Empire of Trebizond on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Empire of Trebizond, or Trapezuntine Empire, was a
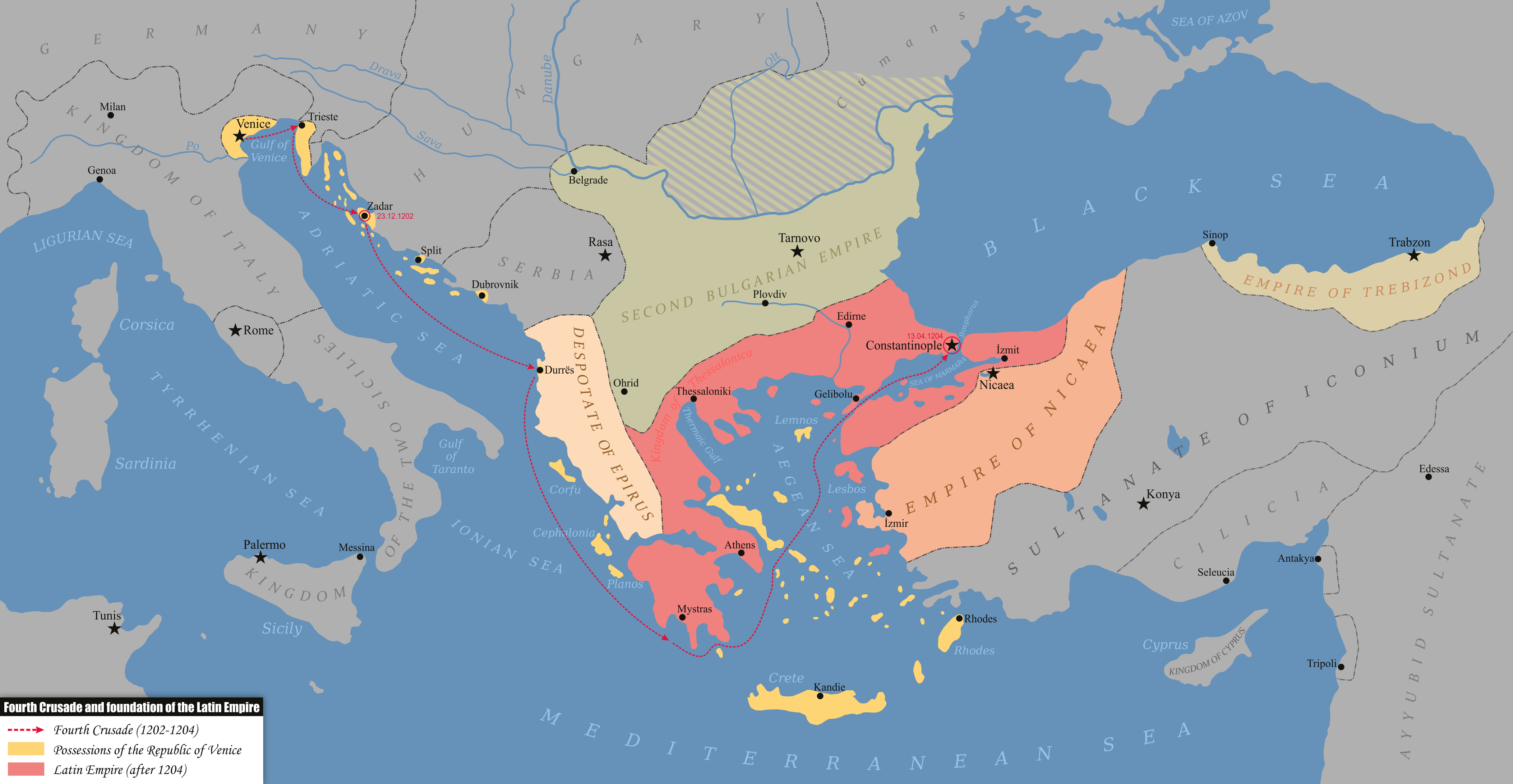 Geographically, the Empire of Trebizond consisted of the narrow strip along the southern coast of the
Geographically, the Empire of Trebizond consisted of the narrow strip along the southern coast of the
 The city of Trebizond was the capital of the theme of Chaldia, which according to the 10th century
The city of Trebizond was the capital of the theme of Chaldia, which according to the 10th century

 The date Alexios entered Trebizond may be narrowed down even further. Sergey Karpov has identified a lead seal of Alexios, on one side "the image of a strategos in the peaked helmet led by hand by St. George" with the inscriptions Ἀλέξιος ὁ Κομνηνός lexios Komnenosand Ὁ Ἅ(γιος) Γεώργιος aint Georgeon either side; on the obverse is a scene of Ἡ Ἁγία Ἀνάστασις he Holy Resurrectionwith the corresponding inscription. Karpov interprets the significance of this image and the inscription as portraying the most important achievement of his life, St. George inviting the victorious prince to enter Trebizond and opening the gates of the city with his left hand. The importance of St. George was that Easter—the date of the Resurrection—in 1204 fell on 25 April, while the memorial date of St. George was 23 April. "So I dared to assume," writes Karpov, "that the seal points out the date of the capture of Trebizond."
Vasiliev points out that the brothers occupied Trebizond too early to have done so in response to the Crusaders capturing Constantinople; Alexios and David began their march on Trebizond before news of the Sack of Constantinople on 13 April 1204 could reach either Trebizond or Georgia. According to Vasiliev, however, their original intention was not to seize a base from which they could recover the capital of the Byzantine Empire, but rather to carve out of the Byzantine Empire a
The date Alexios entered Trebizond may be narrowed down even further. Sergey Karpov has identified a lead seal of Alexios, on one side "the image of a strategos in the peaked helmet led by hand by St. George" with the inscriptions Ἀλέξιος ὁ Κομνηνός lexios Komnenosand Ὁ Ἅ(γιος) Γεώργιος aint Georgeon either side; on the obverse is a scene of Ἡ Ἁγία Ἀνάστασις he Holy Resurrectionwith the corresponding inscription. Karpov interprets the significance of this image and the inscription as portraying the most important achievement of his life, St. George inviting the victorious prince to enter Trebizond and opening the gates of the city with his left hand. The importance of St. George was that Easter—the date of the Resurrection—in 1204 fell on 25 April, while the memorial date of St. George was 23 April. "So I dared to assume," writes Karpov, "that the seal points out the date of the capture of Trebizond."
Vasiliev points out that the brothers occupied Trebizond too early to have done so in response to the Crusaders capturing Constantinople; Alexios and David began their march on Trebizond before news of the Sack of Constantinople on 13 April 1204 could reach either Trebizond or Georgia. According to Vasiliev, however, their original intention was not to seize a base from which they could recover the capital of the Byzantine Empire, but rather to carve out of the Byzantine Empire a
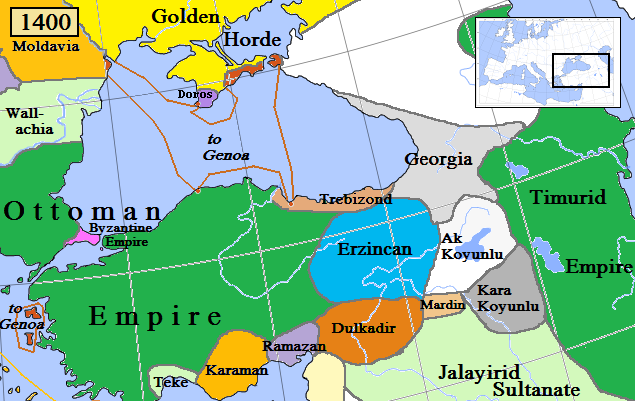 The last years of the fourteenth century were characterized by the increasing Turkish threat. This threat was not from the small Turkmen emirates that bordered Trebizond, but from the dynasty of the Osmanli, a new Turkish power emerging from western Anatolia that would soon consolidate the
The last years of the fourteenth century were characterized by the increasing Turkish threat. This threat was not from the small Turkmen emirates that bordered Trebizond, but from the dynasty of the Osmanli, a new Turkish power emerging from western Anatolia that would soon consolidate the
Perché si dice perdere la Trebisonda
''nationalgeographic.it''. Retrieved October 19, 2019.
monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which a person, the monarch, is head of state for life or until abdication. The political legitimacy and authority of the monarch may vary from restricted and largely symbolic (constitutional monarchy ...
and one of three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
, along with the Despotate of the Morea and the Principality of Theodoro, that flourished during the 13th through to the 15th century, consisting of the far northeastern corner of Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The r ...
(the Pontus) and the southern Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
. The empire was formed in 1204 with the help of the Georgian queen Tamar after the Georgian expedition in Chaldia and Paphlagonia, commanded by Alexios Komnenos a few weeks before the sack of Constantinople. Alexios later declared himself Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother ( e ...
and established himself in Trebizond (modern day Trabzon, Turkey). Alexios and David Komnenos, grandsons and last male descendants of deposed Emperor Andronikos I Komnenos, pressed their claims as "Roman emperors" against Byzantine Emperor Alexios V Doukas. The later Byzantine emperors, as well as Byzantine authors, such as George Pachymeres, Nicephorus Gregoras and to some extent Trapezuntines such as John Lazaropoulos and Basilios Bessarion, regarded the emperors of Trebizond as the "princes of the Lazes", while the possession of these "princes" was also called Lazica. Thus from the point of view of the Byzantine writers connected with the Laskaris and later with the Palaiologos
The House of Palaiologos ( Palaiologoi; grc-gre, Παλαιολόγος, pl. , female version Palaiologina; grc-gre, Παλαιολογίνα), also found in English-language literature as Palaeologus or Palaeologue, was a Byzantine Greek f ...
dynasties, the rulers of Trebizond were not emperors.
After the crusaders of the Fourth Crusade overthrew Alexios V and established the Latin Empire, the Empire of Trebizond became one of three Byzantine successor states to claim the imperial throne, alongside the Empire of Nicaea under the Laskaris family and the Despotate of Epirus under a branch of the Angelos family. The ensuing wars saw the Empire of Thessalonica, the imperial government that sprang from Epirus, collapse following conflicts with Nicaea and Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Mac ...
and the final recapture of Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
by the Empire of Nicaea in 1261. Despite the Nicaean reconquest of Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
, the Emperors of Trebizond continued to style themselves as "Roman emperors" for two decades and continued to press their claim on the Imperial throne. Emperor John II of Trebizond officially gave up the Trapezuntine claim to the Roman imperial title and Constantinople itself 21 years after the Nicaeans recaptured the city, altering his imperial title from "Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother ( e ...
and Autocrat of the Romans" to "Emperor and Autocrat of all the East, Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a la ...
and Perateia".
The Trapezuntine monarchy survived the longest among the Byzantine successor states. The Despotate of Epirus had ceased to contest the Byzantine throne even before the Nicaean reconquest and was briefly occupied by the restored Byzantine Empire , thereafter becoming a Serbian
Serbian may refer to:
* someone or something related to Serbia, a country in Southeastern Europe
* someone or something related to the Serbs, a South Slavic people
* Serbian language
* Serbian names
See also
*
*
* Old Serbian (disambiguat ...
dependency later inherited by Italians, ultimately falling to the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
in 1479. Whilst the Empire of Nicaea had restored the Byzantine Empire through restoring control of the capital, it ended in 1453 with the conquest of Constantinople by the Ottomans. Trebizond lasted until 1461 when the Ottoman sultan Mehmed II conquered it after a month-long siege and took its ruler and his family into captivity. The Crimean Principality of Theodoro, an offshoot of Trebizond, lasted another 14 years, falling to the Ottomans in 1475.
Origins
Trebizond already had a long history of autonomous rule before it became the center of a small empire in theLate Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Ren ...
. Due to its natural harbours, defensible topography and access to silver and copper mines, Trebizond became the pre-eminent Greek colony on the eastern Black Sea shore soon after its founding. Its remoteness from Roman capitals gave local rulers the opportunity to advance their own interest. In the centuries before the founding of the empire the city had been under control of the local Gabras family, which – while officially still remaining part of the Byzantine Empire – minted its own coin.
The rulers of Trebizond called themselves ''Megas Komnenos'' ("Great Comnenus") and – like their counterparts in the other two Byzantine successor states, the Empire of Nicaea and the Despotate of Epirus – initially claimed supremacy as "Emperor and Autocrat of the Romans". However, after Michael VIII Palaiologos of Nicaea recaptured Constantinople in 1261, the Komnenian use of the style "Emperor" became a sore point. In 1282, John II Komnenos stripped off his imperial regalia before the walls of Constantinople before entering to marry Michael's daughter, accepting his legal title of despot. However, his successors used a version of his title, "Emperor and Autocrat of the entire East, of the Iberians
The Iberians ( la, Hibērī, from el, Ἴβηρες, ''Iberes'') were an ancient people settled in the eastern and southern coasts of the Iberian peninsula, at least from the 6th century BC. They are described in Greek and Roman sources (amo ...
and the Perateia" until the Empire's end in 1461.
Geography
 Geographically, the Empire of Trebizond consisted of the narrow strip along the southern coast of the
Geographically, the Empire of Trebizond consisted of the narrow strip along the southern coast of the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, ...
and the western half of the Pontic Alps, along with the Gazarian Perateia, or southern Crimea (soon losing to Genoese Gazaria and Theodorite Gazaria).
The core of the empire was the southern Black Sea coast from the mouth of the Yeşilırmak river, a region known to the Trapezuntines as Limnia, possibly as far east as Akampsis river, a region then known as Lazia; Anthony Bryer has argued that six of the seven ''banda
Banda may refer to:
People
*Banda (surname)
*Banda Prakash (born 1954), Indian politician
*Banda Kanakalingeshwara Rao (1907–1968), Indian actor
*Banda Karthika Reddy (born 1977), Indian politician
*Banda Singh Bahadur (1670–1716), Sikh warr ...
'' of the Byzantine theme of Chaldia were maintained in working order by the rulers of Trebizond until the end of the empire, helped by geography. Geography also defined the southern border of this state: the Pontic Alps served as a barrier first to Seljuk Turks and later to Turkoman marauders, whose predations were reduced to a volume that the emperors could cope with. This territory corresponds to an area comprising all or parts of the modern Turkish provinces
Turkey is divided into 81 provinces ( tr, il). Each province is divided into a number of districts (). Each provincial government is seated in the central district (). For non- metropolitan municipality designated provinces, the central distri ...
of Sinop, Samsun, Ordu, Giresun, Trabzon, Bayburt, Gümüşhane, Rize, and coastal parts of Artvin. In the 13th century, some experts believe the empire controlled the Gazarian Perateia, which included Cherson and Kerch on the Crimean peninsula. David Komnenos, the younger brother of the first Emperor, expanded rapidly to the west, occupying first Sinope, then coastal parts of Paphlagonia (the modern-day coastal regions of Kastamonu, Bartın
Bartın is a city in northern Turkey and the central district of the province of Bartın.
Formerly a district of Zonguldak Province, Bartın was made into a province seat in 1991 with the constitution of its province, including four districts: ...
, and Zonguldak) and Heraclea Pontica (the modern-day Karadeniz Ereğli), until his territory bordered the Empire of Nicaea. The expansion was, however, short-lived: the territories west of Sinope were lost to Theodore I Laskaris by 1214, and Sinope itself fell to the Seljuks that same year, although the emperors of Trebizond continued to fight for its control over the rest of the 13th century.
History
Background
 The city of Trebizond was the capital of the theme of Chaldia, which according to the 10th century
The city of Trebizond was the capital of the theme of Chaldia, which according to the 10th century Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Wester ...
geographer Abul Feda was regarded as being largely a Lazian port. Chaldia had already shown its separatist tendencies in the 10th and 11th centuries, when it came under the control of a local leader named Theodore Gabras, who according to Anna Comnena regarded Trebizond and its hinterlands "as a prize which had fallen to his own lot" and conducted himself as an independent prince. The Byzantine Emperor Alexios I Komnenos confirmed him as governor of Chaldia, but kept his son at Constantinople as a hostage for his good conduct. Nevertheless, Gabras proved himself a worthy guardian by repelling a Georgian attack on Trebizond.Miller, ''Trebizond'', p. 12 One of his successors, Gregory Taronites, also rebelled with the aid of the sultan of Cappadocia, but he was defeated and imprisoned, only to be made governor once more. Another successor to Theodore was Constantine Gabras, whom Niketas describes as ruling Trebizond as a tyrant, and whose actions led Emperor John II Komnenos in 1139 to lead an expedition against him. Although that effort came to nothing, this was the last rebel governor known to recorded history prior to the events of 1204.
Foundation
The empire traces its foundation to April 1204, when Alexios Komnenos and his brother David took advantage of the preoccupation of the central Byzantine government with the encampment of the soldiers of the Fourth Crusade outside their walls (June 1203 – mid-April 1204) and seized the city of Trebizond and the surrounding province of Chaldia with troops provided by their relative,Tamar of Georgia
Tamar the Great ( ka, თამარ მეფე, tr, Literal translation, lit. "King Tamar") ( 1160 – 18 January 1213) queen regnant, reigned as the List of monarchs of Georgia#Kings of unified Georgia (1008–1490), Queen of Kingdom of ...
. Henceforth, the links between Trebizond and Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to t ...
remained close, but their nature and extent have been disputed. However some scholars believe that the new state was subject to Georgia, at least in the first years of its existence, at the beginning of the 13th century.Ostrogorsky, G., Ιστορία του Βυζαντινού κράτους 3 (Athens 1997), pp. 102, 305.
Both men were the grandsons of the last Komnenian Byzantine emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as l ...
, Andronikos I Komnenos, by his son Manuel Komnenos and Rusudan, daughter of George III of Georgia. Andronikos I had been deposed by Isaac II Angelos
Isaac II Angelos or Angelus ( grc-gre, Ἰσαάκιος Κομνηνός Ἄγγελος, ; September 1156 – January 1204) was Byzantine Emperor from 1185 to 1195, and again from 1203 to 1204.
His father Andronikos Doukas Angelos was ...
, while Manuel was blinded (a traditional Byzantine punishment for treason) and died not long after. Alexios and his brother, David, ended up at the court of Queen Tamar of Georgia, who gave them military support to return to Byzantine territory. Vasiliev explains that she had been motivated to do so after the Emperor Alexios III Angelos stole the gifts Tamar had given to a group of visiting monks as they passed through Constantinople. While Michel Kurskanskis has argued in support of Vasiliev's interpretation, he disagrees with Vasiliev over the intent of Tamar's intervention: Vasiliev has argued that the Queen intended to create a buffer state to protect the Georgian Kingdom, while Kurskanskis believes she supported the brothers in their attempt to reclaim the Byzantine throne in Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
.
After marching from Georgia, and with the help of their paternal aunt Queen Tamar, Alexios and David occupied Trebizond in April 1204.Michael Panaretos, Chronicle, ch. 1. Greek text in ''Original-Fragmente, Chroniken, Inschiften und anderes Materiale zur Geschichte des Kaiserthums Trapezunt'', part 2; in ''Abhandlungen der historischen Classe der königlich bayerischen Akademie'' 4 (1844), abth. 1, pp. 11; German translation, p. 41 That same month Alexios was proclaimed emperor at the age of 22, an act considered by later writers as the moment the Empire of Trebizond was founded. Alexios would then proceed to rule his new empire for the next twenty-two years, until his death in February 1222. The throne then passed to his son-in-law Andronikos I Gidos Komnenos.
Up to the civil wars

buffer state
A buffer state is a country geographically lying between two rival or potentially hostile great powers. Its existence can sometimes be thought to prevent conflict between them. A buffer state is sometimes a mutually agreed upon area lying between ...
to protect Georgia from the Seljuk Turks. Kuršanskis, while agreeing with Vasiliev that Tamar was motivated by revenge for Alexios Angelos's insult, proposed a more obvious motivation for the brother's return to Byzantine territory: they had decided to raise the banner of revolt, depose Alexios Angelos, and return the imperial throne to the Komnenos dynasty. However, not long after they had gained control of Trebizond and the neighboring territories, news of the Latin conquest of Constantinople reached them, and the brothers entered the competition for recovery of the imperial city against Theodore I Laskaris in western Anatolia (ruler of the " Empire of Nicaea") and Michael Komnenos Doukas in mainland Greece (ruler of the " Despotate of Epirus").
For most of the 13th century Trebizond was in continual conflict with the Seljuk Sultanate of Rûm and later with the Ottoman Turks, as well as Constantinople, the Italian republics, and especially the Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( lij, Repúbrica de Zêna ; it, Repubblica di Genova; la, Res Publica Ianuensis) was a medieval and early modern maritime republic from the 11th century to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italian coast. During the L ...
. It was an empire more in title than in fact, surviving by playing its rivals against each other, and offering the daughters of its rulers, who were famed for their beauty, for marriage
Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognized union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children, and between t ...
with generous dowries, especially with the Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
rulers of inland Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The r ...
. The common view is that the Empire of Trebizond relied heavily upon wealth gained from its trade with Genoese and Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
merchants to secure for itself the resources necessary to maintain independence.Hewsen, "Armenians on the Black Sea", p. 48
The second son of Alexios I, Manuel I (1238–1263), preserved internal security and acquired the reputation of a great commander. His accomplishments included capturing Sinope Sinope may refer to:
*Sinop, Turkey, a city on the Black Sea, historically known as Sinope
** Battle of Sinop, 1853 naval battle in the Sinop port
*Sinop Province
* Sinope, Leicestershire, a hamlet in the Midlands of England
*Sinope (mythology), in ...
in 1254. He was the first ruler to issue silver coins, which were known as '' aspers''.
The destruction of Baghdad by Hulagu Khan in 1258 diverted the western terminus of the Silk Road north to the Black Sea, and due to its link with their local capital at Tabriz
Tabriz ( fa, تبریز ; ) is a city in northwestern Iran, serving as the capital of East Azerbaijan Province. It is the sixth-most-populous city in Iran. In the Quru River valley in Iran's historic Azerbaijan region between long ridges of vo ...
, Trebizond accumulated tremendous wealth under the suzerainty of the Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
. Western travelers used Trebizond as their starting point for journeys into Asia; these travelers included Marco Polo, who returned to Europe in 1295 by way of Trebizond. The troubled reign of Manuel's youngest son John II (1280–1297) included a reconciliation with the restored Byzantine Empire and the end of Trapezuntine claims to Constantinople. Trebizond enjoyed a period of wealth and influence during the long reign of John's eldest son Alexios II (1297–1330). During his reign, the city of Erzurum
Erzurum (; ) is a List of cities in Turkey, city in eastern Anatolia, Turkey. It is the largest city and capital of Erzurum Province and is 1,900 meters (6,233 feet) above sea level. Erzurum had a population of 367,250 in 2010.
The city uses t ...
was also under Trebizond Empire occupation for a while around the 1310s.
From the civil wars to the end of the 14th century
Following the death of Alexios II, Trebizond suffered a period of repeated imperial depositions and assassinations, despite a short period of stability under his youngest son Basil (1332–1340). Two groups struggled for ascendency: the ''Scholaroi'', who have been identified as being pro-Byzantine, and the ''Amytzantarantes'', who were identified as representing the interests of the native '' archontes''. The years 1347–1348 marked the apex of this lawless period. The Turks took advantage of the weakness of the empire, conquering Oinaion and besieging Trebizond, while the Genoese seized Kerasus. In addition, the Black Death spread from Caffa to ravage Trebizond and other Pontic cities. Bending under the weight of the disasters that accumulated on his states, Emperor Michael abdicated in 1349 in favor of his nephew, Alexios III, who gradually brought the partisans of both factions under control. Under the rule of Alexios III, Trebizond was considered an important trade center and was renowned for its great wealth and artistic accomplishment. It was at this point that their famous diplomatic strategy of marrying the princesses of the Grand Komnenos to neighboring Turkish dynasts began. However, Anthony Bryers has argued against thinking this empire was a wealthy polity, stating that while the income from taxes levied on this trade was "by Byzantine standards" substantial, as much as three quarters of the income of the Emperor came from land "either directly from the imperial estates or indirectly from taxes and tithes from other lands."In the 15th century
 The last years of the fourteenth century were characterized by the increasing Turkish threat. This threat was not from the small Turkmen emirates that bordered Trebizond, but from the dynasty of the Osmanli, a new Turkish power emerging from western Anatolia that would soon consolidate the
The last years of the fourteenth century were characterized by the increasing Turkish threat. This threat was not from the small Turkmen emirates that bordered Trebizond, but from the dynasty of the Osmanli, a new Turkish power emerging from western Anatolia that would soon consolidate the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. Although their expansion was temporarily checked by Tamerlane at the Battle of Ankara in 1402, by the 1430s the Ottomans had recovered their fortunes, seizing large segments of Greece and finally capturing Constantinople itself on 29 May 1453. Manuel III (1390–1417), the second son and successor of Alexios III, had allied himself with Tamerlane, but the mighty conqueror soon left Anatolia, and the empire he had built crumbled with his death. Manuel's son Alexios IV
Alexios IV Angelos or Alexius IV Angelus ( el, Ἀλέξιος Ἄγγελος) (c. 1182 – February 1204) was Byzantine Emperor from August 1203 to January 1204. He was the son of Emperor Isaac II Angelos and his first wife, an unknown Palaio ...
(1417–1429) continued the tradition of political marriages by marrying two of his daughters to rulers of two neighboring Muslim empires: Jihan Shah, khan of the Kara Koyunlu, and Ali Beg, khan of the Ak Koyunlu
The Aq Qoyunlu ( az, Ağqoyunlular , ) was a culturally Persianate,Kaushik Roy, ''Military Transition in Early Modern Asia, 1400–1750'', (Bloomsbury, 2014), 38; "Post-Mongol Persia and Iraq were ruled by two tribal confederations: Akkoyunlu (Wh ...
. His eldest daughter Maria became the third wife of the Byzantine Emperor John VIII Palaiologos.
Alexios IV's eldest son, John IV (1429–1459), could not help but see that his Empire would soon share the fate of Constantinople. The Ottoman sultan Murad II first attempted to take the capital by the sea in 1442, but high surf made the landings difficult and the attempt was repulsed. While Murad's son and successor, Mehmed II, was away laying siege to Belgrade in 1456, the Ottoman governor of Amasya attacked Trebizond, and although defeated, he took many prisoners and extracted a heavy tribute. A Genoese document records the seizure of one of their ships at that port in 1437 by a military Galley on the orders of Emperor John IV.
John IV prepared for the eventual assault by forging alliances. He sent an envoy to the Council of Florence in 1439, the humanist George Amiroutzes, which resulted in the proclamation of the Union of the Catholic and Orthodox Churches, but this proclamation brought little help. He gave his daughter Theodora (also known by the name of Despina Khatun) to the son of his brother-in-law, Uzun Hasan, khan of the Ak Koyunlu
The Aq Qoyunlu ( az, Ağqoyunlular , ) was a culturally Persianate,Kaushik Roy, ''Military Transition in Early Modern Asia, 1400–1750'', (Bloomsbury, 2014), 38; "Post-Mongol Persia and Iraq were ruled by two tribal confederations: Akkoyunlu (Wh ...
, in return for his promise to defend Trebizond. He also secured promises of help from the Turkish emir
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cer ...
s of Sinope and Karamania, and from the king and princes of Georgia.Nicol, ''Last Centuries'', p. 407 Through Theodora and the daughter of Alexios IV of Trebizond (also named Theodora), the Safavid dynasty of Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
that succeeded the Ak Koyunlu, would be of direct partial Pontic Greek ethnicity from its very beginning, Ismail I
Ismail I ( fa, اسماعیل, Esmāʿīl, ; July 17, 1487 – May 23, 1524), also known as Shah Ismail (), was the founder of the Safavid dynasty of Iran, ruling as its King of Kings ('' Shahanshah'') from 1501 to 1524. His reign is ofte ...
being the grandson of Theodora.
After John's death in 1459, his brother David
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". w ...
came to power. David intrigued with various European powers for help against the Ottomans, speaking of wild schemes that included the conquest of Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
. Mehmed II eventually heard of these intrigues and was further provoked to action by David's demand that Mehmed remit the tribute imposed on his brother.
Mehmed's response came in the summer of 1461. He collected a sizable army at Bursa
( grc-gre, Προῦσα, Proûsa, Latin: Prusa, ota, بورسه, Arabic:بورصة) is a city in northwestern Turkey and the administrative center of Bursa Province. The fourth-most populous city in Turkey and second-most populous in t ...
, and in a surprise move marched on Sinope, whose emir quickly surrendered. Then the sultan moved south across eastern Anatolia to neutralize Uzun Hasan. Having isolated Trebizond, Mehmed swept down upon it before the inhabitants knew he was coming, and placed it under siege. The city held out for a month before David surrendered on 15 August 1461. With the fall of Trebizond, the last independent remnant of the Byzantine Empire, as well as the Roman Empire from which the Byzantine Empire sprang, was the Empire of Trebizond's offshoot, the Principality of Theodoro. On December 30, 1475, it would also fall to Ottoman rule.
Culture
Religion
Christianity strongly influenced society in the Empire of Trebizond. According to the Acts of Vazelon, which were written by contemporary monks, most peasants in the Matzouka region of the Empire had first names relating to Christian religious figures. Last names often referred to Christian saints, trades, and place names. In the relatively limited territory of the kingdom of the Grand Komnenoi (known as the “Empire of Trebizond”) there was enough room for three dioceses: Trebizond, which was the onlydiocese
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associat ...
established far in the past, Cerasous and Rizaion in Lazika, both formed as upgraded bishoprics. All three dioceses survived the Ottoman conquest (1461) and generally operated until the 17th century, when the dioceses of Cerasous and Rizaion were abolished. The diocese of Rizaion and the bishopric of Of were abolished at the time due to the Islamisation of the Laz and of the region respectively. Possibly the diocese of Cerasous was deactivated for the same reasons.
In popular culture
The Empire of Trebizond acquired a reputation in Western Europe for being "enriched by the trade from Persia and the East that passed through its capital," according to Steven Runciman, "and by the silver-mines in the hills behind, and famed for the beauty of its princesses." Donald Nicol echoes Runciman's observations: "Most of the emperors were blessed with a progeny of marriageable daughters, and the beauty of the ladies of Trebizond was as legendary as the wealth of their dowries." Its wealth and exotic location endowed a lingering fame on the polity. Cervantes described the eponymous hero of his ''Don Quixote
is a Spanish epic novel by Miguel de Cervantes. Originally published in two parts, in 1605 and 1615, its full title is ''The Ingenious Gentleman Don Quixote of La Mancha'' or, in Spanish, (changing in Part 2 to ). A founding work of Wester ...
'' as "imagining himself for the valour of his arm already crowned at least Emperor of Trebizond." Rabelais had his character Picrochole, the ruler of Piedmont, declare: "I want also to be Emperor of Trebizond." Other allusions and works set in Trebizond continue into the 20th century.
In Italian, there exists the expression "to lose the Trebizond" (''perdere la Trebisonda'') which means "to be bewildered". Trebizond was a port reachable by all the routes that crossed the Black Sea, and therefore a safe shelter in case of storms.''nationalgeographic.it''. Retrieved October 19, 2019.
See also
* List of Trapezuntine emperors * Komnenos dynasty and related family tree * Hagia Sophia, Trabzon * Sumela Monastery * Dorothy Dunnett, a Scottish historical novelist, much of whose book ''The Spring of the Ram'' is set in Trebizond at the time of its fall. *Lawrence Schoonover
Lawrence Schoonover (1906–1980) was an American novelist.
Born in Anamosa, Iowa, Schoonover attended the University of Wisconsin, then worked in advertising before becoming a novelist.
Writing mostly historical fiction, his attention to detai ...
, an American historical novelist, much of whose book ''The Burnished Blade'' is set in Trebizond at its height.
* The Towers of Trebizond, a novel by Rose Macaulay (1881–1958)
Notes
References
Sources and research
Primary sources
* Basilios Bessarion, ''The praise of Trebizond'' * Michael Panaretos, ''Chronicle''Secondary sources
* Anthony Bryer & David Winfield, ''The Byzantine Monuments and Topography of the Pontos'' (DOS. XX), vol. 1–2, Washington, 1985. * Anthony Bryer, ''Peoples and Settlement in Anatolia and the Caucasus, 800–1900'', Variorum collected studies series, London, 1988. * *Jakob Philipp Fallmerayer
Jakob Philipp Fallmerayer (10 December 1790 – 26 April 1861) was a German Tyrolean traveller, journalist, politician and historian, best known for his controversial discontinuity theory concerning the racial origins of the Greeks, and ...
, ''Geschichte des Kaiserthums Trapezunt'' (Munich, 1827–1848)
* George Finlay, ''The History of Greece, from Its Conquest by the Crusaders to Its Conquest by the Turks, and of the Empire of Trebizond: 1204–1461''. Edinburgh: Blackwood, 1851.
* Émile Janssens. ''Trébizonde en Colchide''. Bruxelles: Presses universitaires de Bruxelles, 1969,
* Sergei Karpov
Sergey Pavlovich Karpov (russian: Сергей Павлович Карпов; born 1948) is a leading Russian Byzantinist who specializes in the Empire of Trebizond and the history of Gazaria. His work in Italian archives helped bring to light t ...
, ''L' impero di Trebisonda, Venezia, Genova e Roma, 1204–1461''. Rapporti politici, diplomatici e commerciali. Roma, 1986.
* Sergei Karpov, ''Трапезундская империя и западноевропейские государства, 1204–1461''. ("The Empire of Trebizond and the nations of Western Europe, 1204–1461".) Moscow, 1981.
* Sergei Karpov, ''История Трапезундской империи'' ("A history of the empire of Trebizond"). Saint Petersburg, 2007.
* William Miller, ''Trebizond: The Last Greek Empire,'' (1926; repr. Chicago: Argonaut Publishers, 1968)
* Donald Queller, Thomas F. Madden, ''The Fourth Crusade: The Conquest of Constantinople'', University of Pennsylvania Press, Philadelphia, 2nd ed., 1997.
*
* Rustam Shukurov, ''Великие Комнины и Восток (1204—1461)'' ("The Megas Komnenos and the Orient (1204–1461)"). Saint Petersburg, 2001, 446 pp (in Russian),
* Levan Urushadze, ''The Comnenus of Trabizond and the Bagrationi dynasty of Georgia.'' — J. "Tsiskari", Tbilisi, No 4, 1991, pp. 144–148: in Georgian.
* Fyodor Uspensky
Fyodor Ivanovich Uspensky or Uspenskij (russian: Фёдор Ива́нович Успе́нский ) was a Russian Empire and Soviet Byzantinist. His works are considered to be among the finest illustrations of the flowering of Byzantine studi ...
, From the history of the Empire of Trabizond (''Ocherki iz istorii Trapezuntskoy Imperii''), Leningrad, 1929 (in Russian).
*
*
Further reading
* *External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Trebizond, Empire Of 13th century in the Byzantine Empire 1461 disestablishments Former countries in the Middle East Former monarchies of Asia Empire of Trebizond History of Trabzon Province States and territories established in 1204 States and territories disestablished in 1461 Byzantine rump states Tributary states of the Ottoman Empire Christian states