|
TEAD4
Transcriptional enhancer factor TEF-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TEAD4'' gene. Function This gene product is a member of the transcriptional enhancer factor (TEF) family of transcription factors, which contain the TEA/ATTS DNA-binding domain. Members of the family in mammals are TEAD1, TEAD2, TEAD3 Transcriptional enhancer factor TEF-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TEAD3'' gene. Function This gene product is a member of the transcriptional enhancer factor (TEF) family of transcription factors, which contain the TEA/ATTS ..., TEAD4. TEAD4 is preferentially expressed in the skeletal muscle, and binds to the M-CAT regulatory element found in promoters of muscle-specific genes to direct their gene expression. Alternatively spliced transcripts encoding distinct isoforms, some of which are translated through the use of a non-AUG (UUG) initiation codon, have been described for this gene. Gene ablation experiments in mice (i.e. knockout mice) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TEAD1
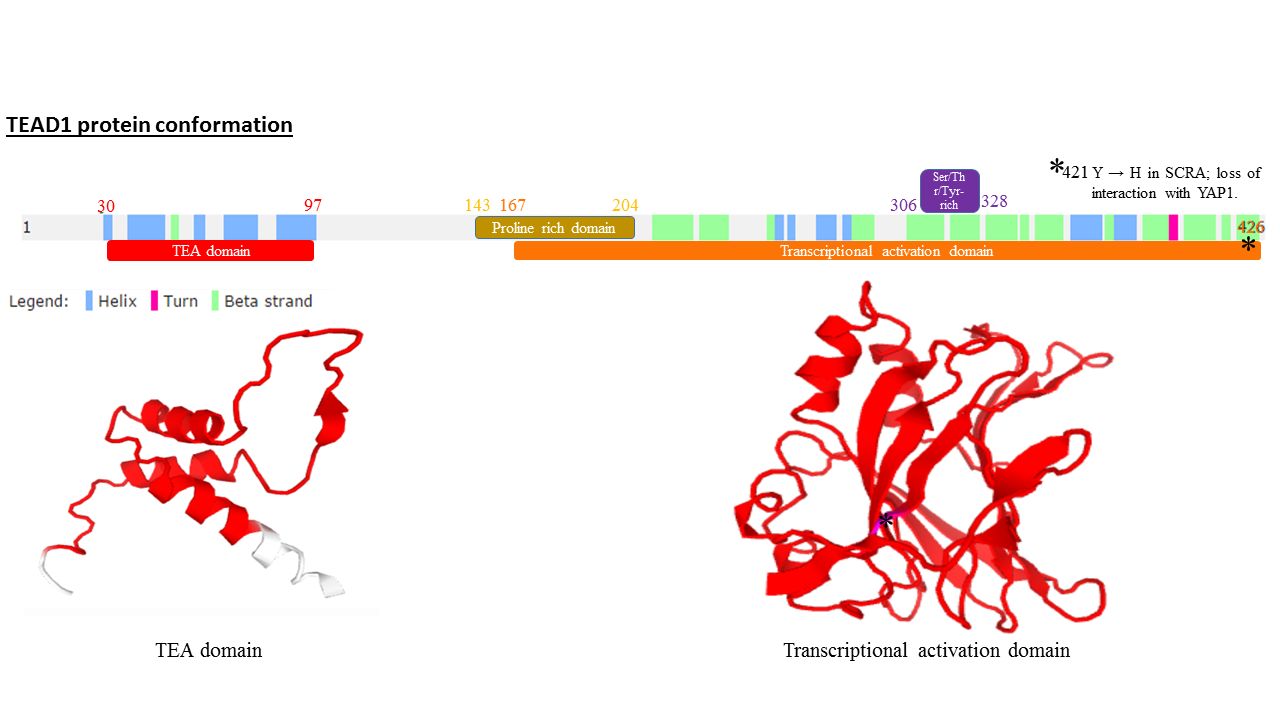
Transcriptional enhancer factor TEF-1 also known as TEA domain family member 1 (TEAD1) and transcription factor 13 (TCF-13) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TEAD1'' gene. TEAD1 was the first member of the TEAD family of transcription factors to be identified. Structure All members of the TEAD family share a highly conserved DNA binding domain called the TEA domain. This DNA binding domain has a consensus DNA sequence 5’-CATTCCA/T-3’ that is called the MCAT element. The three dimensional structure of the TEA domain has been identified Its conformation is close to that of the homeodomain and contains 3 α helixes (H1, H2 and H3). It is the H3 helix that enables TEAD proteins to bind DNA. Another conserved domain of TEAD1 is located at the C terminus of the protein. It allows the binding of cofactors and has been called the YAP1 binding domain, because it is its ability to bind this well-known TEAD proteins co-factor that led to its identification. Indeed, T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TEAD2
TEAD2 (ETF, ETEF-1, TEF-4), together with TEAD1, defines a novel family of transcription factors, the TEAD family, highly conserved through evolution. TEAD proteins were notably found in ''Drosophila'' (Scalloped), ''C. elegans'' (egl -44), ''S. cerevisiae'' and '' A. nidulans''. TEAD2 has been less studied than TEAD1 but a few studies revealed its role during development. Function TEAD2 is a member of the mammalian TEAD transcription factor family (initially named the transcriptional enhancer factor (TEF) family), which contain the TEA/ATTS DNA-binding domain. Members of the family in mammals are TEAD1, TEAD2, TEAD3, TEAD4. Tissue distribution TEAD2 is selectively expressed in a subset of embryonic tissues including the cerebellum, testis, and distal portions of the forelimb and hindlimb buds, as well as the tail bud, but it is essentially absent from adult tissues. TEAD2 has also been shown to be expressed very early during development, i.e. from the 2-cell stage. TEAD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WWTR1
WW domain-containing transcription regulator protein 1 (WWTR1), also known as Transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif (TAZ), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''WWTR1'' gene. WWTR1 acts as a transcriptional coregulator and has no effect on transcription alone. When in complex with transcription factor binding partners, WWTR1 helps promote gene expression in pathways associated with development, cell growth and survival, and inhibiting apoptosis. Aberrant WWTR1 function has been implicated for its role in driving cancers. WWTR1 is often referred to as TAZ due to its initial characterization with the name TAZ. However, WWTR1 (TAZ) is not to be confused with the protein tafazzin, which originally held the official gene symbol TAZ, and is now TAFAZZIN. Structure WWTR1 contains a proline rich region, TEAD binding motif, WW domain, coiled coil region, and a transactivation domain (TAD) containing the PDZ domain-binding motif. WWTR1 (TAZ) lacks a DNA bin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TEAD3
Transcriptional enhancer factor TEF-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TEAD3'' gene. Function This gene product is a member of the transcriptional enhancer factor (TEF) family of transcription factors, which contain the TEA/ATTS DNA-binding domain. Members of the family in mammals are TEAD1, TEAD2, TEAD3, TEAD4. Transcriptional coregulators, such as WWTR1 (TAZ) bind to these transcription factors. TEAD3 is predominantly expressed in the placenta and is involved in the transactivation of the chorionic somatomammotropin-B gene enhancer. It is expressed in nervous system and muscle in fish embryos. Translation of this protein is initiated at a non-AUG (AUA) start codon The start codon is the first codon of a messenger RNA (mRNA) transcript translated by a ribosome. The start codon always codes for methionine in eukaryotes and Archaea and a N-formylmethionine (fMet) in bacteria, mitochondria and plastids. The .... References Further reading * * * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |