|
Tetraminx
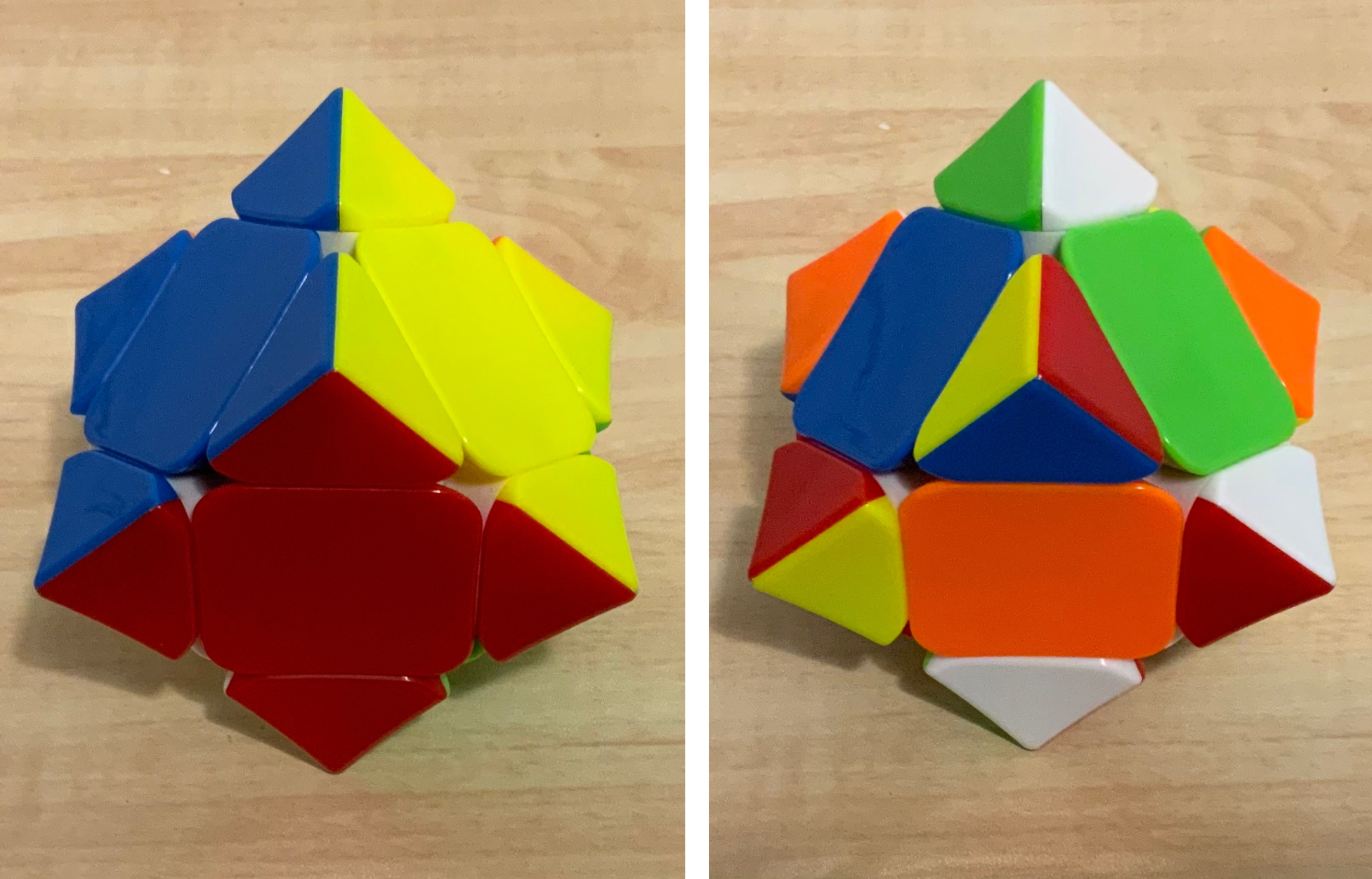
The Pyraminx () is a regular tetrahedron puzzle in the style of Rubik's Cube. It was made and patented by Uwe Mèffert after the original 3 layered Rubik's Cube by Ernő Rubik, and introduced by Tomy Toys of Japan (then the 3rd largest toy company in the world) in 1981. Description The Pyraminx was first conceived by Mèffert in 1970. He did nothing with his design until 1981 when he first brought it to Hong Kong for production. Uwe is fond of saying had it not been for Ernő Rubik's invention of the cube, his Pyraminx would have never been produced. The Pyraminx is a puzzle in the shape of a regular tetrahedron, divided into 4 axial pieces, 6 edge pieces, and 4 trivial tips. It can be twisted along its cuts to permute its pieces. The axial pieces are octahedral in shape, although this is not immediately obvious, and can only rotate around the axis they are attached to. The 6 edge pieces can be freely permuted. The trivial tips are so called because they can be twisted i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyraminx Solved
The Pyraminx () is a regular tetrahedron puzzle in the style of Rubik's Cube. It was made and patented by Uwe Mèffert after the original 3 layered Rubik's Cube by Ernő Rubik, and introduced by Tomy Toys of Japan (then the 3rd largest toy company in the world) in 1981. Description The Pyraminx was first conceived by Mèffert in 1970. He did nothing with his design until 1981 when he first brought it to Hong Kong for production. Uwe is fond of saying had it not been for Ernő Rubik's invention of the cube, his Pyraminx would have never been produced. The Pyraminx is a puzzle in the shape of a regular tetrahedron, divided into 4 axial pieces, 6 edge pieces, and 4 trivial tips. It can be twisted along its cuts to permute its pieces. The axial pieces are octahedral in shape, although this is not immediately obvious, and can only rotate around the axis they are attached to. The 6 edge pieces can be freely permuted. The trivial tips are so called because they can be twisted i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetraminx
The Pyraminx () is a regular tetrahedron puzzle in the style of Rubik's Cube. It was made and patented by Uwe Mèffert after the original 3 layered Rubik's Cube by Ernő Rubik, and introduced by Tomy Toys of Japan (then the 3rd largest toy company in the world) in 1981. Description The Pyraminx was first conceived by Mèffert in 1970. He did nothing with his design until 1981 when he first brought it to Hong Kong for production. Uwe is fond of saying had it not been for Ernő Rubik's invention of the cube, his Pyraminx would have never been produced. The Pyraminx is a puzzle in the shape of a regular tetrahedron, divided into 4 axial pieces, 6 edge pieces, and 4 trivial tips. It can be twisted along its cuts to permute its pieces. The axial pieces are octahedral in shape, although this is not immediately obvious, and can only rotate around the axis they are attached to. The 6 edge pieces can be freely permuted. The trivial tips are so called because they can be twisted i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truncated Tetrahedron
In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 equilateral triangle faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges (of two types). It can be constructed by truncation (geometry), truncating all 4 vertices of a regular tetrahedron at one third of the original edge length. A deeper truncation, removing a tetrahedron of half the original edge length from each vertex, is called Rectification (geometry), rectification. The rectification of a tetrahedron produces an octahedron. A ''truncated tetrahedron'' is the Goldberg polyhedron containing triangular and hexagonal faces. A ''truncated tetrahedron'' can be called a cantic cube, with Coxeter diagram, , having half of the vertices of the cantellated cube (rhombicuboctahedron), . There are two dual positions of this construction, and combining them creates the uniform compound of two truncated tetrahedra. Area and volume The area ''A'' and the volume ''V'' of a truncated tetrahedron of edge leng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GAP Computer Algebra System
GAP (Groups, Algorithms and Programming) is a computer algebra system for computational discrete algebra with particular emphasis on computational group theory. History GAP was developed at Lehrstuhl D für Mathematik (LDFM), Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen, Germany from 1986 to 1997. After the retirement of Joachim Neubüser from the chair of LDFM, the development and maintenance of GAP was coordinated by the School of Mathematical and Computational Sciences at the University of St Andrews, Scotland. In the summer of 2005 coordination was transferred to an equal partnership of four 'GAP Centres', located at the University of St Andrews, RWTH Aachen, Technische Universität Braunschweig, and Colorado State University at Fort Collins; in April 2020, a fifth GAP Centre located at the TU Kaiserslautern was added. Distribution GAP and its sources, including packages (sets of user contributed programs), data library (including a list of small groups) and the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combination Puzzles
A combination puzzle, also known as a sequential move puzzle, is a puzzle which consists of a set of pieces which can be manipulated into different combinations by a group of operations. Many such puzzles are mechanical puzzles of polyhedral shape, consisting of multiple layers of pieces along each axis which can rotate independently of each other. Collectively known as twisty puzzles, the archetype of this kind of puzzle is the Rubik's Cube. Each rotating side is usually marked with different colours, intended to be scrambled, then 'solved' by a sequence of moves that sort the facets by colour. As a generalisation, combination puzzles also include mathematically defined examples that have not been, or are impossible to, physically construct. Description A combination puzzle is solved by achieving a particular combination starting from a random (scrambled) combination. Often, the solution is required to be some recognisable pattern such as "all like colours together" or "all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dogic
The Dogic () is an icosahedron-shaped puzzle like the Rubik's Cube. The 5 triangles meeting at its tips may be rotated, or 5 entire faces (including the triangles) around the tip may be rotated. It has a total of 80 movable pieces to rearrange, compared to the 20 pieces in the Rubik's Cube. History The Dogic was patented by Zsolt and Robert Vecsei in Hungary on 20 October 1993. The patent was granted 28 July 1998 (HU214709). It was originally sold by VECSO in two variants under the names "Dogic" and "Dogic 2", but was only produced in quantities far short of the demand. In 2004, Uwe Mèffert acquired the plastic molds from its original manufacturer at the request of puzzle fans and collectors worldwide, and made another production run of the Dogics. These Dogics were first shipped in January 2005, and are now being sold by Meffert in his puzzle shop, ''Meffert's'' until September 2010 when the lack of interest for Meffert's Dogics made Uwe Meffert stop his Dogic production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megaminx
The Megaminx or Mégaminx (, ) is a dodecahedron-shaped puzzle similar to the Rubik's Cube. It has a total of 50 movable pieces to rearrange, compared to the 20 movable pieces of the Rubik's Cube. History The Megaminx, or Magic Dodecahedron, was invented by several people independently and produced by several different manufacturers with slightly different designs. Uwe Mèffert eventually bought the rights to some of the patents and continues to sell it in his puzzle shop under the Megaminx moniker. It is also known by the name Hungarian Supernova, invented by Dr. Christoph Bandelow. His version came out first, shortly followed by Meffert's Megaminx. The proportions of the two puzzles are slightly different. Description The Megaminx is made in the shape of a dodecahedron, and has 12 faces and center pieces, 20 corner pieces, and 30 edge pieces. The face centers each have a single color, which identifies the color of that face in the solved state. The edge pieces hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skewb
The Skewb () is a combination puzzle and a mechanical puzzle in the style of the Rubik's Cube. It was invented by Tony Durham and marketed by Uwe Mèffert. Although it is cubical in shape, it differs from Rubik's construction in that its axes of rotation pass through the corners of the cube rather than the centres of the faces. There are four such axes, one for each space diagonal of the cube. As a result, it is a ''deep-cut'' puzzle in which each twist affects all six faces. Mèffert's original name for this puzzle was the ''Pyraminx Cube'', to emphasize that it was part of a series including his first tetrahedral puzzle. the Pyraminx. The catchier name Skewb was coined by Douglas Hofstadter in his ''Metamagical Themas'' column. Mèffert liked the new name enough to apply it to the Pyraminx Cube, and also named some of his other puzzles after it, such as the Skewb Diamond. Higher-order Skewbs, named Master Skewb and Elite Skewb, have also been made. In December 2013, Skewb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V-Cube 8
The V-Cube 8 is an 8×8×8 version of the Rubik's Cube. Unlike the original puzzle (but like the 4×4×4 and 6×6×6 cubes), it has no fixed facets: the center facets (36 per face) are free to move to different positions. The design was covered by Panagiotis Verdes' patent from 2007 but Verdes Innovations SA did not produce it for sale until 2014. Other 8×8×8 cubes are produced by various Chinese companies. Methods for solving the 3×3×3 cube work for the edges and corners of the 8×8×8 cube, as long as one has correctly identified the relative positions of the colors — since the center facets can no longer be used for identification. Mechanics The puzzle consists of 296 pieces ("Cubies") on the surface. There are also 84 movable pieces entirely hidden within the interior of the cube, as well as six fixed pieces attached to the central "spider" frame. The V-Cube 9 uses essentially the same mechanism, except that on the latter these hidden pieces (corresponding to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V-Cube 7
The V-Cube 7 is a combination puzzle in the form of a 7×7×7 cube. The first mass-produced 7×7×7 was invented by Panagiotis Verdes and is produced by the Greek company Verdes Innovations SA. Other such puzzles have since been introduced by a number of Chinese companies, some of which have mechanisms which improve on the original. Like the 5×5×5, the V-Cube 7 has both fixed and movable center facets. Mechanics The puzzle consists of 218 unique miniature cubes ("cubies") on the surface. Six of these (the central tiles of the six faces) are attached directly to the internal "spider" frame and are fixed in position relative to one another. The V-Cube 6 uses essentially the same mechanism, except that on the latter the central rows, which hold the rest of the pieces together, are completely hidden. There are 150 center pieces which show one color each, 60 edge pieces which show two colors each, and eight corner pieces which show three colors each. Each piece (or quintet of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V-Cube 6
The V-Cube 6 is a 6×6×6 version of the original Rubik's Cube. The first mass-produced 6×6×6 was invented by Panagiotis Verdes and is produced by the Greek company Verdes Innovations SA. Other such puzzles have since been introduced by a number of Chinese companies, most of which have mechanisms which improve on the original. Unlike the original puzzle (but like the 4×4×4 cube), it has no fixed facets: the center facets (16 per face) are free to move to different positions. Methods for solving the 3×3×3 cube work for the edges and corners of the 6×6×6 cube, as long as one has correctly identified the relative positions of the colors — since the center facets can no longer be used for identification. Mechanics The puzzle consists of 152 pieces ("cubies") on the surface. There are also 66 pieces (60 movable, 6 fixed, and a central "spider" frame) entirely hidden within the interior of the cube. The V-Cube 7 uses essentially the same mechanism, except that on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
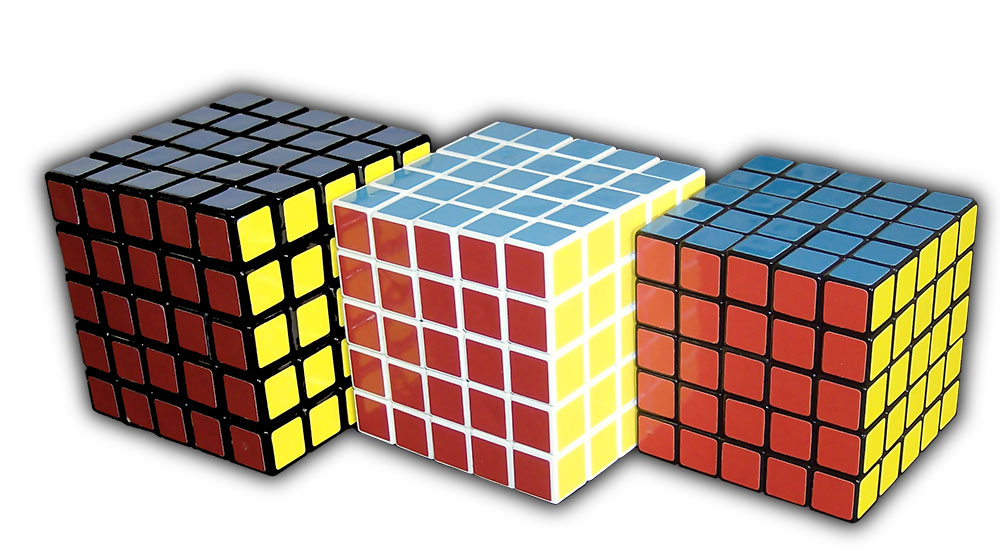
Professor's Cube
The 5x5 Rubik's Cube (also known as the Professor's Cube) is a 5×5×5 version of the original Rubik's Cube. It has qualities in common with both the 3×3×3 Rubik's Cube and the 4×4×4 4x4 Rubik's Cube, and solution strategies for both can be applied the 5x5 Rubik's Cube. History The 5x5 Rubik's cube was invented by Udo Krell in 1981. Out of the many designs that were proposed, Udo Krell's design was the first 5×5×5 design that was manufactured and sold. Uwe Mèffert manufactured the cube and sold it in Hong Kong in 1983. Ideal Toys, who first popularized the original 3x3x3 Rubik's cube, marketed the 5x5x5 cube in Germany as the "Rubik's Wahn" (Wahn means illusion or delusion). When the 5x5x5 cube was marketed in Japan, it was marketed under the name "Professor's Cube". Mèffert reissued the cube under the name "Professor's Cube" in the 1990s. The early versions of the 5×5×5 cube sold at Barnes & Noble were marketed under the name "Professor's Cube" but currently, Barn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)