|
Vilcabamba, Perú
Vilcabamba (in Hispanicized spelling), Willkapampa (Aymara and Quechua) is often called the Lost City of the Incas. Vilcabamba means "sacred plain" in Quechua. The modern name for the Inca ruins of Vilcabamba is Espiritu Pampa (Plain of the Spirits). Vilcabamba is located in Echarate District of La Convención Province in the Cuzco Region of Peru. Vilcabamba was the capital of the Neo-Inca State from 1539 to 1572. The Neo-Inca State was the last refuge of the Inca Empire until it fell to the Spaniards and their indigenous allies in 1572, signaling the end of Inca resistance to Spanish rule. Subsequently, Vilcabamba was abandoned and its location forgotten. In 1911 explorer Hiram Bingham mistakenly identified the abandoned ruin of Machu Picchu as Vilcabamba, but he also visited a ruin called Espiritu Pampa by local Peruvians. In 1964, Gene Savoy identified Espiritu Pampa as the fabled Vilcabamba, a designation widely accepted by archaeologists and historians. Vilcabamba or Espir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg , image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg , other_symbol = Great Seal of the State , other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal , national_motto = "Firm and Happy for the Union" , national_anthem = "National Anthem of Peru" , march = "March of Flags" , image_map = PER orthographic.svg , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Lima , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Peruvian Spanish, Spanish , languages_type = Co-official languages , languages = , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2017 , demonym = Peruvians, Peruvian , government_type = Unitary state, Unitary Semi-presidential system, semi-presidential republic , leader_title1 = President of Peru, President ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Savoy
Douglas Eugene "Gene" Savoy (May 11, 1927 – September 11, 2007) was an American explorer, author, religious leader, and theologian. He served as Head Bishop of the International Community of Christ, Church of the Second Advent from 1971 until his death. Rising to prominence as one of the premier explorers of Peru in the 1960s, he is best known for his claims to have discovered more than 40 lost cities in Peru and is credited with bringing to light a number of Peru’s most important archeological sites, including Vilcabamba, the last refuge of the Incas during the Spanish conquest, and Gran Pajaten, which he named but did not discover. Early life Savoy was born in Bellingham, Washington. At age 17 he enlisted in the U.S. Navy and served two years during World War II, after which he enrolled at the University of Portland to begin studies for the priesthood. Following an incident when one of his professors told him that the ideas he expressed in one of his papers were "very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cura Ocllo
Cura Ocllo (died 1539) was an Inca queen (''Coya''), the wife and sister of Manco Inca Yupanqui,Titu Cusi Yupanqui, 2005, An Inca Account of the Conquest of Peru, Boulder: University Press of Colorado, puppet and later remnant ruler of the Inca Empire from 1533 until his death in 1544. Her abduction and rape by Gonzalo Pizarro contributed to the split between her spouse and the Spanish and the start of the Inca rebellion against the Spanish. Life Her husband was named Sapa Inca in October 1533 after the death of their common brother Túpac Huallpa, who in his turn had succeeded Atahualpa upon his execution by the Spaniards three months earlier. Manco initially worked as a puppet ruler from the Cuzco branch of the Inca royal family of Huayna Capac, having challenged Atahualpa and the northern tribes from Quito in the Inca Civil War. Cura Ocllo had a son, Sayri Tupac, with Manco Inca in 1535, during Manco's time in captivity. During the time when Manco Inca was the puppet rule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonzalo Pizarro
Gonzalo Pizarro y Alonso (; 1510 – April 10, 1548) was a Spanish conquistador and younger paternal half-brother of Francisco Pizarro, the conqueror of the Inca Empire. Bastard son of Captain Gonzalo Pizarro y Rodríguez de Aguilar (senior) (1446–1522) who as colonel of infantry served in the Italian campaigns under Gonzalo Fernández de Córdoba, and in Navarre, with some distinction, and María Alonso, from Trujillo. He was the half brother of Francisco and Hernándo Pizarro and the full brother of Juan Pizarro. Early years in Peru Born in Trujillo, Spain, Gonzalo Pizarro accompanied his eldest brother, Francisco Pizarro, in his third expedition for the conquest of Peru in 1530.Prescott, W.H., 2011, The History of the Conquest of Peru, Digireads.com Publishing, Gonzalo was also the brother of Hernando Pizarro and Juan Pizarro.Hemming, J., 1970, The Conquest of the Incas, New York: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, Inc., A lieutenant of his brother Francisco during the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodrigo Orgóñez
Rodrigo Orgóñez (1490 – 26 April 1538) was Spanish captain under Diego de Almagro. Born in Oropesa, Rodrigo participated in the Italian Campaigns. He accompanied Francisco de Godoy from Nicaragua when they joined Diego's men in reinforcing Pizarro during the Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire.Leon, P., 1998, The Discovery and Conquest of Peru, Chronicles of the New World Encounter, edited and translated by Cook and Cook, Durham: Duke University Press, He proved his loyalty serving as a soldier for 5 years before he was made second in command to conquer and govern the southern portion of the Incan Empire. He helped Almagro in his 1537 coup d'état in Cusco leading the group that surrounded the Amaru Cancha Palace capturing Hernando Pizarro and Gonzalo Pizarro.Prescott, W.H., 2011, The History of the Conquest of Peru, Digireads.com Publishing, He later led an army against the Pizarros but was killed in 1538 during the Battle of Las Salinas. American historian William ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cusco
Cusco, often spelled Cuzco (; qu, Qusqu ()), is a city in Southeastern Peru near the Urubamba Valley of the Andes mountain range. It is the capital of the Cusco Region and of the Cusco Province. The city is the list of cities in Peru, seventh most populous in Peru; in 2017, it had a population of 428,450. Its elevation is around . The city was the capital of the Inca Empire from the 13th century until the 16th-century Spanish conquest of Peru, Spanish conquest. In 1983, Cusco was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO with the title "City of Cuzco". It has become a major tourist destination, hosting nearly 2 million visitors a year. The Constitution of Peru (1993) designates it as the Historical Capital of Peru. Spelling and etymology The indigenous name of this city is . Although the name was used in Southern Quechua, its origin is found in the Aymara language. The word is derived from the phrase ('rock of the owl'), related to the city's foundation myth of the Ayar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Ollantaytambo
The Battle of Ollantaytambo ( es, Batalla de Ollantaytambo, ) took place in January 1537, between the forces of Inca emperor Manco Inca and a Spanish expedition led by Hernando Pizarro during the Spanish conquest of Peru. A former ally of the Spaniards, Manco Inca rebelled in May 1536, and besieged a Spanish garrison in the city of Cusco. To end the stand-off, the besieged mounted a raid against the emperor's headquarters in the town of Ollantaytambo. The expedition, commanded by Hernando Pizarro, included 100 Spaniards and some 30,000 Indian auxiliaries against an Inca army more than 30,000 strong. There is some controversy over the actual location of the battle; according to some, it took place in the town itself, while Jean-Pierre Protzen and John Hemming argue that the nearby plain of Mascabamba better matches the descriptions of the encounter. In any case, the Inca army managed to hold the Spanish forces from a set of high terraces and flood their position to hind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project MUSE
Project MUSE, a non-profit collaboration between libraries and publishers, is an online database of peer-reviewed academic journals and electronic books. Project MUSE contains digital humanities and social science content from over 250 university presses and scholarly societies around the world. It is an aggregator of digital versions of academic journals, all of which are free of digital rights management (DRM). It operates as a third-party acquisition service like EBSCO, JSTOR, OverDrive, and ProQuest. MUSE's online journal collections are available on a subscription basis to academic, public, special, and school libraries. Currently, more than 2,500 libraries worldwide subscribe. Electronic book collections became available for institutional purchase in January 2012. Thousands of scholarly books are available on the platform. History Project MUSE was founded in 1993 as a joint project between the Johns Hopkins University Press and the Milton S. Eisenhower Library at the Johns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitcos
Vitcos was a residence of Inca nobles and a ceremonial center of the Neo-Inca State (1537-1572). The archaeological site of ancient Vitcos, called Rosaspata, is in the Vilcabamba District of La Convención Province, Cusco Region in Peru. The ruins are on a ridge overlooking the junction of two small rivers and the village of Pucyura. The Incas had occupied Vilcabamba, the region in which Vitcos is located, about 1450 CE, establishing major centers at Machu Picchu, Choquequirao, Vitcos, and Vilcabamba. Vitcos was often the residence of the rulers of the Neo-Inca state until the Spanish conquest of this last stronghold of the Incas in 1572. The location of Vitcos was later forgotten until 1911 when explorer Hiram Bingham identified the ruins known to local Peruvians as Rosaspata ( qu, Rusaspata) as ancient Vitcos. The ruins of the Inca ceremonial center of Ñusta Hispana (the "White Rock") are about south of the Inca palace that is the outstanding feature of Rosaspata. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choquequirao
Choquequirao (possibly from Quechua language, Quechua ''chuqi'' metal, ''k'iraw'' infant bed, crib, cot) is an Inca Empire, Incan site in southern Peru, similar in structure and architecture to Machu Picchu. The ruins are buildings and terraces at levels above and below Sunch'u Pata, the truncated hill top. The hilltop was anciently leveled and ringed with stones to create a 30 by 50 m platform. Choquequirao at an elevation of is in the spurs of the Vilcabamba mountain range, Vilcabamba mountain range in the Santa Teresa district, La Convención Province, La Convención Province of the Cusco Region. The complex is 1,800 hectares, of which 30–40% is excavated. The site overlooks the Apurimac River canyon that has an elevation of . The site is reached by a two-day hike from outside Cusco. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
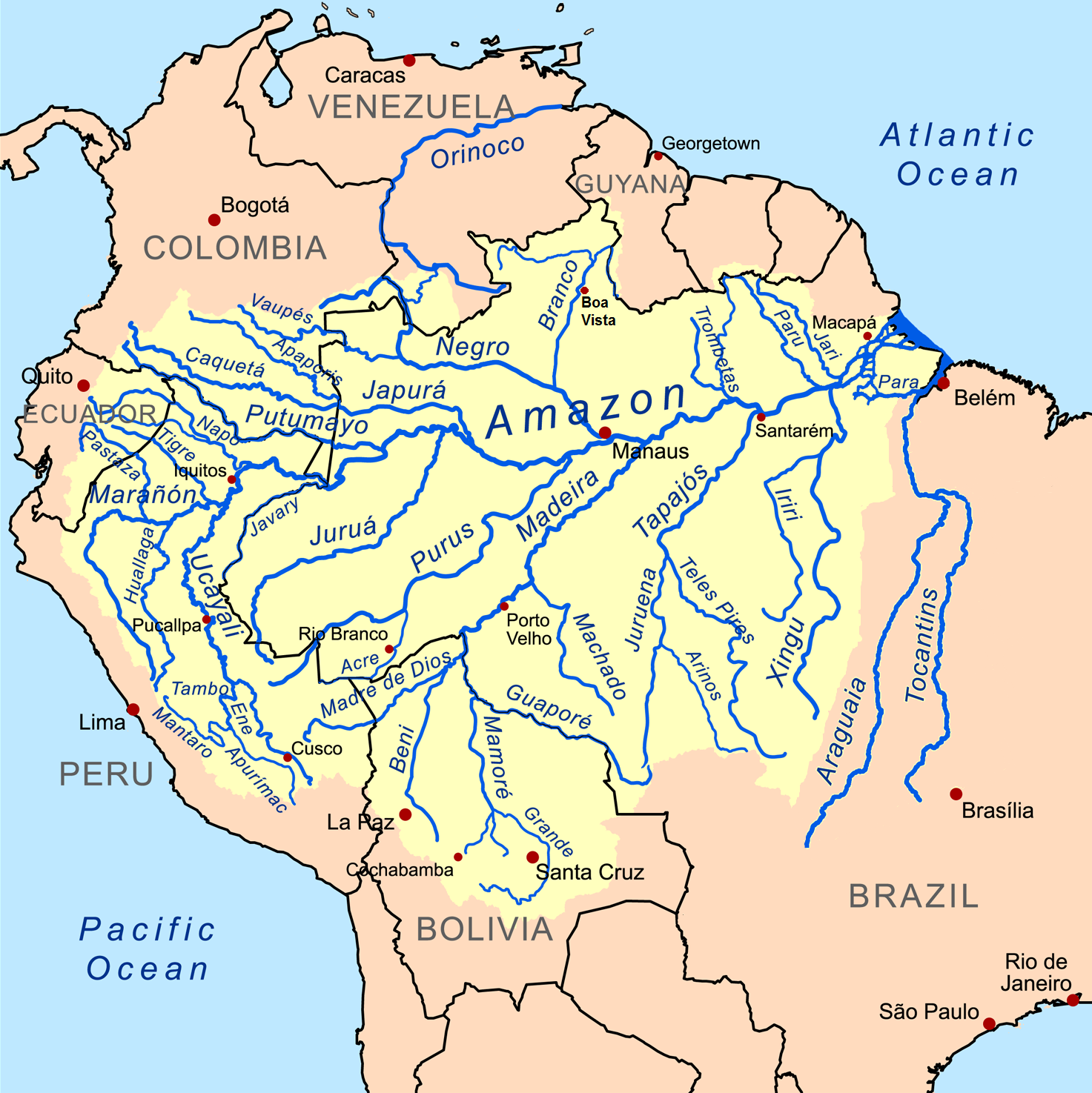
Amazon Basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela. Most of the basin is covered by the Amazon rainforest, also known as Amazonia. With a area of dense tropical forest, this is the largest rainforest in the world. Geography The Amazon River begins in the Andes Mountains at the west of the basin with its main tributary the Marañón River and Apurimac River in Peru. The highest point in the watershed of the Amazon is the second biggest peak of Yerupajá at . With a length of about before it drains into the Atlantic Ocean, it is one of the two longest rivers in the world. A team of scientists has claimed that the Amazon is longer than the Nile, but debate about its exact length continues. The Amazon system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiocarbon Dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon. The method was developed in the late 1940s at the University of Chicago by Willard Libby. It is based on the fact that radiocarbon () is constantly being created in the Earth's atmosphere by the interaction of cosmic rays with atmospheric nitrogen. The resulting combines with atmospheric oxygen to form radioactive carbon dioxide, which is incorporated into plants by photosynthesis; animals then acquire by eating the plants. When the animal or plant dies, it stops exchanging carbon with its environment, and thereafter the amount of it contains begins to decrease as the undergoes radioactive decay. Measuring the amount of in a sample from a dead plant or animal, such as a piece of wood or a fragment of bone, provides information that can be used to calc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |