|
Vienna Award .
{{Set index article ...
The Vienna Award (also called the Vienna Arbitration or Vienna Diktat) was either of two arbitral decisions made by Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy rewarding disputed territory to Hungary. Both decisions were made at the Belvedere Palace, in Vienna, just before and after the Second World War (1939–1945) started. *First Vienna Award (2 November 1938): Hungary received part of southern Czechoslovakia. *Second Vienna Award (30 August 1940): Hungary received Northern Transylvania from Romania Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a dictatorship. Under Hitler's rule, Germany quickly became a totalitarian state where nearly all aspects of life were controlled by the government. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", alluded to the Nazi claim that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which Hitler and the Nazis referred to as the Thousand-Year Reich, ended in May 1945 after just 12 years when the Allies defeated Germany, ending World War II in Europe. On 30 January 1933, Hitler was appointed chancellor of Germany, the head of gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fascist Italy (1922–1943)
The Kingdom of Italy was governed by the National Fascist Party from 1922 to 1943 with Benito Mussolini as Prime Minister of Italy, prime minister. The Italian Fascism, Italian Fascists imposed Authoritarianism, authoritarian rule and crushed political and intellectual opposition, while promoting economic modernization, traditional social values and a rapprochement with the Roman Catholic Church. According to Payne (1996), "[the] Fascist government passed through several relatively distinct phases". The first phase (1922–1925) was nominally a continuation of the parliamentary system, albeit with a "legally-organized executive dictatorship". The second phase (1925–1929) was "the construction of the Fascist dictatorship proper". The third phase (1929–1934) was with less interventionism (politics), interventionism in foreign policy. The fourth phase (1935–1940) was characterized by an aggressive foreign policy: the Second Italo-Ethiopian War, which was launched from Italian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Hungary (1920–1946)
The Kingdom of Hungary ( hu, Magyar Királyság), sometimes referred to as the Regency or the Horthy era, existed as a country from 1920 to 1946 under the rule of Regent Miklós Horthy, who nominally represented the Hungarian monarchy. In reality there was no king, and attempts by King Charles IV to return to the throne shortly before his death were prevented by Horthy. Hungary under Horthy was characterized by its conservative, nationalist and fiercely anti-communist character. The government was based on an unstable alliance of conservatives and right-wingers. Foreign policy was characterized by revisionism — the total or partial revision of the Treaty of Trianon, which had seen Hungary lose over 70% of its historic territory along with over three million Hungarians, who mostly lived in the border territories outside the new borders of the kingdom. Hungary's interwar politics were dominated by an obsession with the territorial losses suffered in this treaty, with the resen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belvedere Palace
The Belvedere is a historic building complex in Vienna, Austria, consisting of two Baroque palaces (the Upper and Lower Belvedere), the Orangery, and the Palace Stables. The buildings are set in a Baroque park landscape in the third district of the city, on the south-eastern edge of its centre. It houses the Belvedere museum. The grounds are set on a gentle gradient and include decorative tiered fountains and cascades, Baroque sculptures, and majestic wrought iron gates. The Baroque palace complex was built as a summer residence for Prince Eugene of Savoy. The Belvedere was built during a period of extensive construction in Vienna, which at the time was both the imperial capital and home to the ruling Habsburg dynasty. This period of prosperity followed on from the commander-in-chief Prince Eugene of Savoy's successful conclusion of a series of wars against the Ottoman Empire. Lower Belvedere On 30 November 1697, one year after commencing with the construction of the Stadtp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vienna
en, Viennese , iso_code = AT-9 , registration_plate = W , postal_code_type = Postal code , postal_code = , timezone = CET , utc_offset = +1 , timezone_DST = CEST , utc_offset_DST = +2 , blank_name = Vehicle registration , blank_info = W , blank1_name = GDP , blank1_info = € 96.5 billion (2020) , blank2_name = GDP per capita , blank2_info = € 50,400 (2020) , blank_name_sec1 = HDI (2019) , blank_info_sec1 = 0.947 · 1st of 9 , blank3_name = Seats in the Federal Council , blank3_info = , blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD , blank_info_sec2 = .wien , website = , footnotes = , image_blank_emblem = Wien logo.svg , blank_emblem_size = Vienna ( ; german: Wien ; ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Vienna Award
The First Vienna Award was a treaty signed on 2 November 1938 pursuant to the Vienna Arbitration, which took place at Vienna's Belvedere Palace. The arbitration and award were direct consequences of the previous month's Munich Agreement, which resulted in the partitioning of Czechoslovakia. Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy had sought a nonviolent way to support the territorial claims of the Kingdom of Hungary, and revision of the 1920 Treaty of Trianon. Nazi Germany had already vitiated the Versailles Treaty by the remilitarization of the Rhineland (7 March 1936) and the ''Anschluss'' of Austria (12 March 1938). The First Vienna Award separated, from Czechoslovakia, territories in southern Slovakia and southern Carpathian Rus' that were mostly Hungarian-populated and "awarded" them to Hungary. Hungary thus regained some of the territories (now parts of Slovakia and Ukraine) that Hungary had lost after World War I under the Treaty of Trianon. Czechoslovakia also ceded to Polan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Czechoslovak Republic
The First Czechoslovak Republic ( cs, První československá republika, sk, Prvá česko-slovenská republika), often colloquially referred to as the First Republic ( cs, První republika, Slovak: ''Prvá republika''), was the first Czechoslovak state that existed from 1918 to 1938, a union of ethnic Czechs and Slovaks. The country was commonly called Czechoslovakia (Czech and sk, Československo), a compound of ''Czech'' and ''Slovak''; which gradually became the most widely used name for its successor states. It was composed of former territories of Austria-Hungary, inheriting different systems of administration from the formerly Austrian ( Bohemia, Moravia, a small part of Silesia) and Hungarian territories (mostly Upper Hungary and Carpathian Ruthenia). After 1933, Czechoslovakia remained the only ''de facto'' functioning democracy in Central Europe, organized as a parliamentary republic. Under pressure from its Sudeten German minority, supported by neighbouring Nazi G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
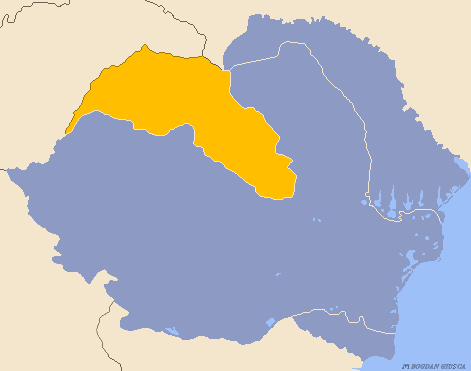
Second Vienna Award
The Second Vienna Award, also known as the Vienna Diktat, was the second of two territorial disputes that were arbitrated by Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. On 30 August 1940, they assigned the territory of Northern Transylvania, including all of Maramureș and part of Crișana, from Romania to Hungary. Background After World War I, the multiethnic Kingdom of Hungary was divided by the 1920 Treaty of Trianon to form several new nation states, but Hungary noted that the new state borders did not follow ethnic boundaries. The new nation state of Hungary was about a third the size of prewar Hungary, and millions of ethnic Hungarians were left outside the new Hungarian borders. Many historically-important areas of Hungary were assigned to other countries, and the distribution of natural resources was uneven. The various non-Hungarian populations generally saw the treaty as justice for their historically-marginalised nationalities, but the Hungarians considered the treaty to have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Transylvania
Northern Transylvania ( ro, Transilvania de Nord, hu, Észak-Erdély) was the region of the Kingdom of Romania that during World War II, as a consequence of the August 1940 territorial agreement known as the Second Vienna Award, became part of the Kingdom of Hungary. With an area of , the population was largely composed of both ethnic Romanians and Hungarians. In October 1944, Soviet and Romanian forces gained control of the territory, and by March 1945 Northern Transylvania returned to Romanian administration. After the war, this was confirmed by the Paris Peace Treaties of 1947. Background The region has a varied history. It was once the nucleus of the Kingdom of Dacia (82 BC–106 AD). In 106 AD the Roman Empire conquered the territory, systematically exploiting its resources. After the Roman legions withdrew in 271 AD, it was overrun by a succession of various tribes, bringing it under the control of the Carpi, Visigoths, Huns, Gepids, Avars, and Slavs. During the 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |