|
Temryuk Of Kabardia
Temryuk Idar or Temroqwa Idar ( Adyghe: Айдарыкъо Темырикъу) was a prince of the Circassian Kabardian princedom and its head of power for part of the sixteenth century. His fame was largely due to the association of his name with the alliance with Ivan IV and the marriage of his daughter, Maria Temryukovna. When Temryuk came to power, he put down the revolts of the disputing princes, and helped Circassia become a military power within the North Caucasus. Alliance with Ivan the Terrible Temroqwa is one of the most controversial leaders in the Circassian history due to his relationship to the Ivan the Terrible. This critical alliance was perceived by Circassian nationalists as a destructive relationship to the Circassian nation, as the alliance was used by the Russian government as "evidence" of the “voluntary joining” of Circassia to the Russian Tsardom, which is historically not accurate, as Circassia was forcefully annexed after the Russo-Circassian War. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabardia
Grand Principality of Great Kabarda or East Circassia was a historical country in the North Caucasus corresponding partly to the modern Kabardino-Balkaria. It had better political organization than its neighbors and existed as a political community from the fifteenth century until it came under Russian control in the early nineteenth century after the Russo-Circassian War. Geography and peoples The Kabardians are the eastern branch of the Circassian nation. To the north were the Nogai steppe nomads, vassals of the Crimean Khanate. To the west were the Abazins, the Besleney, another Circassian tribe. In the east the Kabardians were sometimes in contact with the Kumyks. The country's boundaries fluctuated, as did its political unity and degree of control over outlying areas. The core of Kabardia was Great Kabardia which extended from somewhat east of the north-flowing part of the Kuban River to somewhat east of the north-flowing part of the Terek River. To the east was Lesser Ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russians
, native_name_lang = ru , image = , caption = , population = , popplace = 118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate) , region1 = , pop1 = approx. 7,500,000 (including Russian Jews and Russian Germans) , ref1 = , region2 = , pop2 = 7,170,000 (2018) ''including Crimea'' , ref2 = , region3 = , pop3 = 3,512,925 (2020) , ref3 = , region4 = , pop4 = 3,072,756 (2009)(including Russian Jews and Russian Germans) , ref4 = , region5 = , pop5 = 1,800,000 (2010)(Russian ancestry and Russian Germans and Jews) , ref5 = 35,000 (2018)(born in Russia) , region6 = , pop6 = 938,500 (2011)(including Russian Jews) , ref6 = , region7 = , pop7 = 809,530 (2019) , ref7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Don (river)
The Don ( rus, Дон, p=don) is the fifth-longest river in Europe. Flowing from Central Russia to the Sea of Azov in Southern Russia, it is one of Russia's largest rivers and played an important role for traders from the Byzantine Empire. Its basin is between the Dnieper basin to the west, the lower Volga basin immediately to the east, and the Oka basin (tributary of the Volga) to the north. Native to much of the basin were Slavic nomads. The Don rises in the town of Novomoskovsk southeast of Tula (in turn south of Moscow), and flows 1,870 kilometres to the Sea of Azov. The river's upper half ribbles (meanders subtly) south; however, its lower half consists of a great eastern curve, including Voronezh, making its final stretch, an estuary, run west south-west. The main city on the river is Rostov-on-Don. Its main tributary is the Seversky Donets, centred on the mid-eastern end of Ukraine, thus the other country in the overall basin. To the east of a series of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khanate Of Kazan
The Khanate of Kazan ( tt, Казан ханлыгы, Kazan xanlıgı; russian: Казанское ханство, Kazanskoye khanstvo) was a medieval Tatar Turkic state that occupied the territory of former Volga Bulgaria between 1438 and 1552. The khanate covered contemporary Tatarstan, Mari El, Chuvashia, Mordovia, and parts of Udmurtia and Bashkortostan; its capital was the city of Kazan. It was one of the successor states of the Golden Horde (Kipchak Khanate), and it came to an end when it was conquered by the Tsardom of Russia. Geography and population The territory of the khanate comprised the Muslim Bulgar-populated lands of the Bolğar, Cükätäw, Kazan, and Qaşan duchies and other regions that originally belonged to Volga Bulgaria. The Volga, Kama and Vyatka were the main rivers of the khanate, as well as the major trade ways. The majority of the population were Kazan Tatars. Their self-identity was not restricted to Tatars; many identified themselves simp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrakhan
Astrakhan ( rus, Астрахань, p=ˈastrəxənʲ) is the largest city and administrative centre of Astrakhan Oblast in Southern Russia. The city lies on two banks of the Volga, in the upper part of the Volga Delta, on eleven islands of the Caspian Depression, 60 miles (100 km) from the Caspian Sea, with a population of 475,629 residents at the 2021 Census. At an elevation of below sea level, it is the lowest city in Russia. Astrakhan was formerly the capital of the Khanate of Astrakhan (a remnant of the Golden Horde), and was located on the higher right bank of the Volga, 7 miles (11 km) from the present-day city. Situated on caravan and water routes, it developed from a village into a large trading centre, before being conquered by Timur in 1395 and captured by Ivan the Terrible in 1556. In 1558 it was moved to its present site. The oldest economic and cultural center of the Lower Volga, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temryuk
Temryuk ( rus, Темрю́к, p=tʲɪmˈrʲʉk) is a town and the administrative center of Temryuksky District in Krasnodar Krai, Russia, located on the Taman Peninsula on the right bank of the Kuban River not far from its entry into the Temryuk Bay, amid a field of mud volcanoes. The seaport of Temryuk is situated from the town itself. Population: 41,413 (2020), 26,600 (1975). History Tens of thousands of years ago, the Azov Sea was much larger and covered the delta of the Kuban River. Deposition of silt by the Kuban gradually pushed out the sea and shaped the delta with numerous shallow estuaries. Frequent eruptions of the mud volcanoes contributed to this deposition process. There are about 25 mud volcanoes in the area and some are still active. Situated close to the site of ancient Tmutarakan, Temryuk was vied by various powers as a vantage point at the mouth of the Kuban River. The first recorded settlement on the site was Tumnev, a Tatar fortress, which passed to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taman Peninsula
The Taman Peninsula (russian: Тама́нский полуо́стров, ''Tamanskiy poluostrov'') is a peninsula in the present-day Krasnodar Krai of Russia, which borders the Sea of Azov to the North, the Strait of Kerch to the West and the Black Sea to the South. History The area has evolved over the past two millennia from a chain of islands into today's peninsula. In ancient times the peninsula was known to the Greeks as ''Sindikè chersònesus'' (Greek: Σινδική χερσόνησος, peninsula of the Sindi) and Pontic Greek colonies of Hermonassa and Phanagoria stood on the peninsula, as did the later city of Tmutarakan."Greek colonization in the northern Black Sea area" German Archaeological Institut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million residents within the city limits, over 17 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in the metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's largest cities; being the most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest urban and metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow grew to become a prosperous and powerful city that served as the capital of the Grand Duchy that bears its name. When the Grand Duchy of Moscow evolved into the Tsardom of Russia, Moscow remained the political and economic center for most of the Tsardom's history. Whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catherine Jagiellon
Catherine Jagiellon ( pl, Katarzyna Jagiellonka; sv, Katarina Jagellonica, Lithuanian: ''Kotryna Jogailatė''; 1 November 1526 – 16 September 1583) was a Polish princess and Queen of Sweden as the first wife of King John III. As such, she was also Duchess of Finland (1562–1583) and Grand Princess of Finland (1581–1583). Catherine had significant influence over state affairs during the reign of her spouse and negotiated with the pope to introduce a counter-reformation in Sweden.Katarina Jagellonica urn:sbl:12406, Svenskt biografiskt lexikon (art av Birgitta Lager-Kromnow), hämtad 2013-12-05. She was the mother of the future Sigismund III Vasa, |
Anastasia Romanovna
Anastasia Romanovna Zakharyina-Yurieva (1530 – 7 August 1560) was the first spouse of the Russian Tsar Ivan the Terrible and the first Russian Tsaritsa. She was the mother of Feodor I, the last lineal Rurikid Tsar of Russia and the great-aunt of Michael I of Russia, the first Tsar of the Romanov dynasty. Early life and ancestry Anastasia was the second daughter of the boyar Roman Yurievich Zakharyin-Yuriev, who served as Okolnichy during the reign of Grand Prince Vasily III. The house of Zakharyin-Yuriev was a minor branch of a noble family that had already been at court, so it's possible that Ivan met Anastasia before the bride show, though no records of that exist. One of her uncles had been one of Ivan's guardians during the regency of his mother, Grand Princess Elena Glinskaya, who held all the real power. Anastasia's father was descended from the boyar Feodor "Koshka" ("Cat") Kobyla, fourth son of Andrei Kobyla.Sebag Montefiore, Simon. ''The Romanovs: 1613 to 191 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingushetian
The Ingush (, inh, ГIалгIай, translit=Ghalghaj, pronounced ) per Oxford dictionary "a member of a people living mainly in Ingushetia in the central Caucasus." Ingushetia is a federal republic of Russian Federation. The Ingush are predominantly Sunni Muslims and speak the Ingush language. According to 19th-century scientist Semen Bronevski the Ingush are known as Kisti, Ghalgha, Ingushi and they use the names interchangeably. According to the German scientist Peter Pallas who visited the Caucasus the Ingush are known as Loamaro, Kisti, Ghalghai, Ingush. Etymology The name ''Ingush'' is derived from the ancient village ''Angusht'', which was renamed into ''Tarskoye'' and transferred to North Ossetia in 1944 after the deportation of 23 February 1944, a.k.a. operation "Lentil". The Ingush, a nationality group indigenous to the Caucasus, mostly inhabit Ingushetia. They refer to themselves as Ghalghai (from Ingush: ''Ghala'' ("fortress" or "town") and ''ghai'' ("inhabita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
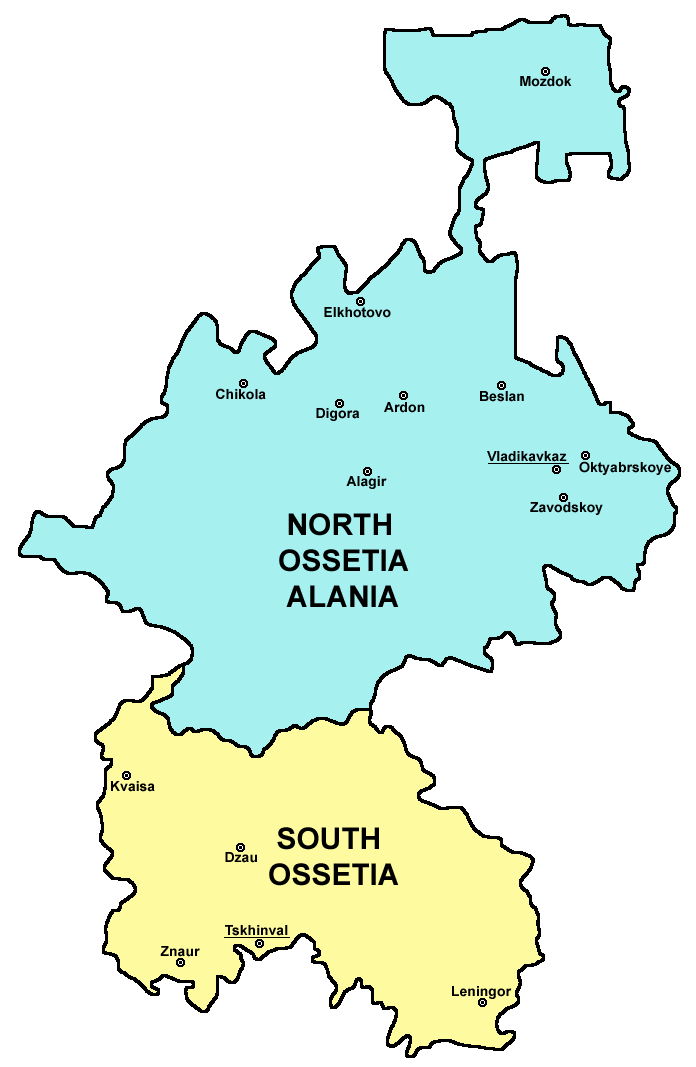
Ossetia
Ossetia ( , ; os, Ирыстон or , or ; russian: Осетия, Osetiya; ka, ოსეთი, translit. ''Oseti'') is an ethnolinguistic region located on both sides of the Greater Caucasus Mountains, largely inhabited by the Ossetians. The Ossetian language is part of the Eastern Iranian branch of the family of Indo-European languages. Most countries recognize the Ossetian-speaking area south of the main Caucasus ridge as lying within the borders of Georgia, but it has come under the control of the ''de facto'' government of the Russian-backed Republic of South Ossetia – the State of Alania. The northern portion of the region consists of the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania within the Russian Federation. Recent history * 1774 — North Ossetia becomes part of the Russian Empire. * 1922 — Creation of the South Ossetian autonomous oblast. North Ossetia remains a part of Russian SFSR, South Ossetia remains a part of Georgian SSR. * 20 September 1990 — South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |