|
Valyrian Steel
Damascus steel was the forged steel of the blades of swords smithed in the Near East from ingots of Wootz steel either imported from Southern India or made in production centres in Sri Lanka, or Khorasan, Iran. These swords are characterized by distinctive patterns of banding and mottling reminiscent of flowing water, sometimes in a "ladder" or "rose" pattern. Such blades were reputed to be tough, resistant to shattering, and capable of being honed to a sharp, resilient edge. Wootz (Indian), Pulad (Persian), Fuladh (Arabic), Bulat (Russian) and Bintie (Chinese) are all names for historical ultra-high carbon crucible steel typified by carbide segregation. "Wootz" is an erroneous transliteration of "utsa" or "fountain" in Sanskrit, however since 1794 it has been the primary word used to refer to historical hypereutectoid crucible steel. History Origins The origin of the name "Damascus Steel" is contentious: the Islamic scholars al-Kindi (full name Abu Ya'qub ibn Ishaq al-Kindi, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watered Pattern On Sword Blade1
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food, energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, H2O, indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. "Water" is also the name of the liquid state of H2O at standard temperature and pressure. A number of natural states of water exist. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice may precipitate in the form of snow. The gaseous state of water is steam or water vapor. Water covers ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It is a unitary republic that consists of 14 governorates (subdivisions), and is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east and southeast, Jordan to the south, and Israel and Lebanon to the southwest. Cyprus lies to the west across the Mediterranean Sea. A country of fertile plains, high mountains, and deserts, Syria is home to diverse ethnic and religious groups, including the majority Syrian Arabs, Kurds, Turkmens, Assyrians, Armenians, Circassians, Albanians, and Greeks. Religious groups include Muslims, Christians, Alawites, Druze, and Yazidis. The capital and largest city of Syria is Damascus. Arabs are the largest ethnic group, and Mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superplasticity
In materials science, superplasticity is a state in which solid Crystallinity, crystalline material is deformed well beyond its usual breaking point, usually over about 600% during tensile deformation. Such a state is usually achieved at high homologous temperature. Examples of superplastic materials are some fine-grained metals and ceramics. Other non-crystalline materials (amorphous) such as silica glass ("molten glass") and polymers also deform similarly, but are not called superplastic, because they are not crystalline; rather, their deformation is often described as Newtonian fluid. Superplastically deformed material gets thinner in a very uniform manner, rather than forming a "neck" (a local narrowing) that leads to fracture. Also, the formation of microvoids, which is another cause of early fracture, is inhibited. In metals and ceramics, requirements for it being superplastic include a fine grain size (less than approximately 20 micrometres) and a fine dispersion of therma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cementite
Cementite (or iron carbide) is a compound of iron and carbon, more precisely an intermediate transition metal carbide with the formula Fe3C. By weight, it is 6.67% carbon and 93.3% iron. It has an orthorhombic crystal structure. It is a hard, brittle material, normally classified as a ceramic in its pure form, and is a frequently found and important constituent in ferrous metallurgy. While cementite is present in most steels and cast irons, it is produced as a raw material in the iron carbide process, which belongs to the family of alternative ironmaking technologies. The name ''cementite'' originated from the theory of Floris Osmond and J. Werth, in which the structure of solidified steel consists of a kind of cellular tissue, with ferrite as the nucleus and Fe3C the envelope of the cells. The carbide therefore ''cemented'' the iron. Metallurgy In the iron–carbon system (i.e. plain-carbon steels and cast irons) it is a common constituent because ferrite can contain at most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national " newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Nanotubes
A scanning tunneling microscopy image of a single-walled carbon nanotube Rotating single-walled zigzag carbon nanotube A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with diameters typically measured in nanometers. ''Single-wall carbon nanotubes'' (''SWCNTs'') are one of the allotropes of carbon, intermediate between fullerene cages and flat graphene, with diameters in the range of a nanometre. Although not made this way, single-wall carbon nanotubes can be idealized as cutouts from a two-dimensional Hexagonal tiling, hexagonal lattice of carbon atoms rolled up along one of the Bravais lattice vectors of the hexagonal lattice to form a hollow cylinder. In this construction, periodic boundary conditions are imposed over the length of this roll-up vector to yield a helical lattice of seamlessly bonded carbon atoms on the cylinder surface. ''Multi-wall carbon nanotubes'' (''MWCNTs'') consisting of nested single-wall carbon nanotubes weakly bound together by van der Waals i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanowires
A nanowire is a nanostructure in the form of a wire with the diameter of the order of a nanometre (10−9 metres). More generally, nanowires can be defined as structures that have a thickness or diameter constrained to tens of nanometers or less and an unconstrained length. At these scales, quantum mechanical effects are important—which coined the term "quantum wires". Many different types of nanowires exist, including superconducting (e.g. YBCO), metallic (e.g. Ni, Pt, Au, Ag), semiconducting (e.g. silicon nanowires (SiNWs), InP, GaN) and insulating (e.g. SiO2, TiO2). Molecular nanowires are composed of repeating molecular units either organic (e.g. DNA) or inorganic (e.g. Mo6S9−xIx). Characteristics upright=1.2, Crystalline 2×2-atom tin selenide nanowire grown inside a single-wall carbon nanotube (tube diameter ~1 nm). file:HgTe@SWCNT.png, A noise-filtered HRTEM image of a HgTe extreme nanowire embedded down the central pore of a SWCNT. The image is also accom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of , with a population of almost 84 million within its 16 constituent states. Germany borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elastic Limit
In materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stress-strain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior. Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed. Once the yield point is passed, some fraction of the deformation will be permanent and non-reversible and is known as plastic deformation. The yield strength or yield stress is a material property and is the stress corresponding to the yield point at which the material begins to deform plastically. The yield strength is often used to determine the maximum allowable load in a mechanical component, since it represents the upper limit to forces that can be applied without producing permanent deformation. In some materials, such as aluminium, there is a gradual onset of non-linear behavior, making the precise yield point difficult to determine. In such a case, the offset yiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tempered Steel
Tempering is a process of heat treating, which is used to increase the toughness of iron-based alloys. Tempering is usually performed after hardening, to reduce some of the excess hardness, and is done by heating the metal to some temperature below the critical point for a certain period of time, then allowing it to cool in still air. The exact temperature determines the amount of hardness removed, and depends on both the specific composition of the alloy and on the desired properties in the finished product. For instance, very hard tools are often tempered at low temperatures, while springs are tempered at much higher temperatures. Introduction Tempering is a heat treatment technique applied to ferrous alloys, such as steel or cast iron, to achieve greater toughness by decreasing the hardness of the alloy. The reduction in hardness is usually accompanied by an increase in ductility, thereby decreasing the brittleness of the metal. Tempering is usually performed after quenchi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendrite (crystal)
A crystal dendrite is a crystal that develops with a typical multi-branching form. The name comes from the Greek word dendron (δενδρον) which means "tree", since the crystal's structure resembles that of a tree. These crystals can be synthesised by using a supercooled pure liquid, however they are also quite common in nature. The most common crystals in nature exhibit dendritic growth are snowflakes and frost on windows, but many minerals and metals can also be found in dendritic structures. History Maximum velocity principle The first dendritic patterns were discovered in palaeontology and are often mistaken for fossils because of their appearance. The first theory for the creation of these patterns was published by Nash and Glicksman in 1974, they used a very mathematical method and derived a non-linear integro-differential equation for a classical needle growth. However they only found an inaccurate numerical solution close to the tip of the needle and they f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
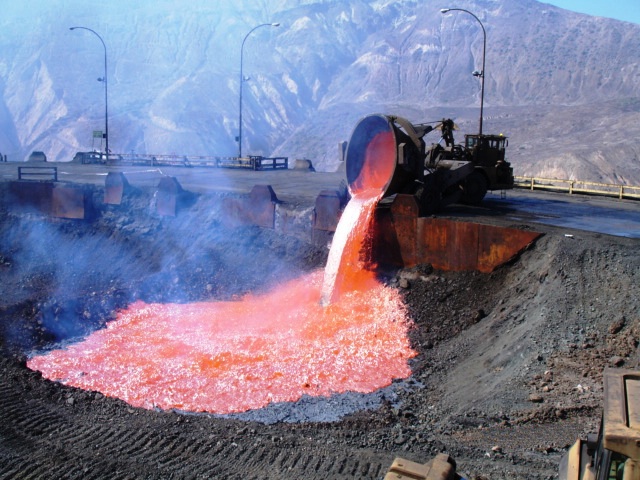
Slag
Slag is a by-product of smelting (pyrometallurgical) ores and used metals. Broadly, it can be classified as ferrous (by-products of processing iron and steel), ferroalloy (by-product of ferroalloy production) or non-ferrous/base metals (by-products of recovering non-ferrous materials like copper, nickel, zinc and phosphorus). Within these general categories, slags can be further categorized by their precursor and processing conditions (e.g., Blast furnace (BF) slags, air-cooled blast furnace (ACBF) slag, basic oxygen furnace (BOF) slag, and electric arc furnace (EAF) slag) . Due to the large demand for these materials, slag production has also significantly increased throughout the years despite recycling (most notably in the iron and steelmaking industries) and upcycling efforts. The World Steel Association (WSA) estimates that 600 kg of by-products (~90 wt% is slags) are generated per tonne of steel produced. Composition Slag is usually a mixture of metal oxides and sili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)