|
Vortaro De Esperanto
The ''Vortaro de Esperanto'' ( en, italic=yes, Dictionary/Lexicon of Esperanto), published by Kazimierz Bein in 1911, was the first monolingual dictionary ever published in Esperanto. It is considered the predecessor of the '' Plena Vortaro de Esperanto'', published in 1930, and of the current ''Plena Ilustrita Vortaro'', whose last edition came out in 2020. The first edition of the ''Vortaro de Esperanto'' was published in 1911, the second in 1922 and the third in 1925 (they were, in truth, merely reprints). Overall 8500 copies of the dictionary were printed; the book was 175 pages long. The only Esperanto dictionary published previously had been the ''Plena Vortaro'', an Esperanto–Esperanto and Esperanto–French dictionary published in 1909 by Émile Boirac; nevertheless, it contained somewhat imprecise definitions in its monolingual section. Esperantologists consider the ''Vortaro de Esperanto'' a valuable source of information about the Esperanto of the early 20th centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plena Vortaro De Esperanto
''Plena Vortaro de Esperanto'' (PV; en, Complete Dictionary of Esperanto) is a monolingual dictionary of the Esperanto language first published by the Sennacieca Asocio Tutmonda (SAT) in 1930, largely considered the first truly comprehensive dictionary written entirely in Esperanto. History French academic Émile Grosjean-Maupin was the original chief editor of the PV, with additional contributions over the years from Albert Esselin, Salomon Grenkamp-Kornfeld, and Gaston Waringhien. Between 1930 and 1996, SAT published 11 editions of the PV, but following the revised and corrected second edition of 1934, revisions over the decades were infrequent. The most significant post-1934 addition was a 63-page supplemental section contributed by Gaston Waringhien to the fourth edition in 1953. The 1934 edition included 6,900 roots, while Waringhien's supplement added an extra 966. Influence Widely lauded upon its first appearance, the ''Plena Vortaro'' has largely been superseded by its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1911 Vortaro Kabe
A notable ongoing event was the race for the South Pole. Events January * January 1 – A decade after federation, the Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory are added to the Commonwealth of Australia. * January 3 ** 1911 Kebin earthquake: An earthquake of 7.7 moment magnitude strikes near Almaty in Russian Turkestan, killing 450 or more people. ** Siege of Sidney Street in London: Two Latvian anarchists die, after a seven-hour siege against a combined police and military force. Home Secretary Winston Churchill arrives to oversee events. * January 5 – Egypt's Zamalek SC is founded as a general sports and Association football club by Belgian lawyer George Merzbach as Qasr El Nile Club. * January 14 – Roald Amundsen's South Pole expedition makes landfall, on the eastern edge of the Ross Ice Shelf. * January 18 – Eugene B. Ely lands on the deck of the USS ''Pennsylvania'' stationed in San Francisco harbor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazimierz Bein
Kazimierz Bein (1872 – June 15, 1959), often referred to by his pseudonym Kabe, was a Polish ophthalmologist, the founder and sometime director of the Warsaw Ophthalmic Institute (''Warszawski Instytut Oftalmiczny''). He was also, for a time, a prominent Esperanto author, translator and activist, until in 1911 he suddenly, without explanation, abandoned the Esperanto movement. Bein became at least as well known for his involvement with Esperanto as for his medical accomplishments, and as much for the manner in which he left the Esperanto movement as for what he had accomplished within it. Life As a young man, Bein participated in the Polish movement for independence from Russia, for which he was exiled for several years; thus he was forced to finish his medical training in Kazan. Bein authored many technical books and articles, and founded the Warsaw Ophthalmic Institute and the Polish Ophthalmological Society. He was also a noted amateur photographer. Esperanto moveme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
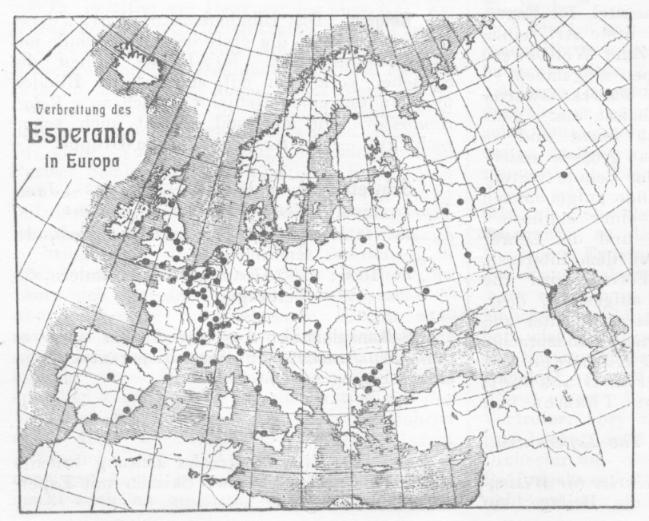
Esperanto
Esperanto ( or ) is the world's most widely spoken constructed international auxiliary language. Created by the Warsaw-based ophthalmologist L. L. Zamenhof in 1887, it was intended to be a universal second language for international communication, or "the international language" (). Zamenhof first described the language in '' Dr. Esperanto's International Language'' (), which he published under the pseudonym . Early adopters of the language liked the name ''Esperanto'' and soon used it to describe his language. The word translates into English as "one who hopes". Within the range of constructed languages, Esperanto occupies a middle ground between "naturalistic" (imitating existing natural languages) and ''a'priori'' (where features are not based on existing languages). Esperanto's vocabulary, syntax and semantics derive predominantly from languages of the Indo-European group. The vocabulary derives primarily from Romance languages, with substantial contributions from Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plena Ilustrita Vortaro
''Plena Ilustrita Vortaro de Esperanto'' (PIV; ''Complete Illustrated Dictionary of Esperanto'') is a monolingual dictionary of the language Esperanto. It was first compiled in 1970 by a large team of Esperanto linguists and specialists under the guidance of Gaston Waringhien and is published by the Sennacieca Asocio Tutmonda (SAT). It may be consulteonlinefor free. The term "illustrated" refers to two features: 1 - The use of clipart-like symbols rather than abbreviations for certain purposes (eg, entries pertaining to agriculture are marked with a small image of a sickle rather than a note like "''Agri''." for "Agrikulturo".) 2 - The occasional use of a line-art sketch illustrating the item being defined. These sketches are not used for most entries. The entries that do have a sketch are most commonly plants and animals, and sometimes tools. History Original publication First published in 1970, the PIV has undergone two revisions to date and is considered by many to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Émile Boirac
Émile Boirac (26 August 1851 – 20 September 1917) was a French philosopher, parapsychologist, promoter of Esperanto and writer. Biography Boirac was born in Guelma, Algeria. He became president of the University of Grenoble in 1898, and in 1902 president of Dijon University. A notable advocate for the universal language, Esperanto, he presided over its 1st Universal Congress (Boulogne-Sur-Mer, France, 7 August to 12 August 1905) and directed the Academy of Esperanto. He was one of the first to use the term "déjà vu", where it appeared in a letter to the editor of Revue philosophique in 1876, and subsequently in Boirac's book ''L'Avenir des Sciences Psychiques'', where he also proposed the term "metagnomy" ("knowledge of things situated beyond those we can normally know") as a more precise description for what was, then, commonly known as clairvoyance. He was one of a group that conducted experiments on the Italian medium Eusapia Palladino. He also investigated anim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esperantology
Esperantology, or Esperanto studies, is a special Esperanto linguistics whose subjects are word construction, word assembly, word introduction and transcription of umbrella terms and proper names. Esperantology principles of word construction are exemplary of the principles of necessity and sufficiency which postulate a balance between conciseness and clarity of the word. Regarding word roots, esperantology sets these principles: * The principle of internationality * The principle of analogy with other language elements * The principle of the vocabulary being economical * The principle of euphony As it is possible to see, all these principles are not always in accordance among themselves; for example the principle of internationality asks for the word ''internacionala'' while the analogy and the dictionary being economical as for the word ''internacia''. In the language, the second and third rule are stronger than the first one. Besides, the absolute validity of the above-mentio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaism
In language, an archaism (from the grc, ἀρχαϊκός, ''archaïkós'', 'old-fashioned, antiquated', ultimately , ''archaîos'', 'from the beginning, ancient') is a word, a sense of a word, or a style of speech or writing that belongs to a historical epoch long beyond living memory, but that has survived in a few practical settings or affairs. Lexical archaisms are single archaic words or expressions used regularly in an affair (e.g. religion or law) or freely; literary archaism is the survival of archaic language in a traditional literary text such as a nursery rhyme or the deliberate use of a style characteristic of an earlier age—for example, in his 1960 novel '' The Sot-Weed Factor'', John Barth writes in an 18th-century style. Archaic words or expressions may have distinctive emotional connotations—some can be humorous (''forsooth''), some highly formal (''What say you?''), and some solemn (''With thee do I plight my troth''). A distinction between archaic and obsole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundamento De Esperanto
''Fundamento de Esperanto'' (English: ''Foundation of Esperanto'') is a 1905 book by L. L. Zamenhof, in which the author explains the basic grammar rules and vocabulary that constitute the basis of the constructed language Esperanto. On August 9, 1905, it was made the only obligatory authority over the language by the Declaration of Boulogne at the first World Esperanto Congress. Much of the content of the book is a reproduction of content from Zamenhof's earlier works, particularly ''Unua Libro''. Content ''Fundamento de Esperanto'' consists of four parts: a foreword, a grammar section, a collection of exercises, and a dictionary. With the exception of the foreword, almost everything in the ''Fundamento'' comes directly from Zamenhof's earlier works, primarily ''Unua Libro''. Esperanto, however, underwent a minor change in 1888 in '' Aldono al la Dua Libro'', in which Zamenhof changed the ending of the temporal correlatives (''when'', ''then'', ''always'', ''sometimes'', ''nev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plena Ilustrita Vortaro De Esperanto
''Plena Ilustrita Vortaro de Esperanto'' (PIV; ''Complete Illustrated Dictionary of Esperanto'') is a monolingual dictionary of the language Esperanto. It was first compiled in 1970 by a large team of Esperanto linguists and specialists under the guidance of Gaston Waringhien and is published by the Sennacieca Asocio Tutmonda (SAT). It may be consulteonlinefor free. The term "illustrated" refers to two features: 1 - The use of clipart-like symbols rather than abbreviations for certain purposes (eg, entries pertaining to agriculture are marked with a small image of a sickle rather than a note like "''Agri''." for "Agrikulturo".) 2 - The occasional use of a line-art sketch illustrating the item being defined. These sketches are not used for most entries. The entries that do have a sketch are most commonly plants and animals, and sometimes tools. History Original publication First published in 1970, the PIV has undergone two revisions to date and is considered by many to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esperanto Dictionaries
Esperanto ( or ) is the world's most widely spoken constructed international auxiliary language. Created by the Warsaw-based ophthalmologist L. L. Zamenhof in 1887, it was intended to be a universal second language for international communication, or "the international language" (). Zamenhof first described the language in '' Dr. Esperanto's International Language'' (), which he published under the pseudonym . Early adopters of the language liked the name ''Esperanto'' and soon used it to describe his language. The word translates into English as "one who hopes". Within the range of constructed languages, Esperanto occupies a middle ground between "naturalistic" (imitating existing natural languages) and ''a'priori'' (where features are not based on existing languages). Esperanto's vocabulary, syntax and semantics derive predominantly from languages of the Indo-European group. The vocabulary derives primarily from Romance languages, with substantial contributions from G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |