thick at the spiral arms (more at the bulg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asterism (astronomy)
An asterism is an observed pattern or group of stars in the sky. Asterisms can be any identified pattern or group of stars, and therefore are a more general concept than the formally defined 88 constellations. Constellations are based on asterisms, but unlike asterisms, constellations outline and today completely divide the sky and all its celestial objects into regions around their central asterisms. For example, the asterism known as the Big Dipper comprises the seven brightest stars in the constellation Ursa Major. Another is the asterism of the Southern Cross, within the constellation of Crux. Asterisms range from simple shapes of just a few stars to more complex collections of many stars covering large portions of the sky. The stars themselves may be bright naked-eye objects or fainter, even telescopic, but they are generally all of a similar brightness to each other. The larger brighter asterisms are useful for people who are familiarizing themselves with the night sky. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summer Triangle
The Summer Triangle is an astronomical asterism in the northern celestial hemisphere. The defining vertices of this imaginary triangle are at Altair, Deneb, and Vega, each of which is the brightest star of its constellation ( Aquila, Cygnus, and Lyra, respectively). The greatest declination is +45° (rounded) and lowest is +9° (rounded) meaning the three can be seen from all places in the Northern Hemisphere and from the home of most of people resident in the Southern Hemisphere. The two stars in Aquila and Cygnus represent the head of an eagle and tail of a swan and these asterisms do not overlap, two small constellations intervening. History The term was popularized by American author H. A. Rey and British astronomer Patrick Moore in the 1950s. The name can be found in constellation guidebooks as far back as 1913. The Austrian astronomer Oswald Thomas described these stars as ''Grosses Dreieck'' (Great Triangle) in the late 1920s and ''Sommerliches Dreieck'' (Summerly Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greco-Roman Mythology
Classical mythology, Greco-Roman mythology, or Greek and Roman mythology is both the body of and the study of myths from the ancient Greeks and ancient Romans as they are used or transformed by reception theory, cultural reception. Along with Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophy and History of political thinking, political thought, mythology represents one of the major survivals of classical antiquity throughout later Western culture. The Greek word ''mythos'' refers to the spoken word or speech, but it also denotes a tale, story or narrative. As late as the Roman conquest of Greece during the last two centuries Before the Common Era and for centuries afterwards, the Romans, who already had gods of their own, adopted much mythology directly from the Greeks while preserving their own Roman (Latin) names for the gods. In storytelling and literature, this thereby caused an equivalence between many Roman and Greek deities; some examples include between the Roman sky god Jupiter (mytho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eagle
Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 68 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, just 14 species can be found—2 in North America, 9 in Central and South America, and 3 in Australia. Eagles are not a natural group but denote essentially any kind of bird of prey large enough to hunt sizeable (about 50 cm long or more overall) vertebrates. Description Eagles are large, powerfully-built birds of prey, with heavy heads and beaks. Even the smallest eagles, such as the booted eagle (''Aquila pennata''), which is comparable in size to a common buzzard (''Buteo buteo'') or red-tailed hawk (''B. jamaicensis''), have relatively longer and more evenly broad wings, and more direct, faster flight – despite the reduced size of aerodynamic feathers. Most eagles are larger than any other raptors apart from some vultures. The smalles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |