|
Tin Telluride
Tin telluride is a compound of tin and tellurium (SnTe); is a IV-VI narrow band gap semiconductor and has direct band gap of 0.18 eV. It is often alloyed with lead to make lead tin telluride, which is used as an infrared detector material. Tin telluride normally forms p-type semiconductor (Extrinsic semiconductor) due to tin vacancies and is a low temperature superconductor. SnTe exists in three crystal phases. At Low temperatures, where the concentration of hole carriers is less than 1.5x1020 cm−3 , Tin Telluride exists in rhombohedral phase also known as α-SnTe. At room temperature and atmospheric pressure, Tin Telluride exists in NaCl-like cubic crystal phase, known as β-SnTe. While at 18 kbar pressure, β-SnTe transforms to γ-SnTe, orthorhombic phase, space group Pnma. This phase change is characterized by 11 percent increase in density and 360 percent increase in resistance for γ-SnTe. Tin telluride is a thermoelectric material. Theoretical studies imply that the n-t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Crystal System
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals. There are three main varieties of these crystals: *Primitive cubic (abbreviated ''cP'' and alternatively called simple cubic) *Body-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cI'' or bcc) *Face-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cF'' or fcc, and alternatively called ''cubic close-packed'' or ccp) Each is subdivided into other variants listed below. Although the ''unit cells'' in these crystals are conventionally taken to be cubes, the primitive unit cells often are not. Bravais lattices The three Bravais lattices in the cubic crystal system are: The primitive cubic lattice (cP) consists of one lattice point on each corner of the cube; this means each simple cubic unit cell has in total one lattice point. Each atom at a lattice point is then shared equally between eight adjacent c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthorhombic Crystal System
In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Orthorhombic lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, resulting in a rectangular prism with a rectangular base (''a'' by ''b'') and height (''c''), such that ''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' are distinct. All three bases intersect at 90° angles, so the three lattice vectors remain mutually orthogonal. Bravais lattices There are four orthorhombic Bravais lattices: primitive orthorhombic, base-centered orthorhombic, body-centered orthorhombic, and face-centered orthorhombic. For the base-centered orthorhombic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of a right rhombic prism;See , row oC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β = 90° it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be described with primitive rhombic axes. Note that the length a of the primit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tin(II) Compounds
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal. Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, the so-called "tin cry" can be heard as a result of twinning in tin crystals; this trait is shared by indium, cadmium, zinc, and mercury in the solid state. Pure tin after solidifying presents a mirror-like appearance similar to most metals. In most tin alloys (such as pewter) the metal solidifies with a dull gray color. Tin is a post-transition metal in group 14 of the periodic table of elements. It is obtained chiefly from the mineral cassiterite, which contains stannic oxide, . Tin shows a chemical similarity to both of its neighbors in group 14, germanium and lead, and has two main oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4. Tin is the 49th most abundant element on Earth and has, with 10 stable isotopes, the largest n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tellurides
The telluride ion is the anion Te2− and its derivatives. It is analogous to the other chalcogenide anions, the lighter O2−, S2−, and Se2−, and the heavier Po2−. In principle, Te2− is formed by the two-e− reduction of tellurium. The redox potential is −1.14 V. :Te(s) + 2 e− ↔ Te2− Although solutions of the telluride dianion have not been reported, soluble salts of bitelluride (TeH−) are known. Organic tellurides ''Tellurides'' also describe a class of organotellurium compounds formally derived from Te2−. An illustrative member is dimethyl telluride, which results from the methylation of telluride salts: :2 CH3I + Na2Te → (CH3)2Te + 2 NaI Dimethyl telluride is formed by the body when tellurium is ingested. Such compounds are often called telluroethers because they are structurally related to ethers with tellurium replacing oxygen, although the length of the C–Te bond is much longer than a C–O bond. C–Te–C angles tend to be closer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoelectric Generator
A thermoelectric generator (TEG), also called a Seebeck generator, is a solid state device that converts heat flux ( temperature differences) directly into electrical energy through a phenomenon called the ''Seebeck effect'' (a form of thermoelectric effect). Thermoelectric generators function like heat engines, but are less bulky and have no moving parts. However, TEGs are typically more expensive and less efficient. Thermoelectric generators could be used in power plants to convert waste heat into additional electrical power and in automobiles as automotive thermoelectric generators (ATGs) to increase fuel efficiency. Radioisotope thermoelectric generators use radioisotopes to generate the required temperature difference to power space probes. History In 1821, Thomas Johann Seebeck discovered that a thermal gradient formed between two different conducting material (has electromagnetic property) can produce electricity. At the heart of the thermoelectric effect is the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
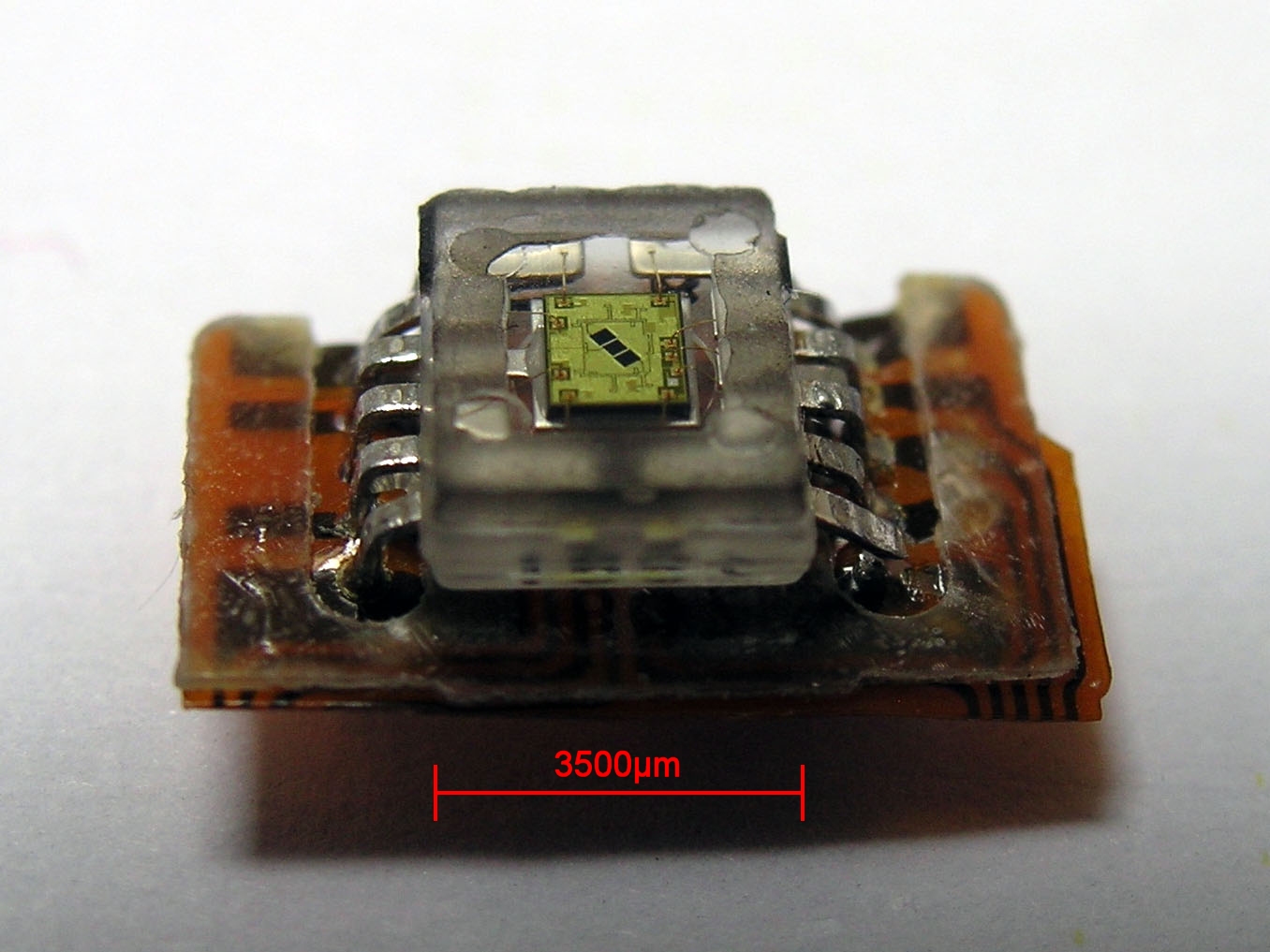
Photodetector
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are sensors of light or other electromagnetic radiation. There is a wide variety of photodetectors which may be classified by mechanism of detection, such as photoelectric or photochemical effects, or by various performance metrics, such as spectral response. Semiconductor-based photodetectors typically photo detector have a p–n junction that converts light photons into current. The absorbed photons make electron–hole pairs in the depletion region. Photodiodes and photo transistors are a few examples of photo detectors. Solar cells convert some of the light energy absorbed into electrical energy. Types Photodetectors may be classified by their mechanism for detection: * Photoemission or photoelectric effect: Photons cause electrons to transition from the conduction band of a material to free electrons in a vacuum or gas. * Thermal: Photons cause electrons to transition to mid-gap states then decay back to lower bands, inducing ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Confinement
A potential well is the region surrounding a local minimum of potential energy. Energy captured in a potential well is unable to convert to another type of energy (kinetic energy in the case of a gravitational potential well) because it is captured in the local minimum of a potential well. Therefore, a body may not proceed to the global minimum of potential energy, as it would naturally tend to do due to entropy. Overview Energy may be released from a potential well if sufficient energy is added to the system such that the local maximum is surmounted. In quantum physics, potential energy may escape a potential well without added energy due to the probabilistic characteristics of quantum particles; in these cases a particle may be imagined to tunnel ''through'' the walls of a potential well. The graph of a 2D potential energy function is a potential energy surface that can be imagined as the Earth's surface in a landscape of hills and valleys. Then a potential well would be a va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead
Lead is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metals, heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale of mineral hardness#Intermediate hardness, soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable nuclide, stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is toxic, even in small amounts, especially to children. Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and base (chemistry), bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the microscopic description of nature in statistical physics, and to the principles of information theory. It has found far-ranging applications in chemistry and physics, in biological systems and their relation to life, in cosmology, economics, sociology, weather science, climate change, and information systems including the transmission of information in telecommunication. The thermodynamic concept was referred to by Scottish scientist and engineer William Rankine in 1850 with the names ''thermodynamic function'' and ''heat-potential''. In 1865, German physicist Rudolf Clausius, one of the leading founders of the field of thermodynamics, defined it as the quotient of an infinitesimal amount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bond-dissociation Energy
The bond-dissociation energy (BDE, ''D''0, or ''DH°'') is one measure of the strength of a chemical bond . It can be defined as the standard enthalpy change when is cleaved by homolysis to give fragments A and B, which are usually radical species. The enthalpy change is temperature-dependent, and the bond-dissociation energy is often defined to be the enthalpy change of the homolysis at 0 K ( absolute zero), although the enthalpy change at 298 K ( standard conditions) is also a frequently encountered parameter. As a typical example, the bond-dissociation energy for one of the C−H bonds in ethane () is defined as the standard enthalpy change of the process : , : ''DH''°298() = Δ''H°'' = 101.1(4) kcal/mol = 423.0 ± 1.7 kJ/mol = 4.40(2) eV (per bond). To convert a molar BDE to the energy needed to dissociate the bond ''per molecule'', the conversion factor 23.060 kcal/mol (96.485 kJ/mol) for each eV can be used. A variety of exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
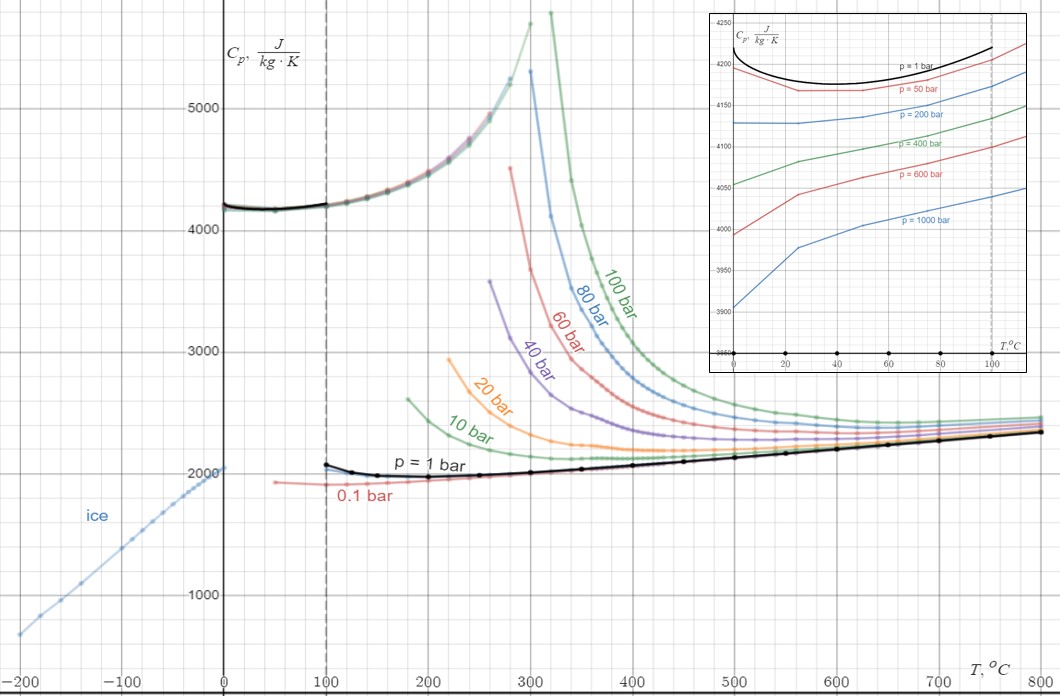
Heat Capacity
Heat capacity or thermal capacity is a physical property of matter, defined as the amount of heat to be supplied to an object to produce a unit change in its temperature. The SI unit of heat capacity is joule per kelvin (J/K). Heat capacity is an extensive property. The corresponding intensive property is the specific heat capacity, found by dividing the heat capacity of an object by its mass. Dividing the heat capacity by the amount of substance in moles yields its molar heat capacity. The volumetric heat capacity measures the heat capacity per volume. In architecture and civil engineering, the heat capacity of a building is often referred to as its thermal mass. Definition Basic definition The heat capacity of an object, denoted by C, is the limit : C = \lim_\frac, where \Delta Q is the amount of heat that must be added to the object (of mass ''M'') in order to raise its temperature by \Delta T. The value of this parameter usually varies considerably dependin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enthalpy Of Sublimation
In thermodynamics, the enthalpy of sublimation, or heat of sublimation, is the heat required to sublimate (change from solid to gas) one mole of a substance at a given combination of temperature and pressure, usually standard temperature and pressure (STP). It is equal to the cohesive energy of the solid. For elemental metals, it is also equal to the standard enthalpy of formation of the gaseous metal atoms. The heat of sublimation is usually expressed in kJ/mol, although the less customary kJ/kg is also encountered. Sublimation enthalpies See also * Heat * Sublimation (chemistry) * Phase transition In chemistry, thermodynamics, and other related fields, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic states ... * Clausius-Clapeyron equation References {{DEFAULTSORT:Enthalpy Of Sublimation Enthalpy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |