|
Ukrainian Greeks
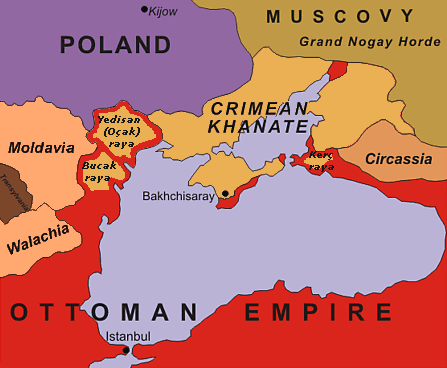
Ukrainian Greeks are a Greek minority that reside in or used to reside in the territory of modern Ukraine. The majority of Ukrainian Greeks live in Donetsk Oblast and are particularly concentrated around the city of Mariupol. According to the 2001 Ukrainian Census, there were 91,548 ethnic Greeks in Ukraine, or 0.2% of the population. However, the actual percentage of those with Greek ancestry is likely to be much higher due to widespread intermarriage between ethnic Greeks and those Ukrainian citizens who are Ukrainian Orthodox, particularly in eastern Ukraine, as well as the absence of strong links to Greece or use of the Greek language by many with Greek ancestry in these areas and who therefore are not classified as Greeks in official censuses. Most Greeks in Ukraine belong to the larger Greek diaspora known as Pontic Greeks. But there are also a small recent group of Greek expats and immigrants to Ukraine. History A Greek presence throughout the Black Sea area existed l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2001 Ukrainian Census
The Ukrainian Census of 2001 is to date the only census of the population of independent Ukraine. It was conducted by the State Statistics Committee of Ukraine on 5 December 2001, twelve years after the last Soviet Union census in 1989.In 2021, there will most likely be no all-Ukrainian census - Minister hromadske.ua (21 April 2020) The was planned to be held in 2011 but has been repeatedly postponed [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, other countries surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. They also form a significant diaspora (), with Greek communities established around the world.. Greek colonies and communities have been historically established on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea, but the Greek people themselves have always been centered on the Aegean and Ionian seas, where the Greek language has been spoken since the Bronze Age.. Until the early 20th century, Greeks were distributed between the Greek peninsula, the western coast of Asia Minor, the Black Sea coast, Cappadocia in central Anatolia, Egypt, the Balkans, Cyprus, and Constantinople. Many of these regions coincided to a large extent with the borders of the Byzantine Empire of the late 11th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
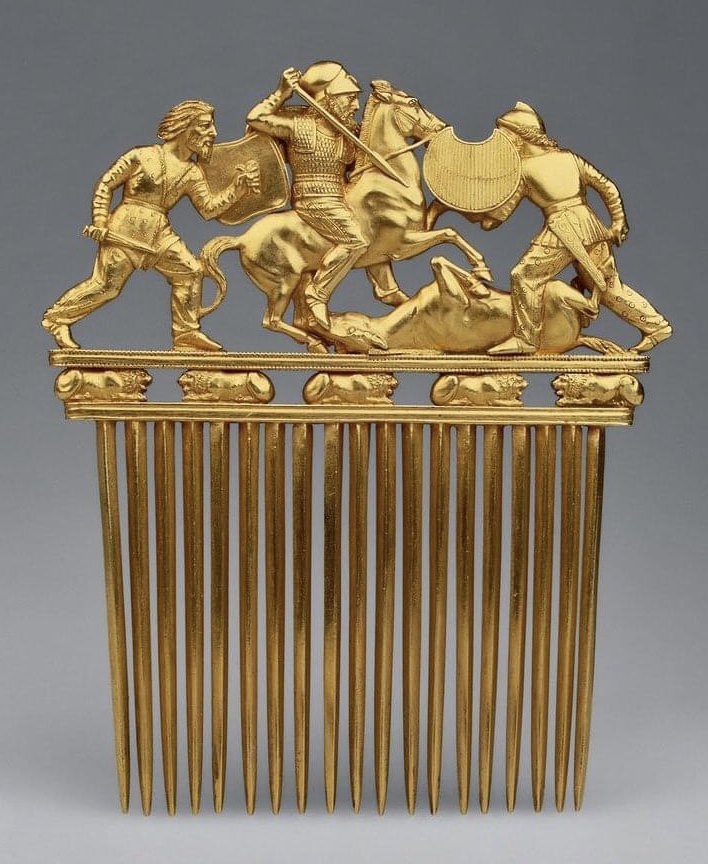
Bosporan Kingdom
The Bosporan Kingdom, also known as the Kingdom of the Cimmerian Bosporus (, ''Vasíleio toú Kimmerikoú Vospórou''), was an ancient Greco-Scythian state located in eastern Crimea and the Taman Peninsula on the shores of the Cimmerian Bosporus, centered in the present-day Strait of Kerch. It was the first truly 'Hellenistic' state, in the sense that a mixed population adopted the Greek language and civilization, under aristocratic consolidated leadership. Under the Spartocid dynasty, the aristocracy of the kingdom adopted a double nature of presenting themselves as ''archons'' to Greek subjects and as kings to barbarians, which some historians consider unique in ancient history.The Bosporan Kingdom became the longest surviving Roman client kingdom. The 1st and 2nd centuries AD saw a period of a new golden age of the Bosporan state. It was briefly incorporated as part of the Roman province of Moesia Inferior from 63 to 68 AD under Emperor Nero, before being restored as a Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, mainly inhabiting Central and Eastern Europe, and the Balkans to the west; and Siberia to the east. A large Slavic minority is also scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, while a substantial Slavic diaspora is found throughout the Americas, as a result of immigration. Present-day Slavs are classified into East Slavs (chiefly Belarusians, Russians, Rusyns, and Ukrainians), West Slavs (chiefly Czechs, Kashubians, Poles, Slovaks and Sorbs) and South Slavs (chiefly Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes). The vast majority of Slavs are traditionally Christians. However, modern Slavic nations and ethnic groups are considerably diverse both genetically and culturally, and relations between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. In his book '' Getica'' (c. 551), the historian Jordanes writes that the Goths originated in southern Scandinavia, but the accuracy of this account is unclear. A people called the ''Gutones''possibly early Gothsare documented living near the lower Vistula River in the 1st century, where they are associated with the archaeological Wielbark culture. From the 2nd century, the Wielbark culture expanded southwards towards the Black Sea in what has been associated with Gothic migration, and by the late 3rd century it contributed to the formation of the Chernyakhov culture. By the 4th century at the latest, several Gothic groups were distinguishable, among whom the Thervingi and Greuthungi were the most powerful. During this time, Wulfila bega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cimmerians
The Cimmerians (Akkadian: , romanized: ; Hebrew: , romanized: ; Ancient Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people originating in the Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into West Asia. Although the Cimmerians were culturally Scythian, they formed an ethnic unit separate from the Scythians proper, to whom the Cimmerians were related and who displaced and replaced the Cimmerians.: "As the Cimmerians cannot be differentiated archeologically from the Scythians, it is possible to speculate about their Iranian origins. In the Neo-Babylonian texts (according to D’yakonov, including at least some of the Assyrian texts in Babylonian dialect) and similar forms designate the Scythians and Central Asian Saka, reflecting the perception among inhabitants of Mesopotamia that Cimmerians and Scythians represented a single cultural and economic group" The Cimmerians themselves left no written records, and most information abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maeotae
The Maeotians (; grc, Μαιῶται, translit=Maiōtai; la, Maeōtae) were an ancient people dwelling along the Sea of Azov, which was known in antiquity as the " Maeotian marshes" or " Lake Maeotis".James, Edward Boucher"Maeotae" and "Maeotis Palus"in the ''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography'', , . Walton & Maberly (London), 1857. Accessed 26 Aug 2014. They are often considered to be the ancestors of the Circassians,Abkhazians, Abazins. Identity The etymology of the name and identity of the people remain unclear. Edward James and William Smith were of the opinion that the term Maeotian was applied broadly to various peoples around the Sea of Azov, rather than the name of the sea deriving from a certain people. Their subdivisions included the Sindi, the Dandarii, the Toreatae, the Agri, the Arrechi, the Tarpetes, the Obidiaceni, the Sittaceni, the Dosci, and "many" others.Strabo. ''Geographica'', xi. . Of these, the Sindi are the best attested, and were probabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern * : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Central Asia and Eastern Turkestan to distinguish them from the related Massagetae of the Aral region and the Scythians of the Pontic steppes. These tribes spoke Iranian languages, and their chief occupation was nomadic pastoralism." * : "Near the end of the 19th century V.F. Miller (1886, 1887) theorized that the Scythians and their kindred, the Sauromatians, were Iranian-speaking peoples. This has been a popular point of view and continues to be accepted in linguistics and historical science .. * : "From the end of the 7th century B.C. to the 4th century B.C. the Central- Eurasian steppes were inhabited by two large groups of kin Iranian-speaking tribes – the Scythians and Sarmatians .. * : "All contemporary historians, archeologists and li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Era
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the original Anno Domini (AD) and Before Christ (BC) notations used for the same calendar era. The two notation systems are numerically equivalent: " CE" and "AD " each describe the current year; "400 BCE" and "400 BC" are the same year. The expression traces back to 1615, when it first appeared in a book by Johannes Kepler as the la, annus aerae nostrae vulgaris (), and to 1635 in English as " Vulgar Era". The term "Common Era" can be found in English as early as 1708, and became more widely used in the mid-19th century by Jewish religious scholars. Since the later 20th century, BCE and CE have become popular in academic and scientific publications because BCE and CE are religiously neutral terms. They are used by others who wish to be sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greeks In Pre-Roman Crimea
Greek city-states first established colonies along the Black Sea coast of Crimea in the 7th or 6th century BC. Several colonies were established in the vicinity of the Kerch Strait, then known as the Cimmerian Bosporus. The density of colonies around the Cimmerian Bosporus was unusual for Greek colonization and reflected the importance of the area. The majority of these colonies were established by Ionians from the city of Miletus in Asia Minor. By the mid-1st century BC the Bosporan Kingdom became a client state of the late Roman Republic, ushering in the era of Roman Crimea during the Roman Empire. Etymology ''Taurica'', ''Tauric Chersonese'', and ''Tauris'' were names by which the Crimean Peninsula was known in classical antiquity and well into the early modern period. The Greeks named the region after its inhabitants, the Tauri: Ταυρικὴ Χερσόνησος (''Taurikē Khersonesos'') or Χερσόνησος Ταυρική (''Khersonesos Taurikē''), "Tauric peni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Turkish War
The Russo-Turkish wars (or Ottoman–Russian wars) were a series of twelve wars fought between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 20th centuries. It was one of the longest series of military conflicts in European history. Except for the war of 1710–11 and the Crimean War, which is often treated as a separate event, the conflicts ended disastrously for the Ottoman Empire; conversely, they showcased the ascendancy of Russia as a European power after the modernization efforts of Peter the Great in the early 18th century. History Conflict begins (1568–1739) Before Peter the Great The first Russo-Turkish War (1568–1570) occurred after the conquest of Kazan and Astrakhan by the Russian tsar Ivan the Terrible. The Ottoman sultan Selim II tried to squeeze the Russians out of the lower Volga by sending a military expedition to Astrakhan in 1569. The Turkish expedition ended in disaster for the Ottoman army, which could not take Astrakhan and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
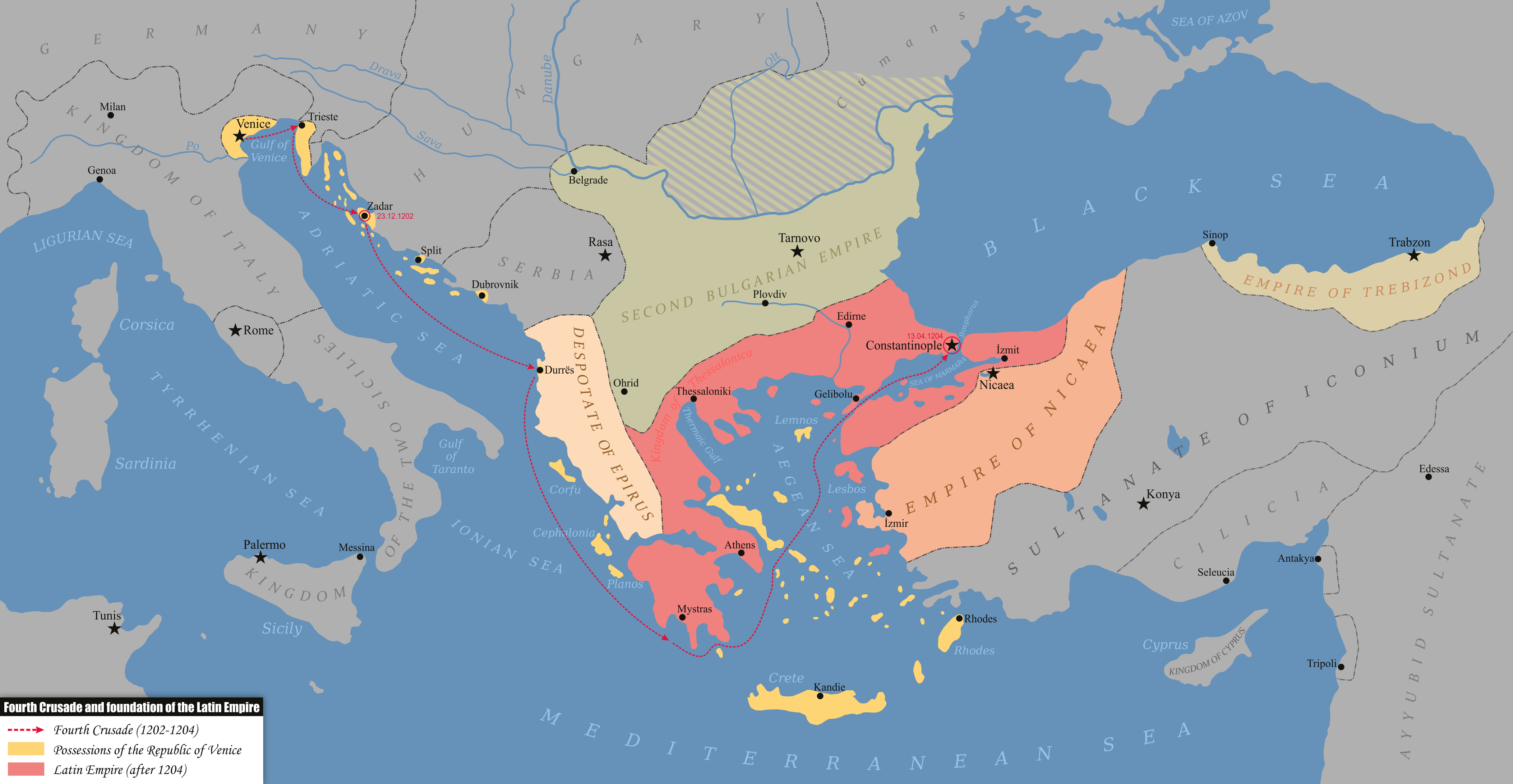
Empire Of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond, or Trapezuntine Empire, was a monarchy and one of three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire, along with the Despotate of the Morea and the Principality of Theodoro, that flourished during the 13th through to the 15th century, consisting of the far northeastern corner of Anatolia (the Pontus) and the southern Crimea. The empire was formed in 1204 with the help of the Georgian queen Tamar after the Georgian expedition in Chaldia and Paphlagonia, commanded by Alexios Komnenos a few weeks before the sack of Constantinople. Alexios later declared himself Emperor and established himself in Trebizond (modern day Trabzon, Turkey). Alexios and David Komnenos, grandsons and last male descendants of deposed Emperor Andronikos I Komnenos, pressed their claims as "Roman emperors" against Byzantine Emperor Alexios V Doukas. The later Byzantine emperors, as well as Byzantine authors, such as George Pachymeres, Nicephorus Gregoras and to some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)