|
WWTR1
WW domain-containing transcription regulator protein 1 (WWTR1), also known as Transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif (TAZ), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''WWTR1'' gene. WWTR1 acts as a transcriptional coregulator and has no effect on transcription alone. When in complex with transcription factor binding partners, WWTR1 helps promote gene expression in pathways associated with development, cell growth and survival, and inhibiting apoptosis. Aberrant WWTR1 function has been implicated for its role in driving cancers. WWTR1 is often referred to as TAZ due to its initial characterization with the name TAZ. However, WWTR1 (TAZ) is not to be confused with the protein tafazzin, which originally held the official gene symbol TAZ, and is now TAFAZZIN. Structure WWTR1 contains a proline rich region, TEAD binding motif, WW domain, coiled coil region, and a transactivation domain (TAD) containing the PDZ domain-binding motif. WWTR1 (TAZ) lacks a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tafazzin
Tafazzin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TAFAZZIN'' gene. Tafazzin is highly expressed in cardiac and skeletal muscle, and functions as a phospholipid-lysophospholipid transacylase (it belongs to phospholipid:diacylglycerol acyltransferases). It catalyzes remodeling of immature cardiolipin to its mature composition containing a predominance of tetralinoleoyl moieties. Several different isoforms of the tafazzin protein are produced from the ''TAFAZZIN'' gene. A long form and a short form of each of these isoforms is produced; the short form lacks a hydrophobic leader sequence and may exist as a cytoplasmic protein rather than being membrane-bound. Other alternatively spliced transcripts have been described but the full-length nature of all these transcripts is not known. Most isoforms are found in all tissues, but some are found only in certain types of cells. Mutations in the ''TAFAZZIN'' gene have been associated with mitochondrial deficiency, Barth syndrome, dilat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Coregulator
In molecular biology and genetics, transcription coregulators are proteins that interact with transcription factors to either activate or repress the transcription of specific genes. Transcription coregulators that activate gene transcription are referred to as coactivators while those that repress are known as corepressors. The mechanism of action of transcription coregulators is to modify chromatin structure and thereby make the associated DNA more or less accessible to transcription. In humans several dozen to several hundred coregulators are known, depending on the level of confidence with which the characterisation of a protein as a coregulator can be made. One class of transcription coregulators modifies chromatin structure through covalent modification of histones. A second ATP dependent class modifies the conformation of chromatin. Histone acetyltransferases Nuclear DNA is normally tightly wrapped around histones rendering the DNA inaccessible to the general transc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TEAD4
Transcriptional enhancer factor TEF-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TEAD4'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b .... Function This gene product is a member of the transcriptional enhancer factor (TEF) family of transcription factors, which contain the TEA/ATTS DNA-binding domain. Members of the family in mammals are TEAD1, TEAD2, TEAD3, TEAD4. TEAD4 is preferentially expressed in the skeletal muscle, and binds to the M-CAT regulatory element found in promoters of muscle-specific genes to direct their gene expression. Alternatively spliced transcripts encoding distinct isoforms, some of which are translated through the use of a non-AUG (UUG) initiation codon, have been described for this gene. Gene ablation experiments in mice (i.e. knockout mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TEAD3
Transcriptional enhancer factor TEF-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TEAD3'' gene. Function This gene product is a member of the transcriptional enhancer factor (TEF) family of transcription factors, which contain the TEA/ATTS DNA-binding domain. Members of the family in mammals are TEAD1, TEAD2, TEAD3, TEAD4. Transcriptional coregulators, such as WWTR1 (TAZ) bind to these transcription factors. TEAD3 is predominantly expressed in the placenta and is involved in the transactivation In the context of gene regulation: transactivation is the increased rate of gene expression triggered either by biological processes or by artificial means, through the expression of an intermediate transactivator protein. In the context of recep ... of the chorionic somatomammotropin-B gene enhancer. It is expressed in nervous system and muscle in fish embryos. Translation of this protein is initiated at a non-AUG (AUA) start codon. References Further reading * * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coactivator (genetics)
A coactivator is a type of transcriptional coregulator that binds to an activator (a transcription factor) to increase the rate of transcription of a gene or set of genes. The activator contains a DNA binding domain that binds either to a DNA promoter site or a specific DNA regulatory sequence called an enhancer. Binding of the activator-coactivator complex increases the speed of transcription by recruiting general transcription machinery to the promoter, therefore increasing gene expression. The use of activators and coactivators allows for highly specific expression of certain genes depending on cell type and developmental stage. Some coactivators also have histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity. HATs form large multiprotein complexes that weaken the association of histones to DNA by acetylating the N-terminal histone tail. This provides more space for the transcription machinery to bind to the promoter, therefore increasing gene expression. Activators are found in all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YAP1
YAP1 (yes-associated protein 1), also known as YAP or YAP65, is a protein that acts as a transcription coregulator that promotes transcription of genes involved in cellular proliferation and suppressing apoptotic genes. YAP1 is a component in the hippo signaling pathway which regulates organ size, regeneration, and tumorigenesis. YAP1 was first identified by virtue of its ability to associate with the SH3 domain of Yes and Src protein tyrosine kinases. ''YAP1'' is a potent oncogene, which is amplified in various human cancers. Structure Cloning of the YAP1 gene facilitated the identification of a modular protein domain, known as the WW domain. Two splice isoforms of the YAP1 gene product were initially identified, named YAP1-1 and YAP1-2, which differed by the presence of an extra 38 amino acids that encoded the WW domain. Apart from the WW domain, the modular structure of YAP1 contains a proline-rich region at the very amino terminus, which is followed by a TID (TEAD tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TEAD2
TEAD2 (ETF, ETEF-1, TEF-4), together with TEAD1, defines a novel family of transcription factors, the TEAD family, highly conserved through evolution. TEAD proteins were notably found in ''Drosophila'' (Scalloped), ''C. elegans'' (egl -44), '' S. cerevisiae'' and '' A. nidulans''. TEAD2 has been less studied than TEAD1 but a few studies revealed its role during development. Function TEAD2 is a member of the mammalian TEAD transcription factor family (initially named the transcriptional enhancer factor (TEF) family), which contain the TEA/ATTS DNA-binding domain. Members of the family in mammals are TEAD1, TEAD2, TEAD3, TEAD4. Tissue distribution TEAD2 is selectively expressed in a subset of embryonic tissues including the cerebellum, testis, and distal portions of the forelimb and hindlimb buds, as well as the tail bud, but it is essentially absent from adult tissues. TEAD2 has also been shown to be expressed very early during development, i.e. from the 2-cell stage. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
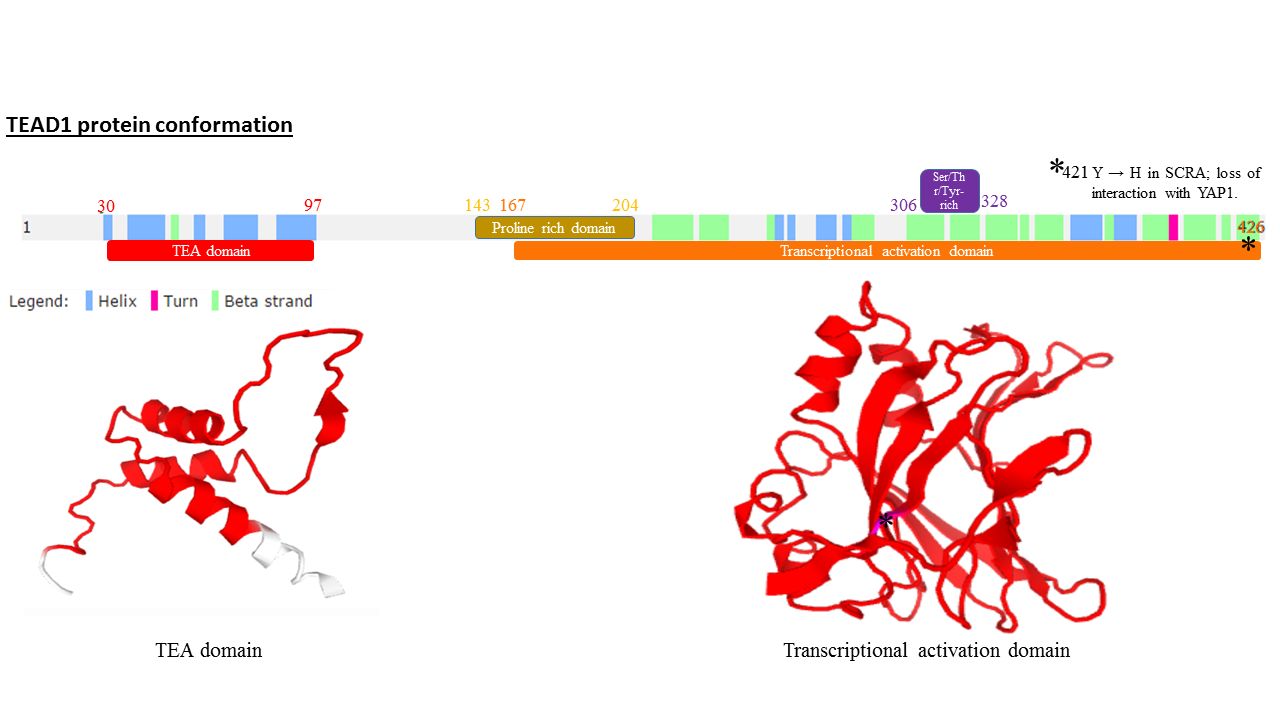
TEAD1
Transcriptional enhancer factor TEF-1 also known as TEA domain family member 1 (TEAD1) and transcription factor 13 (TCF-13) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TEAD1'' gene. TEAD1 was the first member of the TEAD family of transcription factors to be identified. Structure All members of the TEAD family share a highly conserved DNA binding domain called the TEA domain. This DNA binding domain has a consensus DNA sequence 5’-CATTCCA/T-3’ that is called the MCAT element. The three dimensional structure of the TEA domain has been identified Its conformation is close to that of the homeodomain and contains 3 α helixes (H1, H2 and H3). It is the H3 helix that enables TEAD proteins to bind DNA. Another conserved domain of TEAD1 is located at the C terminus of the protein. It allows the binding of cofactors and has been called the YAP1 binding domain, because it is its ability to bind this well-known TEAD proteins co-factor that led to its identification. Indeed, T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
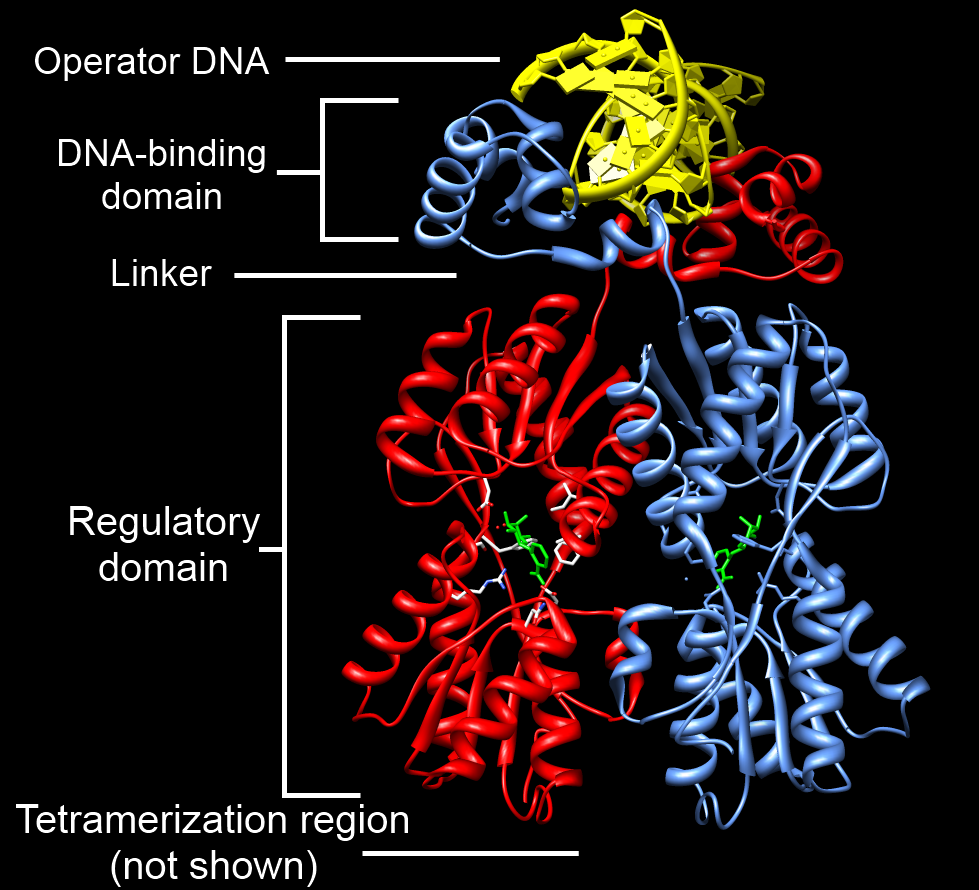
DNA-binding Domain
A DNA-binding domain (DBD) is an independently folded protein domain that contains at least one structural motif that recognizes double- or single-stranded DNA. A DBD can recognize a specific DNA sequence (a recognition sequence) or have a general affinity to DNA. Some DNA-binding domains may also include nucleic acids in their folded structure. Function One or more DNA-binding domains are often part of a larger protein consisting of further protein domains with differing function. The extra domains often regulate the activity of the DNA-binding domain. The function of DNA binding is either structural or involves transcription regulation, with the two roles sometimes overlapping. DNA-binding domains with functions involving DNA structure have biological roles in DNA replication, repair, storage, and modification, such as methylation. Many proteins involved in the regulation of gene expression contain DNA-binding domains. For example, proteins that regulate transcription ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Homology
A protein superfamily is the largest grouping ( clade) of proteins for which common ancestry can be inferred (see homology). Usually this common ancestry is inferred from structural alignment and mechanistic similarity, even if no sequence similarity is evident. Sequence homology can then be deduced even if not apparent (due to low sequence similarity). Superfamilies typically contain several protein families which show sequence similarity within each family. The term ''protein clan'' is commonly used for protease and glycosyl hydrolases superfamilies based on the MEROPS and CAZy classification systems. Identification Superfamilies of proteins are identified using a number of methods. Closely related members can be identified by different methods to those needed to group the most evolutionarily divergent members. Sequence similarity Historically, the similarity of different amino acid sequences has been the most common method of inferring homology. Sequence similarity is con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homodimers
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ''dimer'' has roots meaning "two parts", ''di-'' + '' -mer''. A protein dimer is a type of protein quaternary structure. A protein homodimer is formed by two identical proteins. A protein heterodimer is formed by two different proteins. Most protein dimers in biochemistry are not connected by covalent bonds. An example of a non-covalent heterodimer is the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which is composed of two different amino acid chains. An exception is dimers that are linked by disulfide bridges such as the homodimeric protein NEMO. Some proteins contain specialized domains to ensure dimerization (dimerization domains) and specificity. The G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptors have the ability to form both homo- and heterodimers with severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |