|
Wisłok Wielki
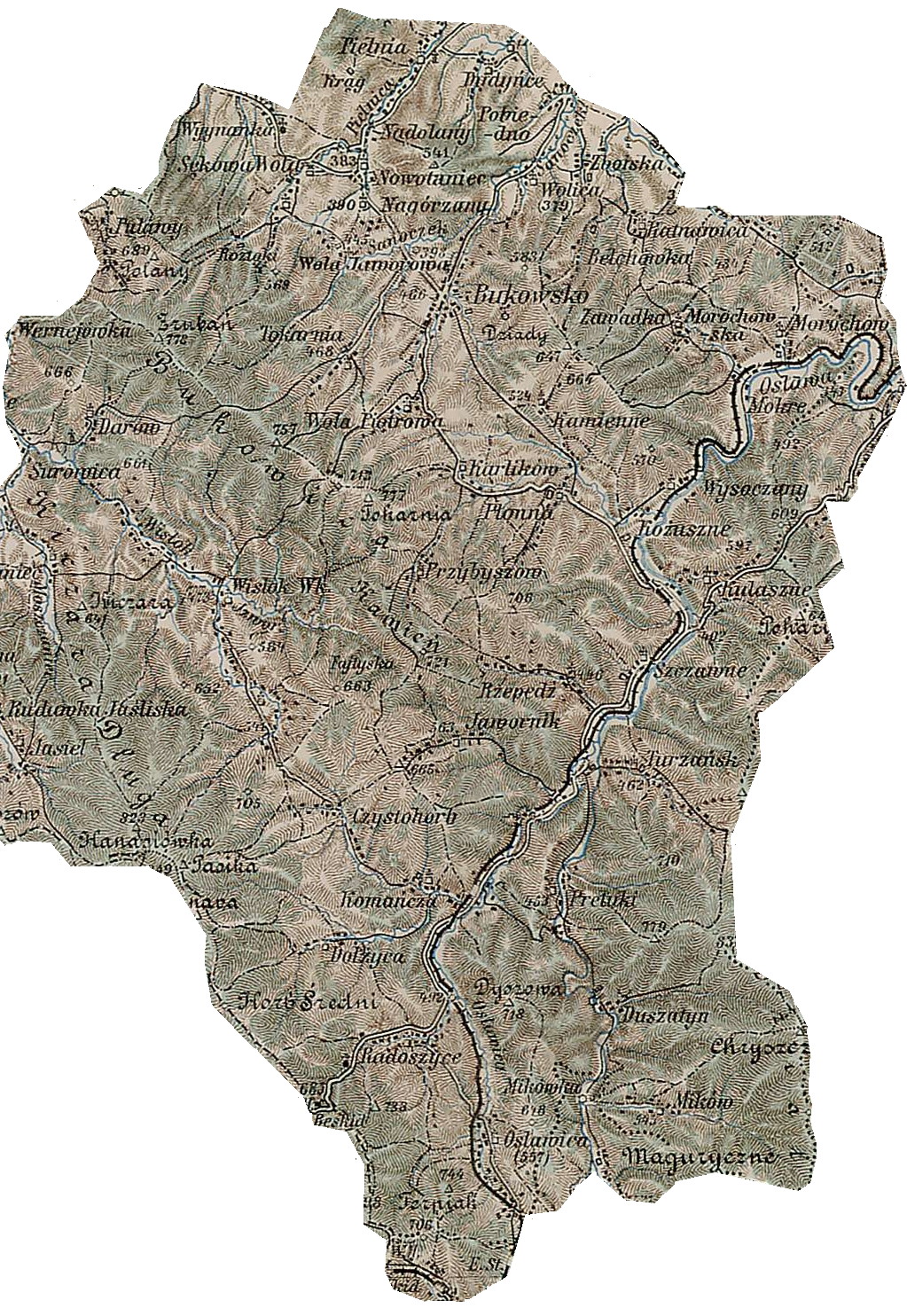
Wisłok Wielki (; uk, Вислік Великий, Vyslik Velykyi) is a village in the Bukowsko Upland mountains. Since 1999 it is situated in the Subcarpathian Voivodship (province) of south-eastern Poland; previously in Krosno Voivodship (1975–1998) and Sanok district, Bukowsko subdistrict, located near the towns of Medzilaborce and Palota (in northeastern Slovakia). It was formerly officially divided into two parts: Wisłok Górny ("upper Wisłok") and Wisłok Dolny ("lower Wisłok"). The name "Wisłok Wielki" means "great Wisłok". History Wisłok Wielki (Vyslik Velykyi: Ukr.) was first mentioned, according to historical accounts, in 1361. In 1785 the village lands comprised . Reportedly at the time, there were 711 Eastern-rite Catholics. The historical record relates that in 1361 the brothers Peter and Paul, "from Hungary," as feudal landholders, "owned" Wisłok Wielki, along with Bukowsko and several other area villages (see Nowotaniec, Zboiska, Humniska etc.). Locate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European Languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch, and Spanish, have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, of which there are eight groups with languages still alive today: Albanian, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic, Germanic, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian, and Italic; and another nine subdivisions that are now extinct. Today, the individual Indo-European languages with the most native speakers are English, Hindi–Urdu, Spanish, Bengali, French, Russian, Portuguese, German, and Punjabi, each with over 100 million native speakers; many others are small and in danger of extinction. In total, 46% of the world's population (3.2 billion people) speaks an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the southwest, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's mostly mountainous territory spans about , with a population of over 5.4 million. The capital and largest city is Bratislava, while the second largest city is Košice. The Slavs arrived in the territory of present-day Slovakia in the fifth and sixth centuries. In the seventh century, they played a significant role in the creation of Samo's Empire. In the ninth century, they established the Principality of Nitra, which was later conquered by the Principality of Moravia to establish Great Moravia. In the 10th century, after the dissolution of Great Moravia, the territory was integrated into the Principality of Hungary, which then became the Kingdom of Hungary in 1000. In 1241 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The people of the Kingdom of Israel and the ethnic and religious group known as the Jewish people that descended from them have been subjected to a number of forced migrations in their history" and Hebrews of historical History of ancient Israel and Judah, Israel and Judah. Jewish ethnicity, nationhood, and religion are strongly interrelated, "Historically, the religious and ethnic dimensions of Jewish identity have been closely interwoven. In fact, so closely bound are they, that the traditional Jewish lexicon hardly distinguishes between the two concepts. Jewish religious practice, by definition, was observed exclusively by the Jewish people, and notions of Jewish peoplehood, nation, and community were suffused with faith in the Jewish God, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Central Europe. The preamble to the Constitution of the Republic of Poland defines the Polish nation as comprising all the citizens of Poland, regardless of heritage or ethnicity. The majority of Poles adhere to Roman Catholicism. The population of self-declared Poles in Poland is estimated at 37,394,000 out of an overall population of 38,512,000 (based on the 2011 census), of whom 36,522,000 declared Polish alone. A wide-ranging Polish diaspora (the '' Polonia'') exists throughout Europe, the Americas, and in Australasia. Today, the largest urban concentrations of Poles are within the Warsaw and Silesian metropolitan areas. Ethnic Poles are considered to be the descendants of the ancient West Slavic Lechites and other tribes that inhabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komancza Republic
The Komancza Republic, also known as the Eastern Lemko Republic, Vyslik Republic, and Lemko Republic, was a short-lived microstate, an association of thirty three Lemko villages, seated in Komańcza in the east of the Lemko Region, that existed between 4 November 1918 and 24 January 1919. It was headed by Head of the Council (голова Повітової Української Національної Ради, Head of the Ukrainian National County Council) Rev. Panteleymon Shpylka. Unlike the contemporaneous Lemko Republic to its west, the Komancza Republic planned to unite with the West Ukrainian People's Republic in an independent Ukrainian state (the Lemko Republic sought unification with the Russian Soviet Republic). Unification of the Komancza Republic and West Ukraine was suppressed by the Second Polish Republic, Polish government as part of the Polish–Ukrainian War. The Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye (1919), Treaty of Saint-Germain made Galicia (Eastern Europe), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galicia (eastern Europe)
Galicia ()"Galicia" ''Collins English Dictionary'' ( uk, Галичина, translit=Halychyna ; pl, Galicja; yi, גאַליציע) is a historical and geographic region spanning what is now southeastern Poland and western Ukraine, long part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.See also: It covers much of such historic regions as Red Ruthenia (centered on Lviv) and Lesser Poland (centered on Kraków). The name of the region derives from the medieval city of Halych, and was first mentioned in Hungarian historical chronicles in the year 1206 as ''Galiciæ''. The eastern part of the region was controlled by the medieval Kingdom of Galicia a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lemko-Rusyn Republic
Lemko-Rusyn People's Republic ( rue, Руска Народна Република Лемків, Ruska Narodna Respublika Lemkiv , Rusyn National Republic of Lemkos), often known also as the Lemko-Rusyn Republic, just the Lemko Republic, or the Florynka Republic was a short-lived state founded on 5 December 1918 in the aftermath of World War I and the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. It was centered on Florynka, a village in the south-east of present-day Poland (on the border with Slovakia, south and south-east of Nowy Targ - Florynka, Krynica-Zdrój, Świetnica, Gładyszów, Sanok). Being Russophile, its intent was unification with a democratic Russia and was opposed to a union with the West Ukrainian People's Republic. A union with Russia proved impossible, so the Republic then attempted to join Subcarpathian Rus' as an autonomous province of Czechoslovakia. This, however, was opposed by the then governor of Subcarpathian Rus', Gregory Žatkovich. The Republic wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lemkos
Lemkos ( rue, Лeмкы, translit= Lemkŷ; pl, Łemkowie; uk, Лемки, translit=Lemky) are an ethnic group inhabiting the Lemko Region ( rue, Лемковина, translit=Lemkovyna; uk, Лемківщина, translit=Lemkivshchyna) of Carpathian Rus', an ethnographic region in the Carpathian Mountains and foothills spanning Ukraine, Slovakia and Poland. Their affiliation with other ethnicities is controversial. Some Lemkos consider their ethnos to be a sub-group of Rusyns (also called Carpatho-Rusyns or Carpatho-Ruthenians). Other Carpathian ethnic groups identifying as Rusyns include the Boykos and Hutsuls. Members of these groups have historically also been given other designations such as ''Verkhovyntsi'' (Highlanders). Among people of the Carpathian highlands, communities speaking the same dialect will identify with a different ethnic label when crossing borders due to the influence of state-sponsored education and media. As well the same community may switch its pref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humniska
Humniska ( uk, Гумниська, ''Humnys’ka'') is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Brzozów, within Brzozów County, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in south-eastern Poland. It lies approximately south-east of Brzozów and south of the regional capital Rzeszów Rzeszów ( , ; la, Resovia; yi, ריישא ''Raisha'')) is the largest city in southeastern Poland. It is located on both sides of the Wisłok River in the heartland of the Sandomierz Basin. Rzeszów has been the capital of the Subcarpathian Vo .... The village has a population of 4,300. References Villages in Brzozów County {{Brzozów-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zboiska, Sanok County
Zboiska ( uk, Збоїська, ''Zboyis’ka'') – ''Boyscza'' 1361, ''Boyska'' 1398, ''Boyschcze'' 1402, ''Bogiska'' 1437, ''Szboyska'' 1539, Zboiska alias ''Uhrynowce'' 1676, is a village in East Małopolska in the Lesser Beskid mountains. It is in the Bukowsko rural commune and the parish of Bukowsko. Zboiska is about 10 miles from Sanok in south-west Poland. It is situated below the main watershed at the foot of the Słonne Mountain, and has an elevation of 340 metres. It is located in the Subcarpathian Voivodship (since 1999), but was previously in Krosno Voivodship (1975–1998) and Sanok district, (10 miles east of Sanok). Twin cities *Topoľovka *Maizières-lès-Metz, France Literature * Adam Fastnacht, Nagórzany n:Slownik Historyczno-Geograficzny Ziemi Sanockiej w Średniowieczu (Historic-Geographic Dictionary of the Sanok District in the Middle Ages), Kraków, (II edition 2002), . *Jerzy Zuba "W Gminie Bukowsko". Roksana, 2004, . Translated by Deborah Greenlee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nowotaniec
Nowotaniec (german: Lobetanz, 1409; yi, ד בנוביטַניץ' Novitanitz; uk, Новотанець, ''Novotanets’'') is a village in south-eastern Poland, inhabited by about 430 (2002), in the Pogórze Bukowskie (Bukowsko Upland) mountains. Situated in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship (since 1999), previously in the Krosno Voivodeship (1975–1998) and the Sanok district, Bukowsko subdistrict, located near the towns of Medzilaborce and Palota (in northeastern Slovakia). Nowotaniec is bordered on the east by Bukowsko, on the north by Wola Sękowa, on the west by Nadolany, on the right bank of the Pielnica river (a tributary of the Wisłok), on the left side of the highway nr 889 from the railroad running from Sanok to Krosno, and on the west by forests covering the slopes of the Bukowica Range. This village consists of one street which runs north to south displaying Latin church stone and several houses. The parish belongs to the Diocese of Przemyśl, deanery of Sanok. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_..jpg)
.jpg)