|
Unconscious Thought Theory
Unconscious thought theory (UTT) posits that the unconscious mind is capable of performing tasks outside of one's awareness, and that unconscious thought (UT) is better at solving complex tasks, where many variables are considered, than conscious thought (CT), but is outperformed by conscious thought in tasks with fewer variables. It was proposed by Ap Dijksterhuis and Loran NordgrenNordgren, L. Loran Nordgren ited 6 June 2010 Available from: http://www.kellogg.northwestern.edu/faculty/directory/nordgren_loran.aspx in 2006. The theory is based primarily on findings from comparing subjects presented with a complex decision (for instance which of several apartments is the best?), and allowed either (1). very little time, (2). ample time, or (3), ample time but are distracted and thereby prevented from devoting conscious attentional resources to it. It is claimed that subjects unable to devote conscious processing to the task outperform both those who can spend time deliberating and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ap Dijksterhuis
Albert Jan "Ap" Dijksterhuis (born 12 November 1968, Zutphen) is a Dutch Social Psychologist at Radboud University Nijmegen. He received his Ph.D in Social Sciences from Radboud University Nijmegen in 1996. His adviser was Ad van Knippenberg. From 1996-1999, he did post-doc work as a Research Fellow of the Royal Dutch Academy of Arts and Sciences, located in Amsterdam. In 2000, he became a professor at the University of Amsterdam, returning to Radboud University Nijmegen in 2006. In 2007, his first book was published, in Dutch, called ‘Het slimme onbewuste’ (‘The Smart Unconscious’). Awards *2005- Award for Distinguished Scientific Early Career Contributions to Psychology - APA *2005- Kurt Lewin Medal - EASP *2007- Wegner Theoretical Innovation Prize - SPSP Research His areas of research have varied, but all deal with unconscious: the perception-behavior link, goalsImplicit Self Esteem Issues and unconscious thought. He works & co-leads the Unconscious lab at Radboud U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive
Cognition refers to "the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, intelligence, the formation of knowledge, memory and working memory, judgment and evaluation, reasoning and computation, problem solving and decision making, comprehension and production of language. Imagination is also a cognitive process, it is considered as such because it involves thinking about possibilities. Cognitive processes use existing knowledge and discover new knowledge. Cognitive processes are analyzed from different perspectives within different contexts, notably in the fields of linguistics, musicology, anesthesia, neuroscience, psychiatry, psychology, education, philosophy, anthropology, biology, systemics, logic, and computer science. These and other approaches to the analysis of cognition (such as embodied cognition) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unconscious Mind
The unconscious mind (or the unconscious) consists of the processes in the mind which occur automatically and are not available to introspection and include thought processes, memories, interests, and motivations. Even though these processes exist well under the surface of conscious awareness, they are theorized to exert an effect on behavior. The term was coined by the German Romantic philosopher Friedrich Schelling and later introduced into English by the poet and essayist Samuel Taylor Coleridge.Christopher John Murray, ''Encyclopedia of the Romantic Era, 1760-1850'' (Taylor & Francis, 2004: ), pp. 1001–1002. Empirical evidence suggests that unconscious phenomena include repressed feelings, automatic skills, subliminal perceptions, and automatic reactions, and possibly also Complex (psychology), complexes, hidden phobias, and desires. The concept was popularized by the Austrian neurologist and Psychoanalysis, psychoanalyst Sigmund Freud. In psychoanalytic theory#The uncon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automaticity
Automaticity is the ability to do things without occupying the mind with the low-level details required, allowing it to become an automatic response pattern or habit. It is usually the result of learning, repetition, and practice. Examples of tasks carried out by 'muscle memory' often involve some degree of automaticity. Examples of automaticity are common activities such as walking, speaking, bicycle-riding, assembly-line work, and driving a car (the last of these sometimes being termed "highway hypnosis"). After an activity is sufficiently practiced, it is possible to focus the mind on other activities or thoughts while undertaking an automatized activity (for example, holding a conversation or planning a speech while driving a car). Characteristics John Bargh (1994), based on over a decade of research, suggested that four characteristics usually accompany automatic behavior: ;Awareness :A person may be unaware of the mental process that is occurring. ;Intentionality :A perso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Conditioning
Classical conditioning (also known as Pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is a behavioral procedure in which a biologically potent stimulus (e.g. food) is paired with a previously neutral stimulus (e.g. a triangle). It also refers to the learning process that results from this pairing, through which the neutral stimulus comes to elicit a response (e.g. salivation) that is usually similar to the one elicited by the potent stimulus. Classical conditioning is distinct from operant conditioning (also called instrumental conditioning), through which the strength of a voluntary behavior is modified by reinforcement or punishment. However, classical conditioning can affect operant conditioning in various ways; notably, classically conditioned stimuli may serve to reinforce operant responses. Classical conditioning was first studied in detail by Ivan Pavlov, who conducted experiments with dogs and published his findings in 1897. During the Russian physiologist's study of digestion, Pav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schema (psychology)
In psychology and cognitive science, a schema (plural ''schemata'' or ''schemas'') describes a pattern of thought or behavior that organizes categories of information and the relationships among them. It can also be described as a mental structure of preconceived ideas, a framework representing some aspect of the world, or a system of organizing and perceiving new information, such as a mental schema or conceptual model. Schemata influence attention and the absorption of new knowledge: people are more likely to notice things that fit into their schema, while re-interpreting contradictions to the schema as exceptions or distorting them to fit. Schemata have a tendency to remain unchanged, even in the face of contradictory information. Schemata can help in understanding the world and the rapidly changing environment. People can organize new perceptions into schemata quickly as most situations do not require complex thought when using schema, since automatic thought is all that is r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthony Greenwald
Anthony Galt Greenwald is a social psychologist and, since 1986, professor of psychology at University of Washington. In 1959, Greenwald received a B.A. from Yale University. In 1961, he received a M.A. from Harvard University, and in 1963, he completed his Ph.D., also at Harvard. After that, he completed a postdoctoral fellowship that lasted from 1963 to 1965 at the Educational Testing Service. Greenwald started teaching in 1965 as an assistant professor in the psychology department at Ohio State University, which continued until 1986. During that time, he was an associate editor for the '' Journal of Personality and Social Psychology'', from 1972 to 1976, before becoming the editor in 1977. From 2001 to 2005, Greenwald was the associate editor of ''Experimental Psychology''. Awards Greenwald has been recognized with a variety of significant awards, including the Donald T. Campbell Award from the Society for Personality and Social Psychology in 1994, Research Scientist Award fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Perception
Visual perception is the ability to interpret the surrounding environment through photopic vision (daytime vision), color vision, scotopic vision (night vision), and mesopic vision (twilight vision), using light in the visible spectrum reflected by objects in the environment. This is different from visual acuity, which refers to how clearly a person sees (for example "20/20 vision"). A person can have problems with visual perceptual processing even if they have 20/20 vision. The resulting perception is also known as vision, sight, or eyesight (adjectives ''visual'', ''optical'', and ''ocular'', respectively). The various physiological components involved in vision are referred to collectively as the visual system, and are the focus of much research in linguistics, psychology, cognitive science, neuroscience, and molecular biology, collectively referred to as vision science. Visual system In humans and a number of other mammals, light enters the eye through the cornea and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Von Helmholtz
Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz (31 August 1821 – 8 September 1894) was a German physicist and physician who made significant contributions in several scientific fields, particularly hydrodynamic stability. The Helmholtz Association, the largest German association of research institutions, is named in his honor. In the fields of physiology and psychology, Helmholtz is known for his mathematics concerning the eye, theories of vision, ideas on the visual perception of space, color vision research, the sensation of tone, perceptions of sound, and empiricism in the physiology of perception. In physics, he is known for his theories on the conservation of energy, work in electrodynamics, chemical thermodynamics, and on a mechanical foundation of thermodynamics. As a philosopher, he is known for his philosophy of science, ideas on the relation between the laws of perception and the laws of nature, the science of aesthetics, and ideas on the civilizing power of science. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affect (psychology)
Affect, in psychology, refers to the underlying experience of feeling, emotion or mood. History The modern conception of affect developed in the 19th century with Wilhelm Wundt. The word comes from the German ''Gefühl'', meaning "feeling." A number of experiments have been conducted in the study of social and psychological affective preferences (i.e., what people like or dislike). Specific research has been done on preferences, attitudes, impression formation, and decision-making. This research contrasts findings with recognition memory (old-new judgments), allowing researchers to demonstrate reliable distinctions between the two. Affect-based judgments and cognitive processes have been examined with noted differences indicated, and some argue affect and cognition are under the control of separate and partially independent systems that can influence each other in a variety of ways (Zajonc, 1980). Both affect and cognition may constitute independent sources of effects within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
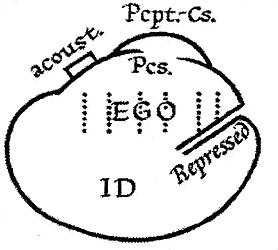
Id, Ego, And Super-ego
The id, ego, and super-ego are a set of three concepts in psychoanalytic theory describing distinct, interacting agents in the psychic apparatus (defined in Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche). The three agents are theoretical constructs that describe the activities and interactions of the mental life of a person. In the ego psychology model of the psyche, the id is the set of uncoordinated instinctual desires; the super-ego plays the critical and moralizing role; and the ego is the organized, realistic agent that mediates between the instinctual desires of the id and the critical super-ego; Freud explained that: The functional importance of the ego is manifested in the fact that, normally, control over the approaches to motility devolves upon it. Thus, in its relation to the id, he egois like a man on horseback, who has to hold in check the superior strength of the horse; with this difference, that the rider tries to do so with his own strength, while the ego uses b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loran Nordgren
Loran F. Nordgren is an American professor of psychology who studies the adoption of new ideas and behaviors. In 2020 he became a professor at Northwestern University's Kellogg School of Management. He is the co-author of ''The Human Element: Overcoming the Resistance That Awaits New Ideas.'' Nordgren completed a B.A. in psychology, magna cum laude, in 2001 at St. Olaf College. He was a Fulbright scholar and completed a Ph.D. in social psychology with distinction at the University of Amsterdam. He was recognized as one of Poets & Quants’ 40 under 40 business school professors. Nordgren is the founder of Candor, a software company that promotes bias-free collaboration and feedback. In 2009, he was a social and experimental psychologist and assistant professor at Northwestern's Kellogg School of Management. Nordren received the Theoretical Innovation Award of the Society of Personality and Social Psychology The Society for Personality and Social Psychology (SPSP) is an acade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |